3. Tension Production Energy Use and Muscular Activity
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Tension
pulling force generated as sarcomeres shorten
Tension of entire muscle depends on
Number of muscle cells contracting
Tension produced in individual muscle fibers (cells) can vary due to
Length-tension relationship
Frequency of stimulation
Length-tension relationship
amount of tension depends on number of cross bridges formed and degree of overlapbetween thick and thin filaments in a muscle fiber.
Skeletal muscle contracts most forcefully over a _____
narrow range of resting sarcomere length
narrow range of resting sarcomere length: Too short
filaments overlap too much so bridges can form effectively
narrow range of resting sarcomere length: Too long
filaments do not overlap sufficiently, resulting in fewer cross bridges and less tension.
Twitch
cycle of contraction/relaxation produced by a single action potential in a muscle fiber.
Twitch: latent phase
Action potential has occurred but no tension is produced as calcium is released.
Twitch: contraction phase
Calcium binding to troponin allows myosin heads to attach to actin, resulting in muscle contraction.
Twitch: relaxation phase
Calcium is reabsorbed, causing myosin heads to detach and the muscle fiber returns to its resting state.
Most muscular activities involve:
sustained muscular contractions produced by high frequency of action potentials
Summation of tension produces
greater force
Summation
repeated stimulation produced before relaxation phase has been completed, causing build up of calcium ions in sarcoplasm
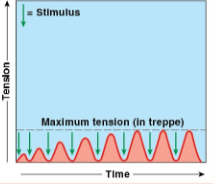
Treppe summation
a phenomenon where muscle contractions increase in strength with repeated stimulation, leading to progressive enhancement of muscle tension.
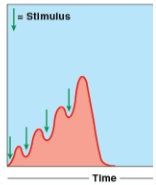
Wave summation
occurs when muscle fibers are stimulated repeatedly at a frequency that does not allow complete relaxation, resulting in increased muscle tension.
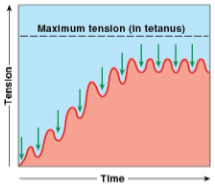
Incomplete tetanus
tension production rises to peak and relaxation period are very brief
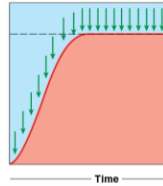
Complete tetanus
is the state where muscle fibers are stimulated at such a high frequency that they do not relax at all between stimuli, resulting in a sustained, maximal contraction.
Motor units
all the muscle fibers innervated by one motor neuron that work together to produce a contraction.
Differences in number and size of motor units in different muscles
control precision and control of movements produced
Small motor unit
consists of a single motor neuron innervating a few muscle fibers, allowing for precise control of movements.
large motor unit
consists of a single motor neuron innervating many muscle fibers, which generates stronger but less precise contractions.
Asynchronous motor unit summation
is a process where motor units are activated at different times to produce smoother and more sustained muscle contractions.
Muscle tone
is the continuous and passive partial contraction of the muscles, important for posture and readiness for action.
Is there a time where there is no motor unit activity in a muscle within a healthy person
No, healthy muscle maintains some level of activity for tone even if no movement is produced
Greater resting muscle tone leads to higher
resting metabolic rate because active muscle cell consume more energy even at rest
Why is it difficult to contract a muscle that has
been overstretched?
A. Little or no calcium can be released from the sarcoplasmic
reticulum if it is stretched
B. Actin becomes detached from the Z disks when muscle
fibers are over stretched
C. Transverse tubules can not conduct action potentials when
distorted by stretching
D. Few if any myosin-actin cross bridges can form when
sarcomeres are overextended
E. The neuromuscular junction becomes detached when a
muscle is too stretched
D. Few if any myosin-actin cross bridges can form when
sarcomeres are overextended
isotonic muscle contraction
tension rises and muscle length changes, Can be concentric or eccentric
Concentric contraction
muscle shortens while generating tension and Z-lines are pulled together
Eccentric muscle contraction
muscle lengthens while generating tension, cross bridges are still active but muscle is being pulled longer by external force
Ex of eccentric contraction
lowering a weight slowly
Are there active mechanisms that cause muscle fiber elongation
No, muscles return to resting length due to contraction of opposing muscle groups, gravity, and some elastic recoil of connective tissue
ATP and creatine phosphate (CP) reserves
only last 15 seconds once contraction begins and must be replenished for sustained activity.
Creatine phosphate reserves
rapid energy buffer for high-intensity muscular activity, helping to regenerate ATP during short bursts of effort.
ATP generation- aerobic cellular respiration
most ATP needed for resting muscle and moderate levels of activity
ATP generation- aerobic AND anaerobic cellular respiration
both are needed to generate additional ATP for peak performance
Aerobic metabolism
Uses O2, released CO2 and produces ATP in mitochondria with citric acid cycle (NADH and FADH2 produced) and ETC, which produces ATP and uses O2 as final e- acceptor
Resting muscle fibers rely on aerobic metabolism of
fatty acids to generate steady, long-lasting source of ATP
How are fatty acids metabolized for resting muscle fibers
absorbed from circulation, broken down through beta-oxidation, to produce 2 acetyl CoA to enter citric acid cycle
Excess ATP
used to store glucose into glycogen —> create creatine phosphate
Moderately active muscle activity
ATP is generated through aerobic metabolism of glucose from stored glycogen and fatty acids, allowing for sustained energy during exercise.
Anerobic metabolism
if oxygen delivery is too slow, cell rely on pyruvate metabolism to generate ATP through lactic acid fermentation.
Peak activity muscle metabolism
oxygen cannot diffuse fast enough for mitochondria to meet ATP demand, so glycolysis becomes the primary source of ATP, but excess pyruvate is produced and builds up in cytosol and is converted to lactic acid.
Build up of hydrogen ions in cytosol from excess lactic acid formation
increases cytosol acidity, which inhibits contraction and causes rapid fatigue
Benefits of anaerobic metabolism
includes rapid ATP production and allows for sustained activity in low oxygen conditions.
disadvantages of anaerobic metabolism
inefficient use of glucose
lactic acid decreases intracellular pH
Recovery period
Rebuild ATP and creatine phosphate reserves
Recycle lactic acid to make pyruvate
Rebuild glycogen reserves
excess post-exercise oxygen consumption – EPOC
is the increased rate of oxygen intake following strenuous activity to restore the body to its resting state. It helps in the recovery processes like ATP replenishment and lactic acid removal.