Cell Bio Unit 3 Chapter 7 Cell Interactions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a glycocalyx?
The “cell coat” on the outer surface of the plasma membrane.(It is a gel-like, sticky later made of sugars and proteins)
What is an ECM?
a interconnected network of molecules and filaments that provide structure to cells and surrounding tissues. It also helps with cellular activities.
What is a basement membrane?
it is a dense layer of ECM that sits below epithelial and endothelial cells.
What are the functions of a basement membrane? ** still kinda unsure
The basement membrane separates the cells from connective tissues, muscle, and fat. Surrounds nerve cells, muscle cells, an fat cells.
What are some of the protein components of the ECM?
collagen, fibronectin, laminin, proteoglycans, and integrins
What are collagens?
a family of fibrous glycoproteins
only found in the ECM
resist pulling forces
can hold a lot of weight without breaking
triple helix structure
What are Fibronectins?
a LARGE protein in the ECM
has a bind site for other ECM components (collagens, proteoglycans, other fibronectin mcs)
are bid site for receptors on cell surface
a polypeptide chain
double helix structure
What are proteoglycans?
HUGE protein-polysaccharide complexes
take up a lot of ECM space
have a core protein molecules with many disaccharide chains branching from it (GAGs)
What is hyaluronic acid?
the core protein of proteoglycans. Where the GAGs attach to
What are GAGs?
chains of disaccharides that branch from a core protein
core protein + many GAGs = proteoglycan
Can be keratan sulfate or chondroitin sulfate
What are laminins?
family of ECM glycoprotein
3 different polypptide chains (disulfide bonds)
T-shaped molececules
influence cell migration, growth, and differentiation
binds to cell-surface receptors
bind to other laminin molecules
What do matrix metalloproteinases do?
they are zinc-containing enzymes
degrade ECM and cell surface protein material
How do integrins function?
membrane proteins
bind cites for receptors
bind ECM ( grab ligands on the outside of the cell) and intracellular environment ( attach to proteins on the inside of the cell)
look a bit like salad tongs and can grab ECM elements like collagen to secure it from moving around too much
What are focal adhesions?
mostly seen in vitro
assists integrin to make connection between ECM and cytoskele
when cell attaches to the bottom of a petri dish, it flattens itself out and anchors itself in certain spots on the dish. Those spots are the focal adhesions
What are hemidesmosomes?
assists integrin to make connection between cytoskele and ECM
similar to focal adhesions, just not in vitro
tightest attachment between cell and ECM
cells anchor to basement membrane with hemidesmosome
a plaque that holds IFs, proteins, and other things
What are the 4 integral membrane proteins that mediate cell-cell adhesions?
selectins
certain IgSF proteins
certain integrin proteins
cadherins
What do selectins do?
family of integral membrane glycoproteins
attach to end of oligosaccharide chain
they are cell surface receptors
mediate adhesion of white blood cells to endothelial cells and platelet flow?? **unsure
What do IgSF proteins do?
AKA immunoglobulin superfamily
mediate cell-cell adhesion
What are cadherins (describe)?
family of glycoproteins
can transmit signals from ECM to cytoplasm
mediate Ca2+ dependent cell-cell adhesions
make up the “bridge” that connected one cell to another adherins junctions
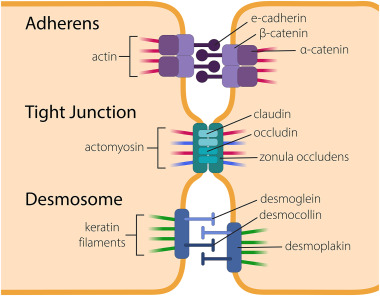
What are adherins junctions (describe structure)?
adherins junction + desmosome on both cells, connected by cadherins
binds to actin filaments (not directly but you get the idea)
What are gap junctions (describe strucuture)
in epithelial cells
act as a tunnel where some ions can pass thru
only in animals
connexin/connexon make up the gap junction and can open and close as necessary
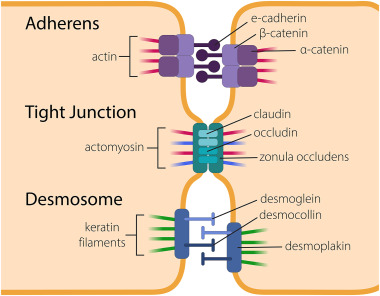
What are tight junctions (describe structure)?
one molecule of claudin
one molecule of occludin
claudin and occludin span the gap between cells
binds to actinomyosin (like adherins junctions bind to actin)
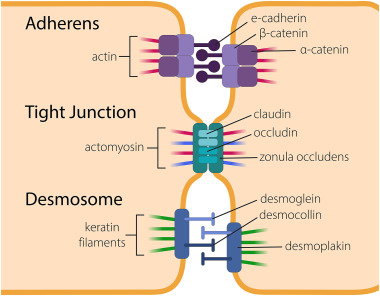
What are desmosomes (describe structure)?
disk-shaped adhesive junctions that are on the inner portion of two cell membranes
cadherin-like molecules span the gap between two cells (like in adherins junctions)
bind keratin filaments (like adherins junctions bind actin)
What type of junctions form the blood-brain barrier?
tight junctions
creates a tight seal so water doesn’t get through
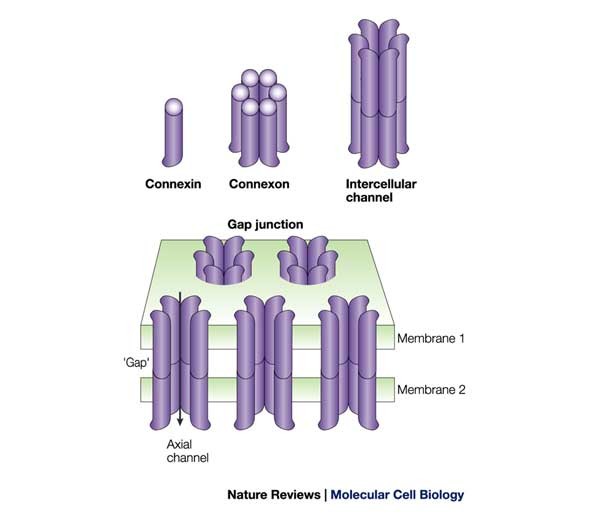
What are connexins? What are connexons?
associated with Gap junctions
pass commpletely thru lipid bilayer
Connexins are the smaller subunit that make up the connexon
there are 6 connexins to ever connexon
flower shape
What are tunneling nanotubes?
a form of long-range communication
connects cell surface proteins, vesicles, organelles from two cells that are far away