BIO 169 Chapter 28: The Reproductive System
1/75
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
(Male) Testes
-male gonads secrete androgens and produce sperm (male gamete)
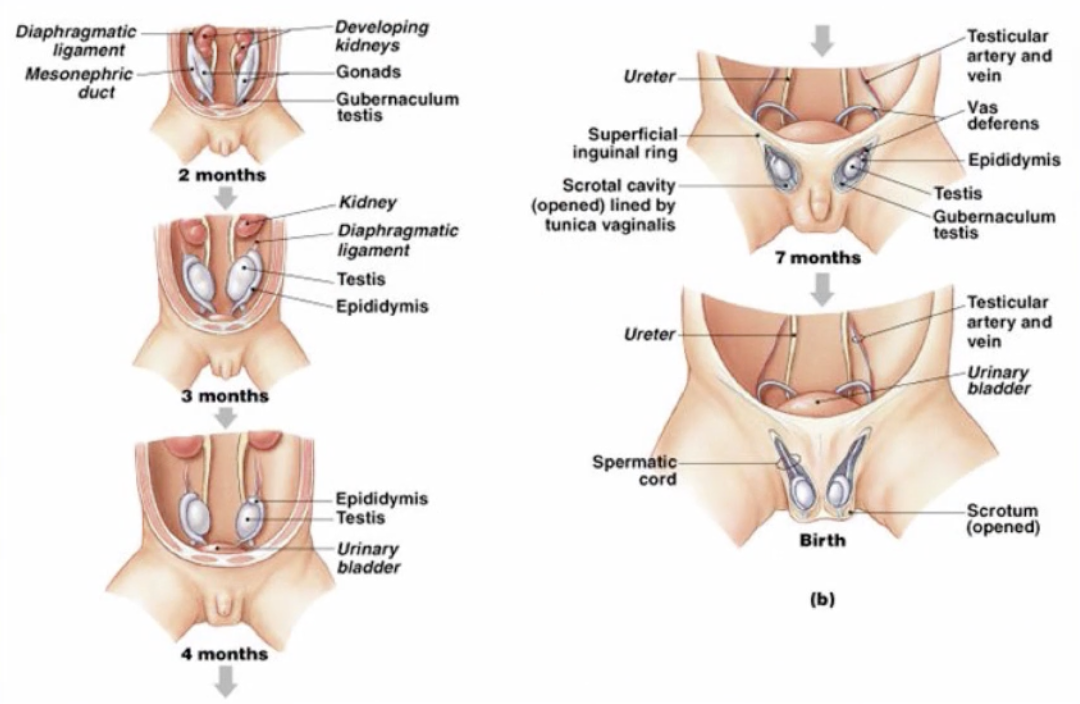
(Male) Descent of Testes
-initially formed inside of body cavity
-during development, testes move inferiorly thru body wall
(Male) Histology of the Testes
-composed of seminiferous tubules connecting to rete testis
-interstitial endocrine cells (produce testosterone)
-immobile spermatozoa moved by cilia from rete testis to epididymis
(Male) Scrotum
-pouch containing testes
-composed of skin, dartos muscle, and fascia
-allows for spermatozoa development at 1.1C lower than body temperature
(Male) Spermatic Cords
-extend between abdominopelvic cavity and testes
-connective tissue and muscle enclose ductus deferens, blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels
(Male) Spermatogenesis
-formation of spermatozoa
-begins in outer portion of tubules and proceeds toward lumen
(Male) Spermatogenesis, Spermatogonia
-divide forming 1° spermatocyte
(Male) Spermatogenesis, Primary (1°) Spermatocyte
-divide forming 2° spermatocyte
(Male) Spermatogenesis, Secondary (2°) Spermatocyte
-divide forming spermatids
(Male) Spermatogenesis, Spermatid
-immature gametes that mature into spermatozoa (spermiogenesis)
(Male) Spermatogenesis, Spermatozoa
-contains head (with nucleus), acrosome (with enzymes), middle piece (with mitochondria), and tail (flagellum for movement)
-released into lumen (spermiation) but remain immobile
(Male) Spermatogenesis, Nurse Cells
-promote spermatogenesis
(Male) Epididymis
-coiled tube on back of testes
-monitor and adjust fluid composition
-comprised of head (receives spermatozoa from efferent ductules), body, and tail (spermatozoa storage and protection)
(Male) Ductus deferens (Vas deferens)
-part of spermatic cord from epididymis tail to ampulla
-moves and stores spermatozoa
(Male) Male Urethra
-passageway from bladder to exterior surface
-serves reproductive/urinary system
-receives fluids from ductus deferens, seminal glands, and bladder
(Male) Accessory Glands
-produce fluid component of semen
(Male) Accessory Glands, Seminal Glands
-active tubular gland that secretes majority of semen volume into ejaculatory duct
(Male) Accessory Glands, Prostate Gland
-muscular organ that encircles urethra
-secretes prostatic fluid
(Male) Accessory Glands, Bulbourethral Glands
-small round glands that secrete alkaline fluid
(Male) Semen
-contains spermatozoa (~100 million), seminal fluid (alkaline, fructose, prostaglandins), and enzymes (antibiotics)
(Male) Semen, Capacitation
-spermatozoa become motile when mixed with seminal fluid and capable of fertilization when exposed to female reproductive tract
(Male) Penis
-tubular organ thru which urethra passes
-conduit for urine and semen
-comprised of root (fixed portion), body, and glans penis (distal end)
(Male) Penis, Erectile Tissue
-multiple vascular channels incompletely separated by connective tissue and smooth muscle
(Male) Penis, Corpora Cavernosa
-two cylindrical masses of erectile tissue surrounded by collagenous sheath
(Male) Penis, Corpus Spongiosum
-slender erectile body surrounded by elastin sheath
(Male) Penis, Non-Arousal
-smooth muscle contracts causing decreased blood flow
(Male) Penis, Arousals
-smooth muscle relaxes causing increased blood flow (erection)
(Male) Hormones, FSH and Testosterone
-targets Nurse cells and promotes spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis
(Male) Hormones, LH
-targets interstitial cells and promotes secondary sex characteristics
(Female) Ovaries
-female gonads secrete estrogen and progesterone and produce oocytes (female gamete)
(Female) Ovarian Support, Ovarian Ligament
-extend from uterus to ovary
(Female) Ovarian Support, Suspensory Ligament
-extend from pelvis to ovary
(Female) Ovarian Support, Mesovarium
-thickened stabilizing mesentery
(Female) Uterine Tubes
-hollow muscular tubes that transport oocyte to uterus
-oocyte movement involves ciliary motion and peristaltic contractions
(Female) Uterine Tubes, Infundibulum
-expanded funnel near ovary with fimbriae (projections)
(Female) Uterine Tubes, Ampulla
-middle segment
(Female) Uterine Tubes, Isthmus
-short segment between ampulla and uterine wall
(Female) Uterus
-provides mechanical and nutritional support for the developing baby
(Female) Uterus, Uterine Body
-fundus is rounded superior portion
-isthmus is constricted inferior end
(Female) Uterus, Cervix
-inferior portion extends to vagina
(Female) Uterus, Perimetrium
-incomplete serous membrane covers fundus, isthmus, and posterior body

(Female) Uterus, Myometrium
-thick, middle muscular layer
-smooth muscle arranged in longitudinal, circular, oblique layers
-provides strong forces during childbirth
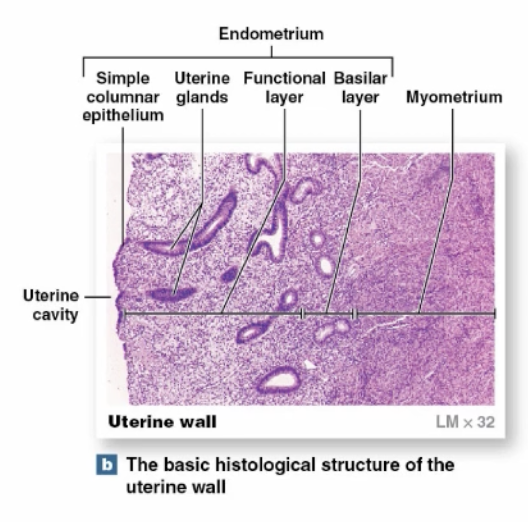
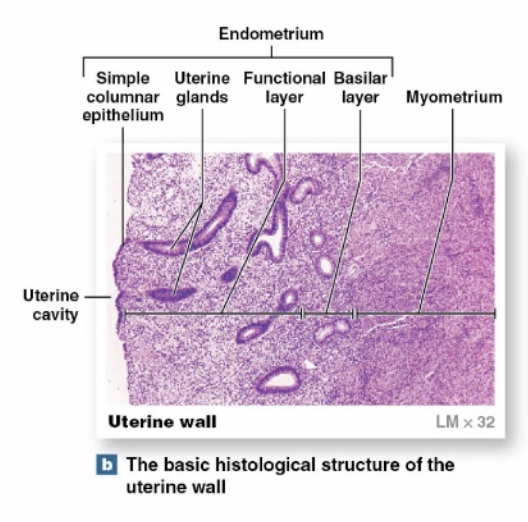
(Female) Uterus, Endometrium
-thin, inner, glandular layer that supports physiological demands
-estrogens cause uterine glands, blood vessels, and epithelia to change monthly
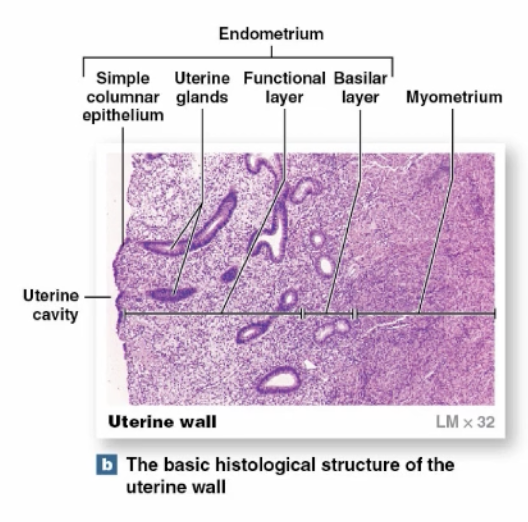
(Female) Uterus, Endometrium Functional Layer
-contains uterine glands
-undergoes most changes in thickness during uterine cycle
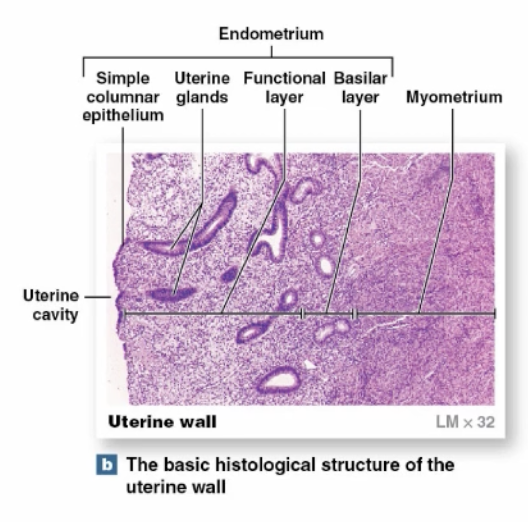
(Female) Uterus, Endometrium Basal Layer
-attaches endometrium/myometrium
-remains relatively constant during uterine cycle
(Female) Vagina
-elastic muscular tube extending from cervix to vestibule
-comprised of epithelia, lamina propria, mucosa (with smooth muscle)
-serves as conduit for menstrual fluids, spermatozoa and during childbirth
(Female) External Genitalia, Vulva
-area containing external genitalia
(Female) External Genitalia, Vestibule
-central space bounded by labia minora (small folds)
(Female) External Genitalia, Clitoris
-small projection of erectile tissue in vestibule
(Female) External Genitalia, Mons Pubis and Labia Majora
-adipose tissue that serve to protect and cover inner structures
(Female) Breasts, Mammary Glands
-specialized organs that produce milk to nourish infant
(Female) Breasts, Nipple
-contains ducts to mammary glands
(Female) Breasts, Areola
-pigmented area around each nipple
(Female) Oogenesis
-ovum production that begins at birth, accelerates at puberty and ends at menopause
(Female) Oogenesis, Oogonia
-in fetal ovaries
-divide forming a primary oocyte (before birth)
(Female) Oogenesis, Primary (1°) Oocyte
-some divide forming secondary oocyte (during ovarian cycle)
(Female) Oogenesis, Secondary (2°) Oocyte
-divide forming ovum (occurs at fertilization)
(Female) Ovarian Follicle
-specialized structures in ovarian cortex where oocyte growth occurs
(Female) Ovarian Follicle, Primordial Ovarian Follicle
-primary oocyte and surrounding follicle cells
(Female) Ovarian Follicle, Primary (1°) Ovarian Follicle
-formed by activated primordial ovarian follicle
(Female) Ovarian Follicle, Secondary (2°) Ovarian Follicle
-forms from primary ovarian follicle
(Female) Ovarian Follicle, Tertiary (3°) Ovarian Follicle
-follicular fluid accumulates causing doubling of size
(Female) Ovarian Cycle
-monthly process of maturation, ovulation, and degeneration of tertiary ovarian follicle
(Female) Ovarian Cycle, Follicular Phase
-tertiary ovarian follicle creates bulge in ovary
-granulosa cells associate with secondary oocyte (corona radiata)
(Female) Ovarian Cycle, Ovulation
-tertiary follicle releases secondary oocyte into pelvic cavity
-oocyte moves into uterine tube via fimbriae or by fluid currents
(Female) Ovarian Cycle, Luteal Phase
-postovulatory phase
(Female) Ovarian Cycle, Corpus Luteum
-forms from remaining granulosa cells
-secrete estrogens
-begin degenerating ~12 days after ovulation
(Female) Ovarian Cycle, Corpus Albicans
-produced from nonfunctional corpus luteum as fibroblasts invade and form scar tissue
-marks end of ovarian cycle
(Female) Uterine Cycle
-repeating series of changes in endometrium
-lasts from 21-35 days
(Female) Uterine Cycle, Menstrual Phase
-degeneration of endometrial functional layer
-constricted blood vessels cause reduced blood flow, O2, and nutrients
-blood vessels rupture releasing blood into connective tissue of functional layer
(Female) Uterine Cycle, Proliferative Phase
-epithelial cells of uterine glands multiply, spread across endometrial surface
-further growth/vascularization restores functional layer
-occurs at same time as enlargement of tertiary ovarian follicles (produces estrogens which stimulate/sustain)
(Female) Uterine Cycle, Secretory Phase
-uterine glands enlarge
-begins at ovulation and persists as long as corpus luteum remains intact
-ends as corpus luteum stops producing hormones
(Female) Female Reproductive Cycle
-controlled by hormones of the pituitary glands and gonads
-forms a complex pattern that coordinates ovarian and uterine cycles
(Female) Female Reproductive Cycle, Release of GnRH
-causes production/secretion of FSH and production of LH
(Female) Female Reproductive Cycle, Follicular Phase of Ovarian Cycle
-FSH stimulates development of tertiary ovarian follicle
-developing ovarian follicles secrete estrogens, FSH levels decline, and LH levels increase
(Female) Female Reproductive Cycle, Luteal Phase of Ovarian Cycle
-LH levels continue to increase leading to ovulation
-corpus luteum secretes progesterone leading to endometrial development
-estrogen levels fall, GnRH levels fall
-if pregnancy does not occur, corpus luteum degenerates, progesterone falls, GnRH increases for new cycle