AQA GCSE Combined Science Trilogy : Physics Paper 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Define vector quantity
a quantity that has both magnitude and direction
Define scalar quantity
A physical measurement that does not contain directional information
Vector quantities have both _________ and _________
magnitude, direction
Scalar quantities have _________ only
magnitude
Force is an example of a ______ quantity
vector
How are arrows used to show vector quantities?
length shows magnitude (size) and arrow points in the direction of the vector
Give four examples of vector quantities
displacement, velocity, force, acceleration
Give four examples of scalar quantities
speed, distance, energy, mass
A _____ is a push or pull on an object that is caused by it interacting with another object
force
Describe the difference between contact and non-contact forces
Contact Forces - when two objects have to be touching for a force to act
Non-Contact Forces - when two objects do not need to be touching for the force to act
Give four examples of contact forces
friction, air resistance, tension in ropes and normal contact forces
Give three examples of non-contact forces
magnetic forces, gravitation forces and electrostatic forces
Describe the forces acting between the Sun and the Earth
The Sun and Earth are attracted to each other by a gravitation force which is a non-contact force. An equal and opposite force of attraction is felt by both the Sun and the Earth
Describe the forces acting between a char and the ground
A chair exerts a force on the ground, whilst the ground pushed back at the chair with the same force (the normal contact force), equal but opposite forces are felt by both the chair and the floor
Weight is the force acting on an object due to _______
gravity
Mass attracts ____ with a universal force of attraction called _______
mass, gravity
On the surface of a planet, gravity makes all things __________ towards the ground and gives everything ______
accelerate, weight
How is mass different to weight?
Mass os the amount of matter in an object which does not change with location. Weight is the force acting on an object due to gravity and does not change with location
Describe what changes weight?
Mass and distance. Greater mass means a stronger gravitational field strength which gives a larger force of weight. Shorter distance between masses increases weight because the gravitational field strength is stronger when closer
How is weight measured?
Weight is measured using a calibrated spring-balance (a newtonmeter).
What is meant by the centre of mass of an object?
The centre of mass of an object is the point at which the mass may be thought to be concentrated.
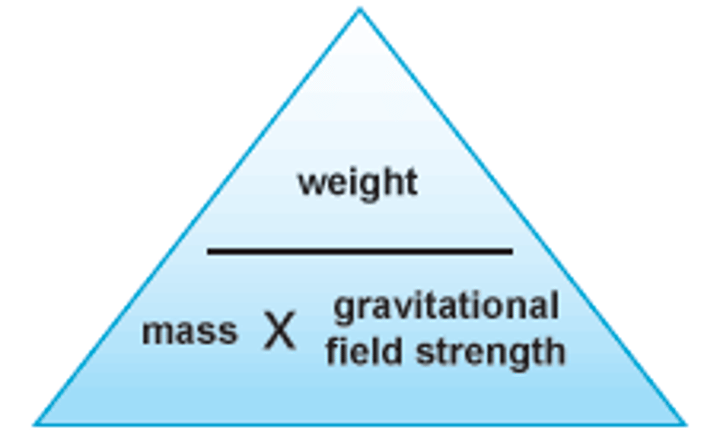
What is the equation that links weight, mass and gravitational field strength?
Weight = mass x gravitational field strength
The _________ force acting on an object has the same effect as all the individual forces acting on that object
resultant
How do you calculate the resultant force of two forces acting along the same line?
Set a direction as positive then add the forces together (e.g. 100N+(-50N) = 50N
Give examples of forces acting on a single object
A car, a person running
What is a free body diagram?
A free body diagram shows all the forces acting on an isolated object, including the magnitude and direction of each force.
How do you use a scale drawing to find the resultant force?
Draw all forces tip to tail and then draw a line from start to finish, this line is the resultant. Measure the length for the magnitude and the angle for direction
How do you know if all the forces acting on an object are in equilibrium?
The free body diagram is a complete loop
What does resolving a force mean?
Resolving a force is to put it into horizontal and vertical components that have the same effect as the original single force
If force is applied to an object and displaces it, the force does ____ on the object
work
Work done is when ______ is transferred
energy
Energy transferred is _____ ____
work done
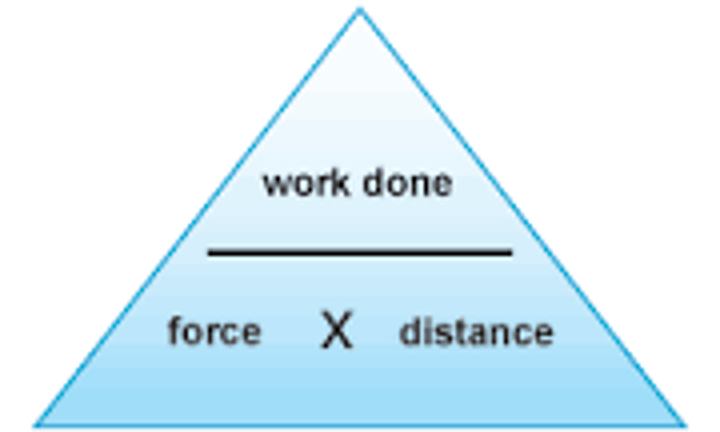
What is the equation that links work done, force and distance moved?
Work done = force x distance
1J of work done is when a force of _N moved an object _m
1,1
What is 1J in newton metres?
1nm
Describe an energy transfer when work is done, for example pushing a block along a carpet
Energy is transferred to the kinetic energy store of the block because it starts to move, but some energy is also transferred to the thermal energy stores of the object, the surface and the surroundings due to friction
Work done is the ______ transferred when a _____ moved an object through a ________
energy, force, distance
Work done against friction can cause a rise in ___________ of the object and its surroundings
temperature
How many forces are needed to bend, compress or stretch an object?
2
What does elastically deformed mean?
The object will return to its original shape after the forces have been removed
What does in-elastically deformed mean?
The object will not return to its original shape after the forces have been removed
The extension of a spring is the __________ between the stretched/compressed length and its original length
difference
The force applied to an object is directly proportional to the _________ of the object up to the limit of proportionality
extension
What is the equation that links force, spring constant and extension?
Force = spring constant x extension
Extension must always be converted to ______
Metres
What is done on a spring when it is stretched or compressed?
Work
When compressing or stretching a spring elastically, all work is transferred to is _______ _________ energy store
elastic potential
How do you calculate the work done in stretching or compressing a spring elastically?
Use the given equation 1/2Ke^2
The limit of _______________ is the point where the force-extension graph starts to curve. Before this point the extension is ____________
proportionality, proportional
The ____ under the force-extension graph of an elastic object is equal to the energy stores in the elastic potential energy store of the object
area
Describe the steps to investigate the link between force and extension [Required Practical]
1) Measure the natural length of the spring (when no load is applied) with a millimetre ruler camped to the stand. Make sure you take the reading at eye level and add a marker (e.g. a thin strip of tape) to the bottom of the spring to make the reading more accurate.
2) Add a mass to the spring and allow it to come to rest. Record the mass and measure the new length of the spring. The extension is the change in length.
3) Repeat this process until you have enough measurements (no fewer than 6)
4) Plot a force-extension graph of your results. It will only start to curve if you exceed the limit of proportionality.
By hanging progressive masses on a suspended spring and measuring extension, what two things can you find? [Required Practical]
Spring constant and the limit of proportionality
Why do a pilot experiment? [Required Practical]
To see if your masses are a suitable size
What has happened if the extension for the mass is more than the previous extensions? [Required Practical]
The limit of proportionality has been exceeded
Why use a minimum of five masses? [Required Practical]
To show a clear pattern on the graph
How do you calculate the force applied by the masses? [Required Practical]
Weight = mass x gravitation potential
Why take readings of the extension at eye level? [Required Practical]
To ensure that you get more accurate readings as it avoids parallax errors
What does the gradient on a force-extension graph show? [Required Practical]
Gradient = spring constant (N/m)
How do you calculate the gradient?
Change in y/Change in x
What is distance?
Distance is a scalar quantity and is just how far an object has moved
What is displacement?
Displace is a vector quantity and it measures the distance and direction in as straight line fro man objects start and finish points
When describing the displacement, how might the direction be given?
Direction could be relative to a point or a three figure angle form north
What is speed?
Speed is a scalar quantity and is just how fast an object is moving
What is velocity?
Velocity is how fast an object is going and in which direction
How can an object have constant speed with a changing direction?
Circular motion (e.g. orbits and roundabouts)
In real life, are speeds constant?
barely, for example, a person's speed varies, speed of sound varies by what it is moving through and wind speed changes with temperature, atmospheric pressure and whether there are building or trees nearby
What is the typical speed of a person walking?
1.5m/s
What is the typical speed of a person running?
3m/s
What is the typical speed of a person cycling?
6m/s
What is the typical speed of a car?
25m/s
What is the typical speed of a train?
55m/s
What is the typical of a plane?
250m/s
What is the typical speed of sound in air?
330m/s
Factors that affect the typical speeds of walking, running and cycling are...
Fitness, age, distance travelled and terrain
How do you calculate the speed using measurement of distance and time?
Distance = velocity x time
What is acceleration?
Acceleration is how quickly the velocity is changing, either speed or direction or both
How do you calculate the average acceleration?
change in velocity / time
Change in velocity =?
final velocity - initial velocity
An object that is slowing down is...
decelerating (with negative acceleration)
How do you estimate everyday acceleration or decelerations?
Use the typical speeds of everyday situations
How do you use the equation v^2 - u^2 = 2as?
Use the three given variables and find the fourth
What is the acceleration value of a falling object near the Earth's surface?
9.8m/s
The distance travelled by an object moving in a straight line can be shown on a ________-____ graph
distance-time
How do you interpret a distance-time graph?
Straight uphill sections mean...
Horizontal lines mean...
Downhill straight sections mean...
A curving upwards graph means object is...
A curving downwards graph means object is...
constant speed
stationary
returning to start
accelerating
decelerating
What does the gradient show on a distance-time graph?
speed
The steeper the gradient means _______ speed
greater
The speed of an accelerating object at a certain time can be found by calculating the gradient of the _______ to the graph at that time
tangent
How do you interpret a velocity-time graph?
Straight uphill sections mean...
Horizontal lines mean...
Downhill straight sections mean...
A curving upwards graph means object is...
A curving downwards graph means object is...
acceleration
constant velocity
deceleration
increasing acceleration
decreasing acceleration
What does the gradient show on a velocity-time graph?
acceleration
A steeper gradient means _______ acceleration
greater
You can find the acceleration of an object by calculating the ________ of its velocity-time graph
gradient
The distance travelled by an object can be found from the velocity-time graph by...
counting the squared and known how far each square represents (base x height)
Frictional forces ______ motion of the object
oppose
Frictional forces ________ with speed
increase
An object falling through a fluid ___________ due to gravity until the frictional forces equal the object's ______ and it reaches its ________ velocity - the resultant force acting on it is ____
accelerates, weight, terminal, zero
Describe how the motion of a falling object changes in terms of the forces acting on it
Initially the accelerating force of weight is greater than the frictional forces slowing it down so it accelerates. As it moves faster frictional forces increase. This gradually reduces the acceleration until the frictional forces equal the accelerating force, the resultant force will be zero and the object is at terminal velocity
Draw or describe the velocity-time graph of a falling object
Steep gradient to start with due to large acceleration which gradually decreases until the object reaches terminal velocity. From this point, the graph is flat as the forces are balanced and the resultant acting on the object is zero
Give two factors affecting the terminal velocity of an object
Shape and area
Gravity is the accelerating force for all masses so they would all fall at the same rate except for ___ __________
air resistance
Terminal velocity is determined by its ____ in comparison to its weight
drag