Module 2 - Phonetics
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Phonetics
Study of speech sounds
Acoustic Phonetics
Physical properties of speech sounds.
Auditory phonetics
How listeners perceive speech sounds
Articulatory phonetics
How speech sounds are produced
Pulmonic egressive airstream mechanism
How most speech sounds are made; air is pushed out of the lungs.
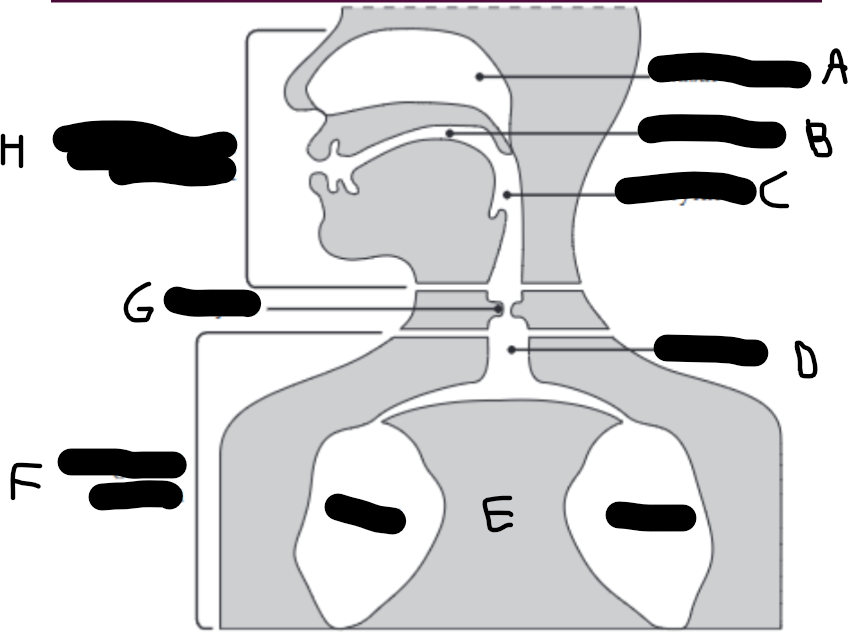
What is E?
The lungs.
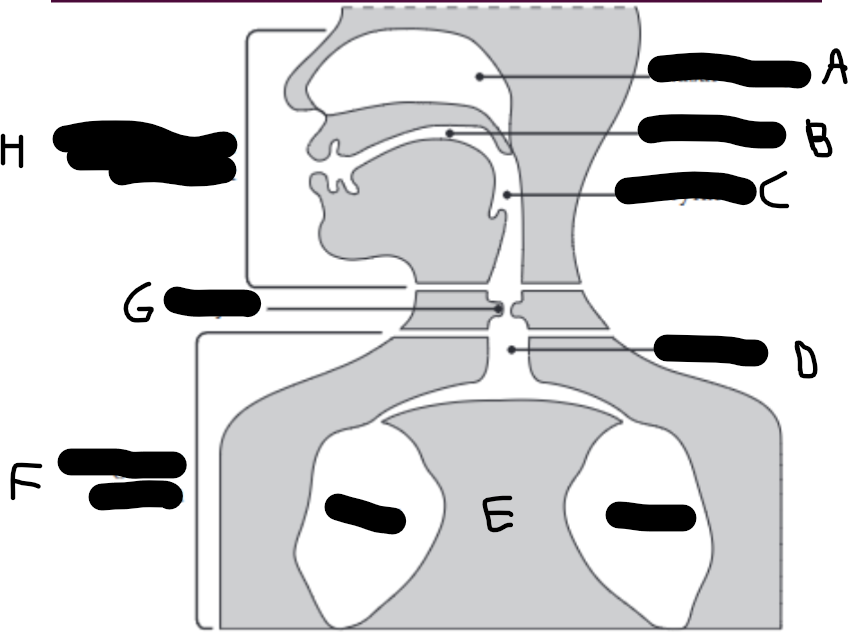
What is D?
The trachea (wind pipe).
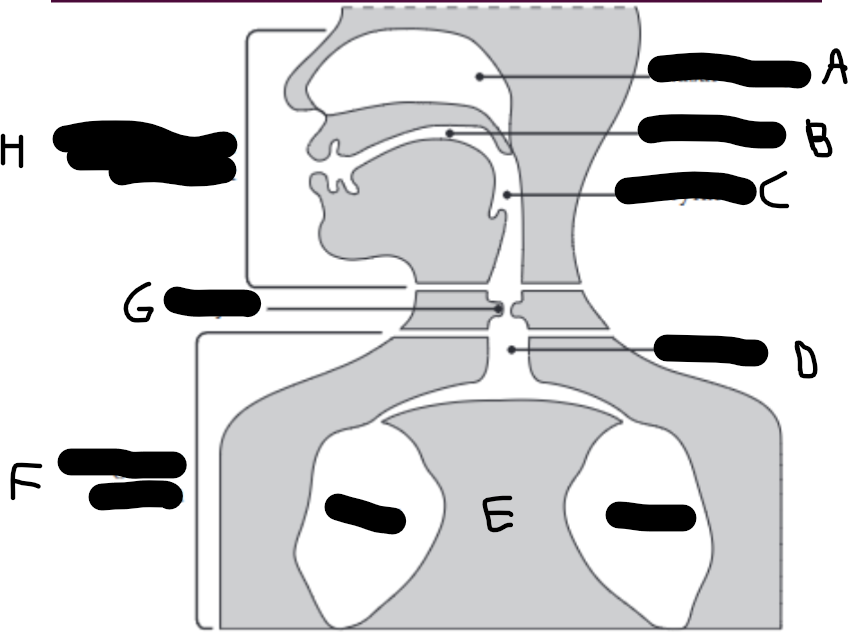
What is G?
The larynx
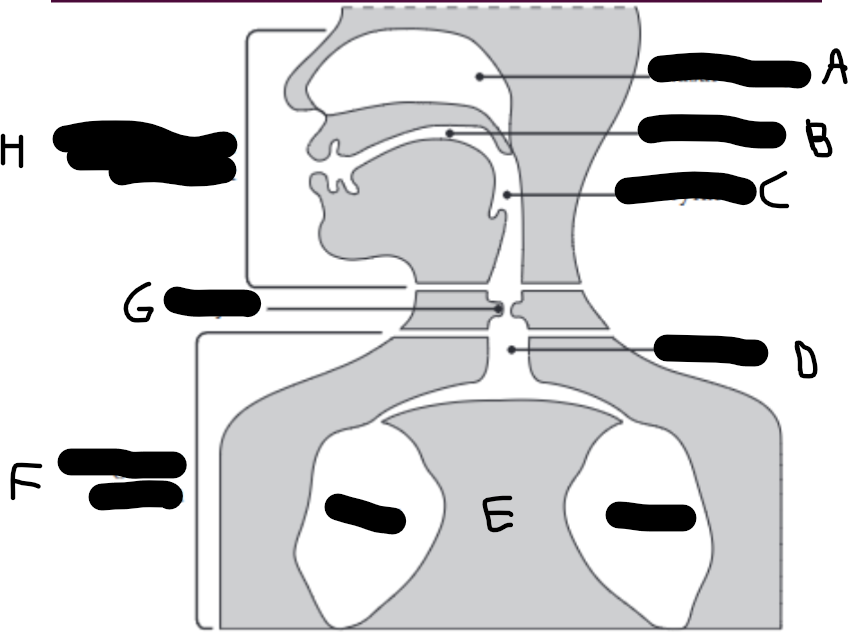
What is C?
The pharynx.
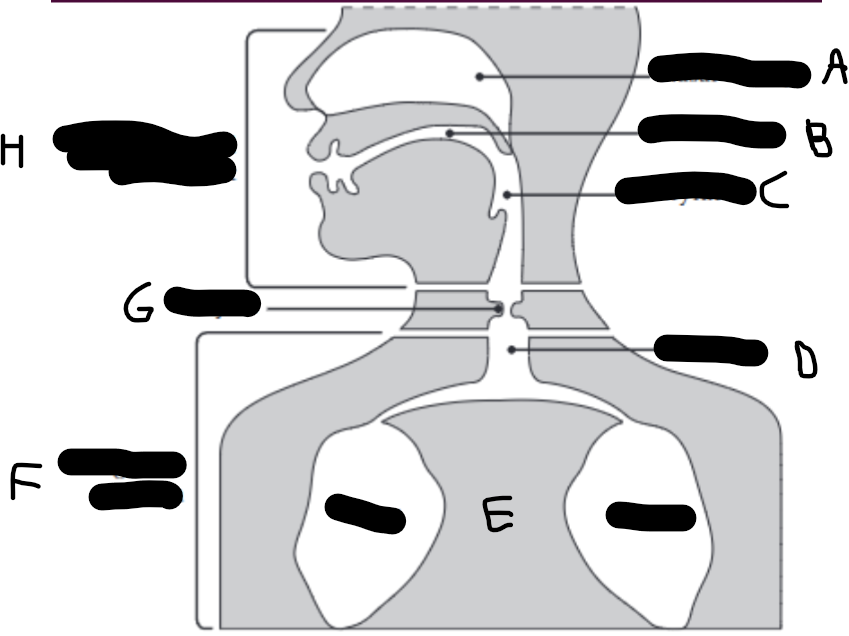
What is H?
The vocal tract.
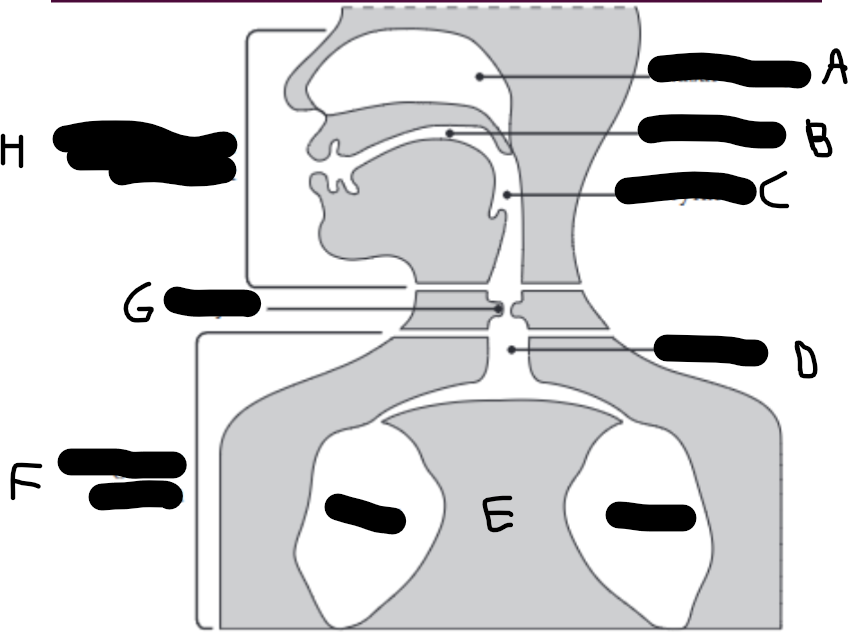
What is B?
Oral cavity.
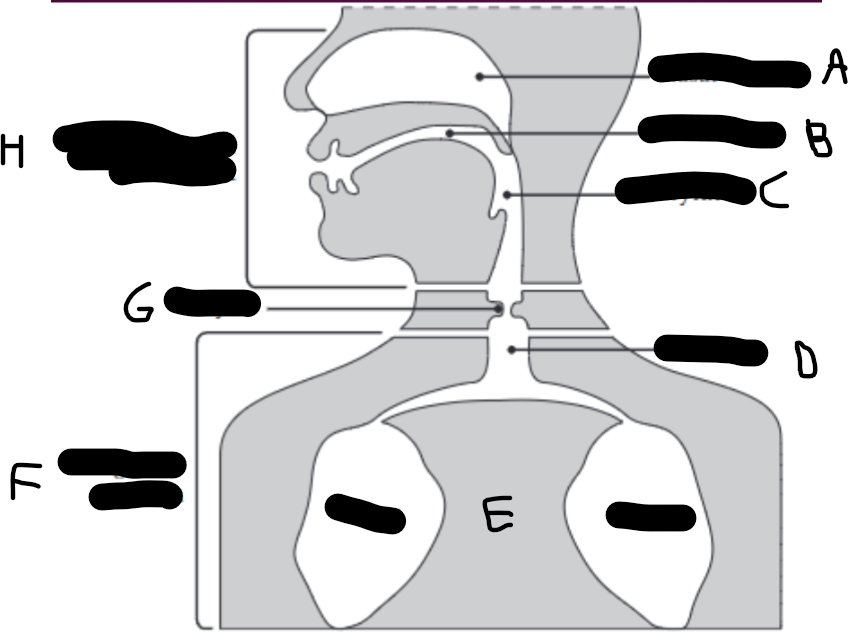
What is A?
Nasal cavity
Articulators
Lips, tongue, and teeth; help us modify different speech sounds
IPA
International Phonetic Alphabet; represents speech sounds of world languages
Why IPA instead of English letters? (4)
same sound, different spellings
same spelling, different sounds
2 letters to represent one sound
silent letters
Phone
Speech sound
Segments
Discrete phones (include consonants and vowels)
Consonants
Obstruct airflow
Vowels
Shape airflow
Suprasegmentals
“On top” of segments, affect entire strings of phones
Syllable
Unit of speech (contains the onset and the rhyme)
Onset
The first consonant
Rhyme
Vowel and following consonant.
Nucleus
Vowel
Coda
Consonant following vowel
What is articulatory description based on?
Voicing, place of articulation, manner of articulation.
Voicing
If vocal cords vibrate
Place of articulation
Where air stream is obstructed
Manner of articulation
How air stream is obstructed
Voiceless
No vibration, vocal cords are open
Voiced
Vibration, vocal cords are closed
Bilabial
Lips coming together
Labiodental
Bottom lip + top teeth
Interdental
Tongue between teeth
Alveolar
Tongue tip + alveolar ridge
Post-alveolar
Tongue between alveolar ridge and pallate
Palatal
Tongue body on pallate
Velar
Back of tongue to soft pallate
Glottal
Using glottis
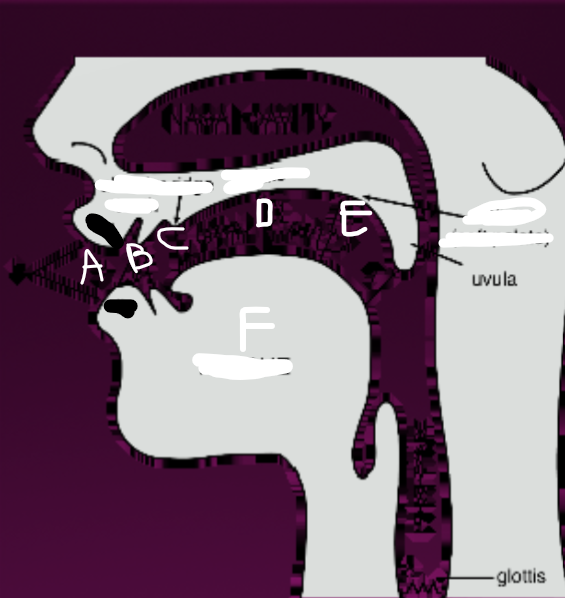
What is A?
Lips
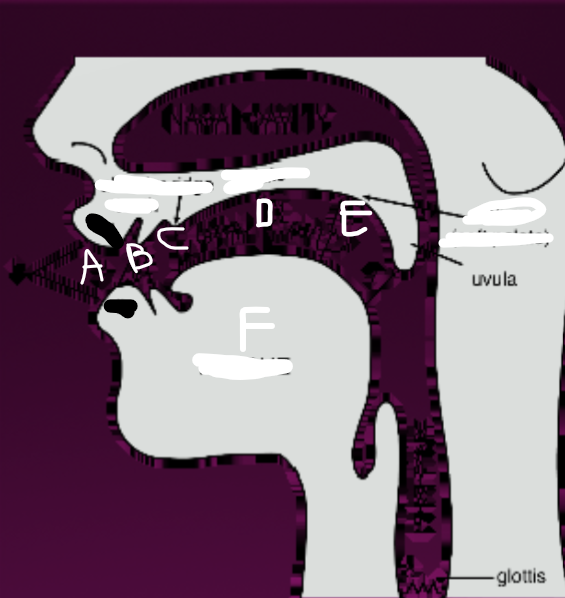
What is B?
Teeth
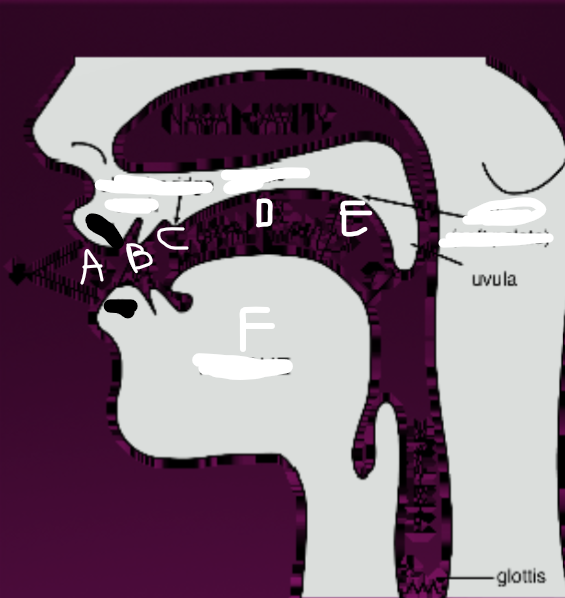
What is C?
Alveolar ridge
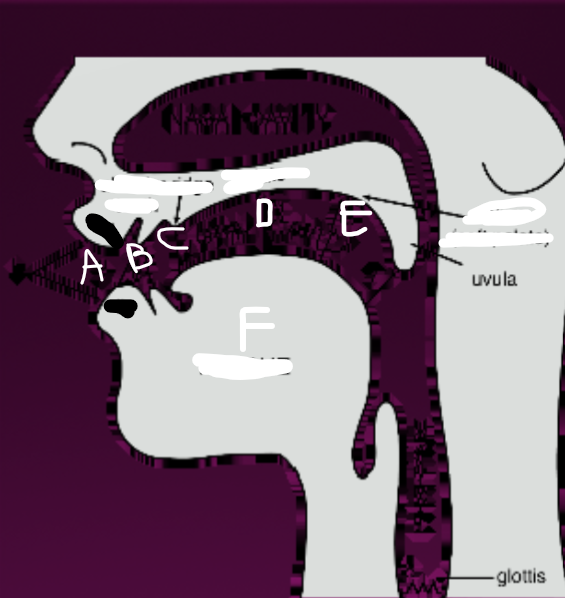
What is D?
Palate
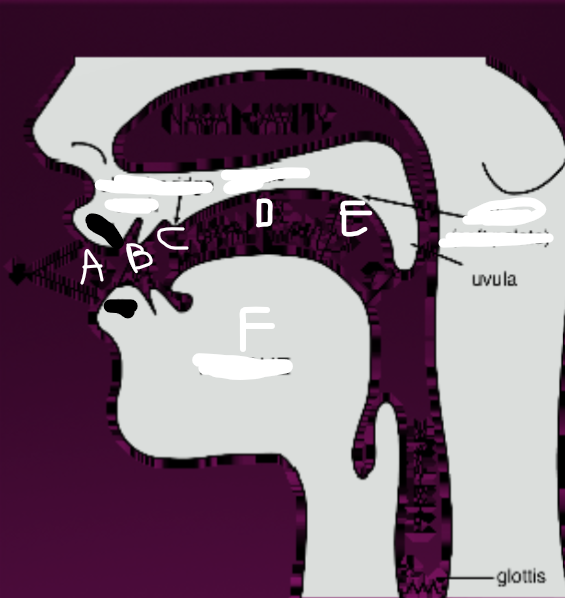
What is E?
Velum (soft palate)
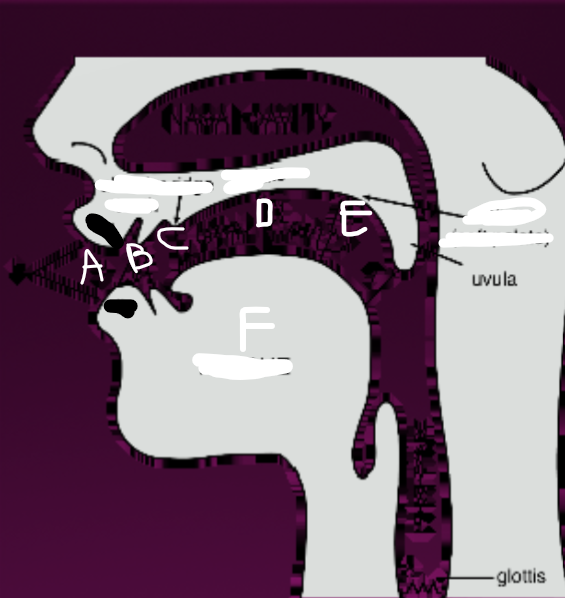
What is F?
Tongue
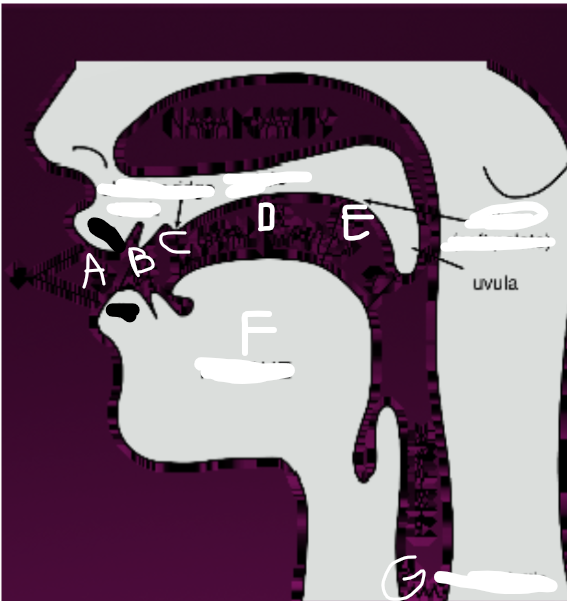
What is G?
Glottis
Stop
Complete stop in airflow, then release
Fricative
Obstruct air enough to cause hissing
Affricate
Complete stop followed by frication
Tap
Quick stop
Nasal
Velum is lowered, air passes through nose
Approximant
Obstruct air, but not enough for frication. Includes liquids and glides.
Liquid
More obstruction, depends on placement in word
Glide
Slight closure