POD parasitology 2
1/332
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
333 Terms
what species are under class cestoda (tapeworms)?
taenia spp
echinococcus spp
dipylidium caninum
anoplocephala perfoliata
moniezia spp
diphyllobothrium latum
cestode general adult morphology:
3 body regions
no mouth or digestive tract (absorb nutrients)
hermaphroditic
what are the 3 cestode body regions:
scolex (holdfast)
neck (germinal region)
strobila (chain of developing segments)
cestode general egg morphology:
hexacanth embryo fully developed within embryophore
eggs shed in feces or, more commonly, shed into environment within degenerating segments
cestode general life cycle:
indirect
eggs in feces
hexacanth embryo infects intermediate host→migrates to final site of development and transforms into infective form→transmission occurs when intermediate host is eaten→scolex of juvenile tapeworm attaches to gut and matures (produces eggs)
what are the major taenia spp?
taenia pisiformis
taenia taeniaeformis
taenia crassiceps
taenia saginata
what kind of larva are taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) larvae?

where do adult taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) infect?
small intestine of dogs
what animal do larval taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) infect?
rabbits
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) adult morphology:
shiny white strobila, up to 2 m long
scolex with 4 suckers and 2 rows of hooks on the rostellum
single genital pore on each rectangular segment
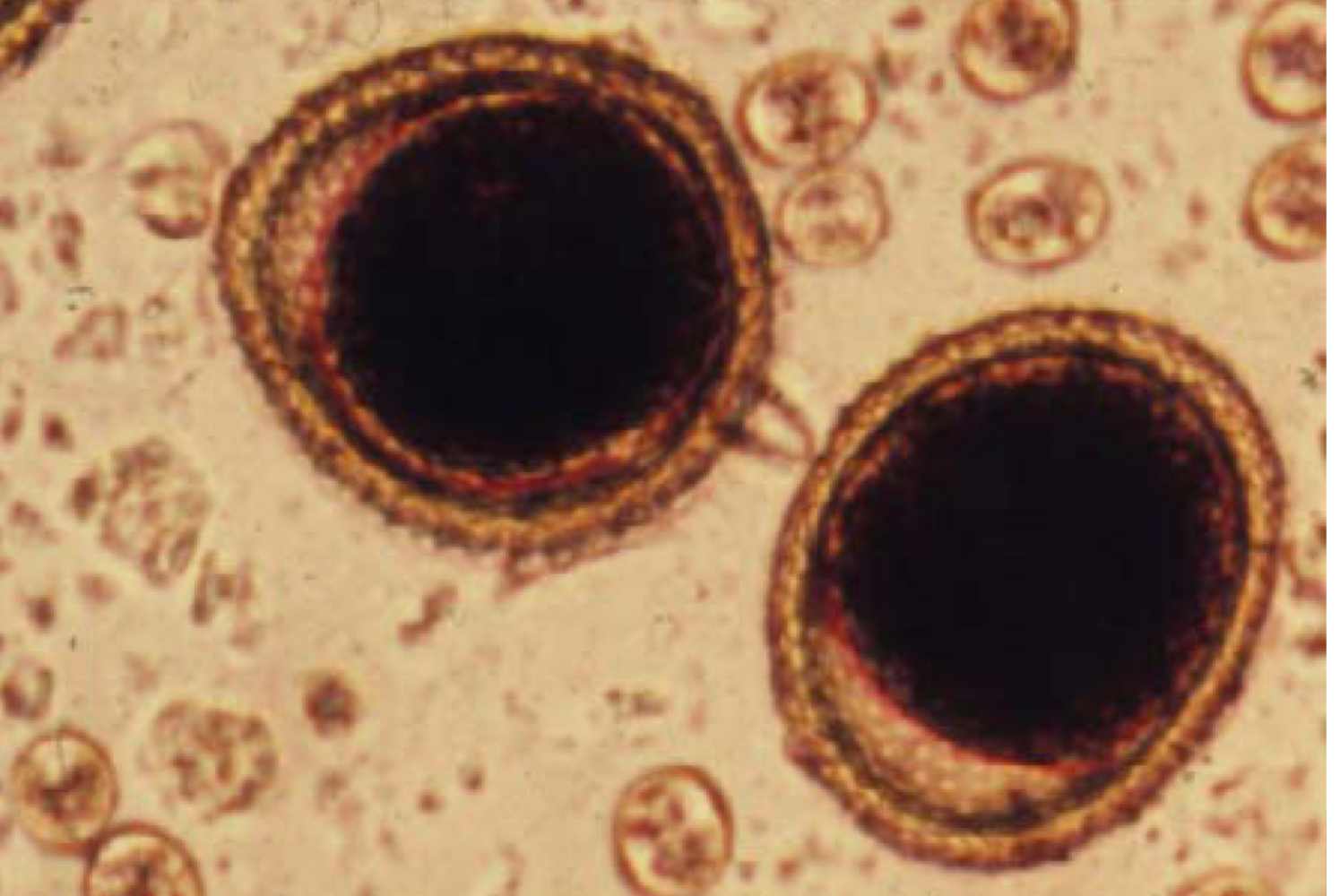
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) egg morphology:
40 micrometers
thick radially striated embryophore (shell)
found as single eggs
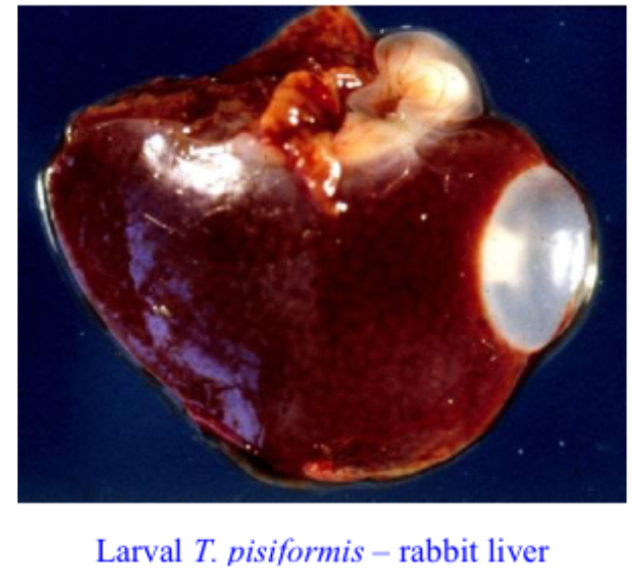
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) larva morphology:
cysticerus
fluid filled bladder containing invaginated scolex (bladder worm surrounded by host cyst)
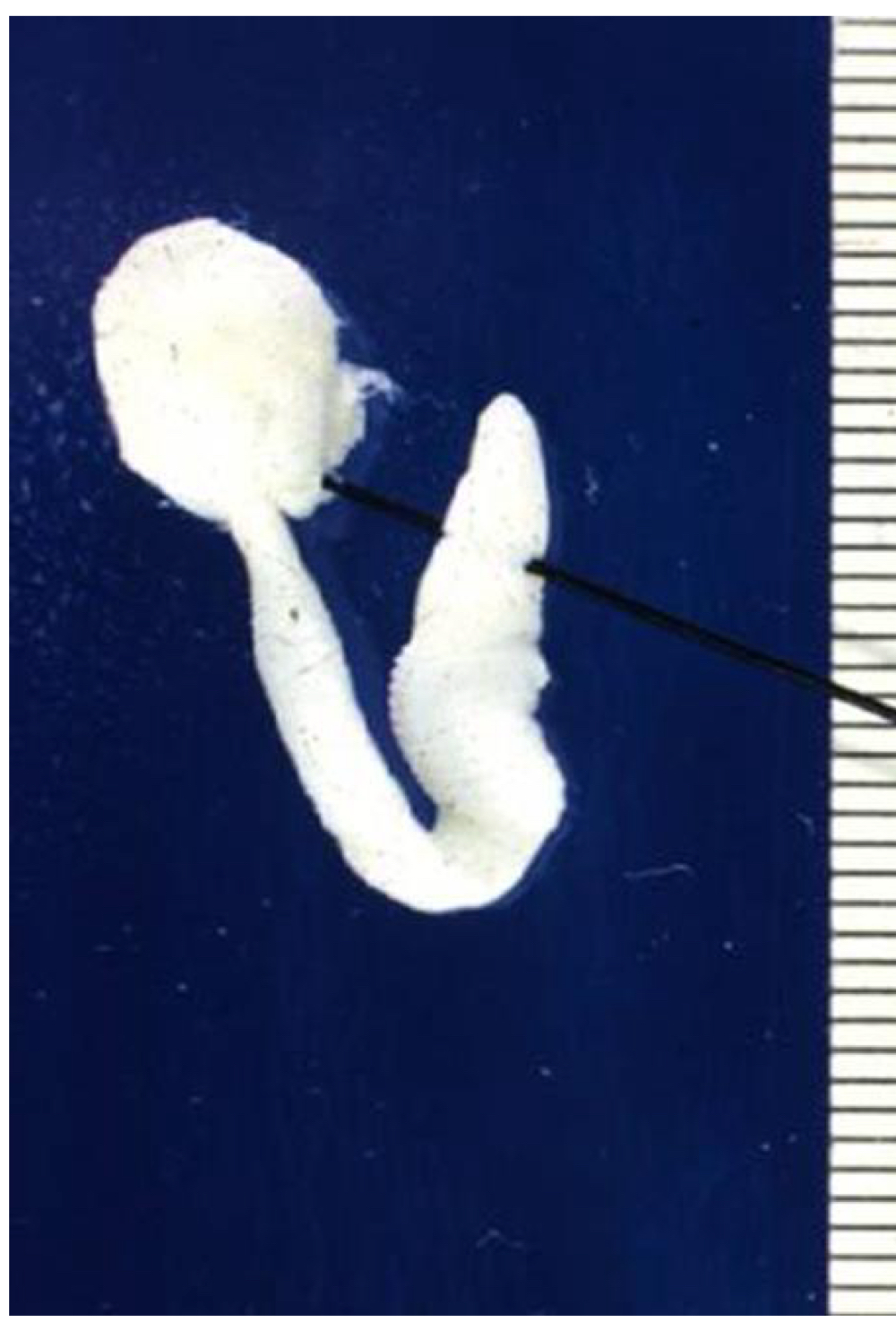
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) life cycle:
predator-prey life cycle
eggs released from segments ingested by IH
hexacanth larvae hatch and migrate to peritoneal cavity or liver to mature to cysticerus
when dog eats rabbit, scolex in cysticerus evaginates, attaches to gut and begins to form strobila
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) PPP:
6-8 weeks
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) signs:
presence of motile gravid segments in feces or perianal regions
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) treatment:
cestodicides
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm) prevention:
prevent hunting to block transmission
taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm) intermediate host is…
rodents (found in liver)
taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm) definitive host is…
cats (found in small intestine)
taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm) adult morphology:
scolex with 4 suckers and 2 rows of hooks on rostellum
strobila up to 60cm long
what kind of larva are taenia taeniaeformis larvae?
strobilocerus (partially developed cysticerus with scolex evaginated and a small, 1 cm strobila connected to fluid filled bladder)
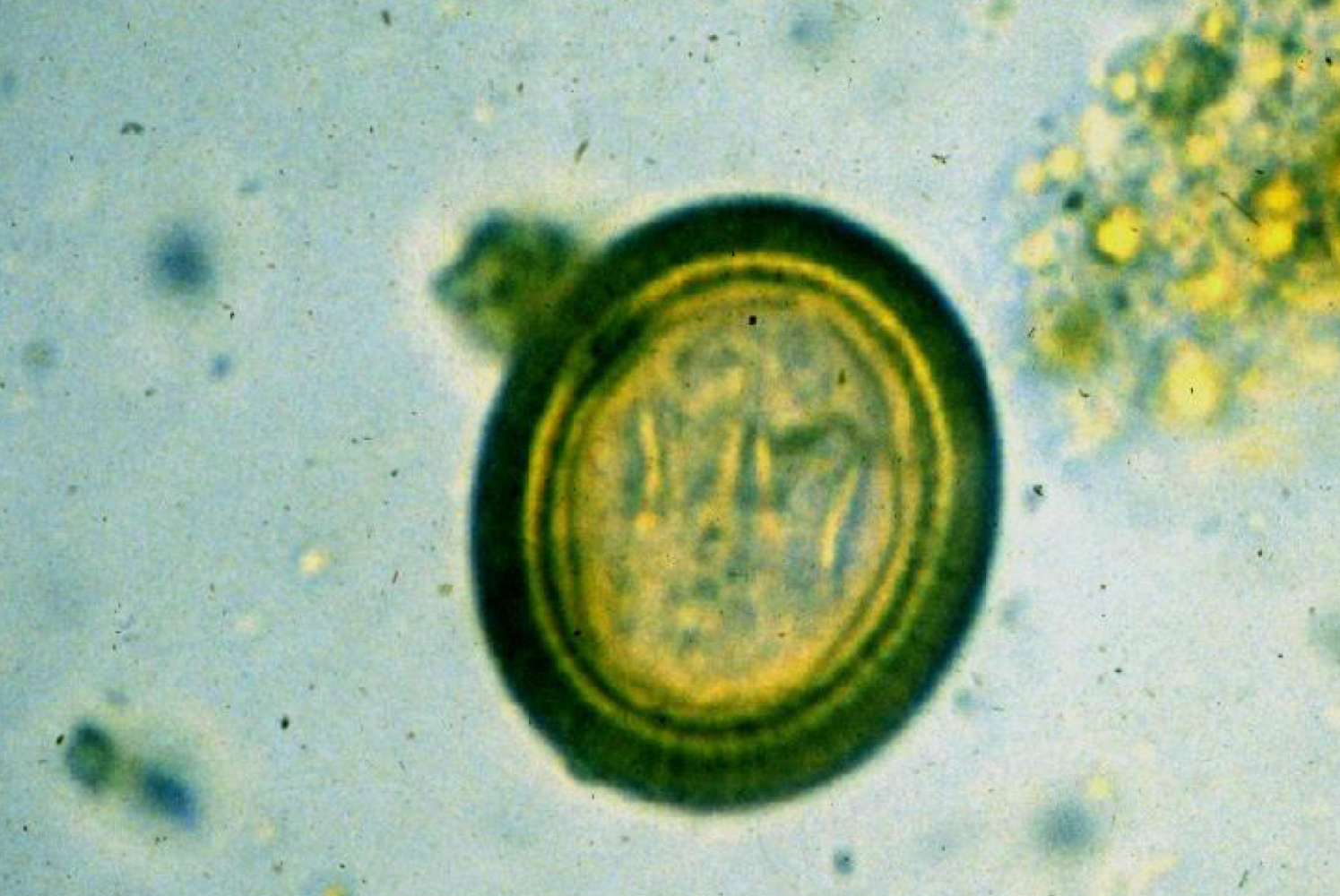
taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm) egg morphology:
40 micrometers
thick radially striated embryophore (shell)
found as single eggs
taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm) life cycle:
predator-prey life cycle
eggs released from segments ingested by IH
hexacanth larvae hatch and migrate to peritoneal cavity or liver to mature to cysticerus
when cat eats rodent, scolex in cysticerus evaginates, attaches to gut and begins to form strobila
taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm) treatment:
cestodicides
taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm) prevention:
prevent hunting to block transmission
what kind of larva are taenia crassiceps larvae and why is it important?
budding cysticerus amplifies infections
taenia crassiceps is a zoonotic threat to humans if what animal becomes infected?
dogs
taenia saginata IH is…
cattle (found in muscle)
taenia saginata DH is…
humans (found in small intestine)
what kind of larva are taenia saginata larvae?

taenia saginata adult morphology:
white, up to 8m long
unarmed rostellum with 4 suckers
segments with one lateral genital pore irregularly alternating from side to side
taenia saginata life cycle:
cattle ingest eggs, hatches and hexacanth larvae penetrate small intestine to appear in muscle
larva develop into cysticercus
humans eat undercooked meat containing cysticercus, which evaginates and attaches to small intestine and matures
what are the major echinococcus spp?
echinococcus granulosus
echinococcus multilocularis
echinococcus granulosus has a sylvatic life cycle with…
wolves (DH) and moose (IH)
echinococcus granulosus adult morphology:
smallest tapeworm of dogs (less than 1 cm long)
scolex has 4 suckers and 2 rows of prominent hooks
strobila only 3-4 segments long
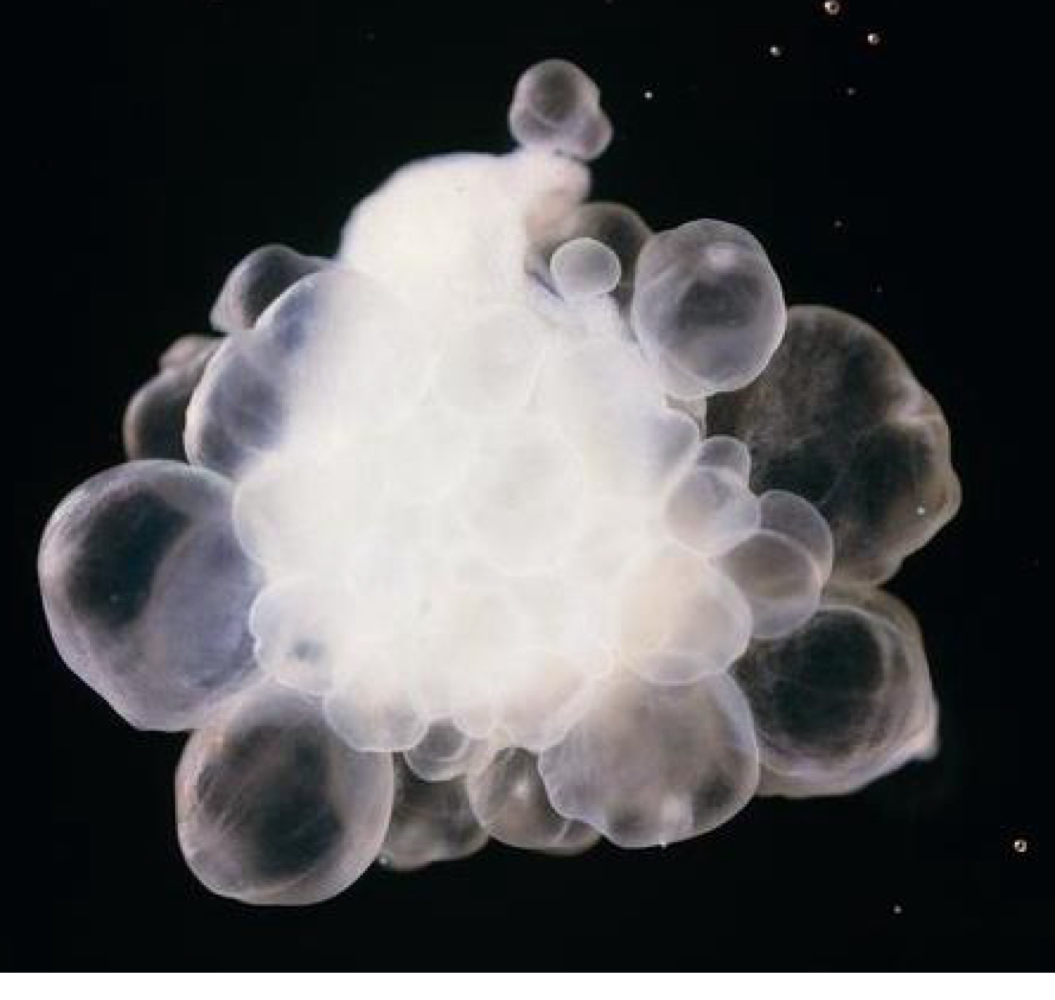
what kind of larva are echinococcus granulosus larvae?
allows for massive asexual replication (up to 50cm in diameter)
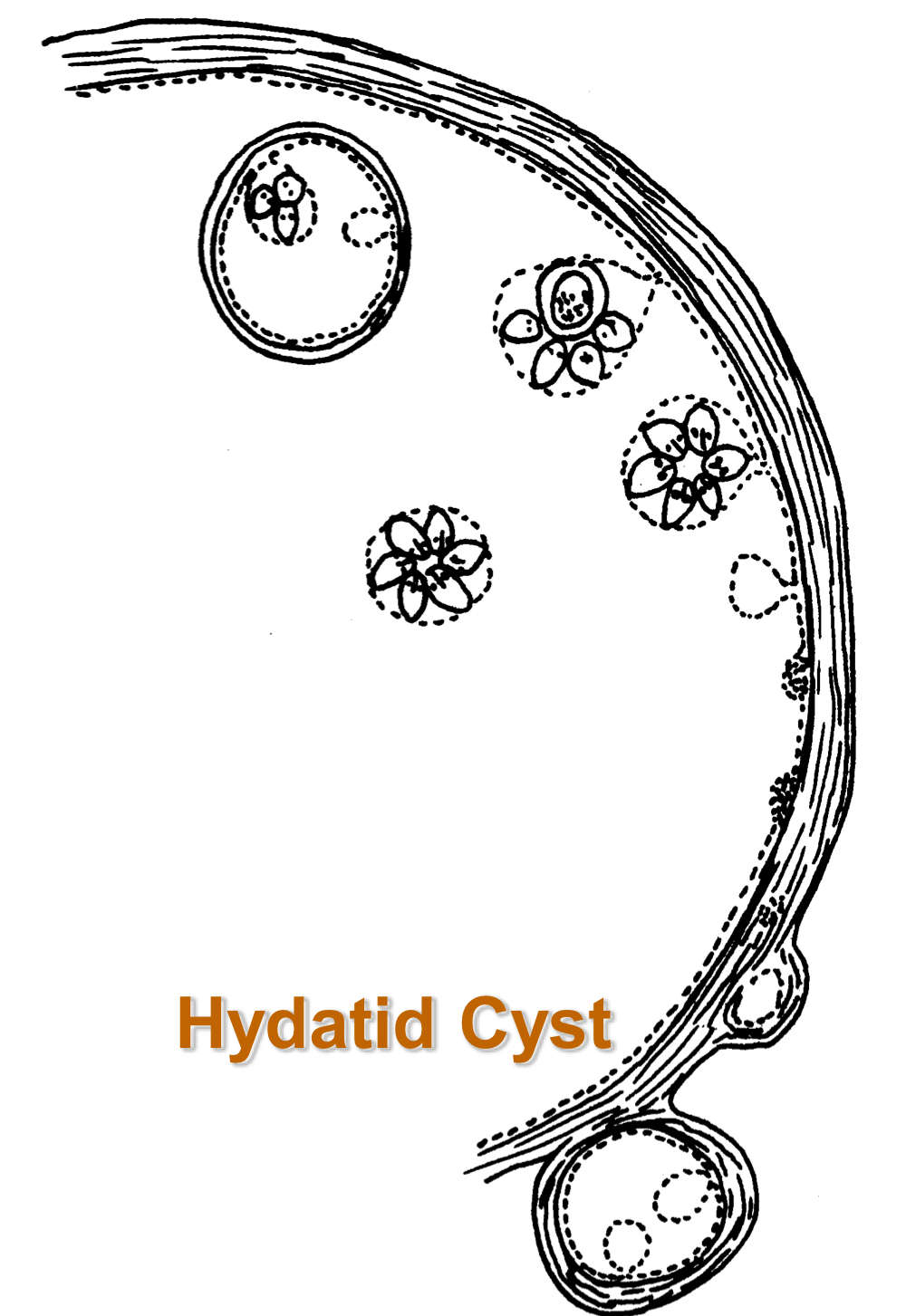
echinococcus granulosus egg morphology:
40 micrometers
thick radially striated embryophore (shell)
found as single eggs
echinococcus granulosus pathogenesis in humans:
humans act as IH
hydatid cysts in liver, lungs, or other organs cause space occupying lesion with pressure necrosis as they grow
rupture of cysts can cause anaphylactic shock and death
echinococcus granulosus diagnosis in humans:
radiology
echinococcus granulosus diagnosis in dogs:
eggs in feces
echinococcus granulosus treatment in dogs:
praziquantel
echinococcus granulosus treatment in humans:
surgery and antihelmintics
echinococcus mulitlocularis has a sylvatic life cycle with…
fox (DH) and rodents (IH)
echinococcus mulitlocularis adult morphology:
smallest tapeworm of dogs (less than 1 cm long)
scolex has 4 suckers and 2 rows of prominent hooks
strobila only 3-4 segments long
echinococcus mulitlocularis larva morphology:
alveolar hydatid cyst (hydatid cyst not confined by capsule)
exogenous budding of cyst acts like neoplasm to invade surrounding tissue
echinococcus mulitlocularis egg morphology:
40 micrometers
thick radially striated embryophore (shell)
found as single eggs
echinococcus multilocularis pathogenesis in humans:
humans act as IH
alveolar hydatid cysts in liver with metastasis to other organs makes it difficult to control
echinococcus multilocularis diagnosis in dogs:
eggs in feces
echinococcus multilocularis treament in dogs:
praziquantel
echinococcus multilocularis diagnosis in humans:
radiology
echinococcus multilocularis treatment in humans:
surgery (often unsuccessful due to metastasis)
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) IH is…
fleas or biting lice
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) DH is…
dogs, cats, humans (small intestine)
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) adult morphology:
scolex with 4 suckers and a rostellum with several rows of fine hooks
strobila up to ½ meter long
segments are somewhat barrel shaped with pores on each side
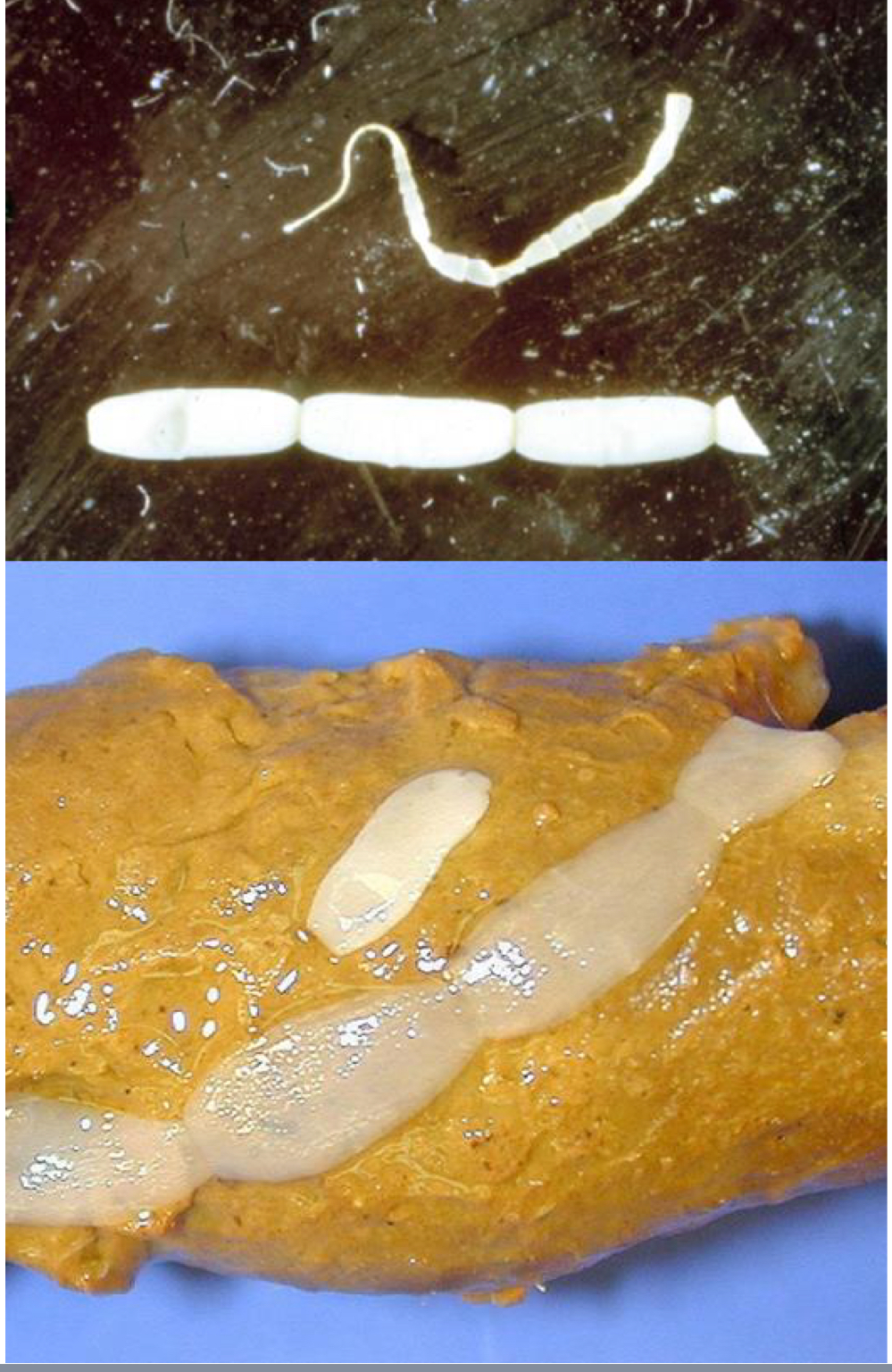
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) larva morphology:
found in hemoceol (body cavity) of insect IH
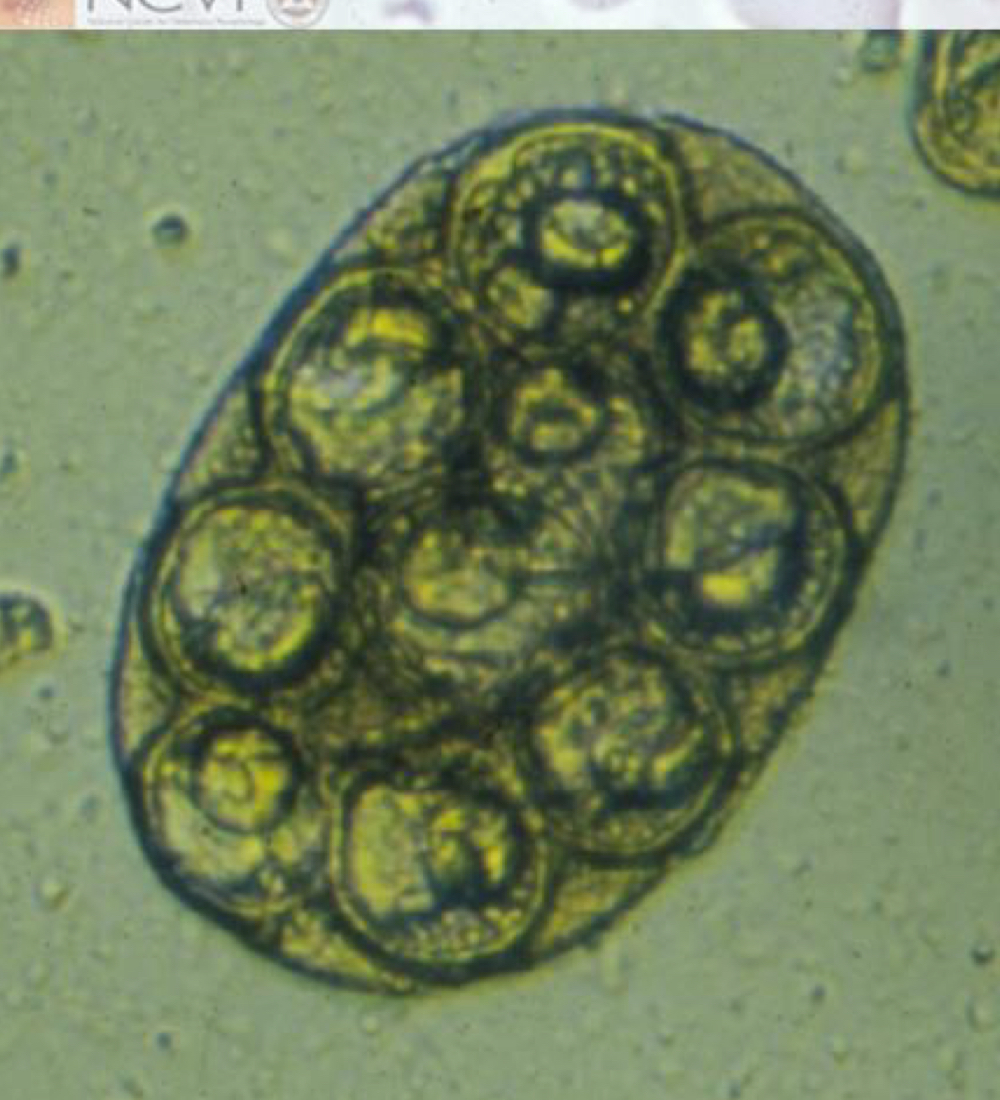
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) egg morphology:
eggs in packets
eggs are each 40 micrometers with a thick unstriated embryophore
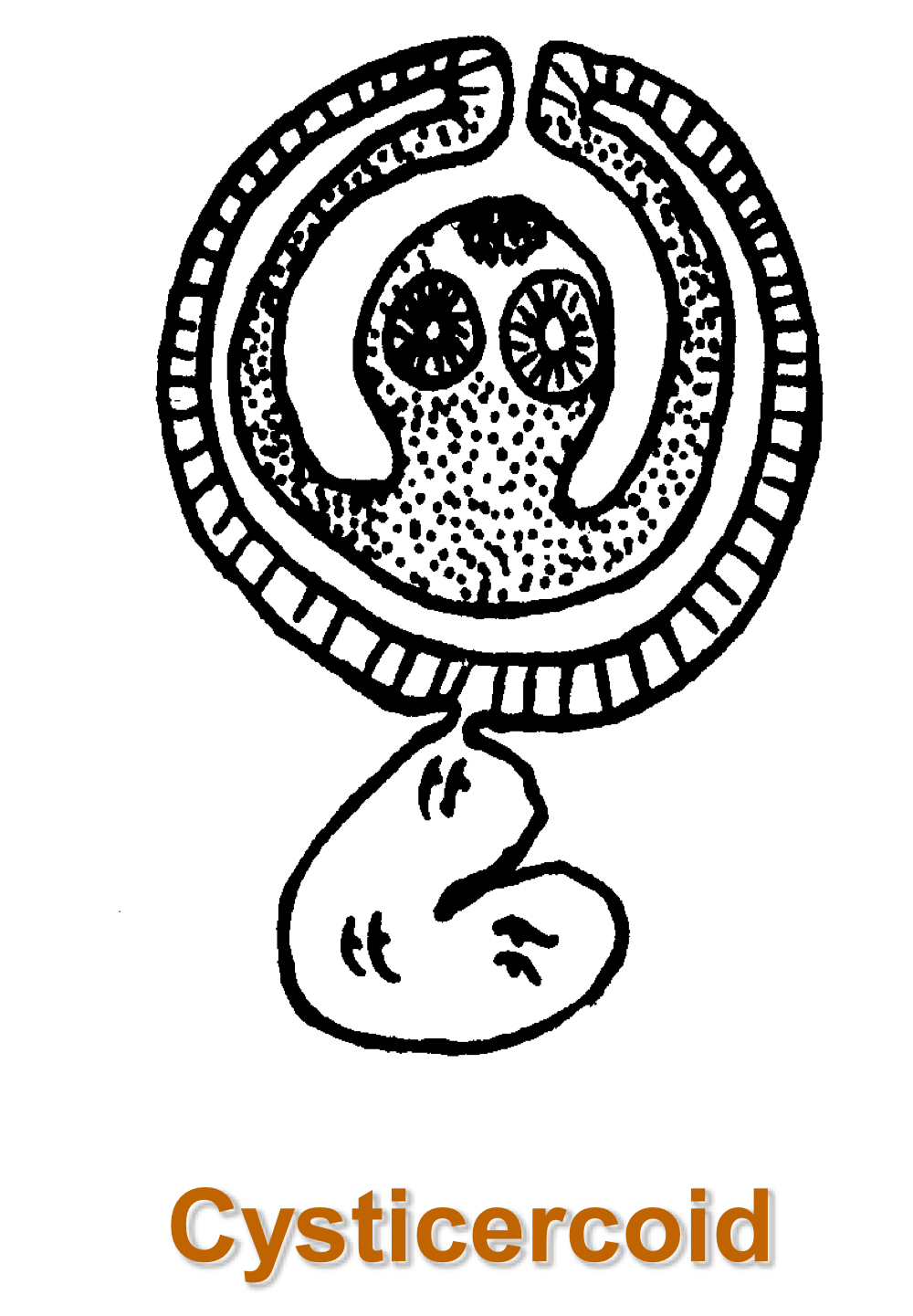
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) life cycle:
eggs passed within motile segments
liberated eggs ingested by flea larvae
hexacanth embryo hatches from embryophore and penetrates body cavity of insect
cysticeroid matures there
when adult flea is ingested, scolex attaches to gut and strobila matures
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) PPP:
2-3 weeks
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) signs:
migrating gravid segment
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) diagnosis:
segments in feces
squashes of segments (± rehydration) for egg masses
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) treatment:
cestodicides
dipylidium caninum (double-pored tapeworm) prevention:
flea control
anoplocephala perfoliata DH is…
equine (ileocecal junction)
anoplocephala perfoliata IH is…
oribatid mites
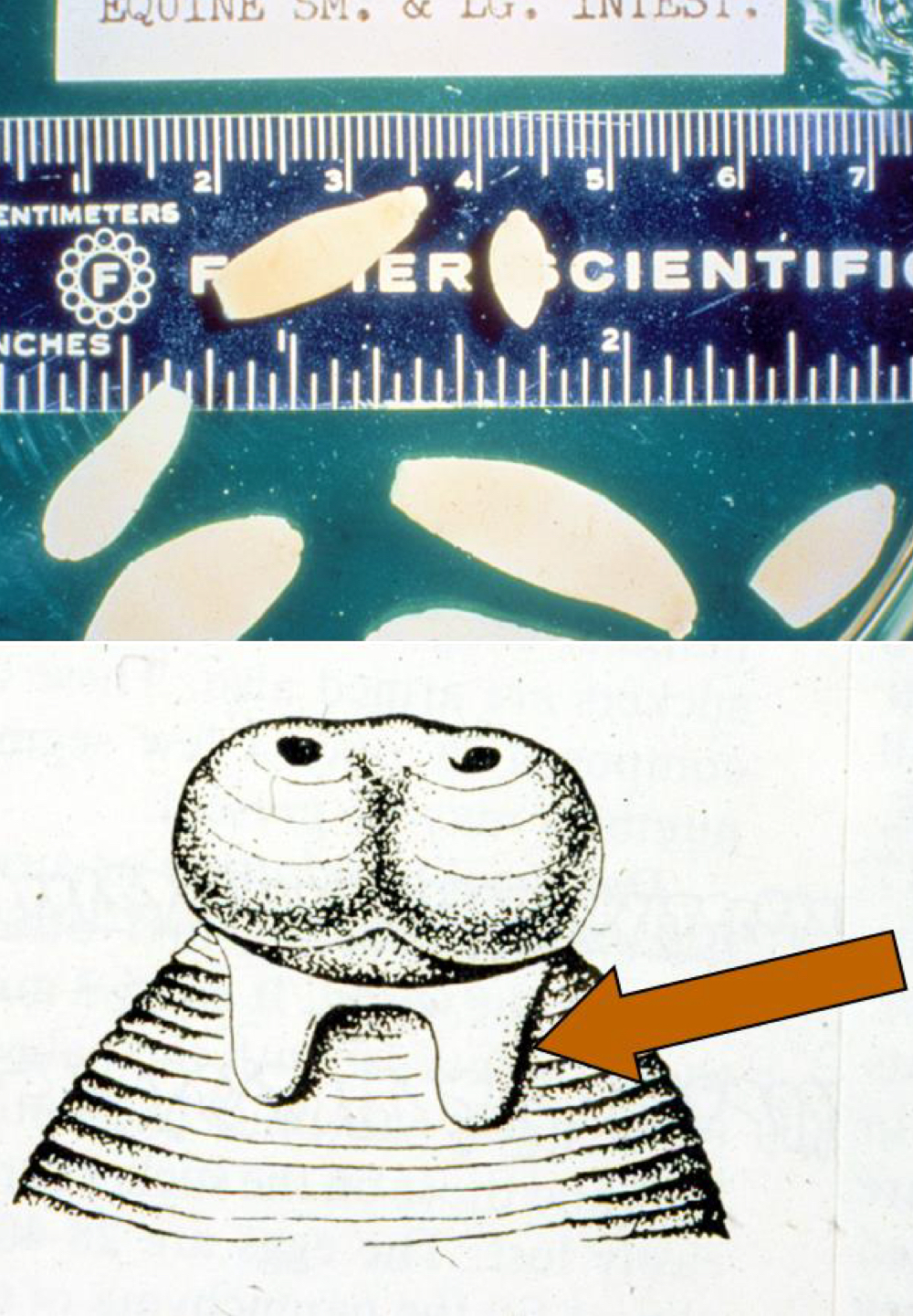
anoplocephala perfoliata adult morphology:
up to 8 cm long, flat, wedge shaped
unarmed scolex with 4 suckers each with a lappet
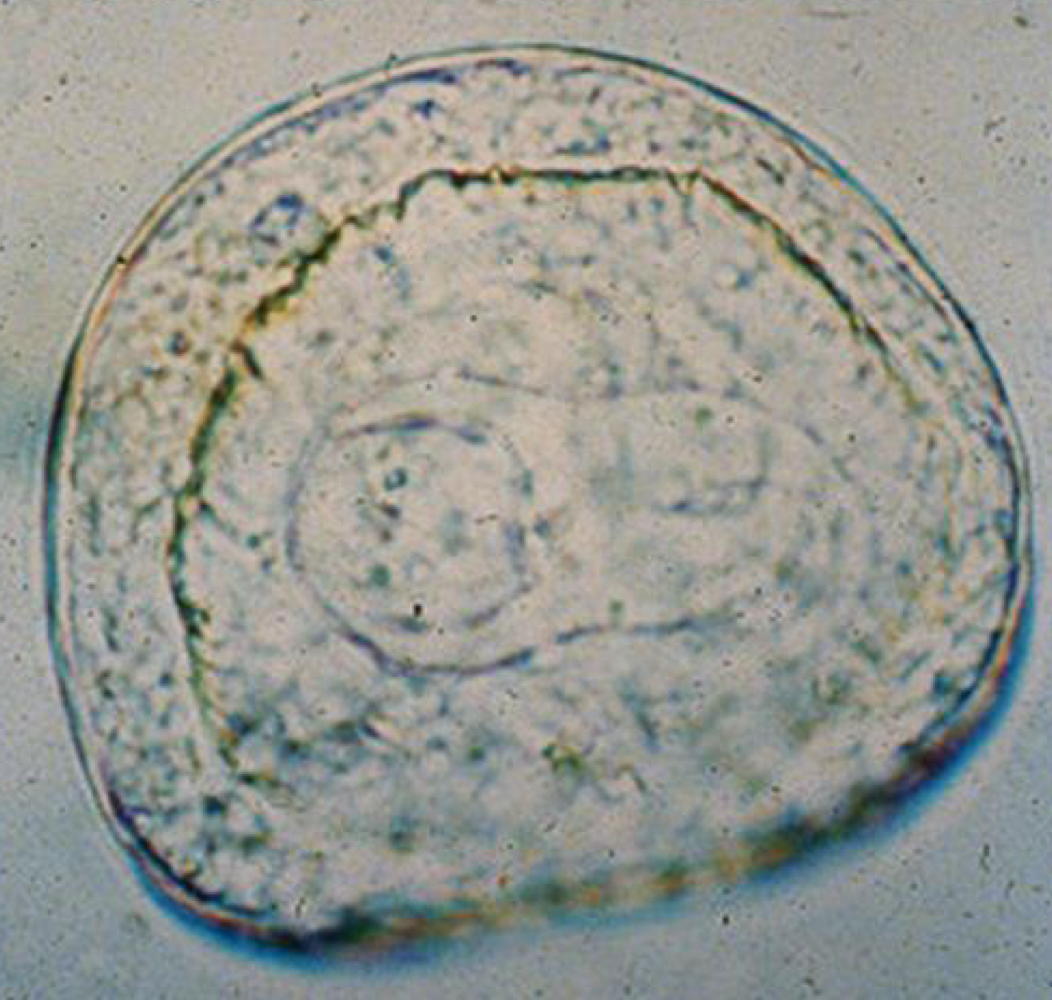
anoplocephala perfoliata egg morphology:
irregular eggs with pyriform apparatus (pair of prong like processes)
moniezia spp DH are…
cattle, sheep, goats (small intestine)
moniezia spp IH are…
oribatid mites
moniezia spp treatment:
albendazole
diphyllobothrium latum first IH is…
copepod
diphyllobothrium latum second IH is…
fish
diphyllobothrium latum kind of larva in first IH is…
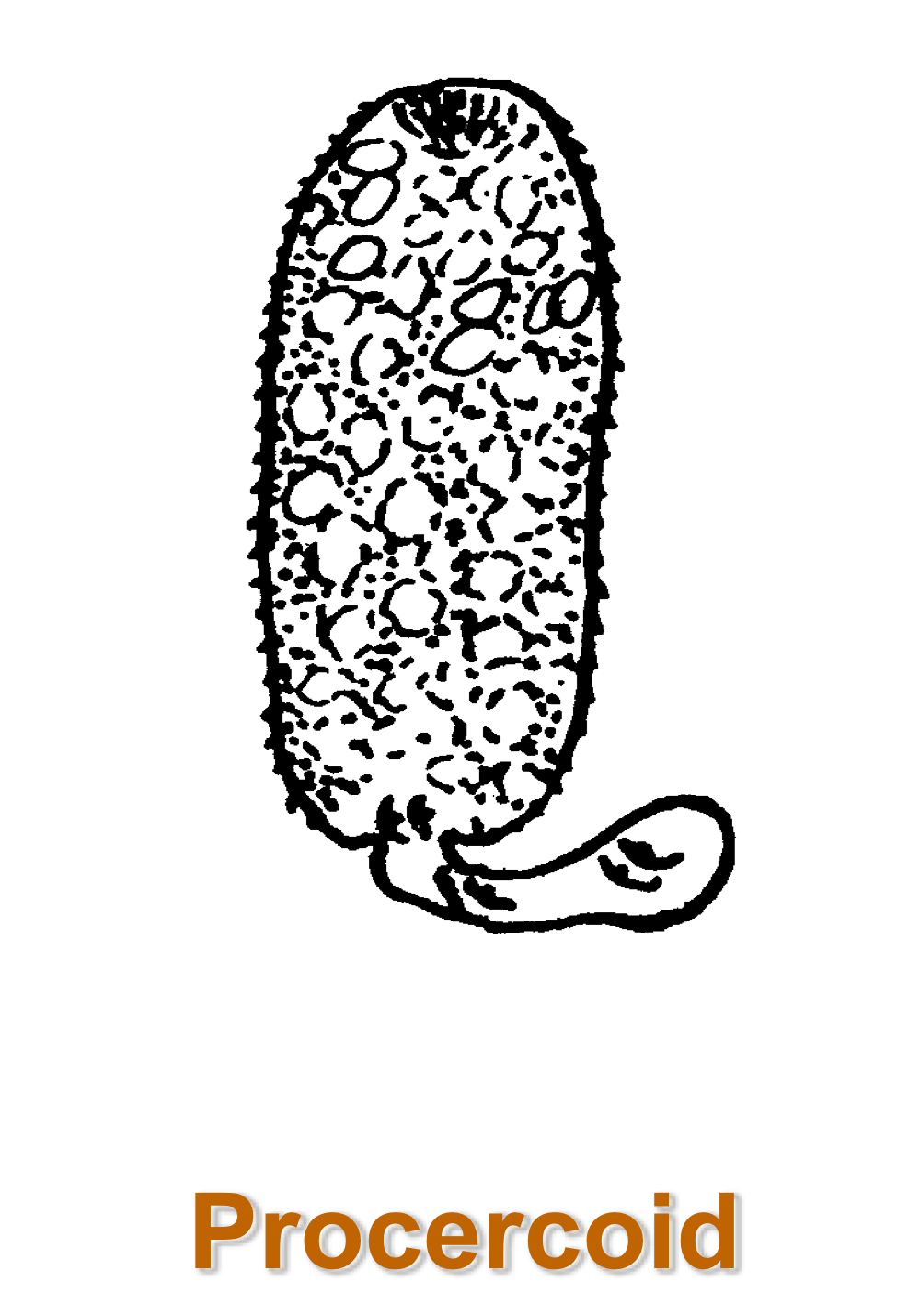

diphyllobothrium latum kind of larva in second IH is…
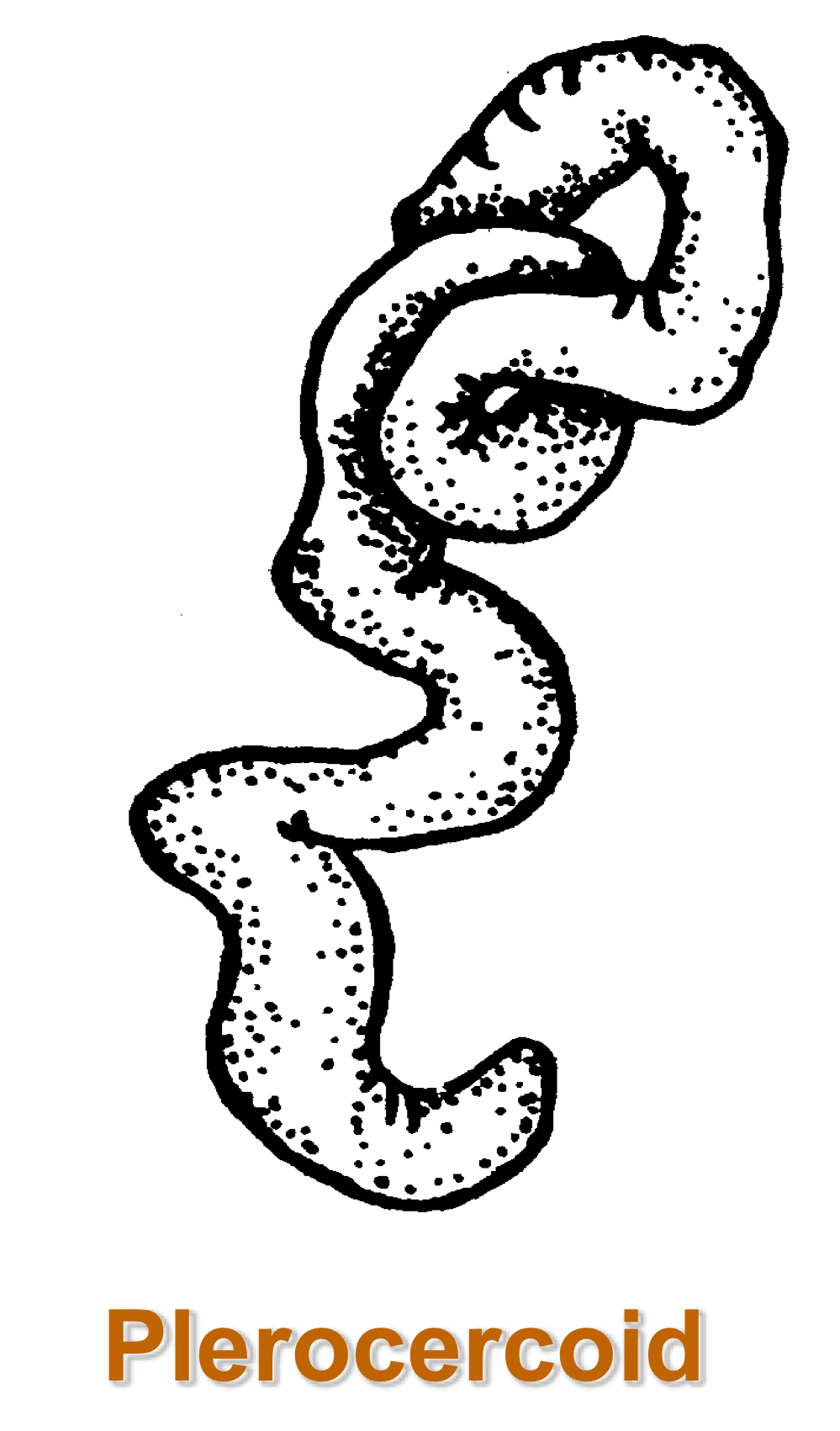

diphyllobothrium latum DH is…
fish eating mammals including humans
diphyllobothrium latum adult morphology:
scolex has pair of bothria (grooves)
large strobila (some many meters long)
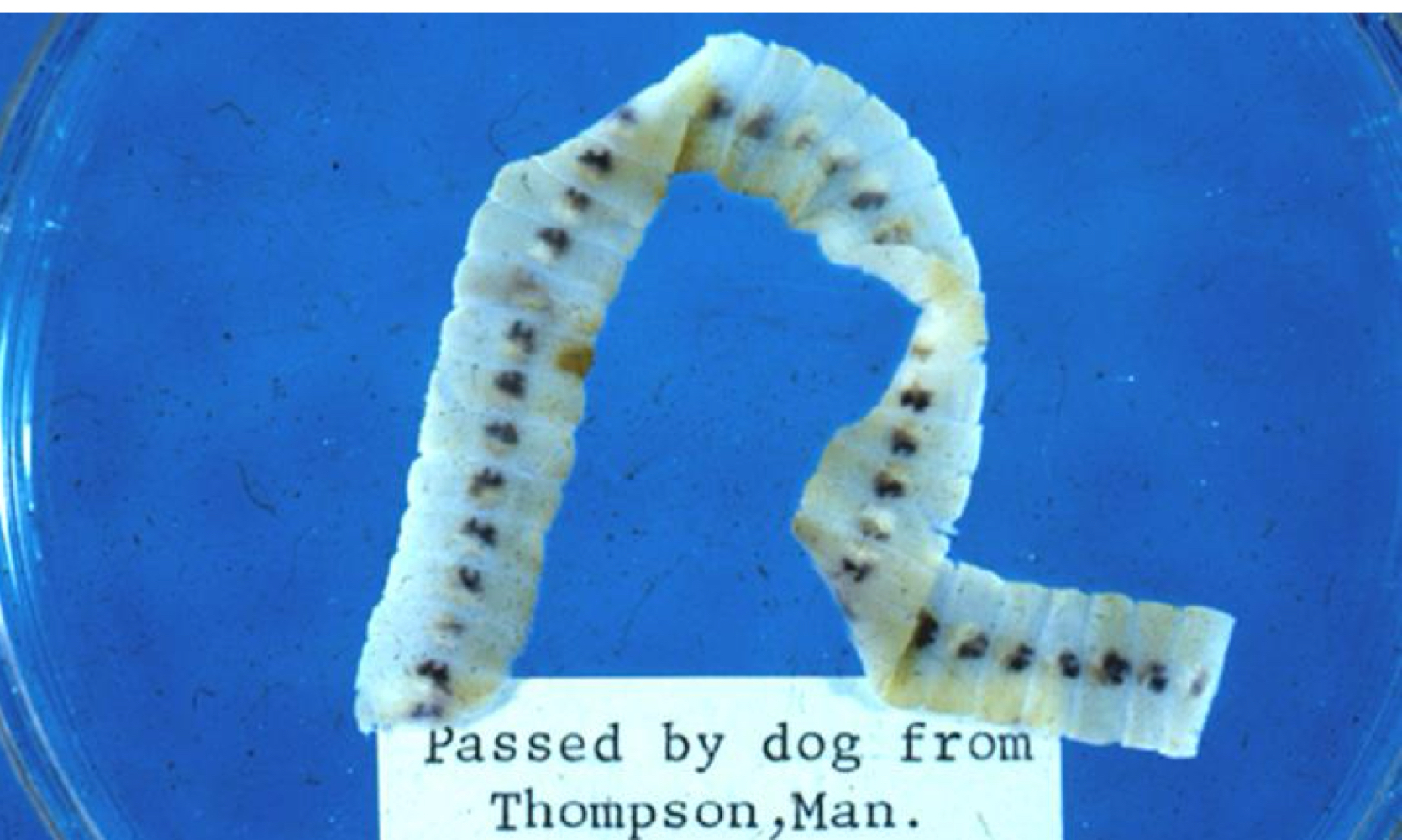

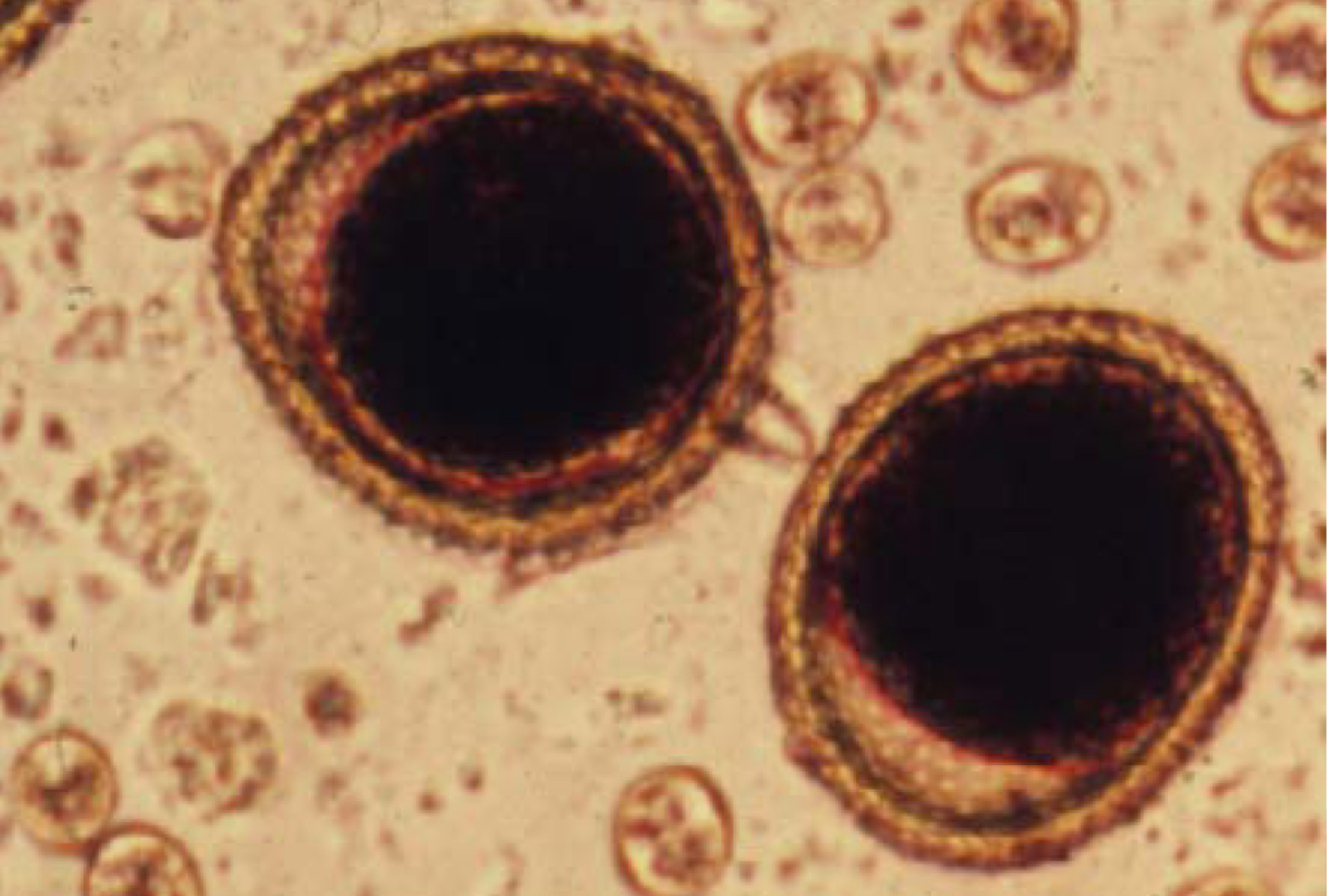
diphyllobothrium latum egg morphology:
operculate, light brown egg with ciliated hexacanth larva
ciliated hexacanth embryo called coracidium
diphyllobothrium latum pathogenesis in humans:
may cause pernicious anemia (B12 deficiency) in genetically predisposed people
what are the orders of nematodes?
rhabditida (rhabditids, threadworms)
strongylida (strongylids, hookworms, lungworms)
oxyurida (pinworms, oxyurids)
ascaridida (ascarids)
spirurida (spirurids, filarids, Dracunculus)
enoplida (trichurids, dioctophyme, capillarids, trichinella)
nematode general features:
elongate tubular bodies
thick, resistant cuticle
muscles under cuticle
hydrostatic pressure maintains shape and rigidity
simple alimentary tract
separate sexes
male nematode anatomy:
single convoluted tube consisting of testes, vas deferens, and ejaculatory duct
sometimes supplemented with cuticular spines
some have pronounced copulatory bursa
female nematode anatomy:
pair of blind ended ovaries leading to uteri
common vagina and vulva
often store sperm for protracted periods
nematode general life cycle:
egg→L1→L2→L3→L4→L5→adults (L3s are the infective form)
life cycle can be divided among different hosts
nematode tracheal migration
extensive migration leading to alveoli from which larvae move up the airways to the trachea to the gut
nematode somatic migration
stay in bloodstream to be distributed around body
nematode mucosal migration
penetrate gastric pits or mucosa for a period of development prior to returning to lumen as adult
ascarids (roundworms) general features:
adults are host specific
various life strategies, most involving tracheal migration
resistant eggs
infect small intestine of DH (exception is heterakis gallinarum)
ascarid pathogenesis:
poor growth
obstruction in heavy infection
lesions from migrating stages
ocular or visceral larval migrans associated with tracheal migration
what are the major species of ascarids?
toxocara canis
toxocara cati
toxocaris leonina
parascaris equorum
ascaris suum
ascaridia galli
heterakis gallinarum
baylisascaris procyonis
toxocara canis adult morphology:
large, heavy bodied, up to 18cm
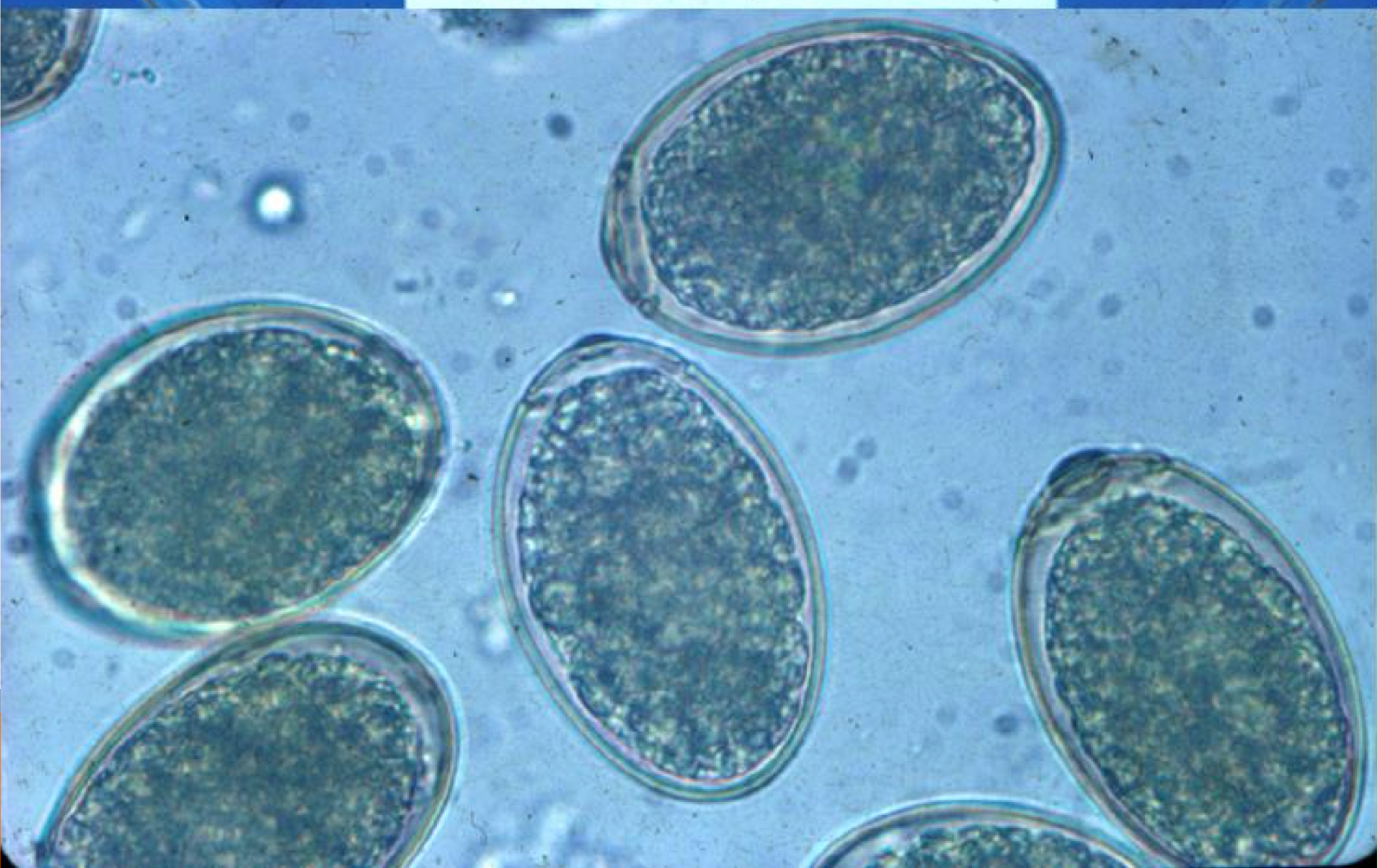
toxocara canis egg morphology:
thick shelled, pitted egg containing single cell when passed in feces
toxocara canis DH is…
dogs (small intestine)
hypobiosis
pause in development by nematodes
toxocara canis life cycle:
no intermediate hosts
larvae develop to L3 in egg→infective eggs are ingested by dog
fate of larvae depends on host
< 3 months: primarily tracheal migration with PPP of 4-5 weeks
3-6 months: increasingly somatic migration
> 6 months: only somatic migration
pups in utero infected by transplacental migration of larvae from bitch to fetus
transplacental and transmammary transmission of toxocara canis:
some hyobiotic larvae are mobilized by pregnancy
enter liver and lung of fetus and wait for birth of pup
tracheal migration to form adults (PPP: 3 weeks)
some larvae may enter milk and infect pups by transmammary route
toxocara canis intestinal phase signs:
heavy infections: cachexia, unthriftiness, vomit with worms, painful abdomen, death
toxocara canis migration phase signs:
eosinophilia
focal lesions
eosinophilic gastroenteritis or lung problems
toxocara canis should be treated with anthelmintics that…
do not induce hyperactivity in roundworms or kill worms quickly
toxocara cati DH is…
cats (small intestine)
toxocara cati adult morphology:
10 cm worms with cervical alae that give arrowhead appearance to worm
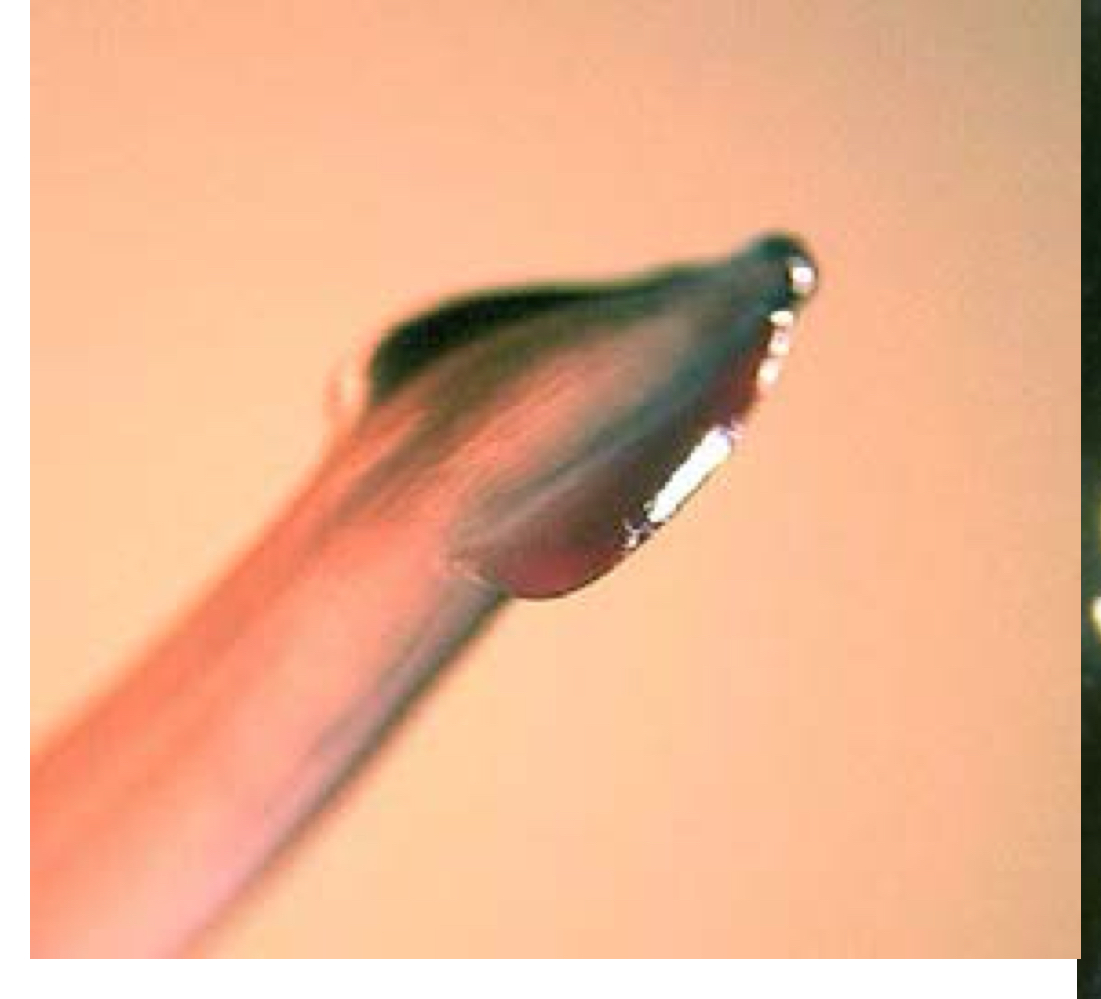

toxocara cati egg morphology:
thick shelled, pitted egg containing single cell when passed in feces