UN03: Early Christian and Byzantine Art & Architecture Illustrated Glossary
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
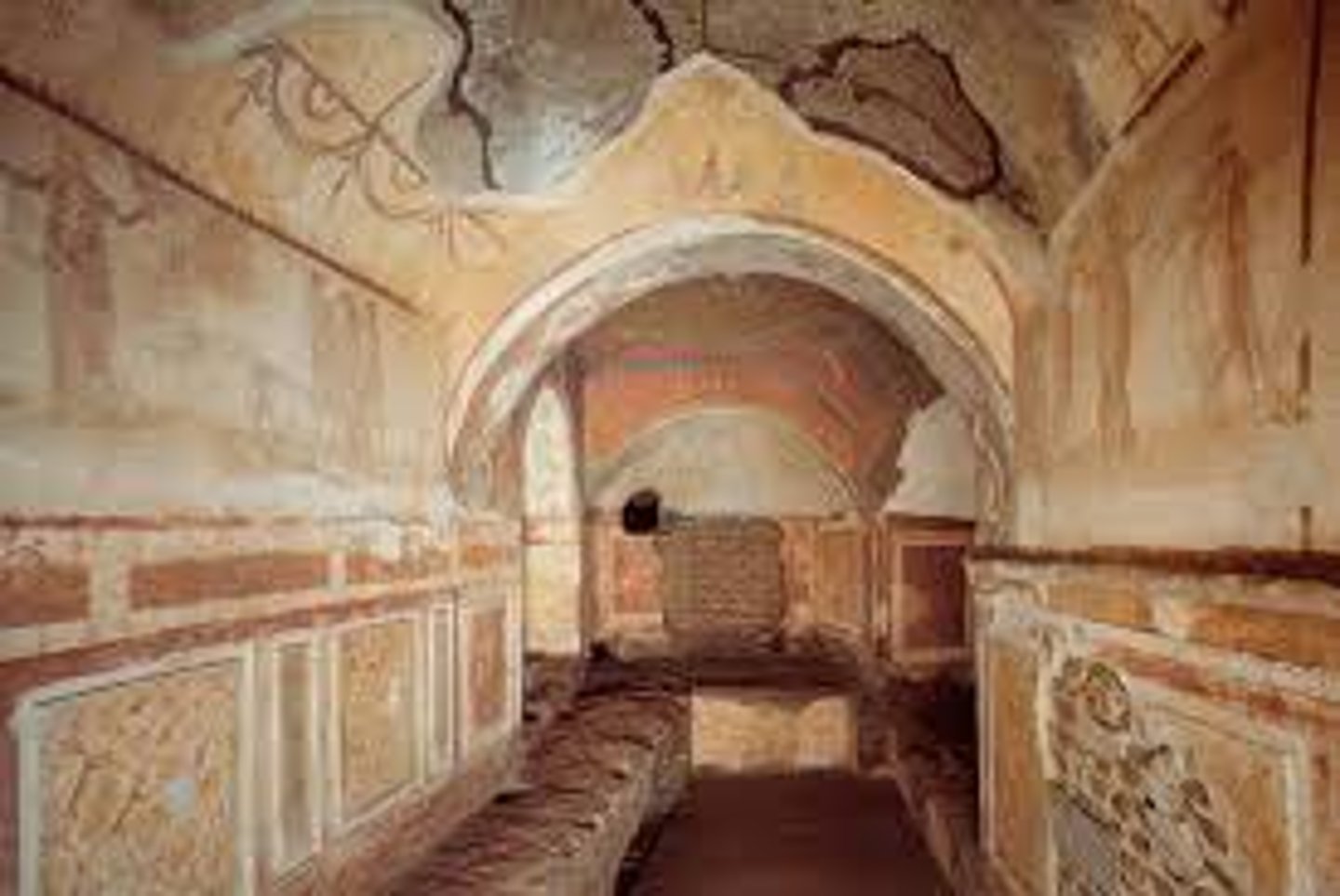
catacombs
An underground cemetery, esp. one consisting of tunnels and rooms with recesses dug out for coffins and tombs.

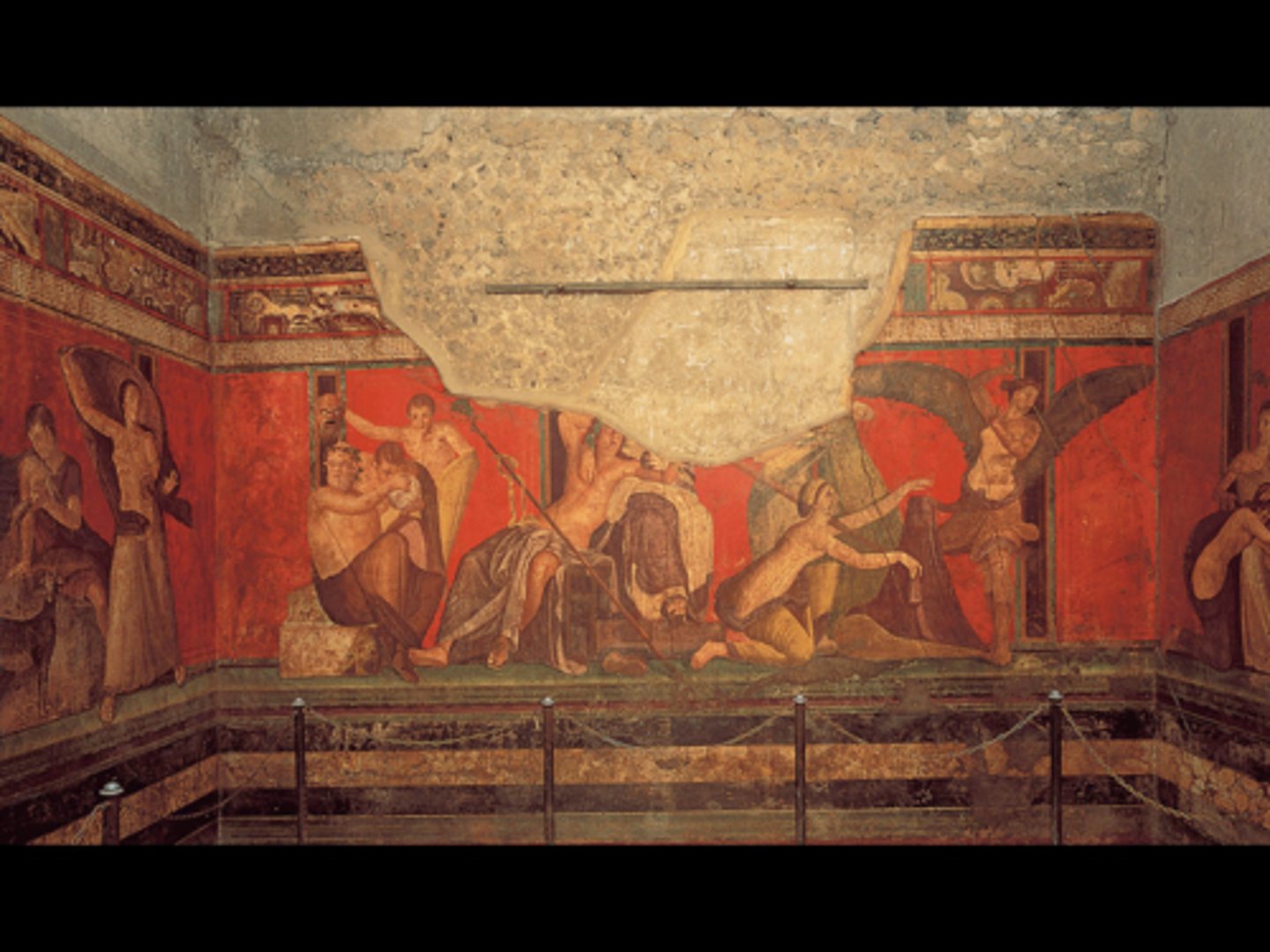
fresco secco
the technique of painting on dry plaster with pigments mixed in water.

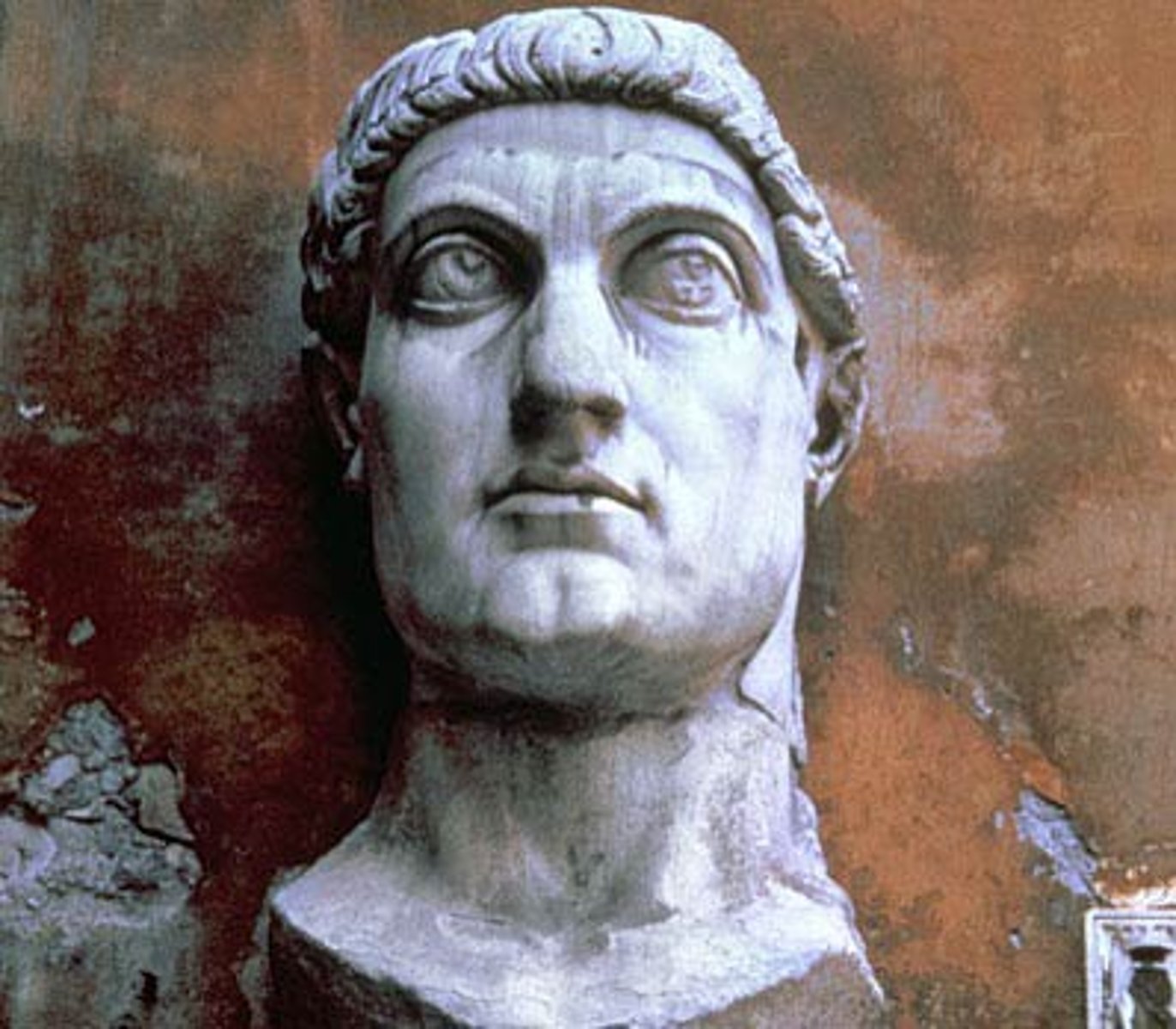
Constantine the Great
Emperor of Rome who adopted the Christian faith and stopped the persecution of Christians (280-337)

Spolia
the re-use of earlier building material or decorative sculpture on new monuments

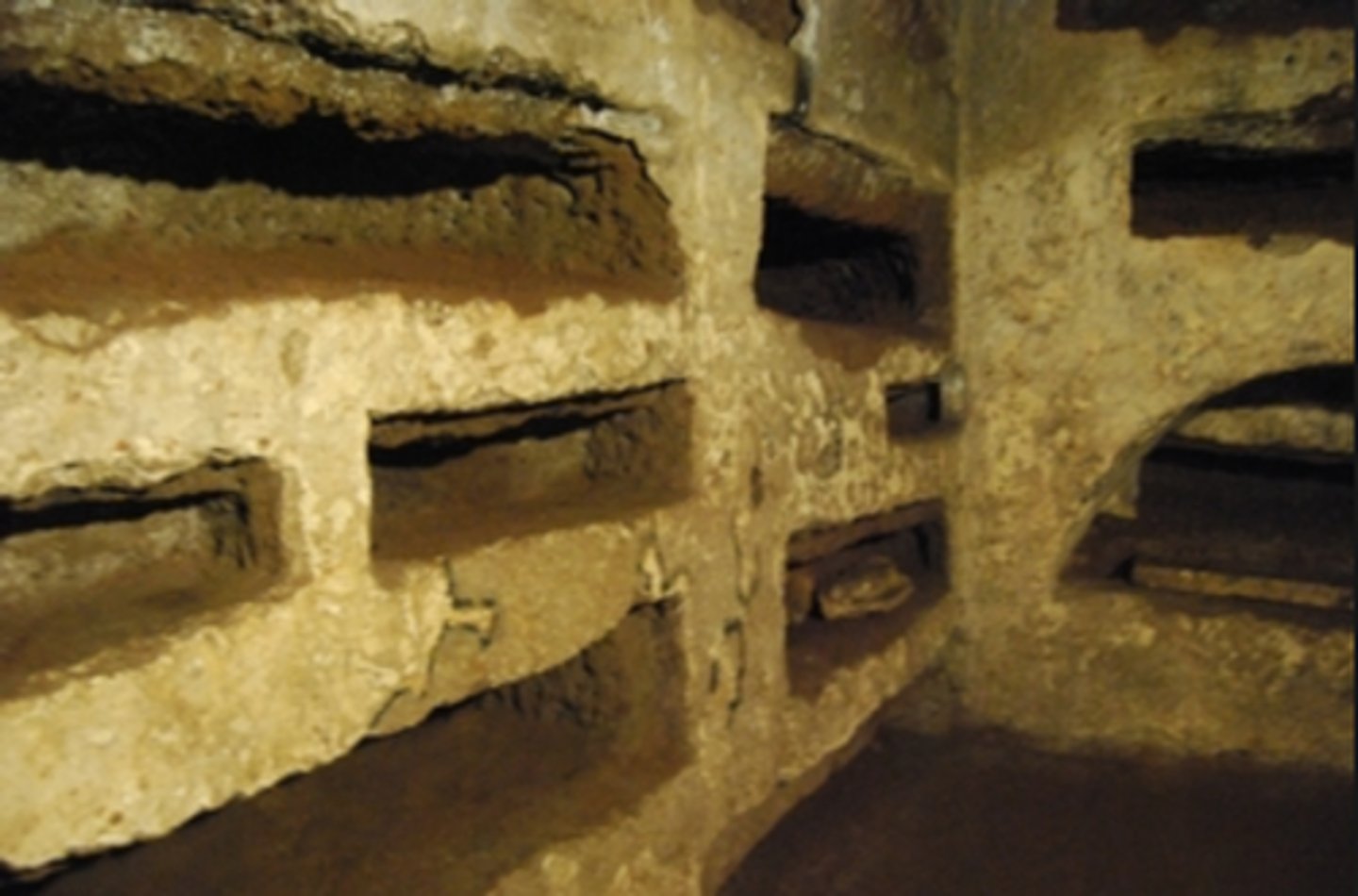
loculi
openings in the walls of catacombs to receive the dead

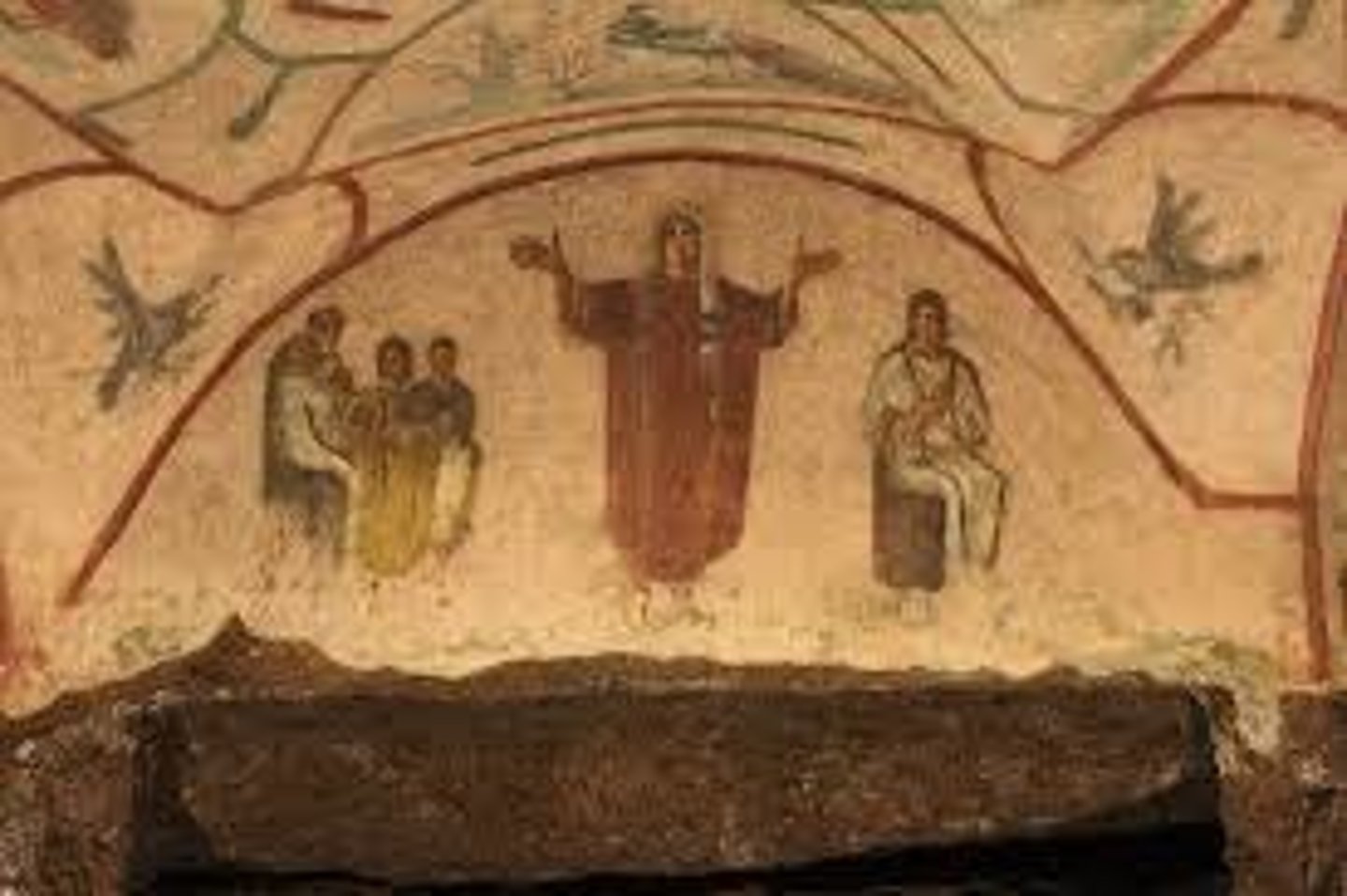
Orant
In Early Christian art, a figure with both arms raised in the ancient gesture of prayer.

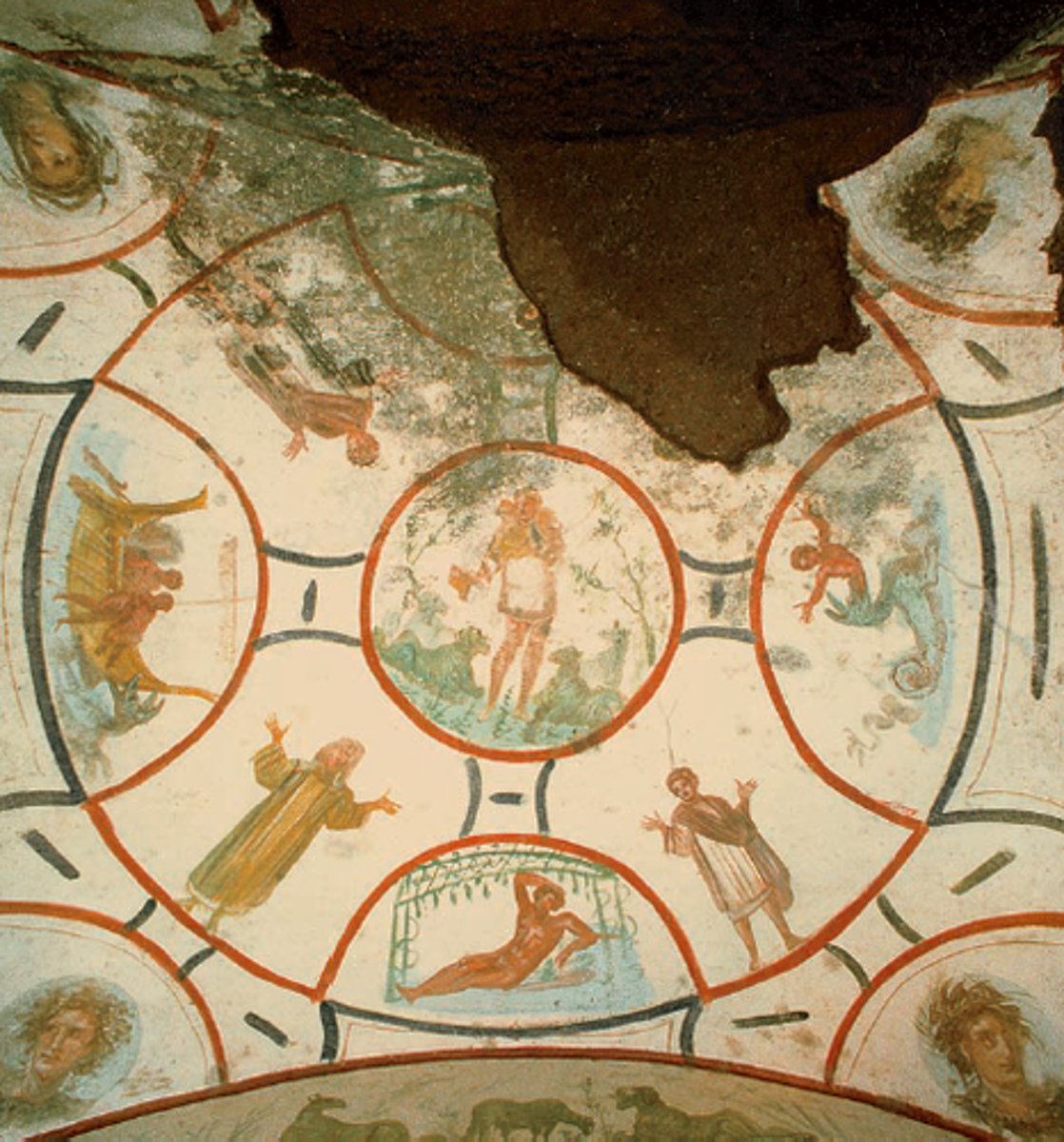
Old Testament
The forty-six books that make up the first part of the Bible and record salvation history before the coming of the Savior, Jesus Christ.

New Testament
The second part of the Christian Bible, containing descriptions of the life and teachings of Jesus and of his early followers

The Good Shepherd
Most common depiction of Jesus in the first centuries of Christianity. used to show Jesus' guidance for Christians and his love for those who follow him.

archetypal composition
Images in Christian art that stay relatively the same in structure, figures and imagery regardless of the time period in which they are created

Christogram
The three initial letters of Christ's name in Greek, which came to serve as a monogram for Christ.

Chi Rho Iota
The first three letters of Christ's name in Greek. (in Latin XPI) The symbol, often called a chi-rho, is a monogram of Christ.
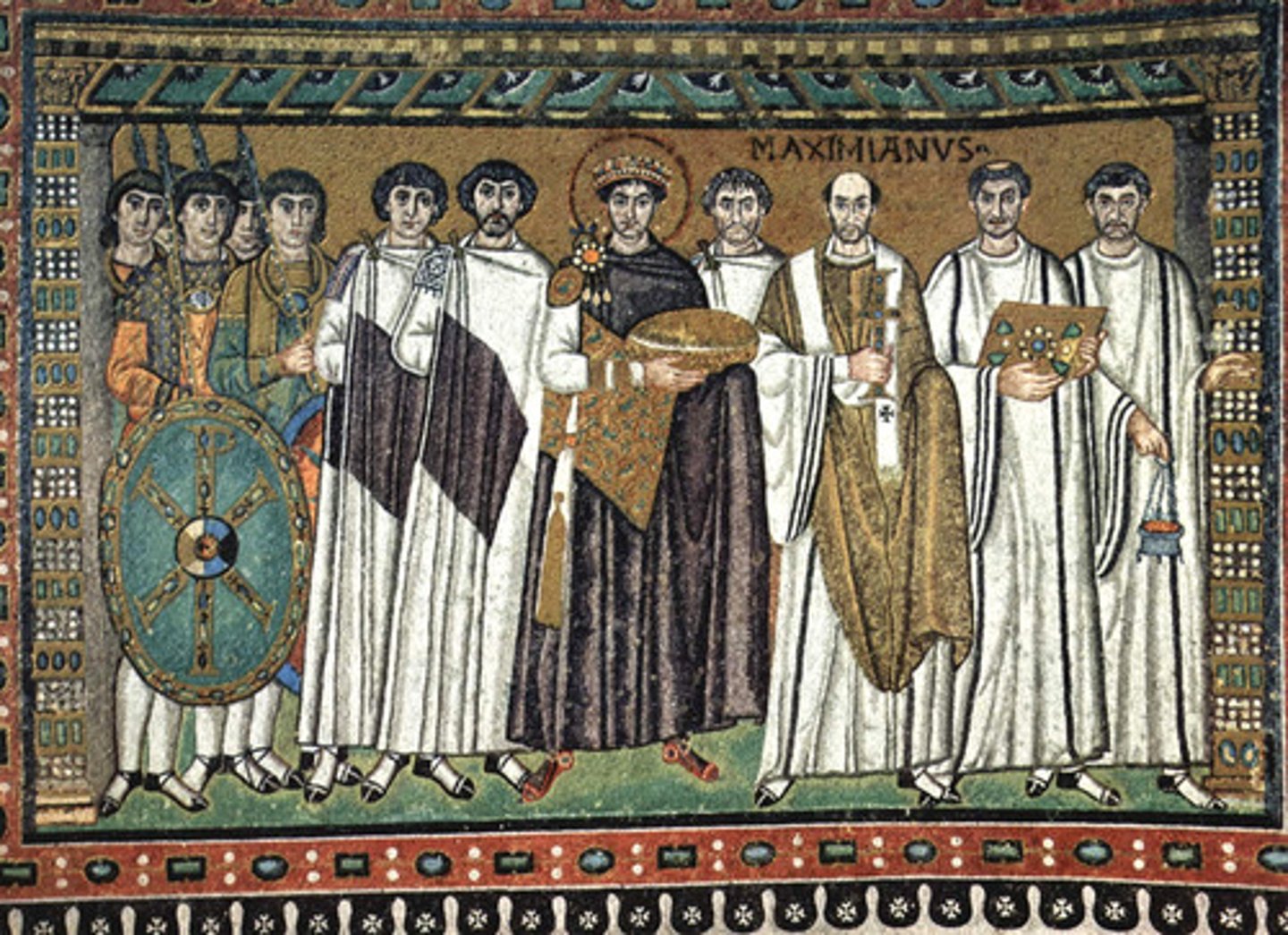

Prefiguration
In Early Christian art, the depiction of Old Testament persons and events as prophetic forerunners of Christ and New Testament events.

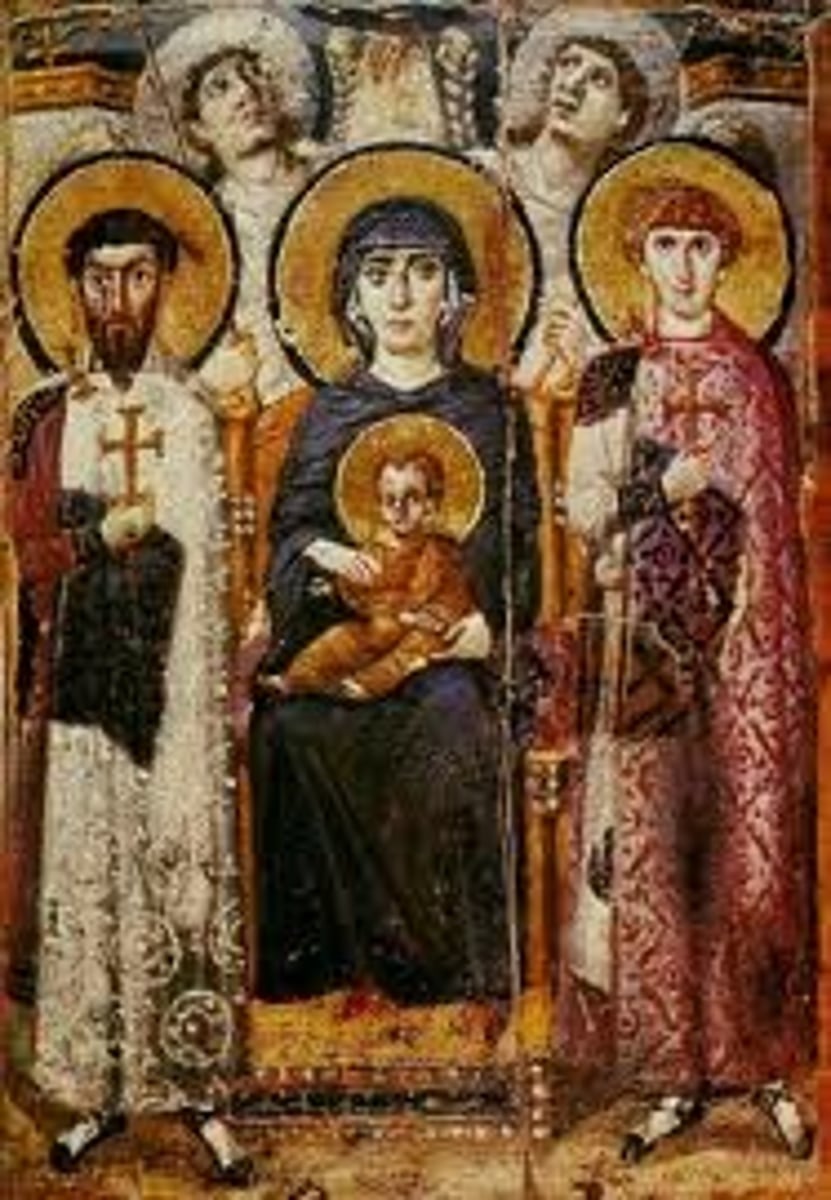
Theotokos
A Greek title for Mary meaning "God bearer"

Codex
an unbound manuscript of some ancient classic (as distinguished from a scroll)

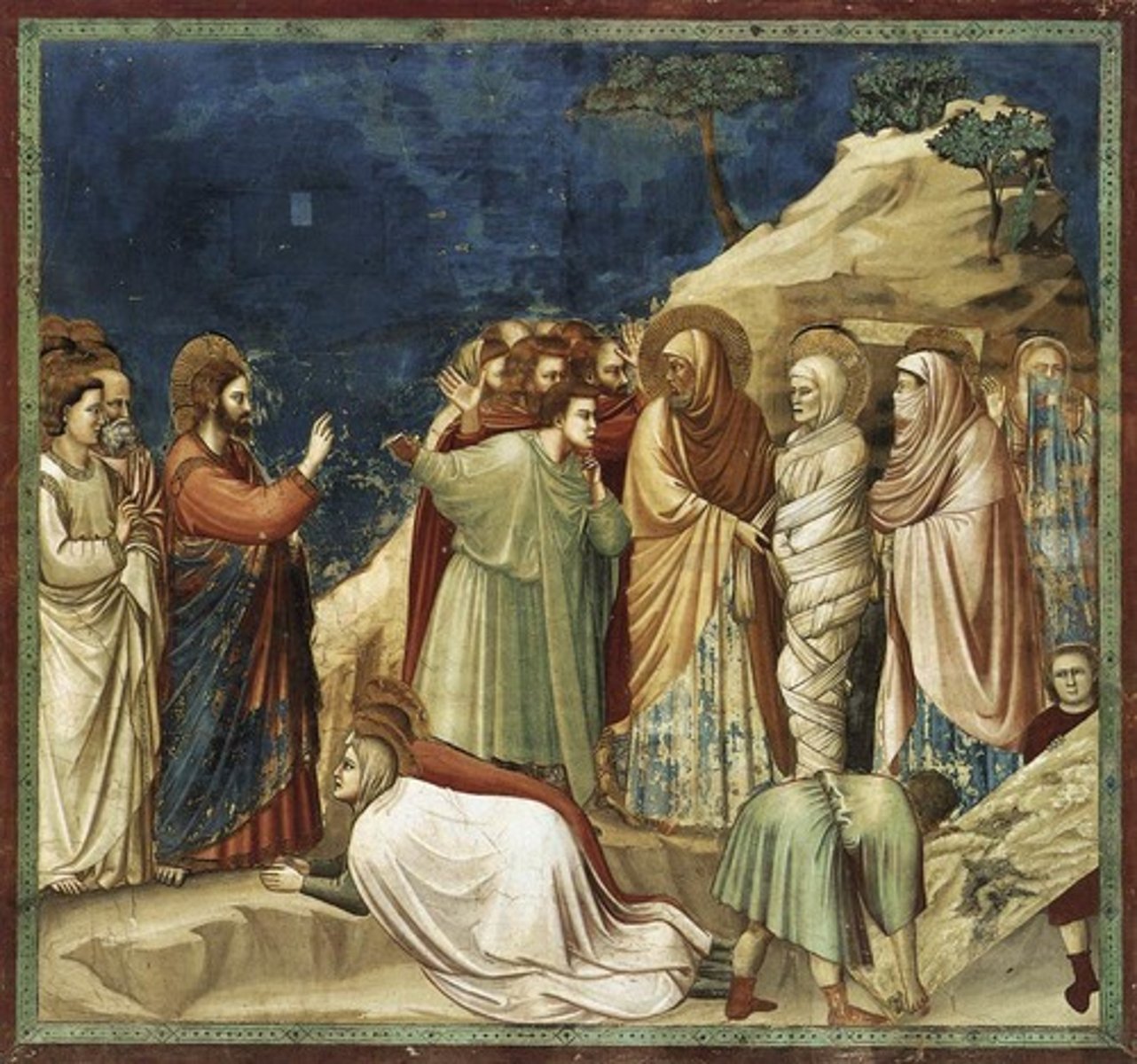
Book of Genesis
First book of the Bible containing the stories of God's covenants and journeys with the Israelites

continuous narrative
a work of art that contains several scenes of the same story painted or sculpted in a single frame
Aventine Hill
One of the Seven Hills of Rome where a temple to Juno [Hera] once stood; now the location of Santa Sabina
![<p>One of the Seven Hills of Rome where a temple to Juno [Hera] once stood; now the location of Santa Sabina</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6c8f9466-0546-441b-94d0-6d97a3975f54.jpg)
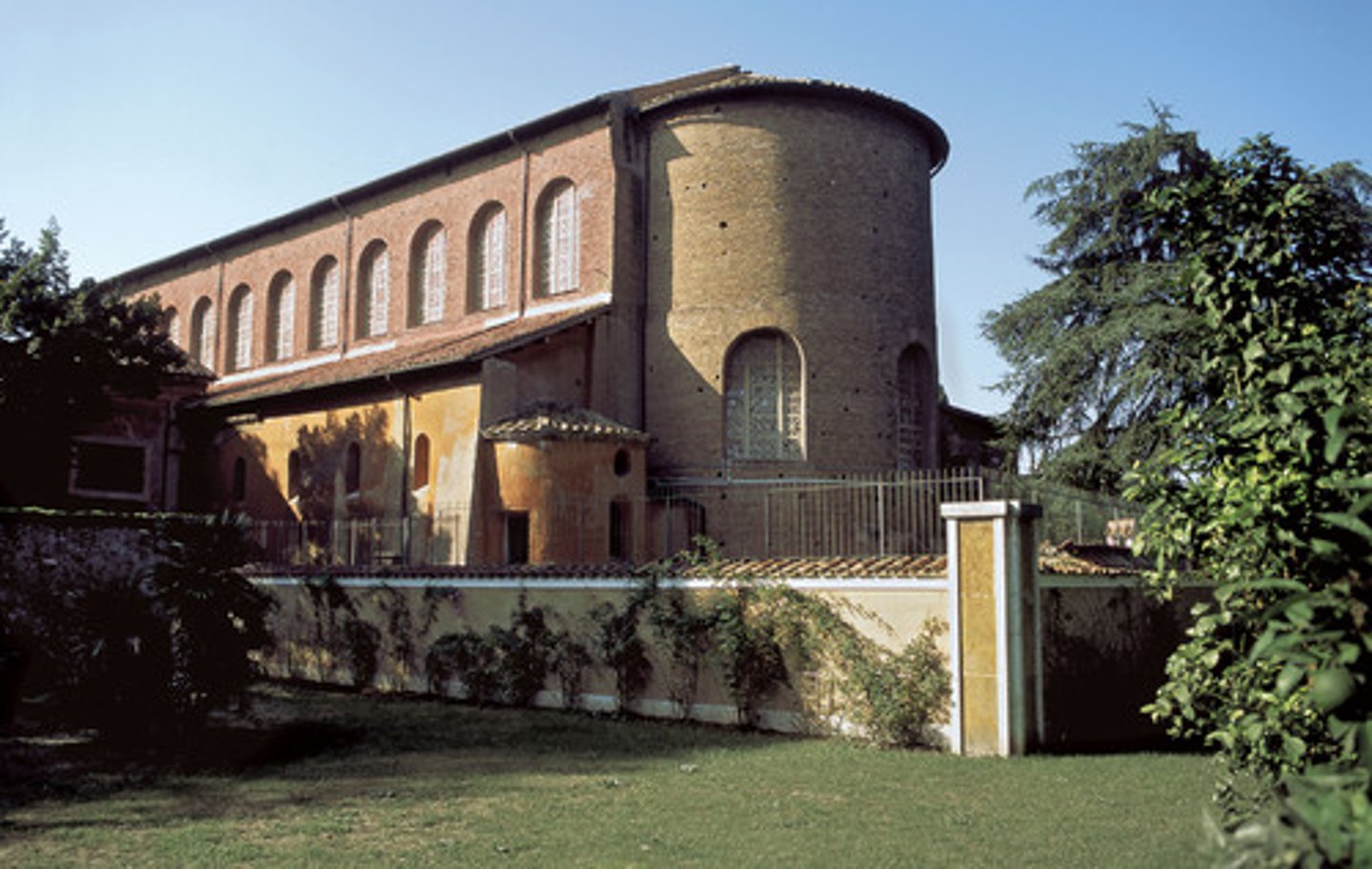
Santa Sabina
Basilica located on the Aventine Hills in Rome, Italy. Late Antique Europe. c. 422-432 C.E. Brick and stone, wooden roof.

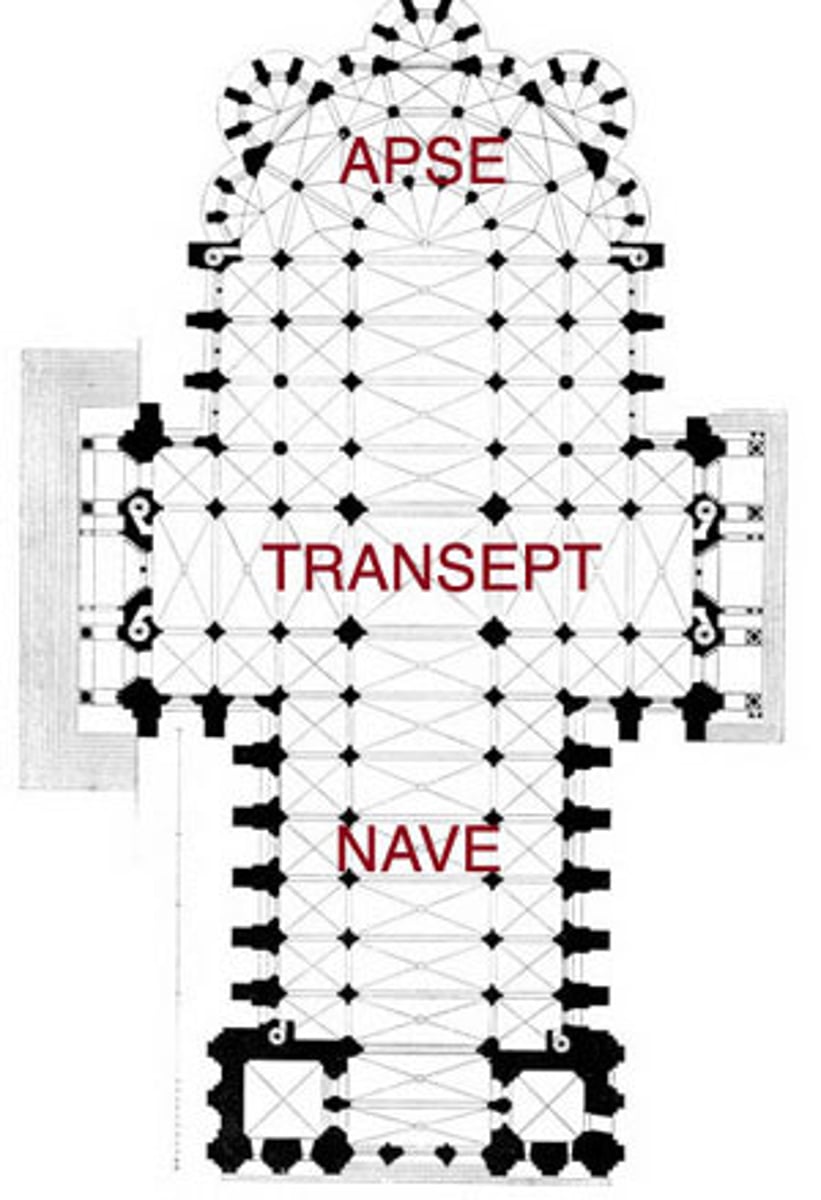
Apse
A recess, usually semicircular, in the wall of a Roman basilica or at the east end of a church.
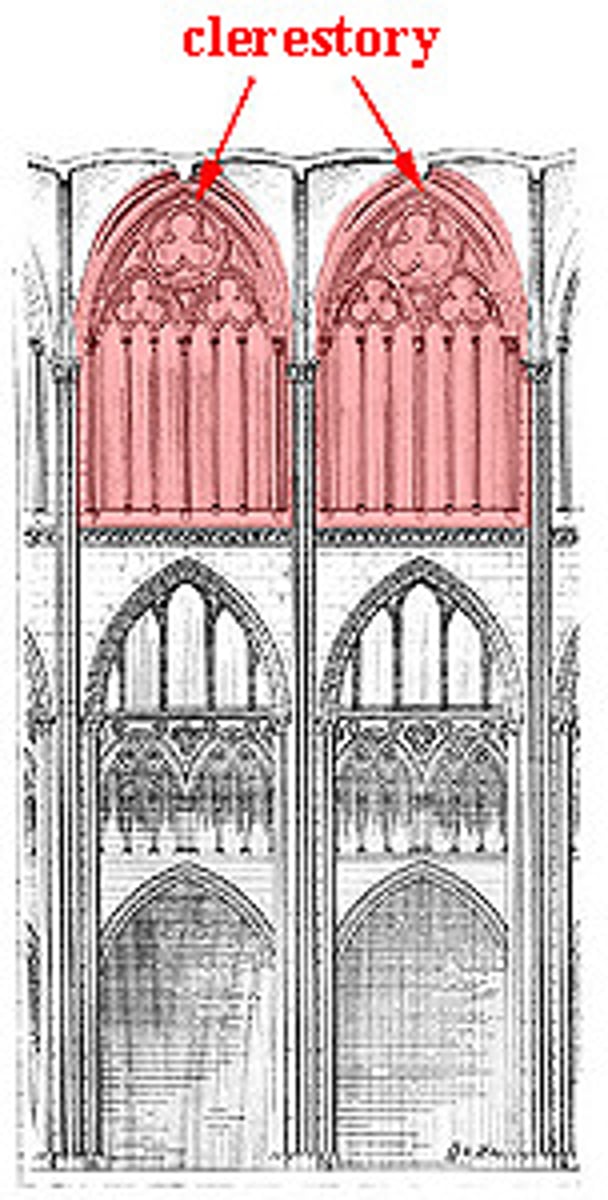
Clerestory
part of an interior wall rising above the adjacent roof with windows admitting light
Nave
the central part of a church building, intended to accommodate most of the congregation
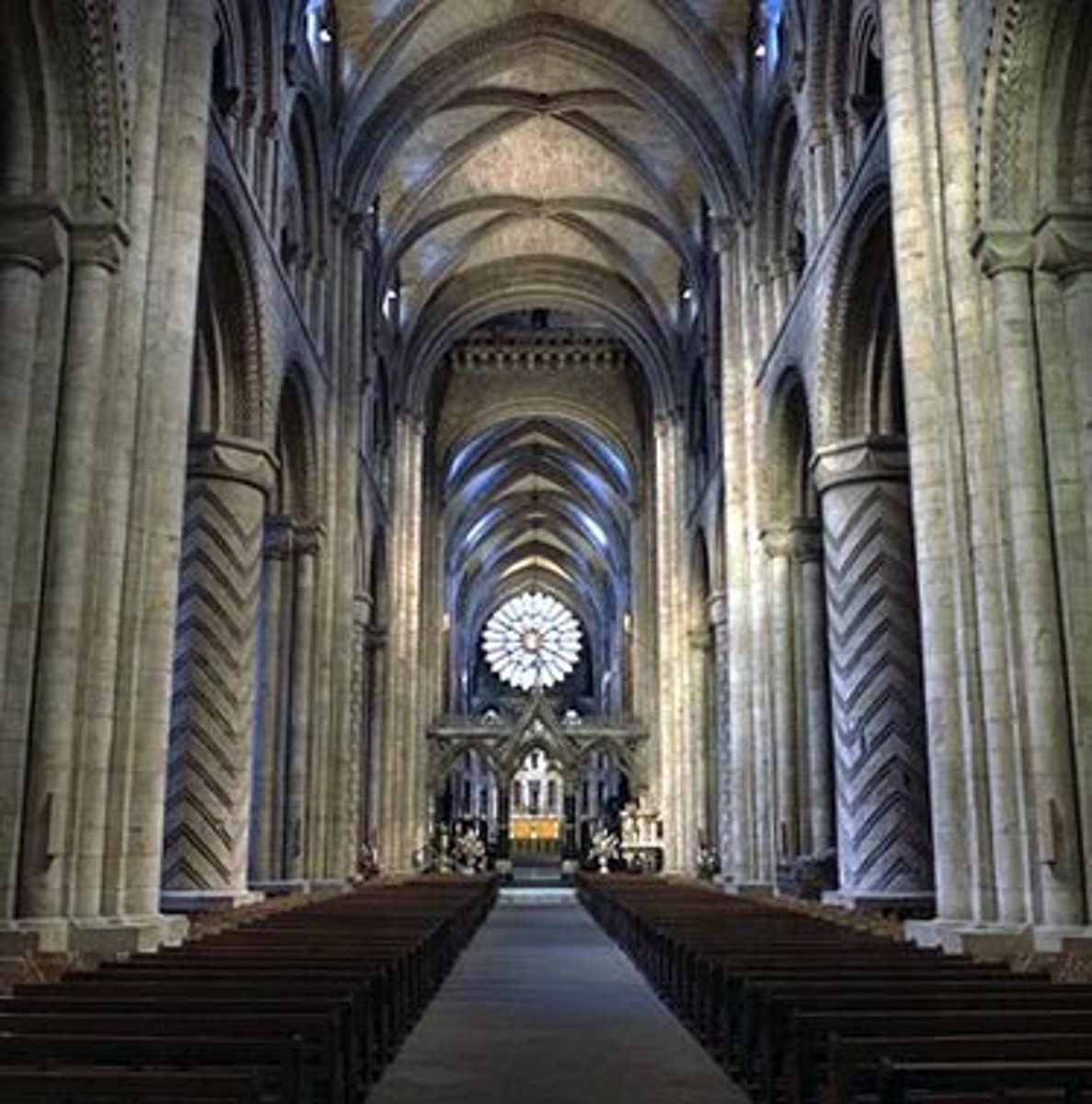

Octagonal Church
eight sided church
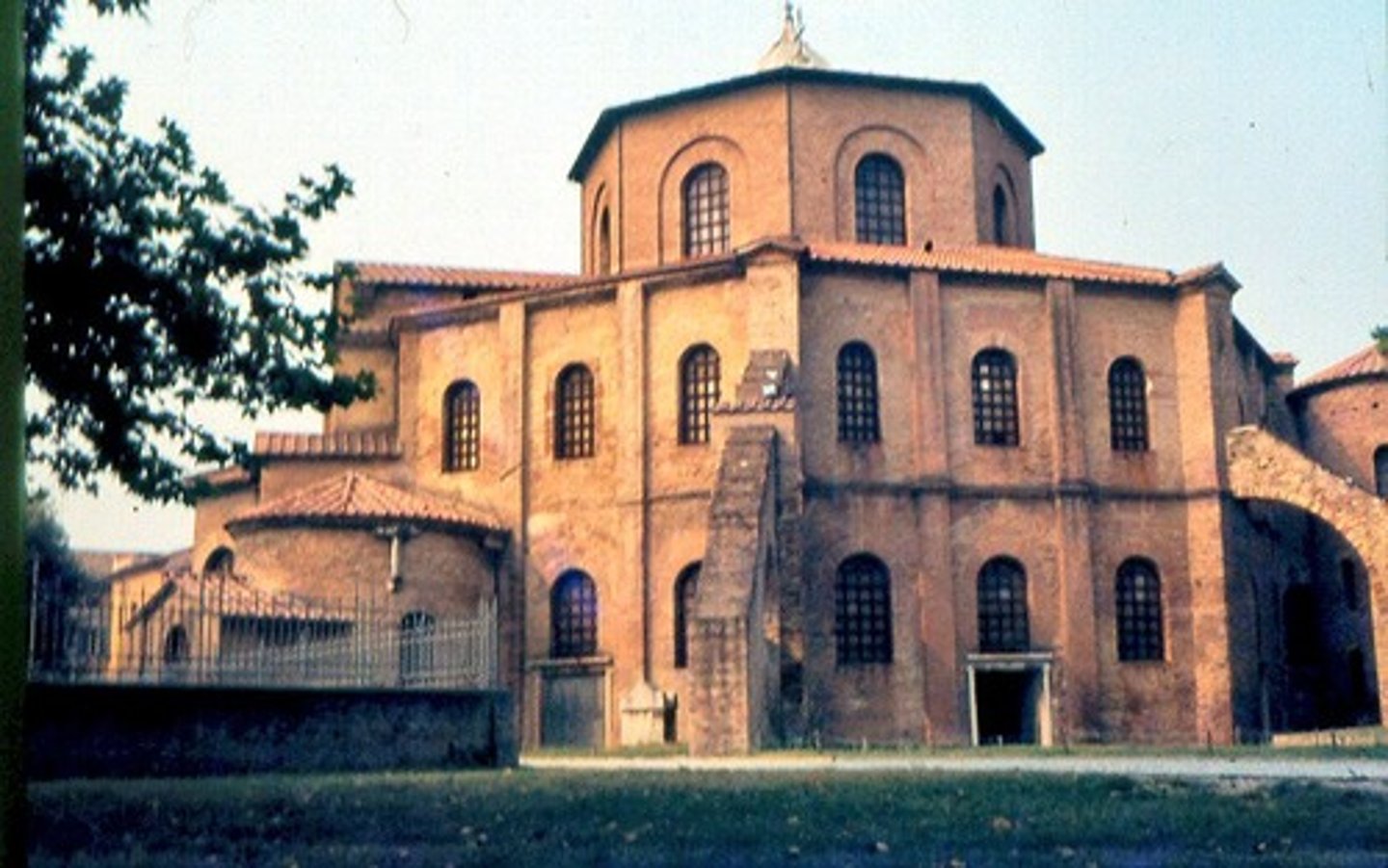

Gallery
the second floor of San Vitale reserved for female worshippers
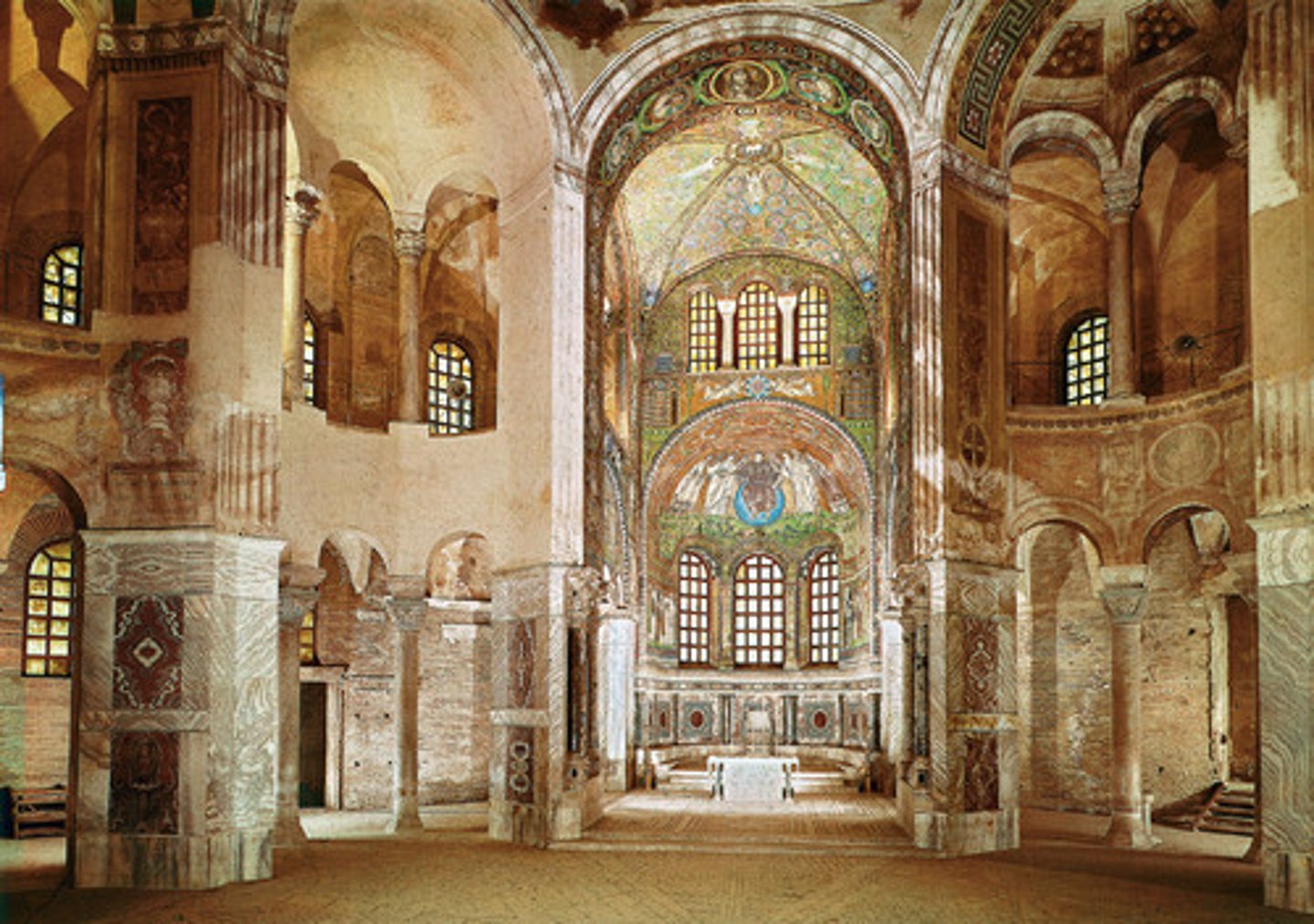

Apsidal church
a church oriented towards the location of the altar located in the apse of the church
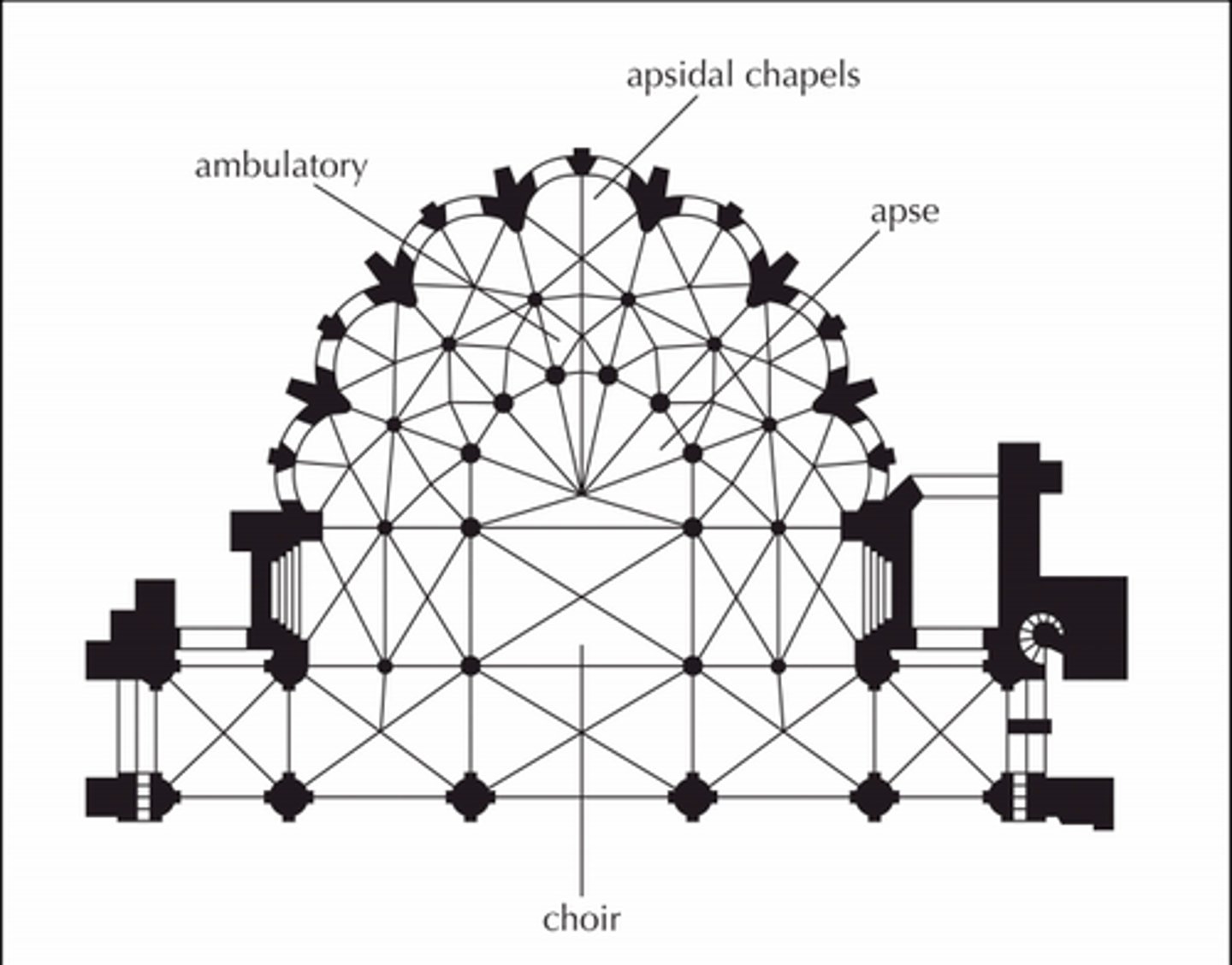
Sanctuary
a sacred place; any place of refuge located in a temple or church and limited in access by the public.
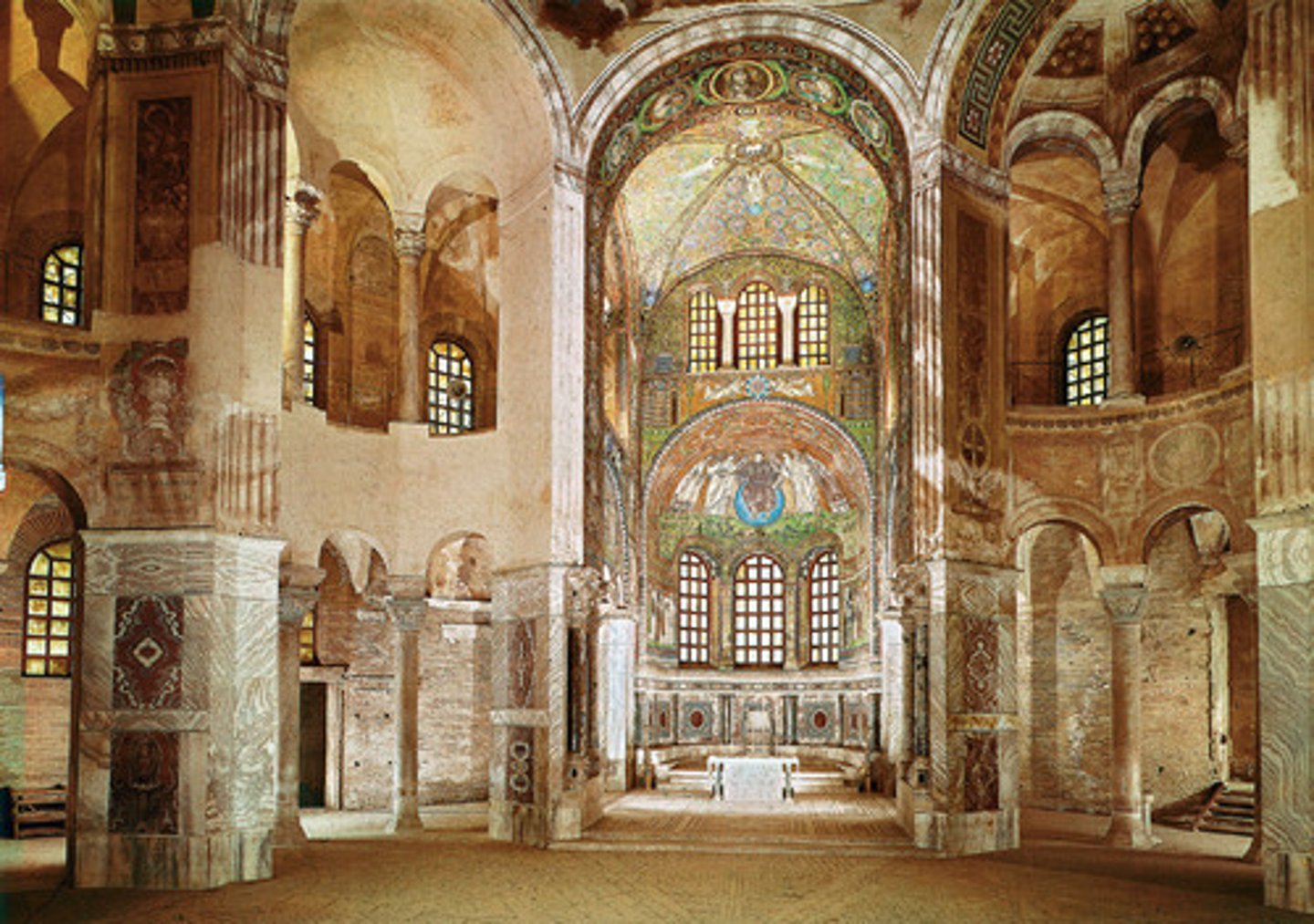

Justinian
Byzantine emperor in the 6th century A.D. who reconquered much of the territory previously ruler by Rome, initiated an ambitious building program , including Hagia Sofia, as well as a new legal code
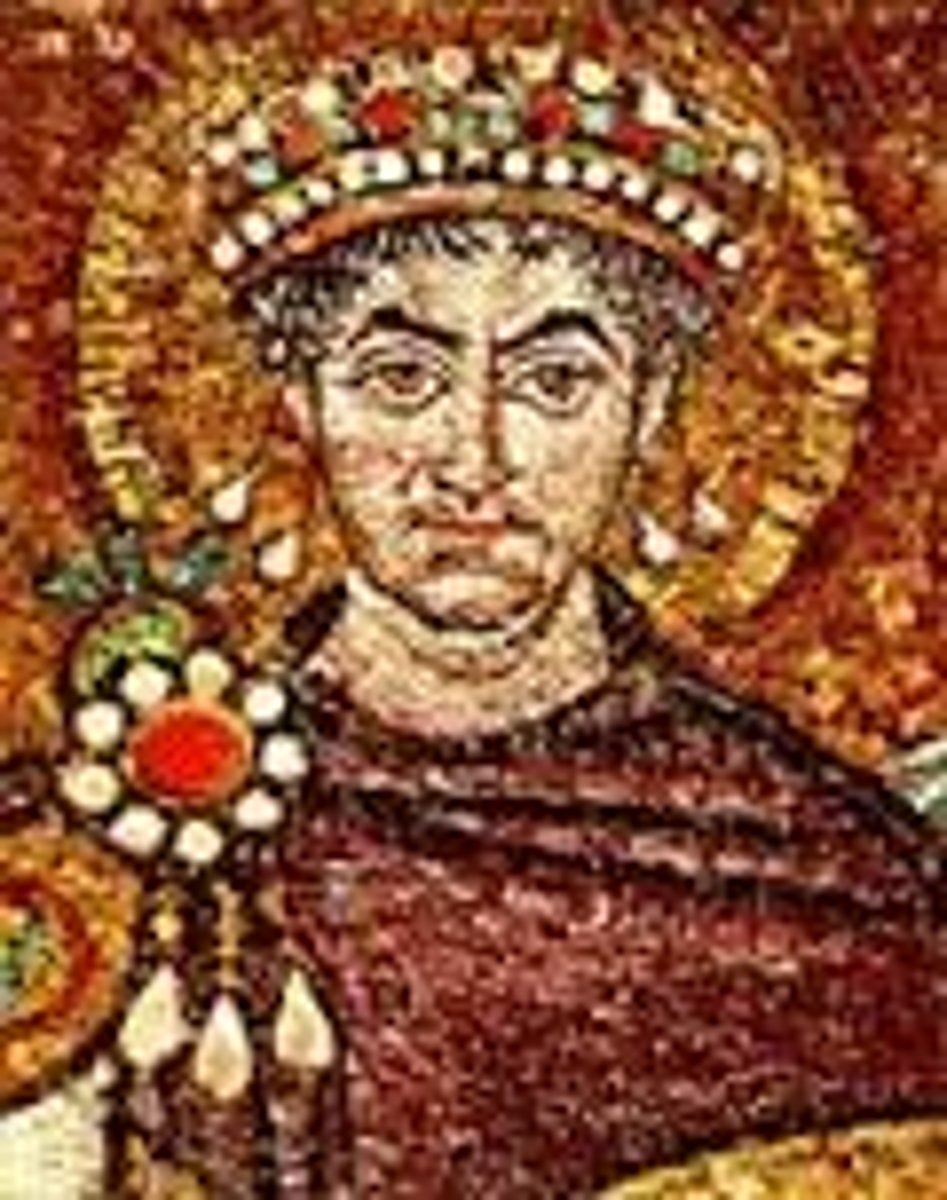

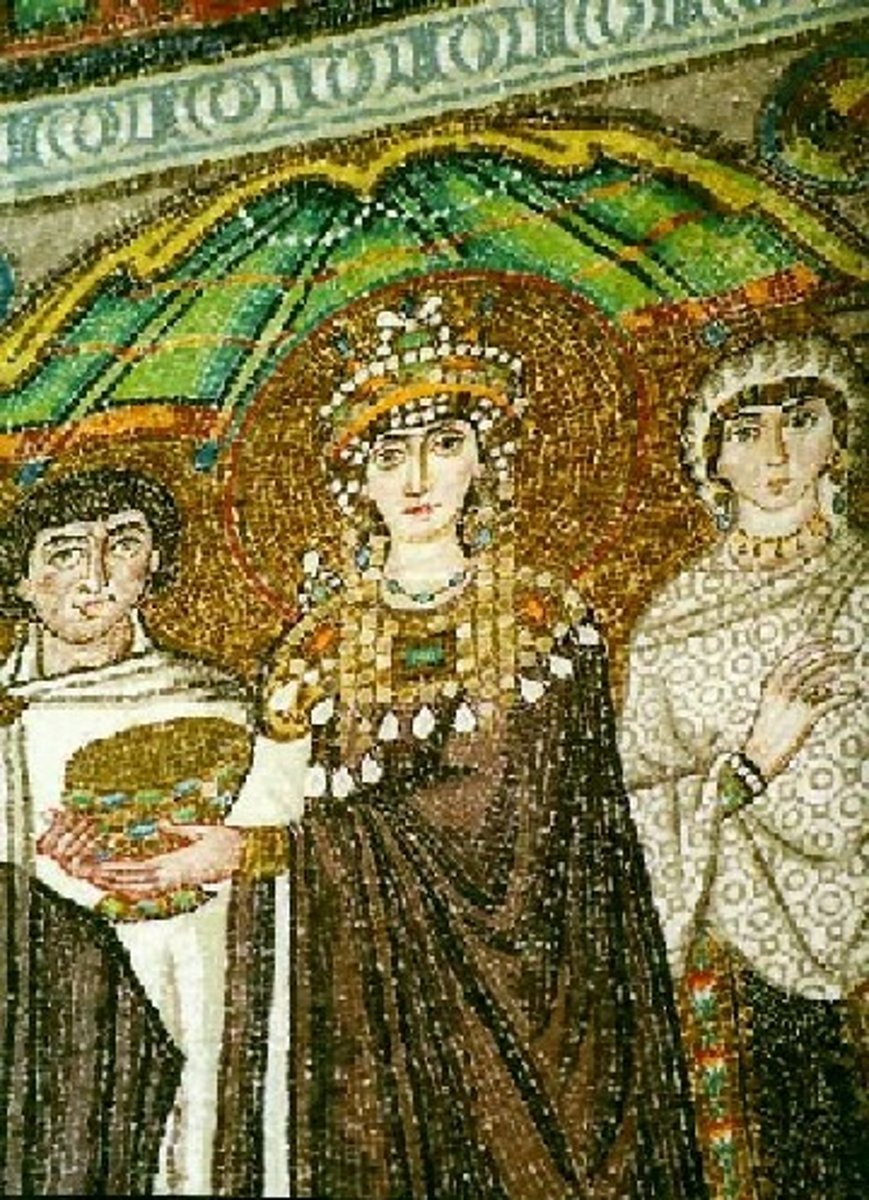
Theodora
the wife of Justinian, she helped to improve the status of women in the Byzantinian Empire and encouraged her husband to stay in Constntinople and fight the Nike Revolt.

Pendentive
a curved triangle of vaulting formed by the intersection of a dome with its supporting arches.
Deesis
a tripartite icon in the byzantine tradition, usually showing Christ enthroned between the Virgin Mary and St. John the Baptist, who intercede on behalf of humankind

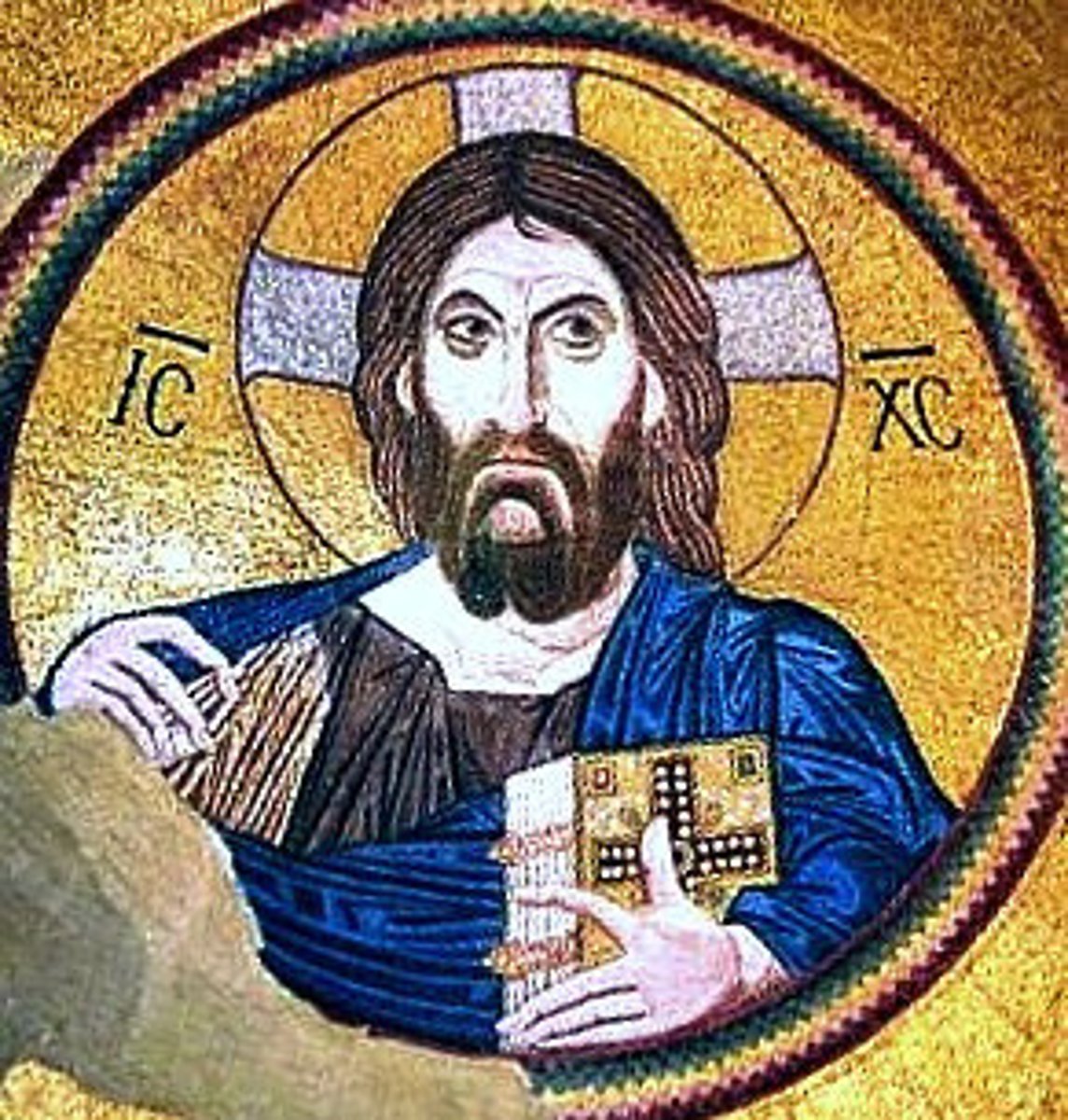
Pantokrator
Greek, "ruler of all." Christ as ruler and judge of heaven and earth.

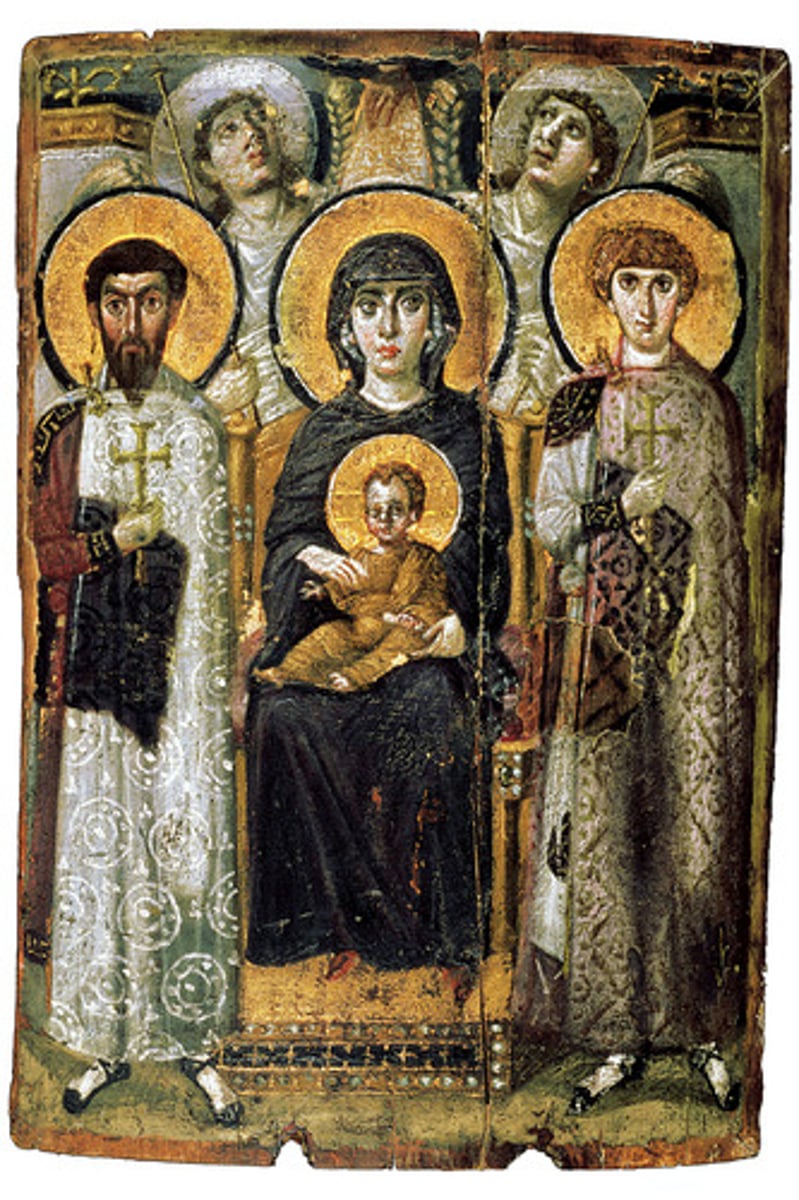
Encaustic
A painting technique in which pigment is mixed with wax and applied to the surface while hot.
Icon
a painting which is a representation or image of a sacred personage, often considered sacred itself

sedes sapientiae
Latin, "throne of wisdom." A Romanesque sculptural type depicting the Virgin Mary with the Christ Child in her lap.
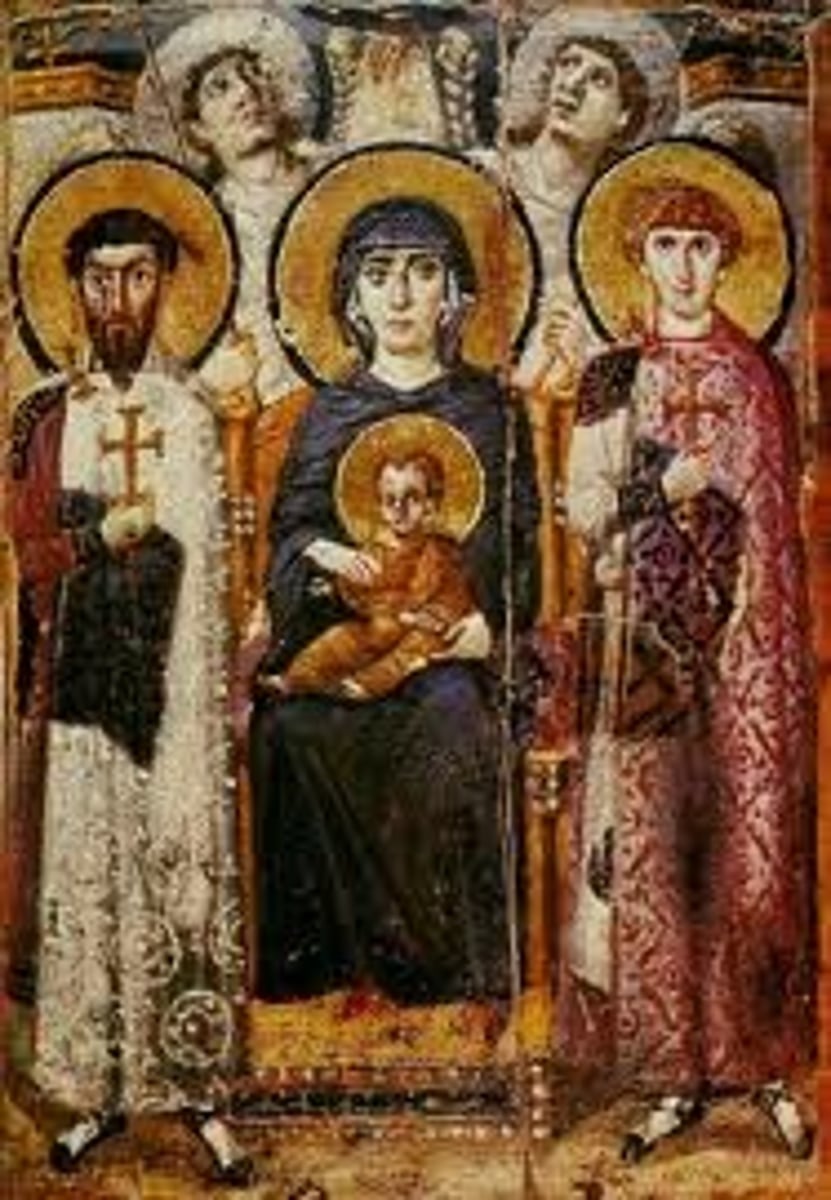

Milius Christi
Soldier of Christ; a warrior saint in Christian art
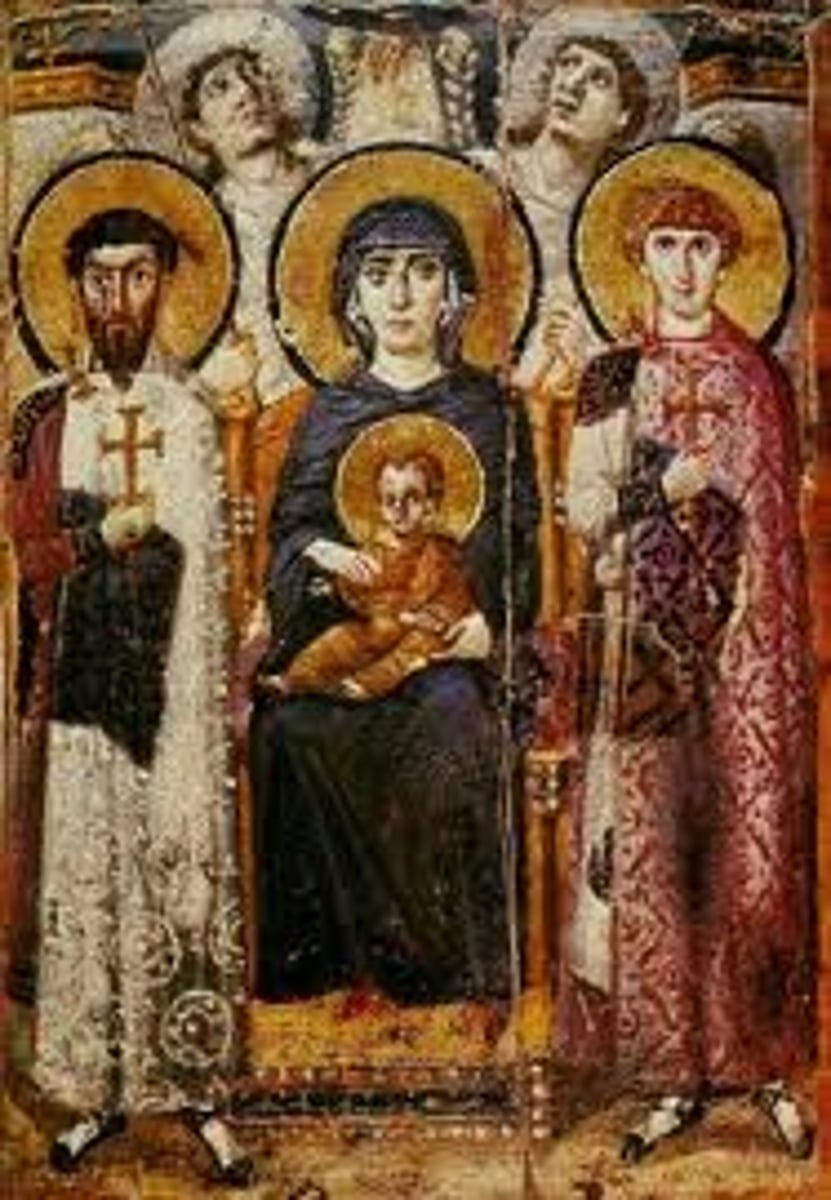

Christ in Majesty
Christ seated on a throne as ruler of the world, always seen frontally in the center of the composition, and often flanked by other sacred figures, whose membership changes over time and according to the context; borrowed directly from images of Roman emperors
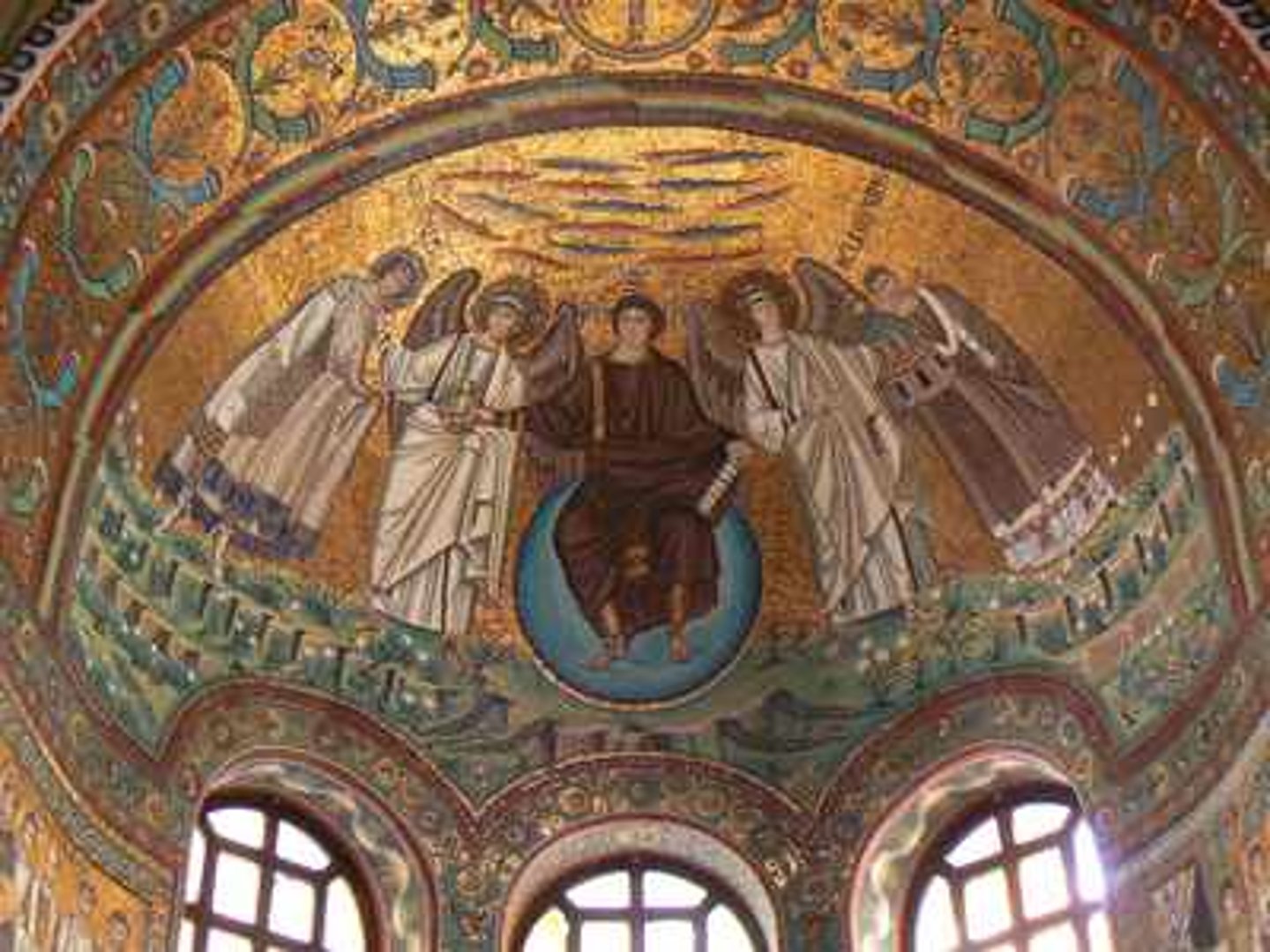

Manera Greca
in the Greek style. A reference to the flattened highly stylized forms and figures in Greek and Byzantine art
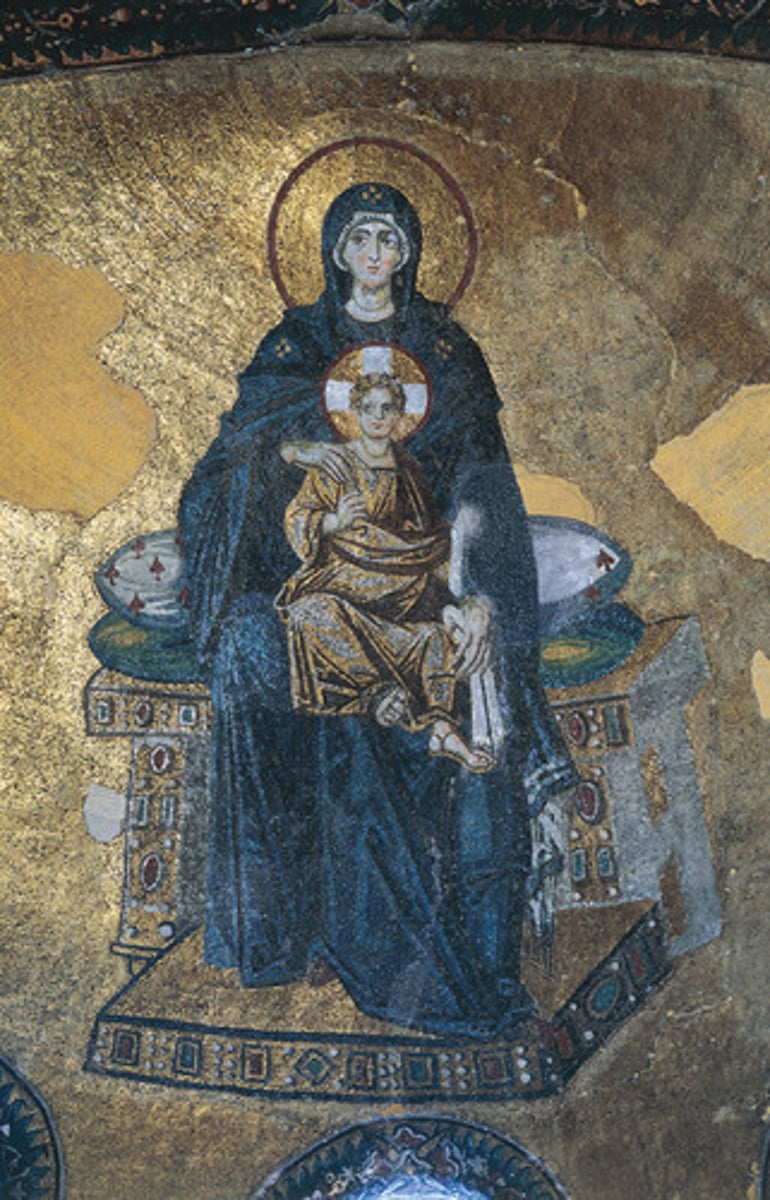

Blue
Colour associated with Virgin Mary
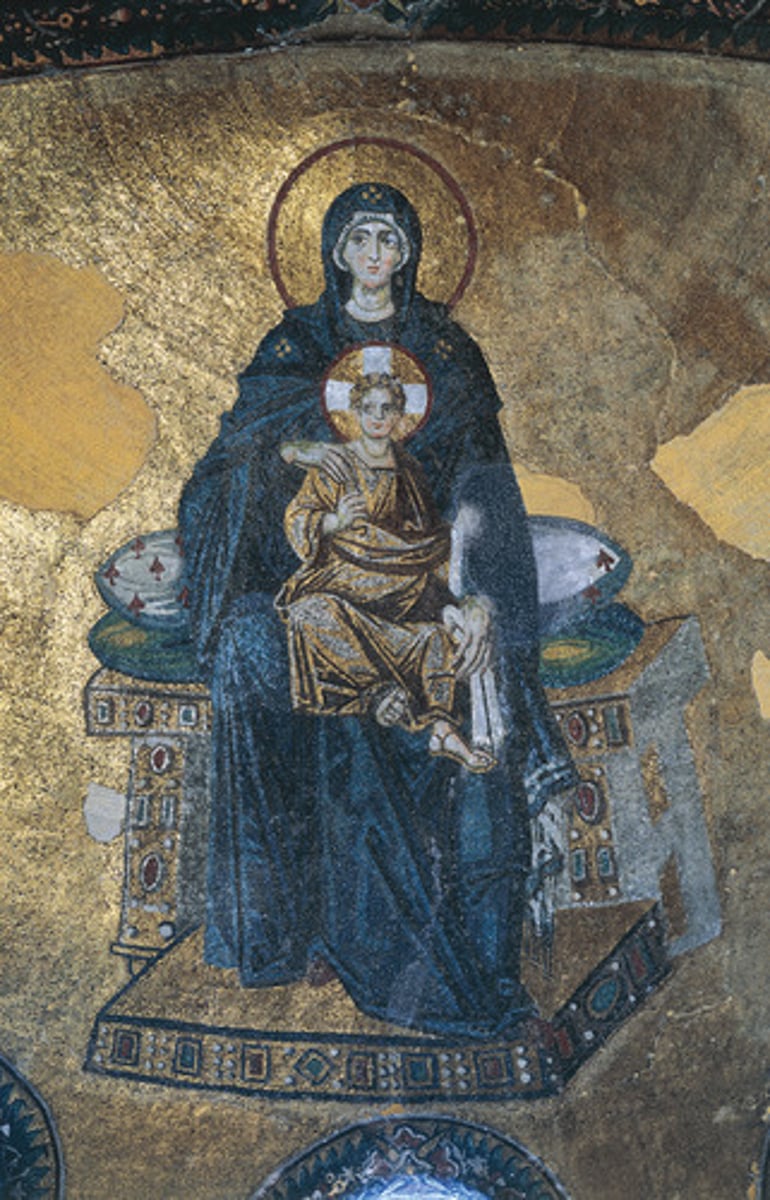

Purple
Colour associated with Imperial Rome and later Imperial Byzantine rulers
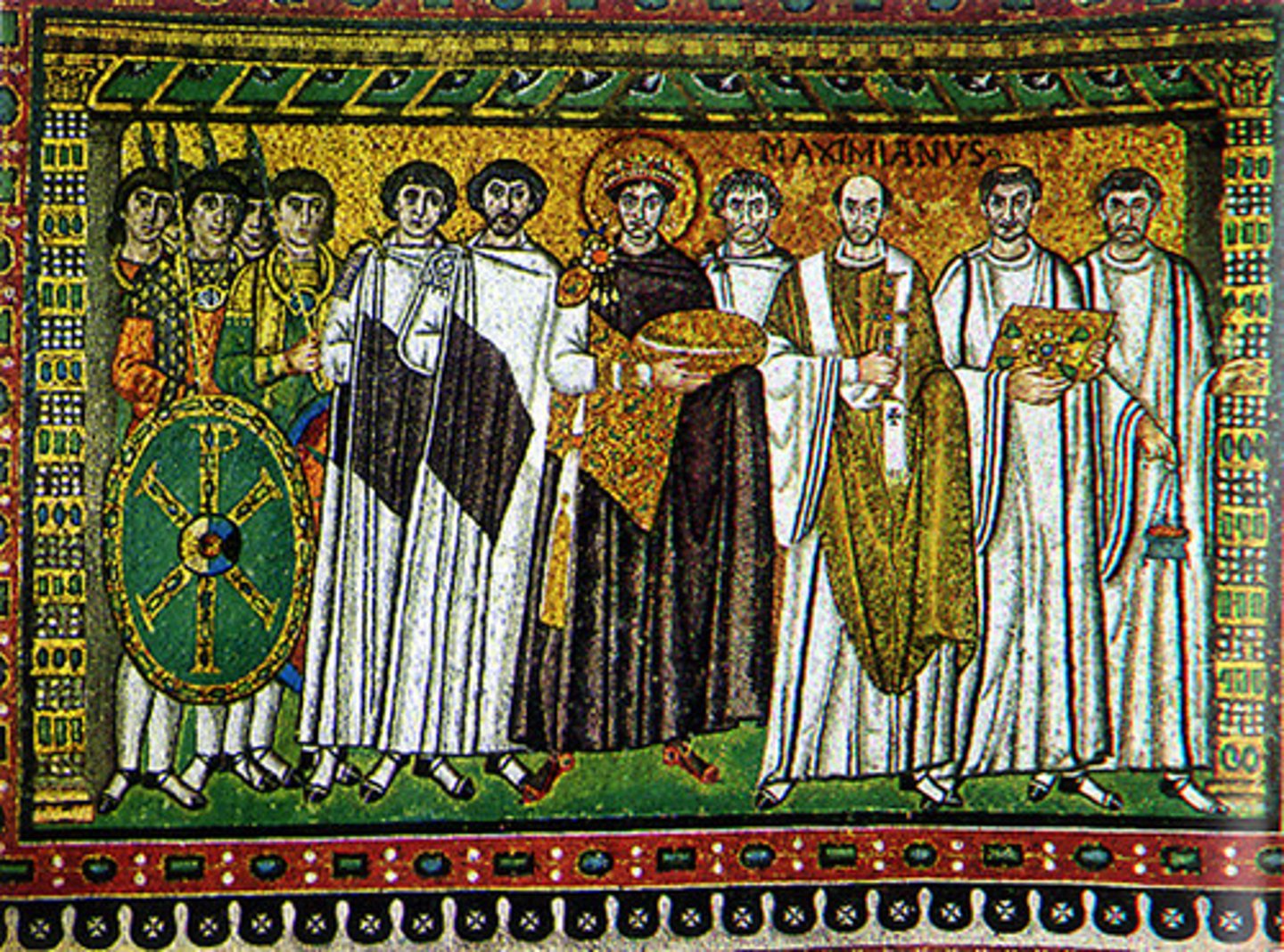

Green
Colour associated with Paradise or the Garden of Eden
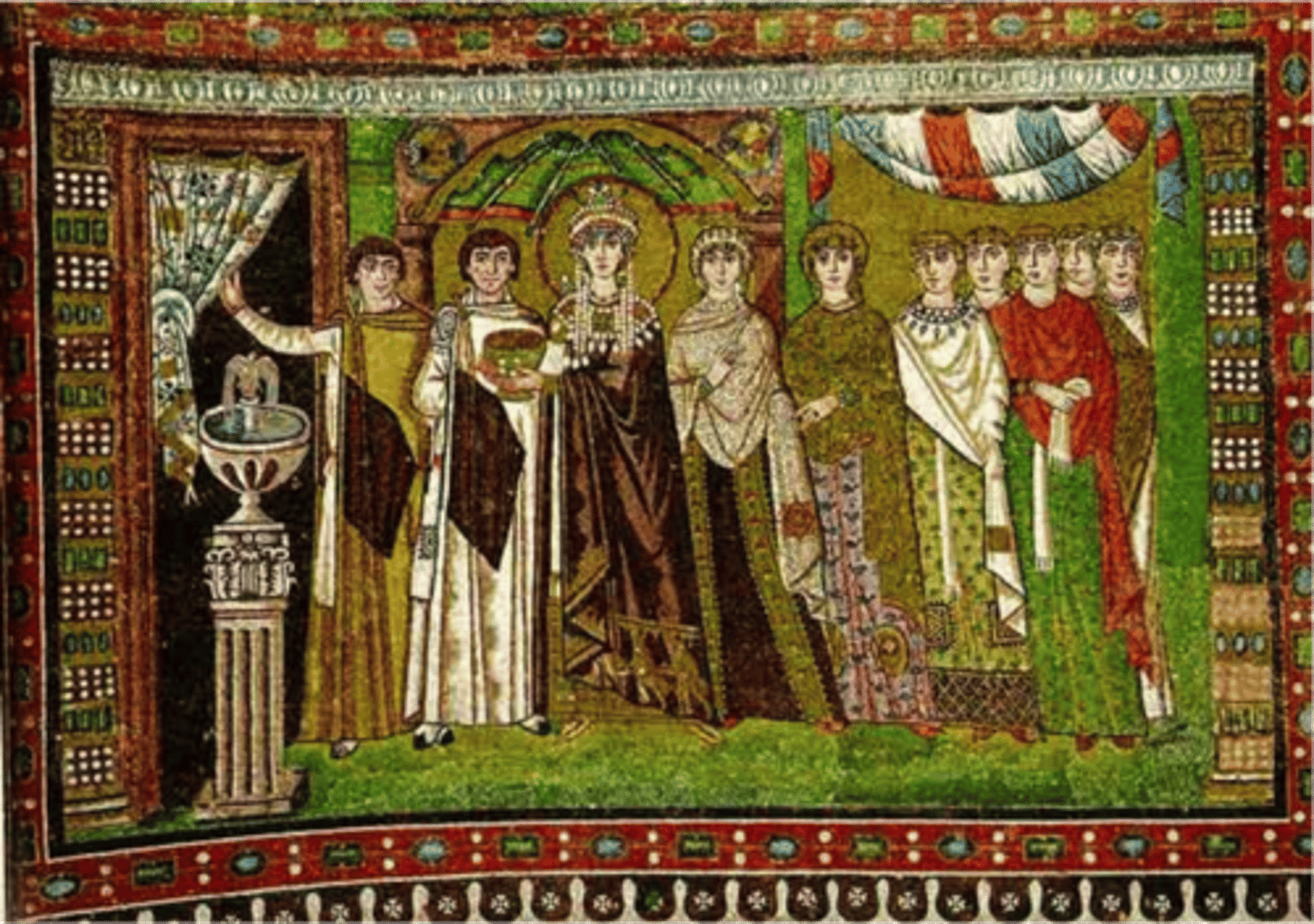

Red
Colour associated with the sacrifice of Christ or that of martyrs to the Christian faith
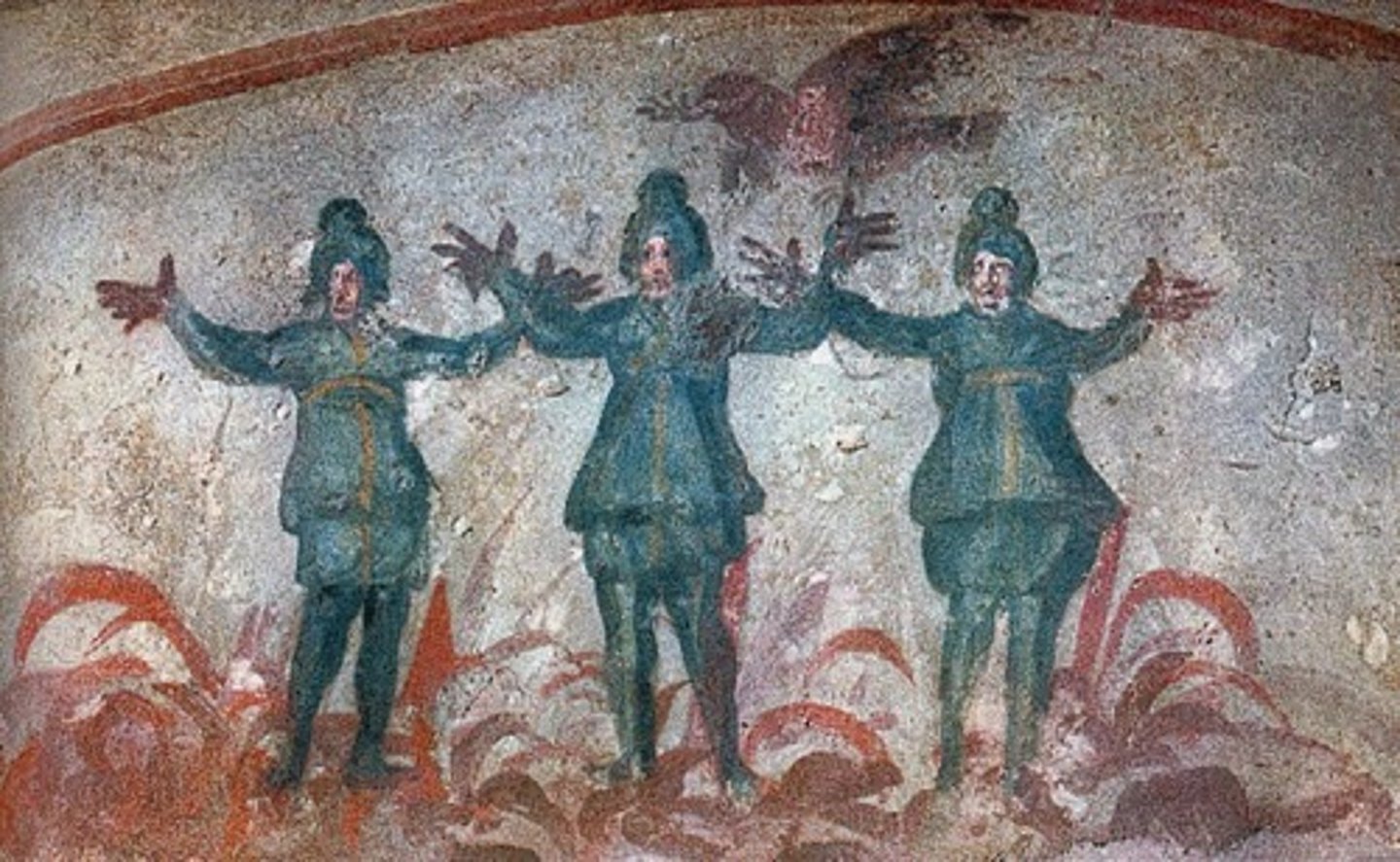

Brown
Colour associated with humility and modesty; often used by monastic clergy
