Cancer Chemotherapy
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HNI 333 Pharmacology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
cancer
2nd leading cause of death in the US; 3 treatment modalities:
– Surgery (4 solid tumors), Radiation, Drugs (4 disseminated __+localized __)
anti-cancer medications
four major classes of _-__ __:
– Cytotoxic Agents: kill the cell (v common)-official cancer chemotherapy
– Hormones & Hormones Antagonists: influence hormones interacting w cancer cells
– Biologic Response Modifiers: modify the immune syst
– Targeted Drugs: bind to a specific molecule that promotes cancer growth
cancer cell
characteristics of __ __:
– Persistent proliferation: (doesnt respond to feedback mechanisms that control cellgrowth)
– Invasive growth: breaks through basement membrane
– Metastases: enters lymphatics or circulation+travels
– Immortality
true
(T/F) cancer etiology- abnormalities are due to alterations in DNA
– Activation of oncogenes: genes that cause cancer
– Deactivation of tumor suppressor genes: normally would suppress replication of cells that are cancerous
cell cycle
Sequence of events that a cell goes through from one mitotic division to the next
– G1: cell prepares to make new DNA
– S: DNA synthesis takes place
– G2: cell prepares for mitosis
– M: Mitosis occurs
• Daughter cells can then re-enter G1 or enter the G0 phase (a resting phase)
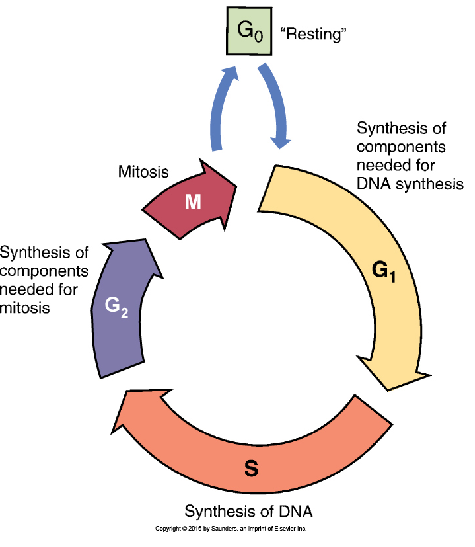
growth fraction
the ratio of proliferating cells to G0 cells—tissues w more proliferating cells than resting cells have increased __ __
– chemotherapy is more toxic to tissues w high __ __. most drugs act by blocking DNA synthesis or miosis
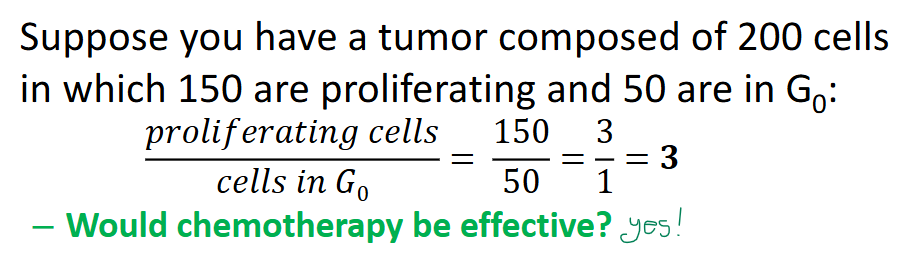
true
(T/F) More common cancers (solid tumors of breast, lung, prostate, colon) have low growth fraction (has time to repair during G0)
Rarer cancers (testicular, ALL, hodgkin’s lymphoma) have a high growth fraction
debulking
Reducing the size of the tumor by surgery or radiation (follow w chemo for residuals); increases drug effectiveness
– as cancer cells grow, more cells enter G0→ less likely to be influenced by drugs and have poor blood supply to the core of the tumor
toxicity
= is dose selective- often must reduce drug dose to minimize damage to normal cells
– damage to normal cells is dependent on growth fraction
bone marrow suppression
major toxicity of chemotherapy – yields neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia
neutropenia
effect of bone marrow suppression: promotes infection risk+opportunistic infections (candidiasis)
– normally:2500-7000 cells/mm2; lowest neutrophil count (Nadir) is btwn 10-14 days after dose (highest risk of infection- fever)
– neutrophil count recover in a week
– can administer Filgrastim (neupogen) to stim neutrophil production
thrombocytopenia
effect of bone marrow suppression: promotes bleeding risk (commonly-nose+gums)
– normally 150,000-450,00/mm3
anemia
effect of bone marrow suppression; HGB <12 (women) and <13.5 (men)
– less common than neutropenia+thrombocytopenia
– can administer Erythropoietin to stim RBC production but may shorten survival and cannot be given in myeloid cancers (AML/CML) as it may stim those cancers
GI tract injury
major toxicity of chemotherapy: epithelial lining has very high growth fraction thus yields Stomatitis and Diarrhea
– Stomatitis: inflammation of oral mucous; develops days after onset of chemo+can last up to 2 weeks after therapy ends- ulceration can occur w infections. relieved w oral antifungals and anesthetic(lidocaine)/ antihistamine(diphendyamine) mouth wash
– Diarrhea: occurs by impairing absorption of fluids and other nutrients- can be slowed by administration of oral opioid agonist (loperamide)
nausea and vomiting
major toxicity of chemotherapy: from direct stimulation of the chemoreceptor trigger zone in brain
– can be immediate and severe, more profound than other meds, treated w ondansetron (zofran)
alopecia
major toxicity of chemotherapy: occurs from injury to hair follicles
– begins 7-10 days after treatment onset & maximized in 1-2months but regenerates 1-2 months after last treatment
– may be slowed by cooling the scalp
reproductive system
major toxicity of chemotherapy: high growth function in testes and developing fetus
– both highly susceptible esp to alkylating agents
– risk of fetal abnormality is worst in 1st trimester but after 18 weeks risk is low
true
(T/F) Challenges of chemotherapy:
– Tumors are made of heterogenous cells (cells may have diff morphology, growth rate, metastatic ability. can influence effectiveness of drugs)
• Core of solid tumors have poor vascularity– difficult getting drugs into the core of the tumor
• BBB– Difficult to treat CNS tumors
cytotoxic agents
largest class and works directly to kill cancer cells; most toxic to tumors w high growth fraction
– eight major groups that: interfere w DNA synthesis, block mitosis, disrupt protein synthesis, and some are phase-specific
alkylating agents
two main groups: nitrogen mustards and nitrosureas
– binds an alkyl group to a specific nitrogen atom in guanine (some form cross-links btwn DNA strands) → result is DNA miscoding, scission of strand, or inhibition of DNA replication
– non phase-specific but more effective during replication+ resistance is common
cyclophosphamide
a nitrogen mustard (aka Cytoxan), most common alkylating compound+ bifunctional & broad spectrum
– Pro drug that is converted to active form in liver (has delayed onset of action)
– adversely: Acute hemmorrhagic cystitis and bone marrow suppression (limiting dose); N&V + alopecia
Mesna
medication given for the adverse effect of Acute Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Cyclophosphamide (nitrogen mustards)
– administer __ and adequate hydration to minimize effects of the bleeding bladder inflammation
nitrosureas
ex: Carmustine; broad spectrum and highly lipophilic
– bifunctional alkylating compound= connects 2 strands of DNA+prevents them from separating. administered via IV or biodegradable wafer (for brain tumors)
– adversely: bone marrow suppression (limiting dose; nadir 4-6 wks after dose), pulmonary fibrosis+N&V+alopecia
platinum compounds
ex: Cisplatin, first line therapy for ovarian & non-small cell lung cancer when given w paclitaxel
– forms cross-links btwn and within strands of DNA
– only approved for metastatic testicular + ovarian + advanced bladder cancer
platinum compounds adverse
adverse effects of __ __:
– Kidney damage (limiting dose): can be reduced w hydration+diuretic therapy
– Severe N&V (within hour of dose), Peripheral Neuropathy, and mild bone marrow suppression
antimetabolites
structural analogs of important natural substances—disrupt normal processes by mimicry, only effective against cells involved replication (by inhibiting enzymes or being incorporated into DNA)
classes:
– Folic Acid Analogs: Methotrexate
– Pyrimidine Analogs: Cytarabine
– Purine Analogs: Mercaptopurine
folic acid analogs
ex: Methotrexate (rhematrex, trexall); inhibits an enzyme in folic acid activation→ prevents folic acid synthesis (needed for DNAsynthesis), also induces apoptosis
– S-phrase specific
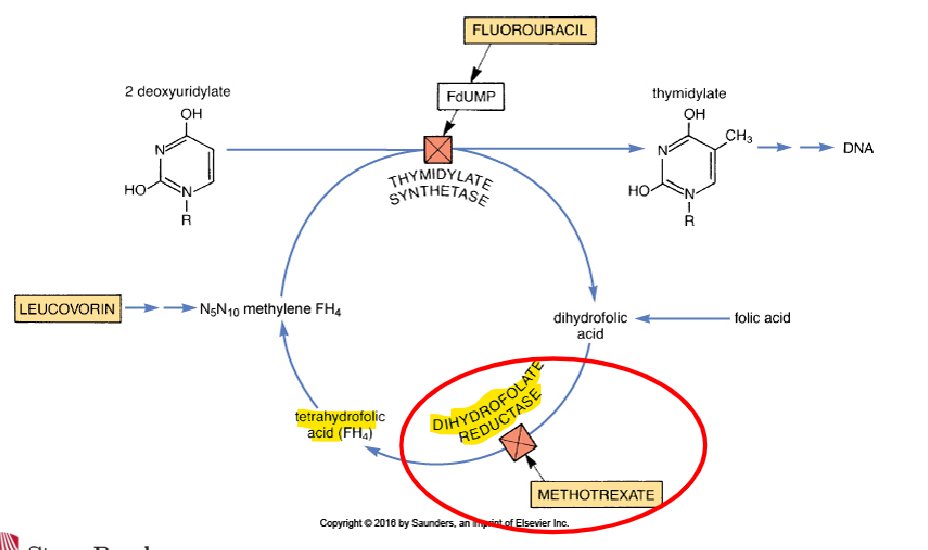
methotrexate adverse
adverse effects of __:
– Bone Marrow Suppression (limiting dose), Fetal Malformation, Kidney Damage (minimize by hydrating and alkylating urine)
– Pulmonary infiltrates and fibrosis, oral and GI ulceration, N&V
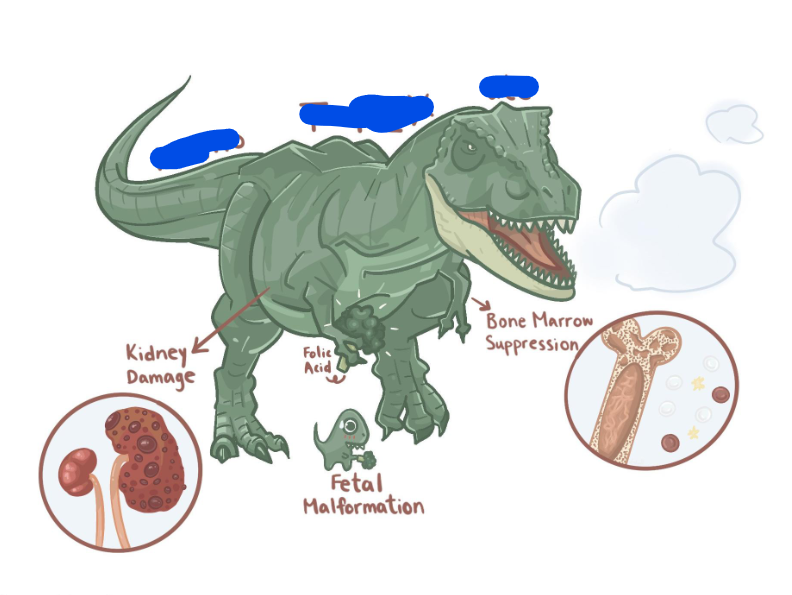
Burger King Fries
“Me Thot Rex Ate (Methotrexate) Burger King Fries":
B=bone marrow suppression
K=kidney damage
F=fetal malformation
leukovorin
Administration: Methotrexate requires transport protein for uptake but cancer cells lack it→ Large doses needed to FORCE methotrexate into cell but dangerous for normal cells
– Co-administration with __ “rescues” normal cells. __ is a precursor of folic acid.
– this med requires the same transport protein as methotrexate. cancer cells lack the transport protein so they wont be able to take up __ and will not be rescued
Pyrimidine analogs
ex: Cytarabine (cytosine arabinoside or Ara-C)—Prodrug thats activated within cells, structurally similar to pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, uracil)
– incorporated into DNA & suppresses further DNA synthesis, S-phase specific
– adversely: bone marrow sup (limiting dose), pulmonary edema, liver damage, kidney damage
pyrimidine analog adverse
think about flavors of pie... Blueberry, Lemon and Keylime:
B=bone marrow suppression
L=liver injury
K=kidney injury
purine analogs
ex: Mercaptopurine (purinethol)—Prodrug that activates within cells, structurally similar to purines (adenine, guanine, hypoxanthene), used for cancer or immunosuppression
– after activation, it interferes w purine synthesis and nucleic acid synthesis; S-phase specific
– adversely: bone marrow sup (limiting dose) and mild hepatotoxicity (↑bilirubin and LFTs)
topoisomerase
enzyme necessary for DNA replication and RNA synthesis
– permits relaxation of coiled DNA, promotes synthesis of RNA+DNA replication+DNA repair, later reseals the strand
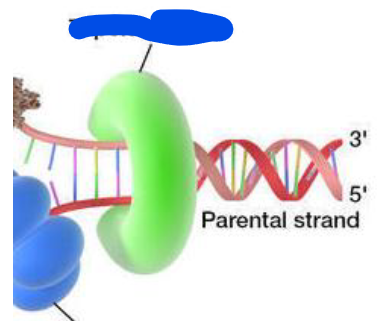
topoisomerase inhibitor
ex: Etoposide (Toposar)— permits opening of the DNA but doesnt permit repair! cell death due to accumulation of DNA w multiple breaks, (high protein binding)
– adversely: bone marrow suppression (dose limiting)
antitumor antibiotics
type of antibiotics that includes Anthracyclines (-rubicin) and Non-Anthracyclines(-mycin)—only for treating cancer via damaging cells by direct interaction w DNA
– conventional vs liposomal type: liposomal associated with infusion-associated symptoms but more likely to target cancer cells and not normal cells
anthracyclines
ex: Doxorubicin; type of antitumor antibiotic that works via:
– Intercalation with DNA: slips btwn base pairs and binds to DNA →distorts DNA structure
– Inhibition of topoisomerase II: doxorubicin allows cleaving function of DNA but not repair= apoptosis
anthracyclines adverse
adverse effects of __:
– Bone marrow suppression (limiting dose)
– Cardiotoxicity (arrhythmias) leading to HF: may appear asap or years after dose, check 4 palpitations/edema/SOB, dexrazoxane(Zinecard) may offer protection but ↑bone marrow sup,
– Infusion-related symptoms w/ Liposomal form: chest/back pain or flushing; disappear when infusion is stopped &doesnt return when restarted at slower rate
ABC Do XYZ

non-anthracyclines
ex: Dactinomycin (Actinomycin D), type of antitumor antibiotic
– Intercalates w DNA and distorts structure. also Inhibits RNA and protein synthesis
– adversely: bone marrow suppression (also oral+GI muscositis, N&V+alopecia)
mitotic inhibitors
drugs that act during M phase and holds two groups:
– Vinca alkaloids (vincristine and vinblastine) and Taxanes (paclitaxel)
vinca alkaloids
ex: Vincristine or Vinblastine; type of mitotic inhibitor and derived from periwinkle flower
– block mitosis during metaphase and disrupts assembly of microtubules by binding to tubulin (part of microtubules), cell stops in metaphase (cant be pulled to poles during anaphase)= apoptosis
– vincristine is bone marrow sparing! but for vinblastine bone marrow sup is dose-limiter but otherwise less adverse effects
vinca alkloids adverse
adverse effects of __ __:
– Peripheral neuropathy (dose-limiting): occurs in almost all pts—disrupts neurotubules in neurons (necessary for enzyme/organelle transport)= ↓reflexes, weakness, paresthesia, sensory loss; but minimal brain injury (cant cross BBB)
– Alopecia
taxanes
ex: Paclitaxel (Taxol); type of mitotic inhibitor and first line therapy for ovarian cancer+non-small cell lung cancer when used w cisplastin
– promotes formation of microtubule bundles, inhibits cell division→ promotes apoptosis
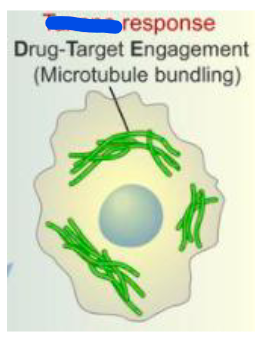
taxane adverse
adverse effects of __:
– Bone marrow suppression (dose limiting)
– Severe hypersensitivity reaction w Taxol: hypotension, dyspnea, angioedema, urticaria (pretreat w glucocorticoid, antihistamine, H2 receptor antagonist)
– Peripheral neuropathy

asparaginase
__ is an enzyme that converts asparagine into aspartic acid; used for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL);
– asparagine is an essential amino acid for protein synthesis (cells w/o asparagine cant make proteins)
– adversely: coagulation deficiencies and liver/kidney/pancreas damage (from inhibition of protein synthesis), and CNS depression
breast cancer drugs
drugs for __ __:
– Hormones and Hormone Antagonists: Anti-estrogens (Tamoxifen), Aromatase inhibitors (Anastrozole), Kinase inhibitor (Lapatinib)
– Biologic response modifiers: Anti-HER2 Antibodies (Trastuzumab)
antiestrogen
drugs that block estrogen receptors= deprives tumor cells of growth-promoting influence of estrogen; ex: Tamoxifen (gold standard endocrine treatment 4 breast cancer)
– indications: estrogen receptor positive breast cancer
– adversely: increased risk of endometrial cancer&thrombosis, hot flashes, fluid retention, vaginal discharge/menstrual irregularities, teratogenic, and has a reduced effect to CYP450 inhibitors
antiestrogen mechanisms
mechanism of action of __(Tamoxifen): Prodrug that converts into an active metabolite—
– Blocks estrogen receptors in breast cancer cells: prevents estradiol from binding (which normally stims growth+proliferation)= ↓proliferation and ↑tumor regression
– Activates estrogen receptors in bone, liver, and uterus: can ↑bone density, ↑clotting factors, ↑risk of endometrial cancer
aromatase inhibitors
ex: Anastrozole; for ER positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women
– normally: adrenal androgens are converted into estrogen by aromatase in peripheral tissues, Anastrozole blocks aromatase→ estrogen synthesis from androgens is reduced still undetectable= this deprives estrogen-dependent breast cancer from growing
– doesnt block estrogen produced by ovaries and adversely: musculoskeletal pain, osteoporosis & fractures
anti-HER2 antibodies
anti human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 antibodies= Trastuzumab (Herceptin); given to HER2 positive breast cancer
– normally: HER2 receptor on the cell membrane regulates cell growth but overexpression causes tumor growth, Trastuzumab (monoclonal antibody) blocks HER2 receptor= inhibits cell proliferation+ promotes antibody-dependent cell death
anti-her2 antibodies adverse
adverse effect of _-_ __:
– Cardiotoxicity – ventricular dysfunction and HF (caution in women w heart disease or when combining with paclitaxel)
– Flu-like symptoms: fatigue, chills, fever, nausea
– Potentially fatal hypersensitivity reaction: urticaria, bronchospasm, angioedema, hypotension
– Infusion reaction (chills, fever, nausea): fades w prolonged treatment
No bone marrow suppression!!
kinase inhibitor
ex: Lapatinib; used for HER2 positive breast cancer only in combo w other drugs
– inhibits two enzymes involved in cell signal transduction and blocks signal promoting growth of tumor
– adversely: diarrhea, N&V, fatigue, rash, may severe liver injury
androgen deprivation therapy
type of therapy used in prostate cancer; disease usually progresses after 18-24 months following therapy
– 90% of androgens come from testes &10% produced by adrenal+prostate
– drug therapy more effective than castration= blocks testosterone receptors+lowers testosterone production
GnRH agonists
ex: Leuprolide; Gonadotropin-releasing hormone __;
– GnRH synthetic analog and mimics it to bind to receptors in pituitary, initial transient release of hormones that increase testosterone production; w continuous exposure GnRH is desensitized and testosterone production declines! =chemical castration
– no effect on androgens produced by adrenal/prostate but adversely: hot flashes, erectile dysfunction, reduced libido, gynecomastia, reduced muscle mass, ↑risk of osteoporosis and bone fracture
androgen receptor blockers
ex: Flutamide; used for prostate cancer and often administered w GnRH Agonist (Leuprolide) to suppress initial flare and activity due to adrenal/prostate production of androgens
– blocks androgen receptors
– adversely: N&V, rare liver toxicity, Hot flashes, Erectile dysfunction, Reduced libido, Gynecomastia, Reduced muscle mass, Increased risk of osteoporosis and bone fracture,
GnRH antagonists
ex: Degarelix (Firmagon); used for advanced prostate cancer
– blocks the GnRH receptors in pituitary and reduces production of hormones that stim the testes to produce testosterone= no initial flare of prostate cancer
– adversely: Injection site reactions, Hot flashes, Erectile dysfunction, Reduced libido, Gynecomastia, Reduced muscle mass, Increased risk of osteoporosis and bone fracture,
CYP17 Inhibitor
ex: Abiraterone; used w prednisone to treat metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
– inhibits CYP17, an enzyme necessary for androgen synthesis
– adversely: hypokalemia and edema (from excessive aldosterone secretion from androgen blockade), joint swelling, hepatotoxicity, Hot flashes, Erectile dysfunction, Reduced libido, Gynecomastia, Reduced muscle mass
targeted anti-cancer meds
medications that bind to a specific molecule that promotes cancer growth (vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF])— prevents synthesis of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) to support growth of cancer
angiogenesis inhibitors
ex: Bevacizumab; suppress formation of new blood vessels= deprive solid tumors of blood supply but cant kill existing tumors
– monoclonal antibody that binds to VEGF ∴ cannot bind to receptors on vascular endothelium that promote vessel growth= new vessel growth doesnt occur
angiogenesis inhibitors adverse
adverse effects of __ __:
– Nephrotic syndrome
– GI Perforation: stop drug and never use again
– Hemorrhage: brain, lung, GI, vaginal
– Thromboembolism: stop drug and never use again
