MOD 1 - Avascular Necrosis
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
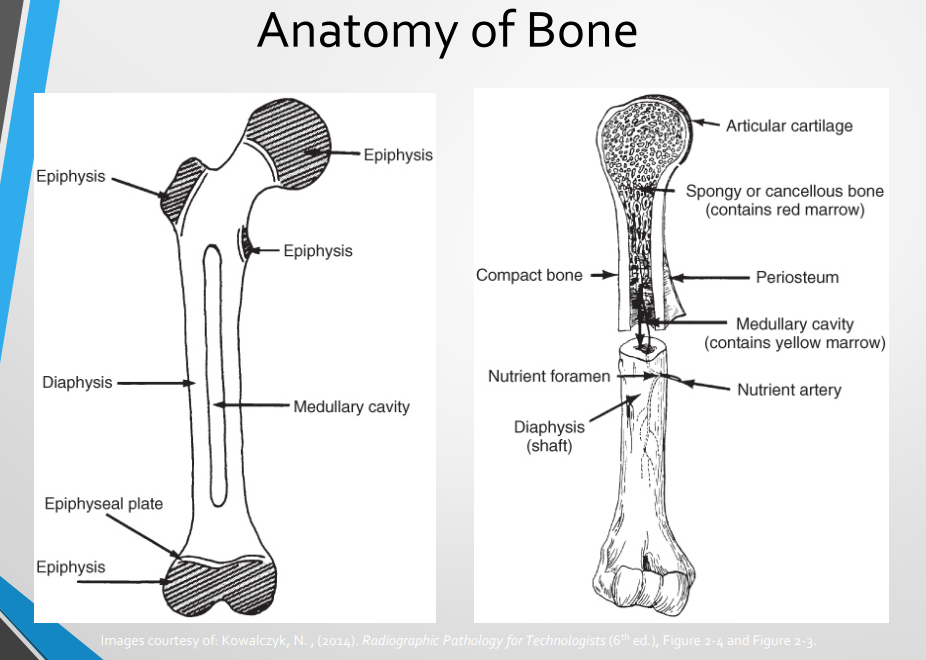
Epiphyseal Pathologies Covered
Ischemic Necrosis
Leg-Calve-Perthes Disease
Osteochondritis
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease
Kohler’s Disease
Osgood Schlatter’s Disease
Kienbock’s Disease
Ischemic necrosis (adults) - Classification
depends on the cause
idiopathic 25%
secondary disease (trauma)
Ischemic necrosis (adults) - Description
following trauma, particularly with joint dislocation and joint capsule tear
common in hip, shoulder, scaphoid, knee, ankle
30-60 y/o
Ischemic Necrosis (adults) - Pathogenesis
micro fractures in early stages → fragmentation, compression and resorption in later stages → left untreated can lead to collapse of bone and/or arthritis
Ischemic Necrosis (adults) - Signs and Symptoms
pain
limp
loss of function
Ischemic Necrosis (adults) - Radiographic Appearance
MRI, CT and Nuclear scans are better at detecting early stages
Crescent sign = radiolucent subcortical band representing a fracture line
Later Stages = flat femoral head, combo of sclerotic (dense) and lytic (translucent) regions
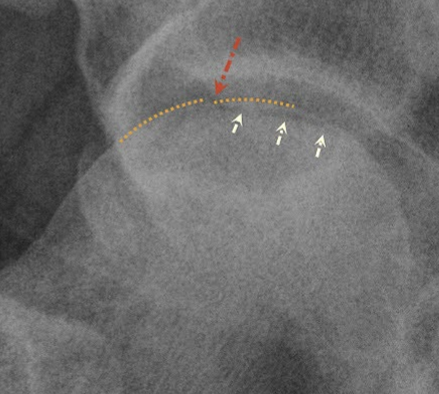
Ischemic Necrosis (adults) - Treatment
analgesics and NSAID
exercise, physiotherapy
immobilization, rest
surgery
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Definition
Temporary loss of blood supply at the femoral head ossification center
Affects the epiphyseal plate before closure of the growth plate, thus affects peds
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Classification
hereditary, traumatic, inflammatory, metabolic
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Etiology
cause is obscure
avascular necrosis
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Common Age Group
children 3-12 (peak 5-7)
predominately males 4:1
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Pathogenesis
Early/Avascular
loss of blood supply to the FH leading to decrease in size
increased joint space, lateral femoral displacement
Fragmentation (of epiphyses)
crescent sign
blurred FH outlines
Repair
return of blood supply
new bone deposits
wide short femoral neck
Healed/Deformity
enlarged and flattened FH
enlarged GT
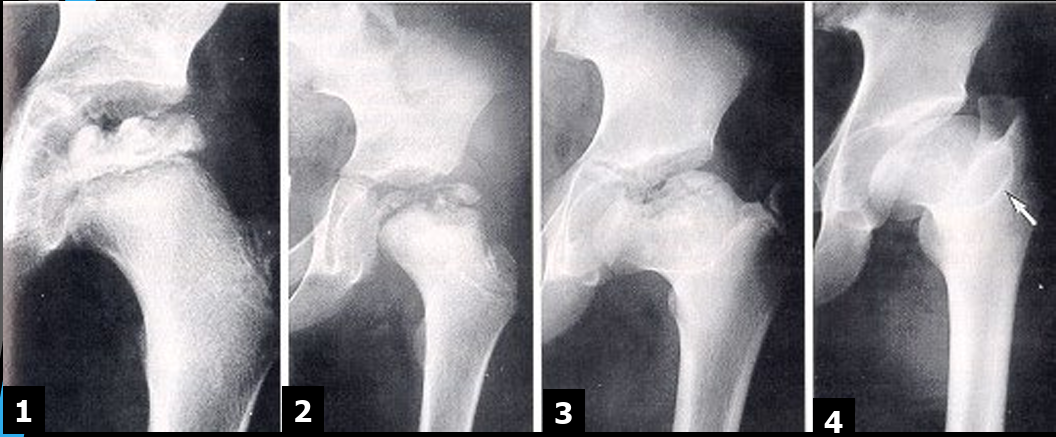
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Signs and Symptoms
include vague groin pain extending down towards knee
limping
decreased ROM
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Radiographic Appearance
FH = flat, small
Epiphyseal Plate = increased density, widening
FN = widened and decreased length
GT = enlarged
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease - Treatment
no cure, have to let it run thru all stages
casting, traction, bedrest
osteotomy, internal fixation
Osteochondritis Dissecans - Description
name should be Osteochondroses as there is no primary inflammation
Osteochondritis Dissecans - Classfication
Traumatic, causing avascular necrosis of the end of a bone
Osteochondritis Dissecans - Pathogenesis
Idiopathic, traumatic
Small fragments of subchondral bone necrotize if displaced, undisplaced frags may reattach and revascularize
frags are known as “joint mice”
high incidence in medial condyle 75%
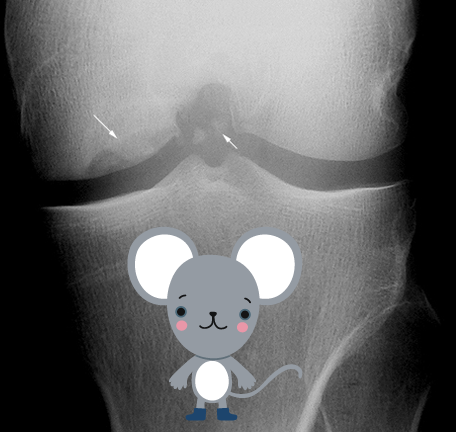
Osteochondritis Dissecans - Common Group
age 11- 20 yrs
active in sports
Osteochondritis Dissecans - Signs and Symptoms
joint effusion
clicking
locking
tenderness
Osteochondritis Dissecans - Radiographic Appearance
cartilage fragments are only seen on CT, MRI, NM
aim is to assess location of frag within joint space and origin
requires tunnel/notch view for best assessment
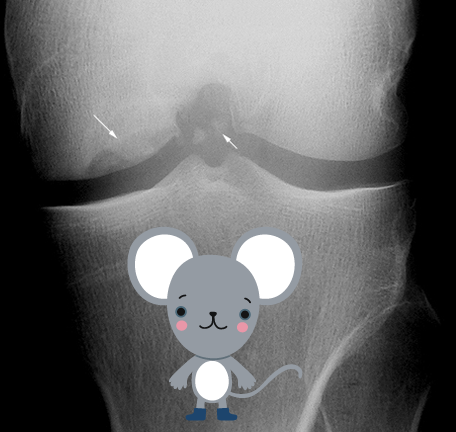
Osteochondritis Dissecans - Treatment
joint arthroscope to remove joint mice and/or secure loose cartilage
drilling to stimulate healing of subchondral bone
Non surgical: protected WB or immobilization
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease - Classfication
Traumatic, causing avascular necrosis of the end of a bone
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease - Etiology
avascular necrosis of 2nd MT head (smt 3rd)
disruption of growth plate due to trauma or increased stress
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease - Common Group
teen athletes who land with impact on the balls of their feet and young teen females who regularly wear high heeled shoes
adolescence females 5:1 (age 13-18 yrs)
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease - Pathogenesis
Growing epiphyseal site experiences avascular necrosis due to repeated micro fractures where the middle of the metatarsal meets the growth plate
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease - Signs and Symptoms
tenderness and pain
localized
aggravated with activity
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease - Radiographic Appearance
Bone scan and MRI are better for early stages
Initial Stage
articular cortex irregularity
sclerosis/lucency
altered joint space
Later Stage
enlarged, flattened and fragmented head
altered joint space
Freiberg Kohler’s Disease - Treatment
no known treatment
conservative:
reduced activity
non WB
invasive:
surgery for excision
osteochondral transplant
Kohler’s Disease - Classification
traumatic
Kohler’s Disease - Etiology
trauma - usually compression type injury
avascular necrosis of navicular bone
Kohler’s Disease - Pathogenesis
compression and/or injury during development phase, thus predom affects children 3-7 yrs (males)
Kohler’s Disease - Signs and Symptoms
midfoot pain and swelling
pt walks with increased weight on lat. side of foot
Kohler’s Disease - Radiographic Appearance
patchy and/or homogenic sclerosis (increased density)
severe cases bone collapses and fragments
abnormal architecture evident into adulthood
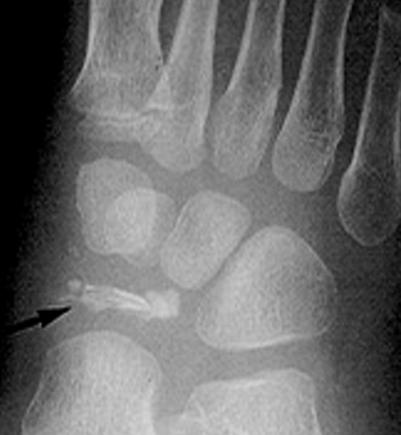
Kohler’s Disease - Treatment
resolves with time
pain killers
cast for 6-8 weeks
arch supports
Classification - Osgood Schlatter’s
inflammatory
can be traumatic
Etiology - Osgood Schlatter’s
repetitive strain
commonly seen in active teens
Pathogenesis - Osgood Schlatter’s
traction force of the patellar tendon causes inflammation and fragmentation of the immature tibia
S&S - Osgood Schlatter’s
swollen tibial tuberosity area
painful on resisted knee extension
limping
pain
Rad - Osgood Schlatter’s
ST swelling
loss of sharp patellar tendon margins
tibial tub fragmentation
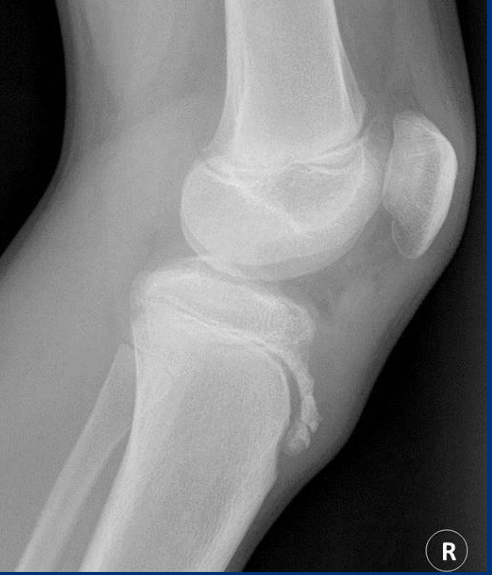
Treatment - Osgood Schlatter’s
rest
ice
physical therapy
NSAID
surgery (rare)
Classification - Kienbock’s disease
traumatic
degenerative
idiopathic
Etiology - Kienbock’s disease
exact cause is unknown
however, association seen between negative ulnar variance (rly short ulna compared to radius)
repetitive trauma/load to the lunate
lack of blood supply
Pathogenesis - Kienbock’s disease
stage 1 = x-ray appears normal, osteonecrosis only seen on MRI or bone scane
2 = sclerosis of lunate
3a = lunate collapse (no carpal instability → radioscahpoid angle <60)
3b= lunate collapse (carpal instability → radioscahpoid angle >60)
4 = lunate collapse with degenerative arthritis
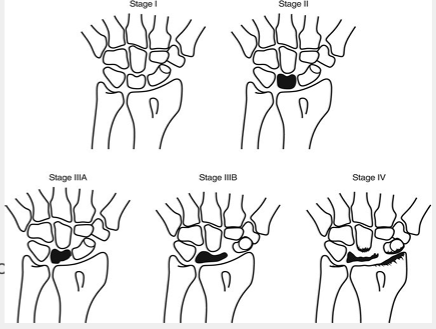
Rad - Kienbock’s disease
best seen on MRI
dense/brighter lunate (sclerosis)
S&S - Kienbock’s disease
center wrist pain
swelling
stiffness
crepitation (creaking/crackling sound with movement)
irreg. lunate shape
changes in carpal alignment
Treatment - Kienbock’s disease
no definitive cure
NSAIDS, immoblization
occupational therapy
surgery (proximal row carpectomy, fusion/arthodesis)