CHEM121 - EXAM 3 REVIEW
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
speed of light ( c )
2.998 × 108 m/s
photons
discrete amounts of energy absorbed or emitted by atoms
quanta
used by Planck to explain the radiation emitted by incandescent objects
used by Einstein to explain the photoelectric effect
work function (Φ)
the radiant energy required to dislodge a photoelectron from a metal surface
electron transitions between energy levels in an atom produce…
atomic emission spectra and atomic absorption spectra consisting of narrow lines at wavelengths corresponding to the change in energy of the electrons
matter waves
proposed by De Broglie
all moving particles have wave properties
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
both the position and momentum of an electron cannot be precisely known at the same time
Schrödinger wave equation
mathematical expressions called wave functions (𝛙)
𝛙2 defines the regions within an atom, called orbitals
orbitals
describe the probability of finding an electron at a given distance from the nucleus
have characteristic three-dimensional sizes, shapes, and orientations that are depicted by boundary-surface representations
principal quantum number n
defines orbital size and energy level
angular momentum quantum number l
defines orbital shape
magnetic quantum number ml
defines orbital orientation in space
spin quantum number ms
allows two opposite-spin electrons to share an orbital
Pauli exclusion principle
states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same four values of n, l, ml, and ms
aufbau principle
electrons fill the lowest-energy atomic orbitals of a ground-state atom first
electron configuration
set of numbers and letters expressing the number of electrons that occupy each orbital in an atom
electron configuration order
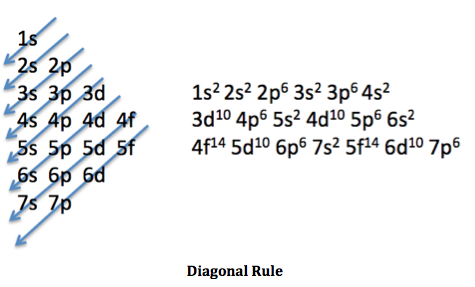
degenerate
having the same energy
Hund’s rule
states that in any set of degenerate orbitals, one electron must occupy each orbital before a second electron occupies any orbital in the set
effective nuclear charge (Zeff)
the net nuclear charge experienced by outer-shell electrons when they are shieled by inner-shell electrons
atomic radius / sizes of atoms
the size of atoms increase down a group of elements because valence-shell electrons with higher n values are farther from the nucleus
the size of atoms decrease across a row of elements because the valence electrons experience higher effective nuclear charges.
ionization energy (IE)
the energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of atoms or ions in the gas phase
increases with increasing effective nuclear charge across a row and decrease down a group
photoelectron spectra
plots the relative number of electrons in an element and their binding energies
can be used to identify metals and determine their electron configurations
electron affinity (EA)
the energy change that occurs when one mole of electrons combines with one mole of atoms or ions in the gas phase
calculating frequency from wavelength
ν = c/λ
calculating the energy of a photon
E = hc/λ
Planck’s constant (h)
6.626 × 10-34 J
electrostatic potential energy (Eel)
a measure of the strength of the attractions between cations and anions in an ionic compound
directly proportional to the product of the ion charges and inversely proportional to the distance between the nuclei of the ions
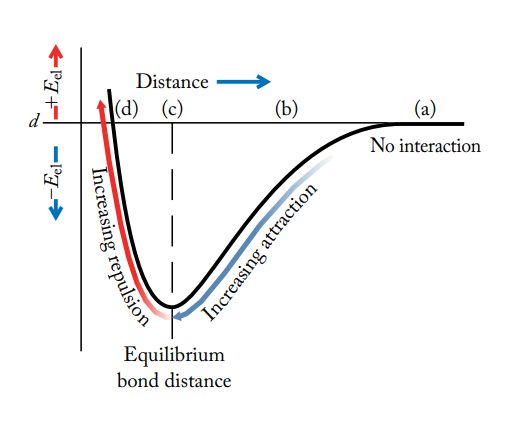
polar covalent bonds
unequal electron sharing between atoms of different elements
electronegativity generally increases with…
increasing ionization energy
isoelectronic
having the same total number of electrons
metallic bond
delocalization of electrons
covalent bond
sharing of electrons
ionic bond
transfer of electrons