History & Basics of the Electromagnetic Spectrum 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Who discovered X-rays and when?
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen on November 8, 1895.
Explain how X-rays were discovered.
Accidentally: while working with a Crookes tube, Roentgen noticed a covered screen coated with barium platinocyanide glowing (fluorescing) even though the tube was shielded—evidence of a new penetrating ray he called “X-rays.”
How were X-rays discovered?
Accidentally, when Roentgen noticed fluorescence of platinocyanide-covered cardboard in his lab while working with a Crookes tube.
What is fluorescence?
The emission of light by a substance after it absorbs radiation.
What was the first radiograph ever taken?
The hand of Mrs. Roentgen, exposed for 15 minutes, showing her bones and wedding ring.
When did Roentgen receive the Nobel Prize in Physics and for what?
In 1901; he received the first Physics Nobel for the discovery of X-rays.
How did the public initially view the discovery of X-rays?
As a novelty (sensationalized at first), but it quickly became important for medical imaging and therapy.
What early commercial/novelty use appeared in the slides?
Shoe sales (shoe-fitting fluoroscopes were promoted in stores).
What remark did Roentgen make during his experiments?
"I have discovered something interesting, but I do not know if my observations are correct."
What type of energy are X-rays?
A form of electromagnetic radiation.
Do X-rays behave like waves or particles?
Both — they exhibit wave–particle duality.
How does energy affect whether X-rays act more like waves or particles?
Higher energy → more photon-like (particle behavior); lower energy → more wave-like.
What is a photon?
A small bundle (quantum) of energy; when X-rays interact with matter, they behave more like particles.
What does wavelength represent?
The distance between two successive crests or troughs — one full cycle.
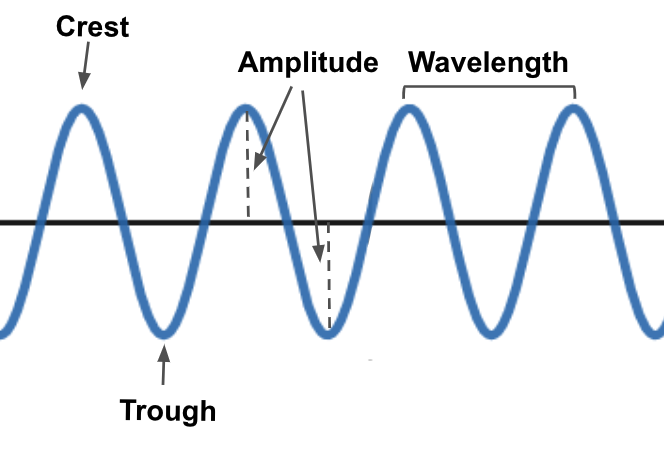
What units of wavelength are commonly used in radiography?
Angstroms (Å). 1 Å = 0.1 nm = 10⁻¹⁰ m.
What is the wavelength range of diagnostic X-rays?
Approximately 0.1 – 1.0 Å.
What does frequency represent?
The number of waves (cycles) passing a point per second.
What is a hertz (Hz)?
The SI unit of frequency; 1 Hz = one cycle (event) per second.
How are energy, wavelength, and frequency related in EM radiation?
Higher energy → higher frequency and shorter wavelength (inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency).
At what speed does all electromagnetic radiation travel?
About 186,000 miles per second (the speed of light).
When was the first radiation skin damage noted?
In 1898: erythema (reddening) of the skin in people exposed to high doses.
What was the first x-radiation–induced death recorded?
1904.
What principle guides radiation safety?
ALARA — As Low As Reasonably Achievable.
Who does ALARA primarily apply to,
Primarily occupational exposure for imaging professionals, but also applied to patient exposure
What is the concept of dose optimization?
Radiation exposure should be appropriate to the procedure and avoid unnecessary exposure
What are the three fundamental methods of radiation protection?
Time, Distance, and Shielding
How should the X-ray field size be managed?
Limit exposure field to the area of interest (collimation)
What technical factors should be selected to minimize exposure?
Use the right kVp and mAs to create a diagnostic image while minimizing patient exposure
What are other best practices in radiation protection?
Avoid duplicate exams.
Screen for pregnancy.
Use a mental checklist and perform consistently