Autosomal dominant inheritance 11/11 & 11/13
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts of autosomal dominant inheritance and associated terminologies related to single-gene diseases.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Mendelian Trait/ Monogenic Trait
A particular genotype at a single locus is the primary determinant of the trait.
Dominant Disorder (trait)
A human monogenic disorder determined by a nuclear gene, manifested in the heterozygote.
A mutation is dominant when heterozygosity for a genetic variant causes a clear pathological phenotype.
The normal allele on its own is not sufficient to secure normal function.
Aa will be effected
Heterozygote
An individual with two different alleles for a specific gene.
Variable Expressivity
The degree of expression of the phenotype among individuals with the same genotype.
Penetrance
The probability that a person with a particular genotype will express the related phenotype.
I.e. the likelihood that a person carrying a disease-associated genotype will develop the disease.
Ex. A person with achondroplasia allele will develop the disease, 100% penetrate
Complete penetrance
Reduced penetrance
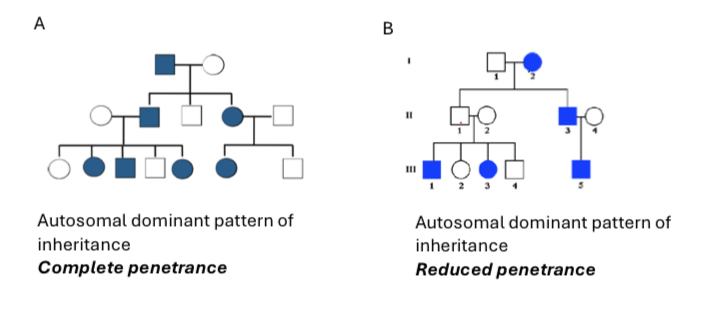
Reduced Penetrance
An individual carrying a disease-causing genotype might not exhibit the disease phenotype at all, even though he or she can transmit the disease-causing mutation to the next generation.
Obligate carrier: an individual who has an affected parent and affected children and therefore he/she must be a carrier of the mutation.
Achondroplasia
An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by skeletal dysplasia.
Marfan Syndrome
An autosomal dominant multisystem disorder caused by mutations in the FBN1 gene.
Neurofibromatosis
An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by growth of multiple benign tumors in different parts of the body.
Huntington Disease
An autosomal dominant neurological disorder caused by mutations in the HD gene, characterized by progressive movement disturbances.
Tri-nucleotide Repeat Expansion
An abnormal long expansion of trinucleotides that can cause certain genetic disorders, including Huntington disease.
Anticipation
The phenomenon where signs and symptoms of genetic disorders become more severe and appear at earlier ages as the disorder is passed through generations.
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Dominant traits have a distinctive pattern of inheritance
Every affected individual should have at least one affected parent. Successive generations are affected.
Males and females are affected equally, autosomal trait
The phenotype in homozygous dominant individuals (AA) is often more severe than the heterozygous phenotype (Aa).
Autosomal Dominant and Recurrence risk
The likelihood of an offspring inheriting an autosomal dominant trait from an affected parent. Each child has a 50% chance of being affected if one parent carries the dominant allele.
Clinical examples of autosomal dominant disorders and factors affecting pedigree patterns
Achondroplasia
Marfan syndrome
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and type 2
Huntington disease