Ag Policy Exam 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Trade-offs, Opportunity-Costs, Margin, Incentives, Exchange, Markets, Government
7 Economic Principles
Agricultural Policy
Set of laws, regulations, and government interventions related to agricultural production, distribution, consumption, and rural development.
Purpose of policy
To stabilize food production, ensure food security, protect farmers, and manage natural resources.
Free Marketer
Policy interventions in agricultural markets should promote economic efficiency.
Food Security
Policy interventions should ensure that everyone has access to food.
Regulator
Policy interventions should provide rational coordination and control of activities.
Identify, Assess, Inform, Provide Recommendations
Welfare Analysis
Demand
An economic concept that describes a consumer’s desire to buy goods and services, and how much they are willing to pay for them.
Elasticity
A general concept used to quantify the sensitivity or response in one variable (quantity) when another variable changes (price).
Own-price elasticity
Measures how much the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in its own price.
Cross-price elasticity
Measures how the quantity demanded of one good changes in response to a change in the price of another good.
Income elasticity
Measures how the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in consumers’ income.
Supply
The amount of a resource that firms, or producers, are willing and able to provide to the market
Shut down point
The price at which a firm would exit the market.
MC = Min (Average Total Cost)
Long-run shut-down point
MC = Min (Average Variable Cost)
Short-run shut-down point
Market Equilibrium
Where demand and supply meet on a graph.
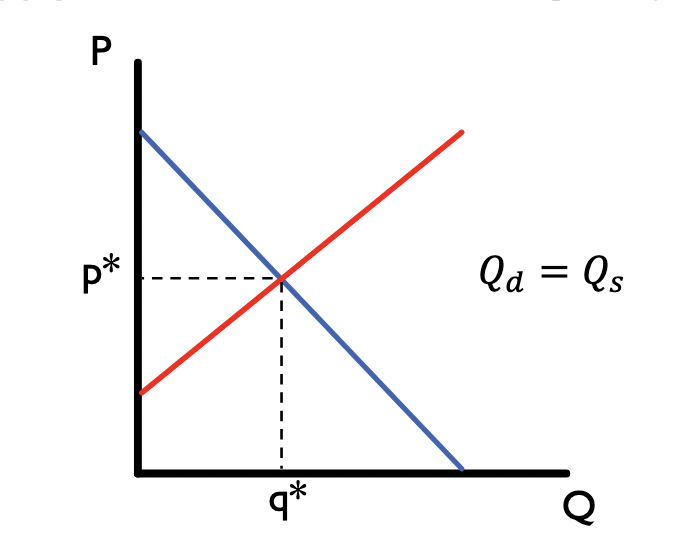
Simultaneously
Demand and supply interact _________ to generate market price.
Pre-emption Act - Early Republic
Allowed settlers to purchase up to 160 acres of public land at a low price before it was offered for sale to the general public, giving squatters the first right to buy the land they were already living on.
Homestead Act - Early Republic
Granted 160 acres of free public land to settlers who lived on and improved the land for at least five years, encouraging westward expansion and agricultural development.
USDA - Early Republic
Created to support farmers and improve agriculture through research, education, and services that promote food production and rural development.
Morrill Act
Granted federal land to states to fund the establishment of land-grant colleges, which focused on teaching agriculture, engineering, and the mechanical arts to make higher education more accessible and practical.
Sherman Antitrust Act - Early Republic
The first federal law to prohibit monopolies and other business practices that restricted trade or competition in the marketplace.
McNary-Haugen Farm Act - WW1
A proposed bill in the 1920s that aimed to raise agricultural prices by having the government buy surplus crops and sell them overseas; it was passed by Congress twice but vetoed both times by President Coolidge.
Smooth-Hawley Tariff Act - WWI
The raised U.S. tariffs on thousands of imported goods to protect American businesses and farmers, but it worsened the Great Depression by reducing international trade.
New Deal - Great Depression
A series of programs and reforms launched by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the 1930s to provide relief for the unemployed, recover the economy, and reform the financial system during the Great Depression.
Mechanization and Labor - WW2
The use of machines in agriculture and industry grew, reducing the need for manual labor, while labor shortages arose as many workers joined the military.
Agriculture Adjustment Act (AAA) - WW2
Aimed to stabilize farm prices and support farmers’ incomes by controlling production and providing price supports for key crops.