CFF 2: Occlusion and Mandibular Movements
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
lingual and mesial
In the normal relationship, the mandibular teeth are positioned slightly__________ to their counterparts.
True
T/F: The loss of a single tooth can have significant effects on the stability of both arches
1st molars
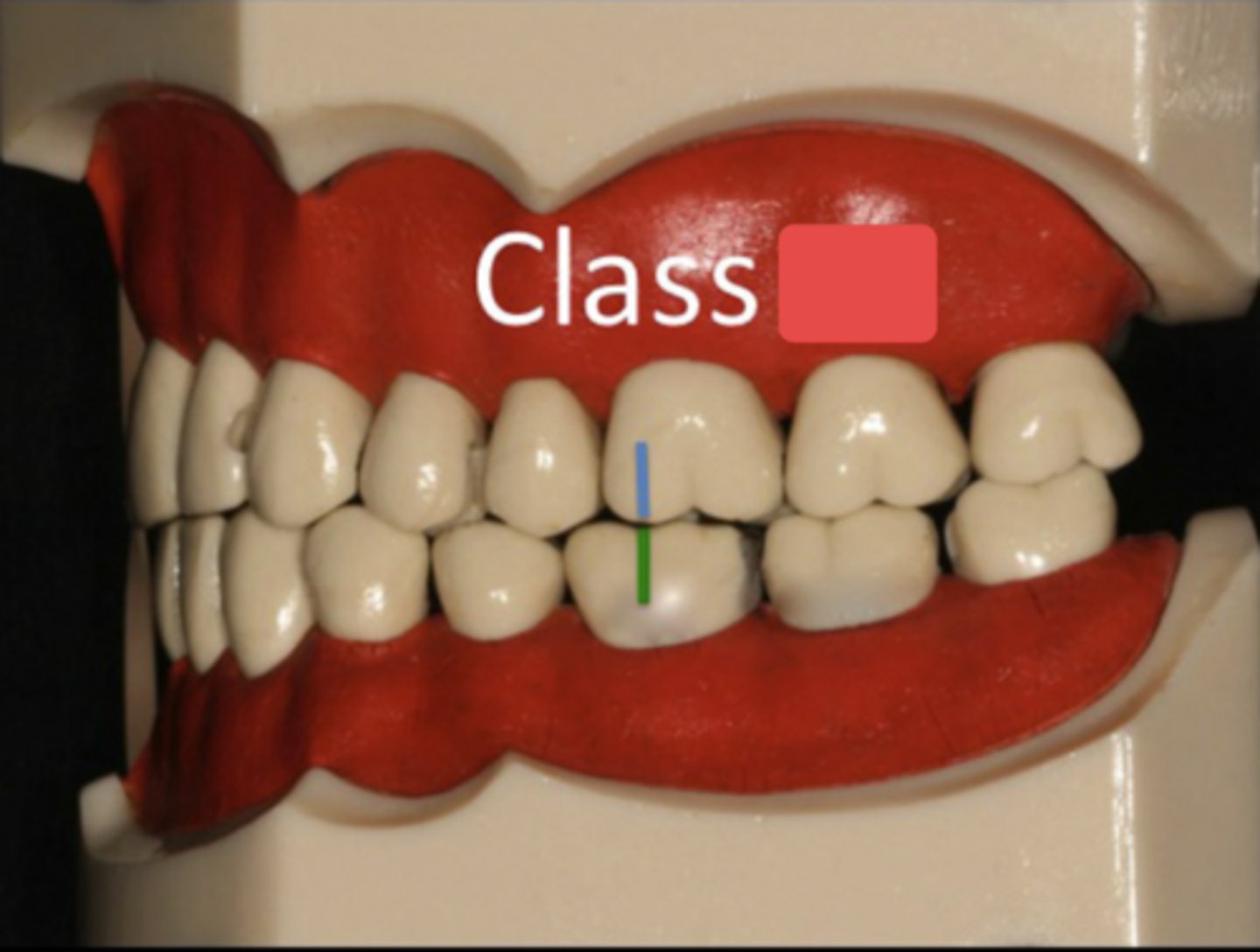
occlusion classes are assessed in relationship to what teeth?
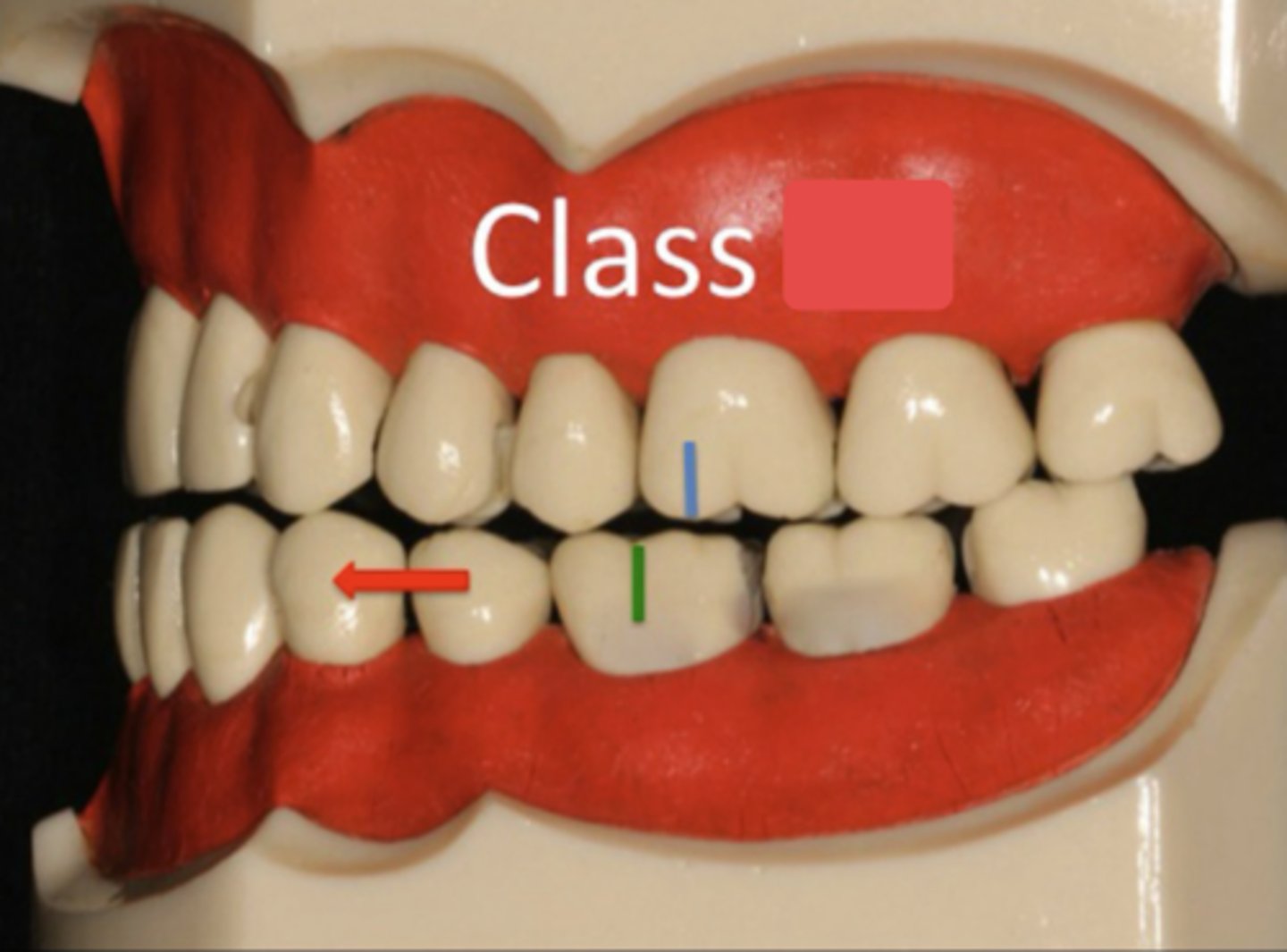
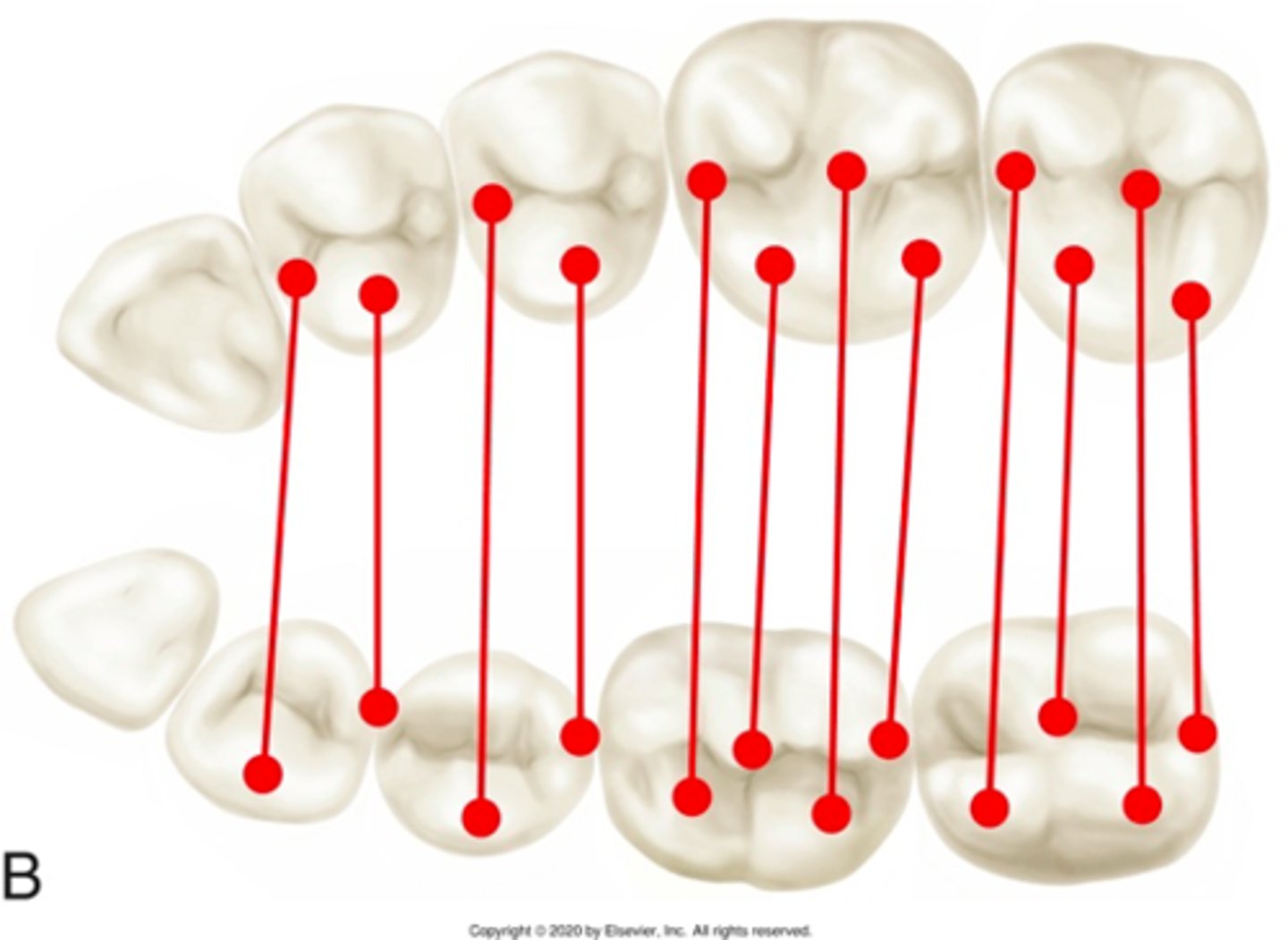
class I
ID the class:
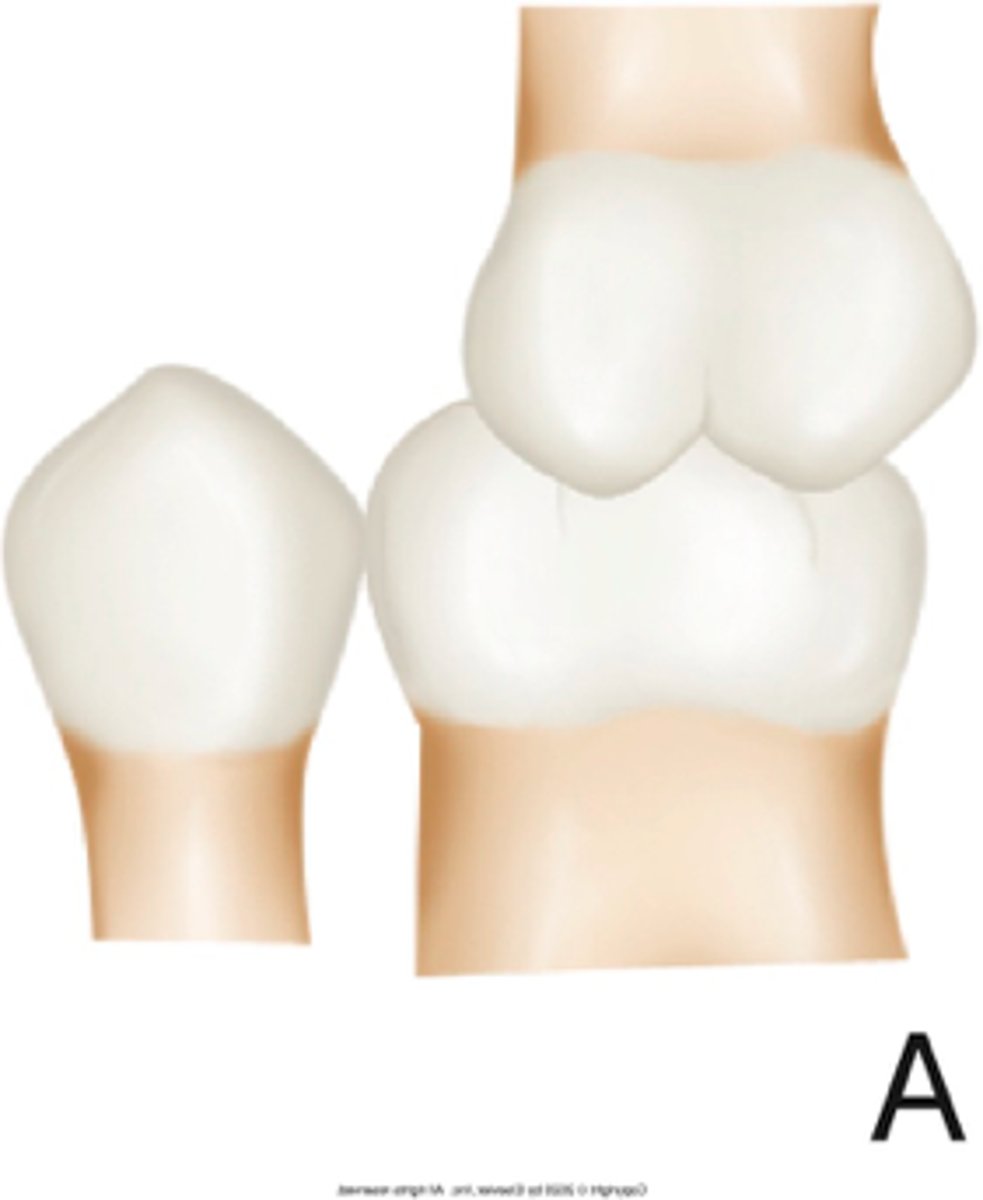
The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar is aligned directly over the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar
buccal groove
in a class I occlusal relationship, the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary 1st molar is aligned directly over the ________ of the mandibular first molar
mesiobuccal cusp
in a class I occlusal relationship, the ________ of the maxillary first molar is aligned directly over the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar
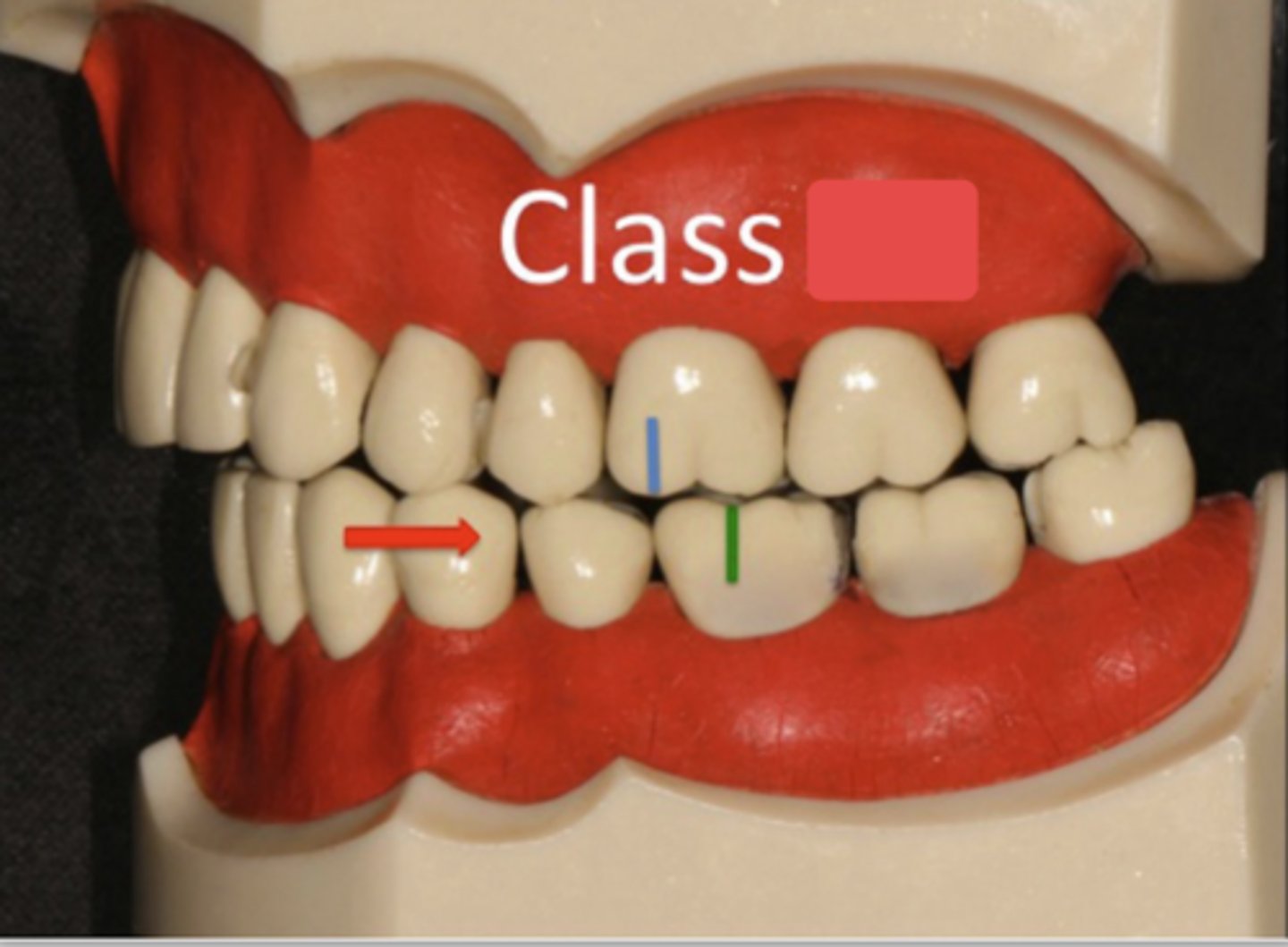
class II
ID the class:
The mesiobuccal cusp of the mandibular first molar is aligned with the buccal groove of the maxillary first molar
class II
ID the class:
•Each occlusal contact pair is situated to the distal
•The mandibular dental arch is posterior to the maxillary dental arch in one or both lateral segments
The mandibular first molar is distal to the maxillary first molar
distal
in a class II occlusion, the mandibular 1st molar is ______ to the maxillary 1st molar
class III
ID the class:
The distobuccal cusp of the mandibular first molar is situated in the embrassure between the maxillary second molar and first molar
mesial
in a class III occlusion, the mandibular 1st molar is ______ to the maxillary 1st molar
False - they are static
T/F: You observe the occlusal relationship of posterior teeth while the teeth are in motion
All teeth have specific "ideal" positions in the dental arch
- He defined "normal" and "abnormal" occlusion in a very strict manner
What did Angle hypothesize about occlusion?
Labial
The maxillary anterior teeth are normally positioned _________ to the mandibular anterior teeth
Half
Maxillary anterior teeth overlap the mandibular anterior teeth almost _______ the length of the mandibular crowns
Labial inclination makes them less resistant
Why are anterior teeth not suited to resist heavy occlusal forces?
Lighter contact than posterior teeth, sometimes even no contact
How does the contact of anterior teeth differ from posterior teeth?
Guide the mandible through the various lateral movements
What is the main role of anterior guidance?
horizontal overlap (overjet)
Define the following:
Distance between the labial incisal edge of the maxillary incisor and the labial surface of the mandibular incisor in the intercuspal position
Incise food
Speech, lip support, and esthetics
Anterior teeth are primarily responsible for what?
vertical overlap (overbite)
Define the following:
•Distance between the incisal edges of the opposing anterior teeth.
•Average 3-5mm
3-5mm
the average distance between the incisal edges of the opposing anterior teeth is :
class I
ID the occlusion classification:
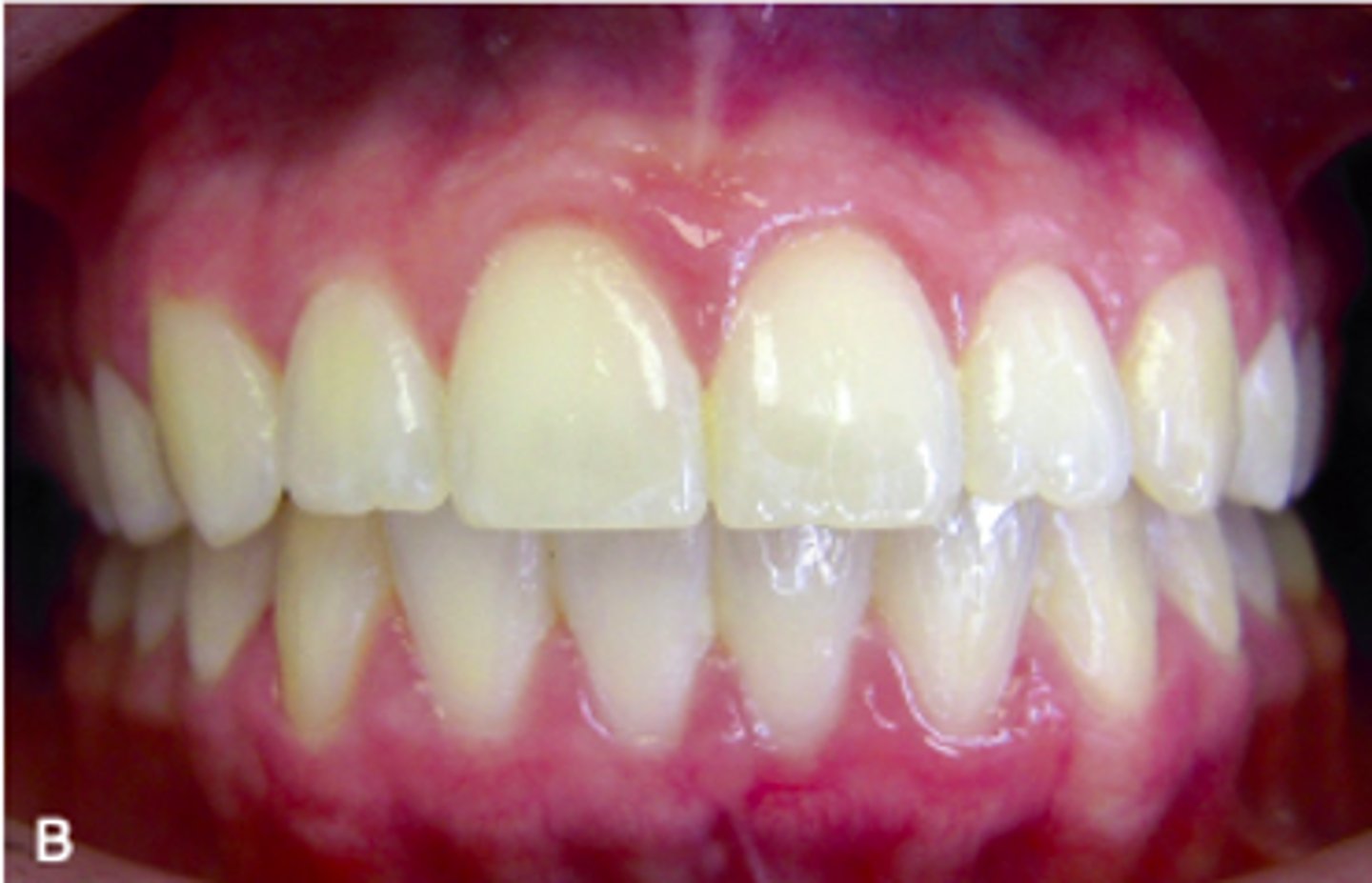
class II, division 1 (deep-bite)
ID the occlusion classification:
class II, division 2
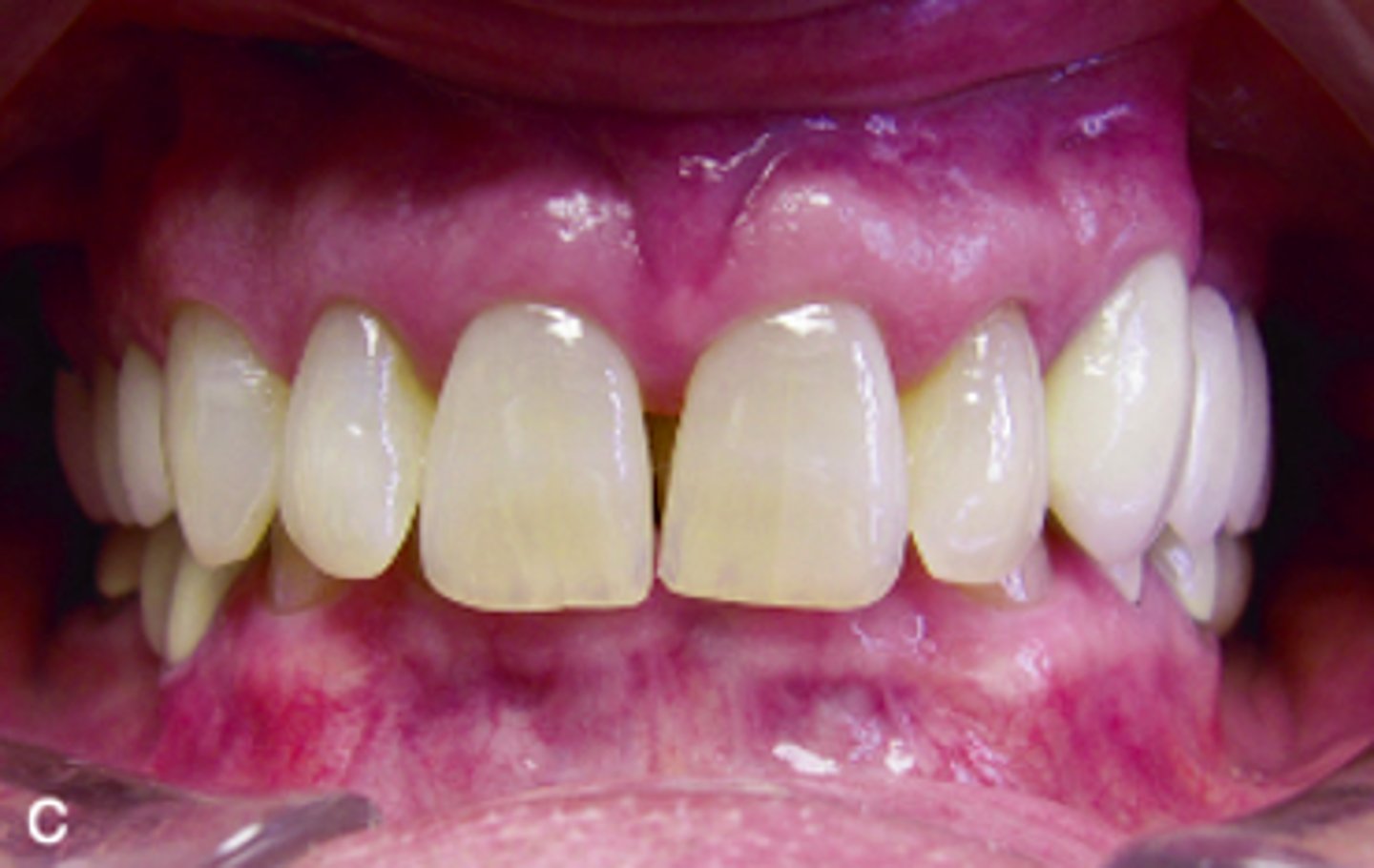
ID the occlusion classification:
class III (end to end)
ID the occlusion classification:
class III
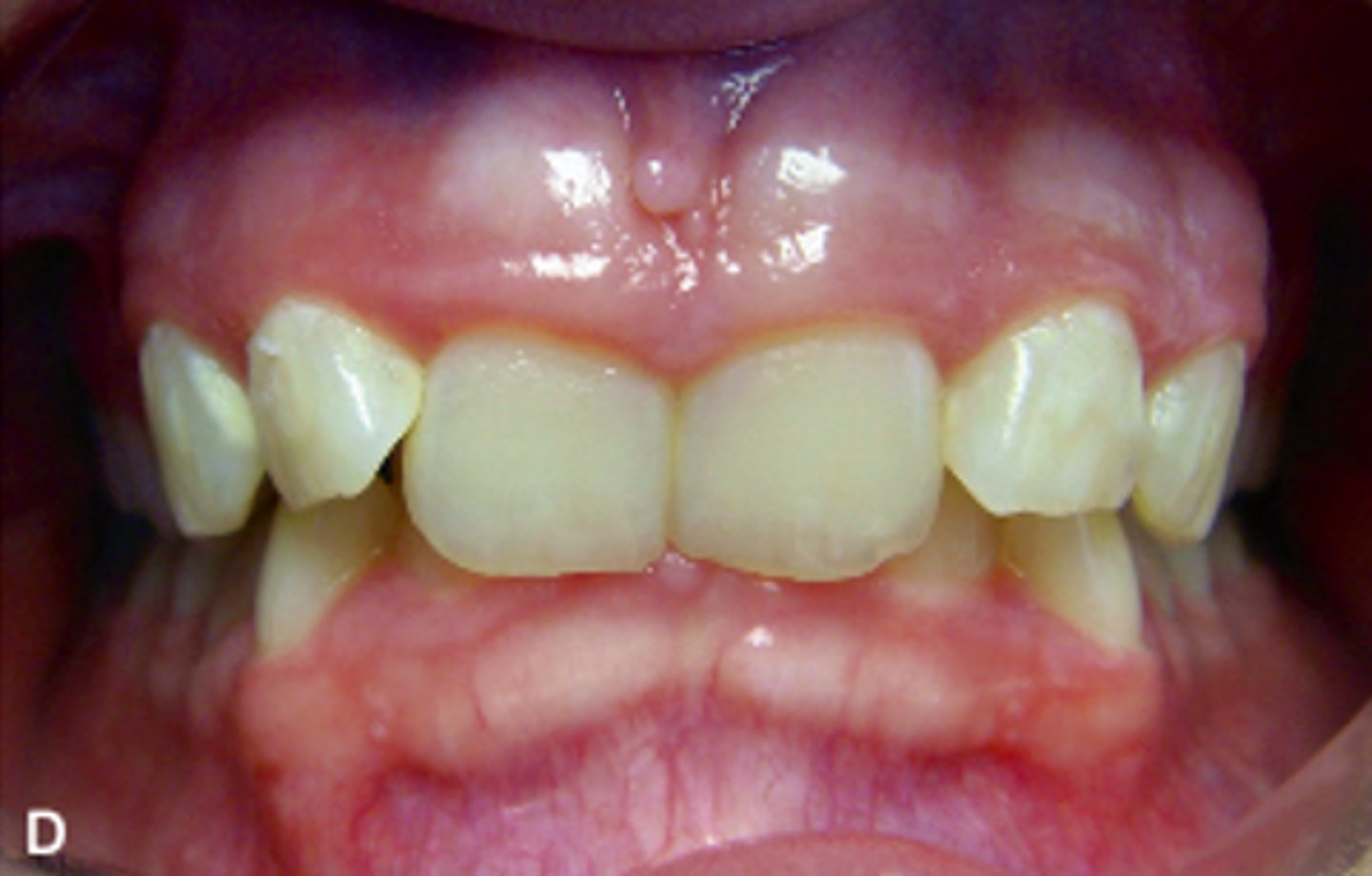
ID the occlusion classification:
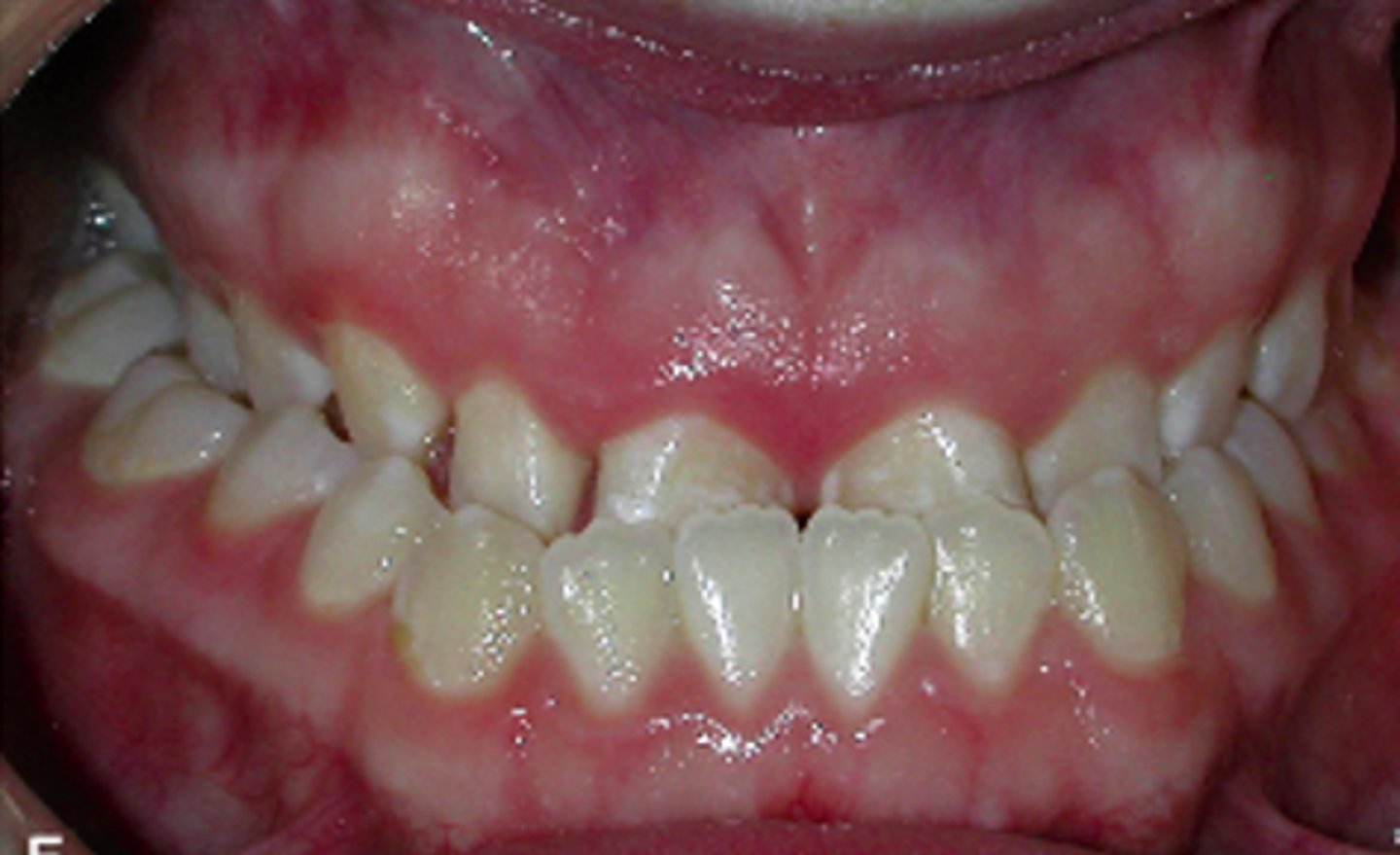
Anterior openbite
ID the occlusion classification:
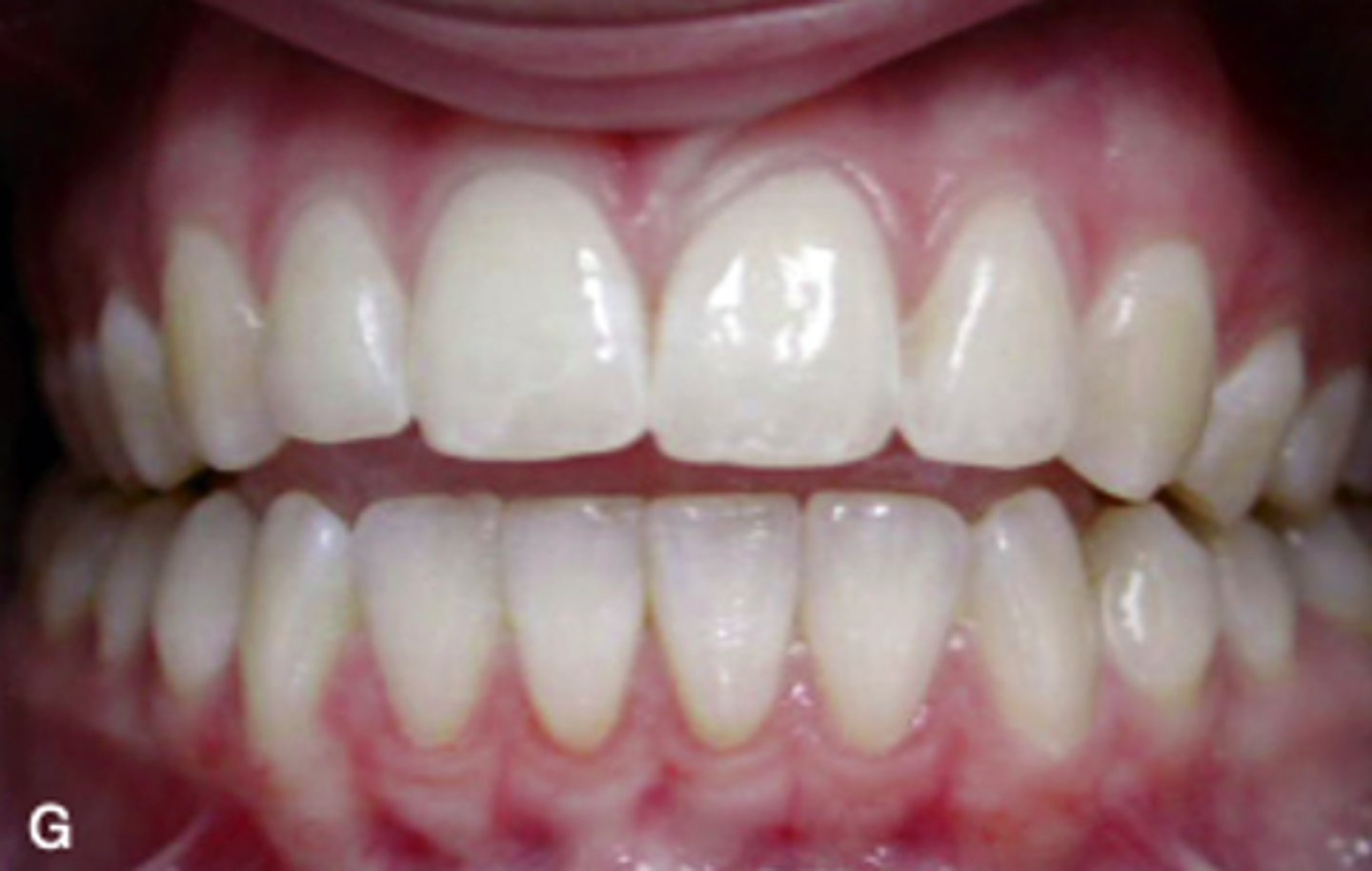
class I
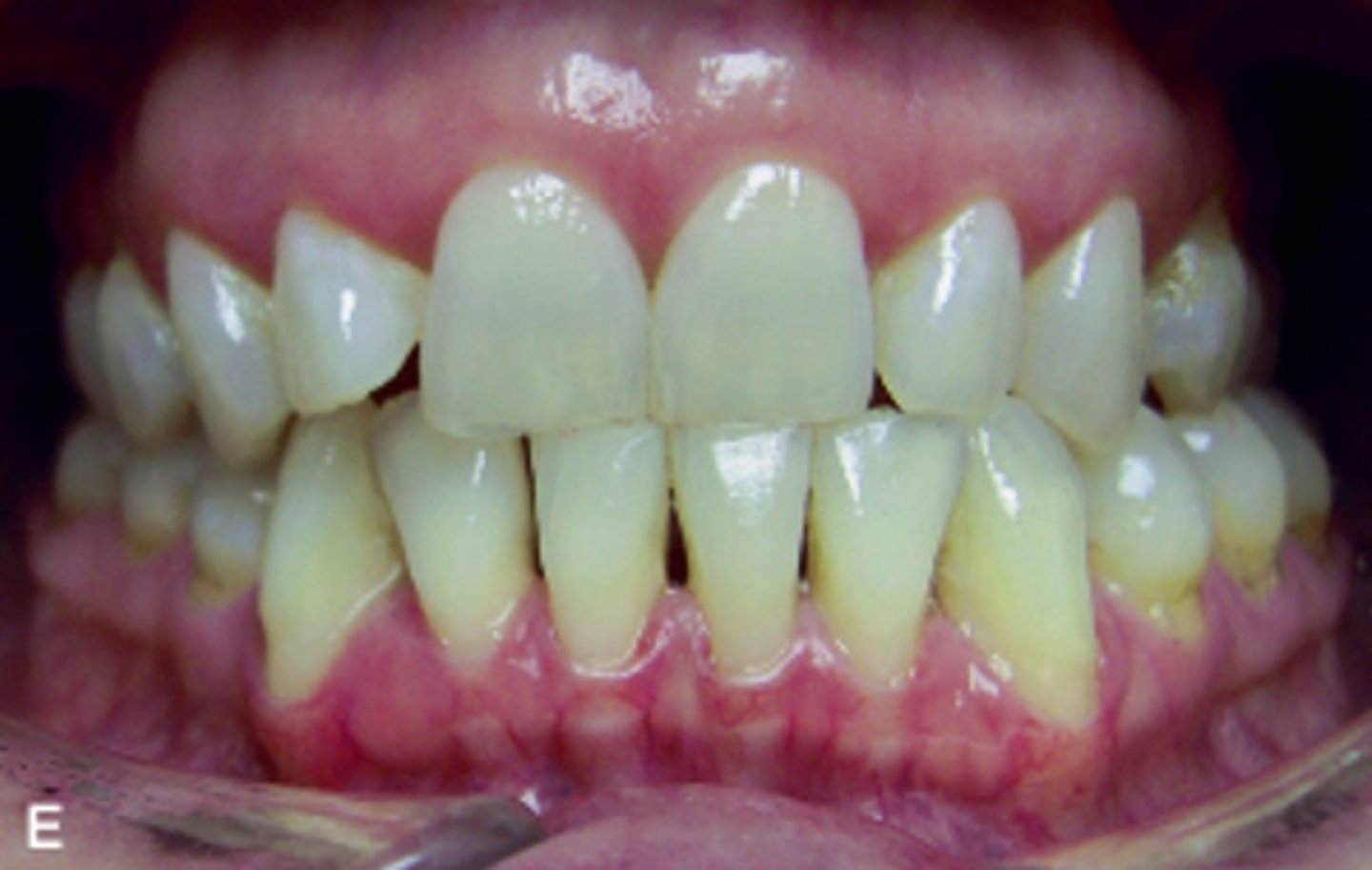
ID the occlusion classification:
class I
ID the occlusion classification:
class I
ID the occlusion classification:
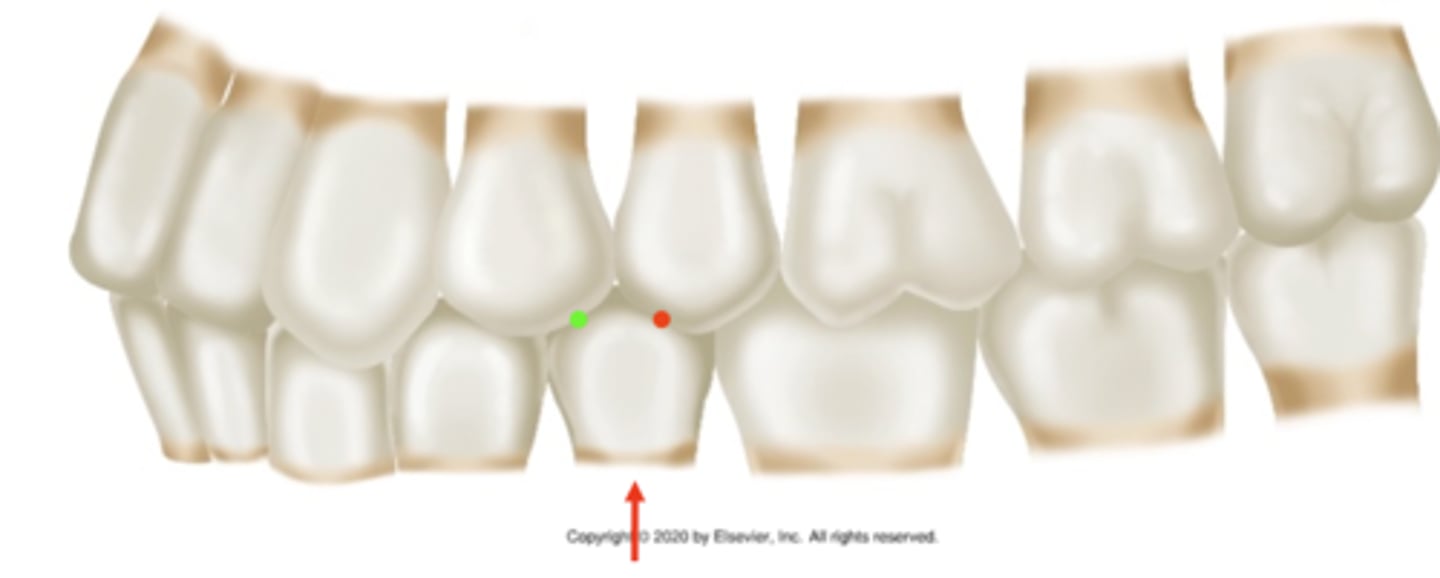
class II
ID the occlusion classification:
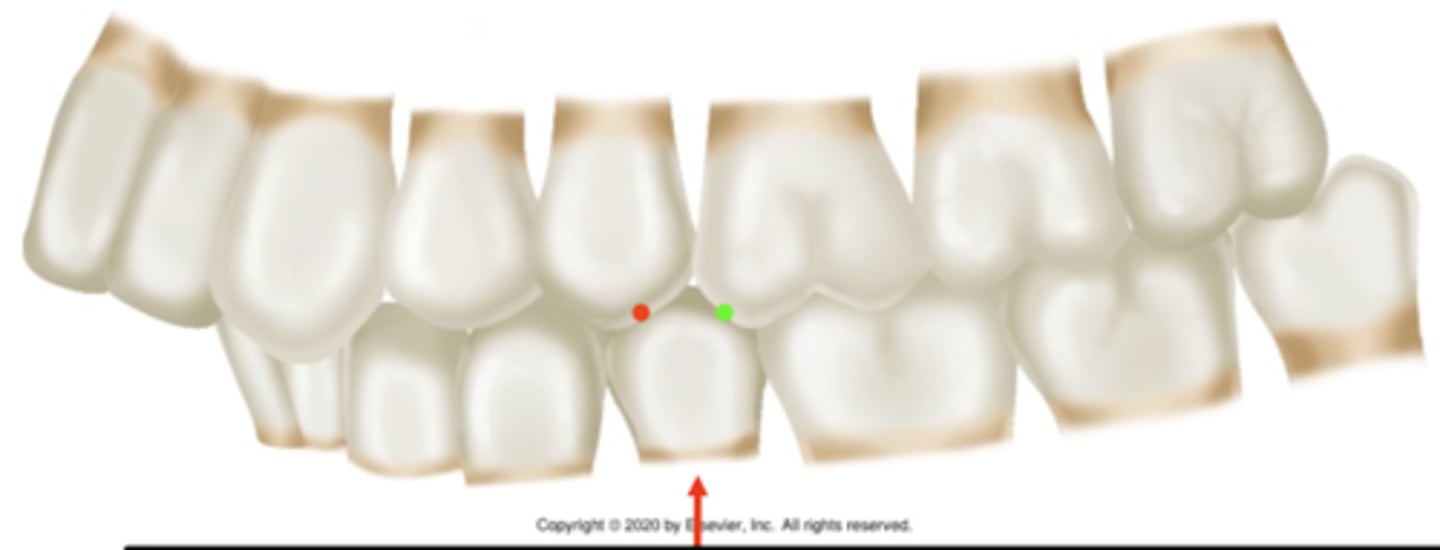
class II
ID the occlusion classification:
class II
ID the occlusion classification:
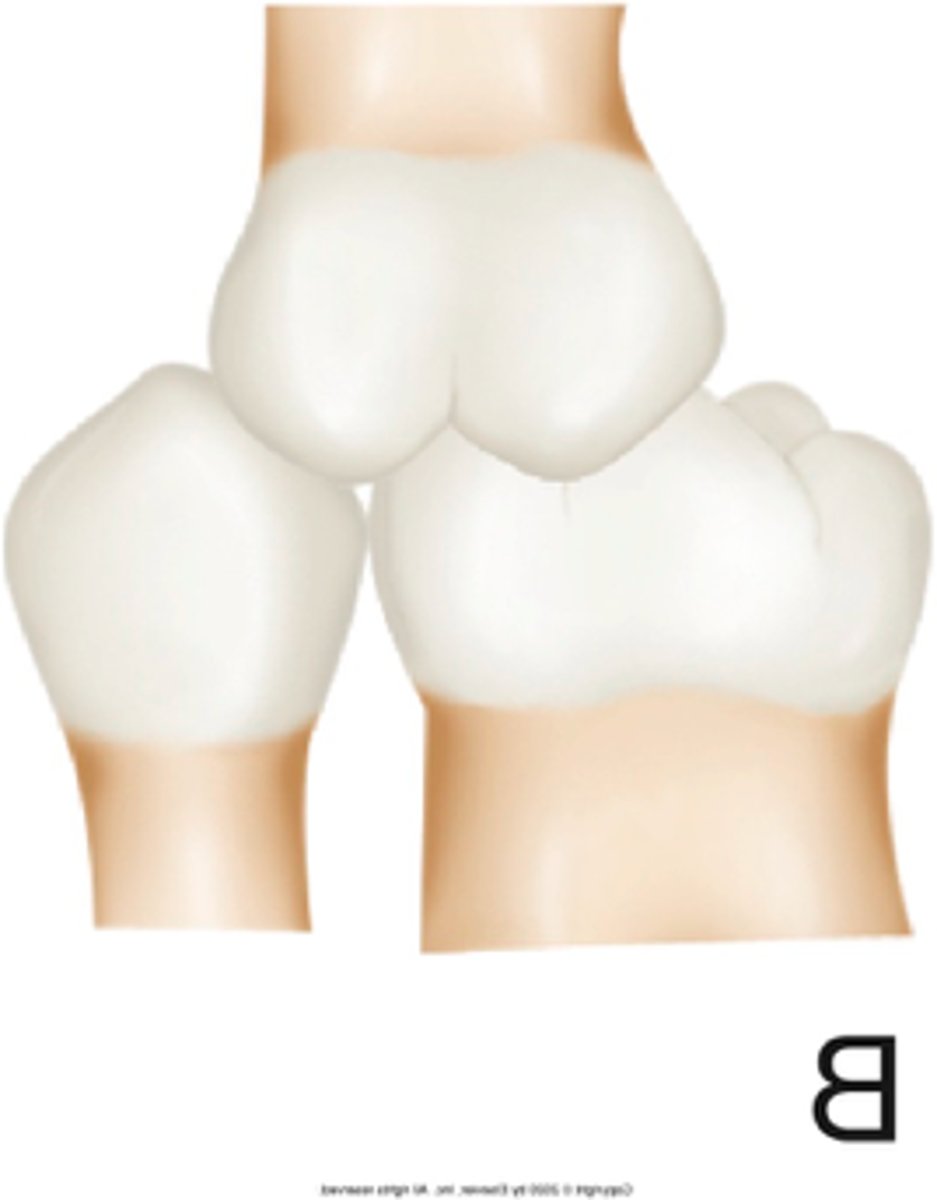
class III
ID the occlusion classification:
class III
ID the occlusion classification:
class III
ID the occlusion classification:
class I
ID the occlusion classification:
class II
ID the occlusion classification:
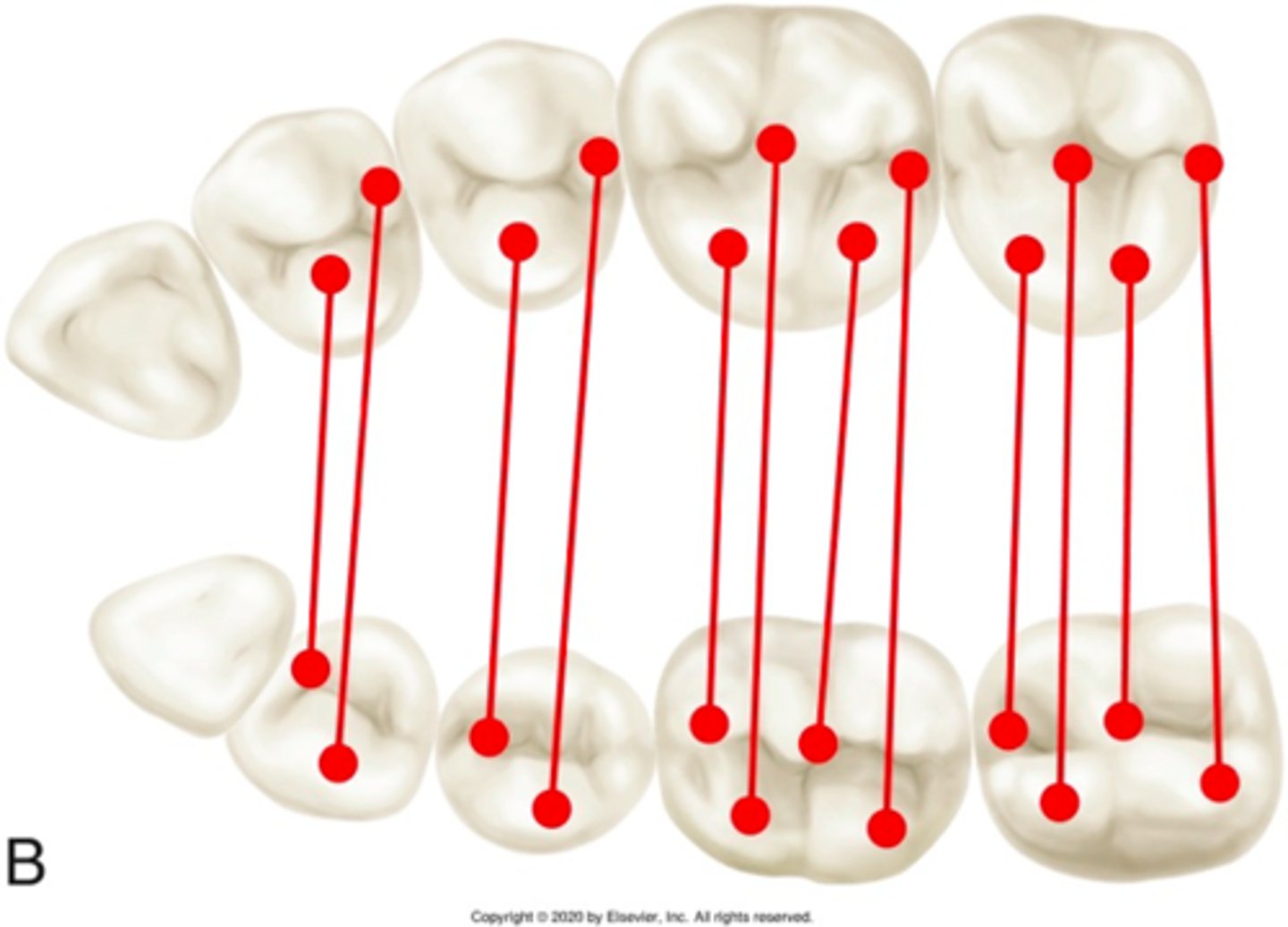
class III
ID the occlusion classification:
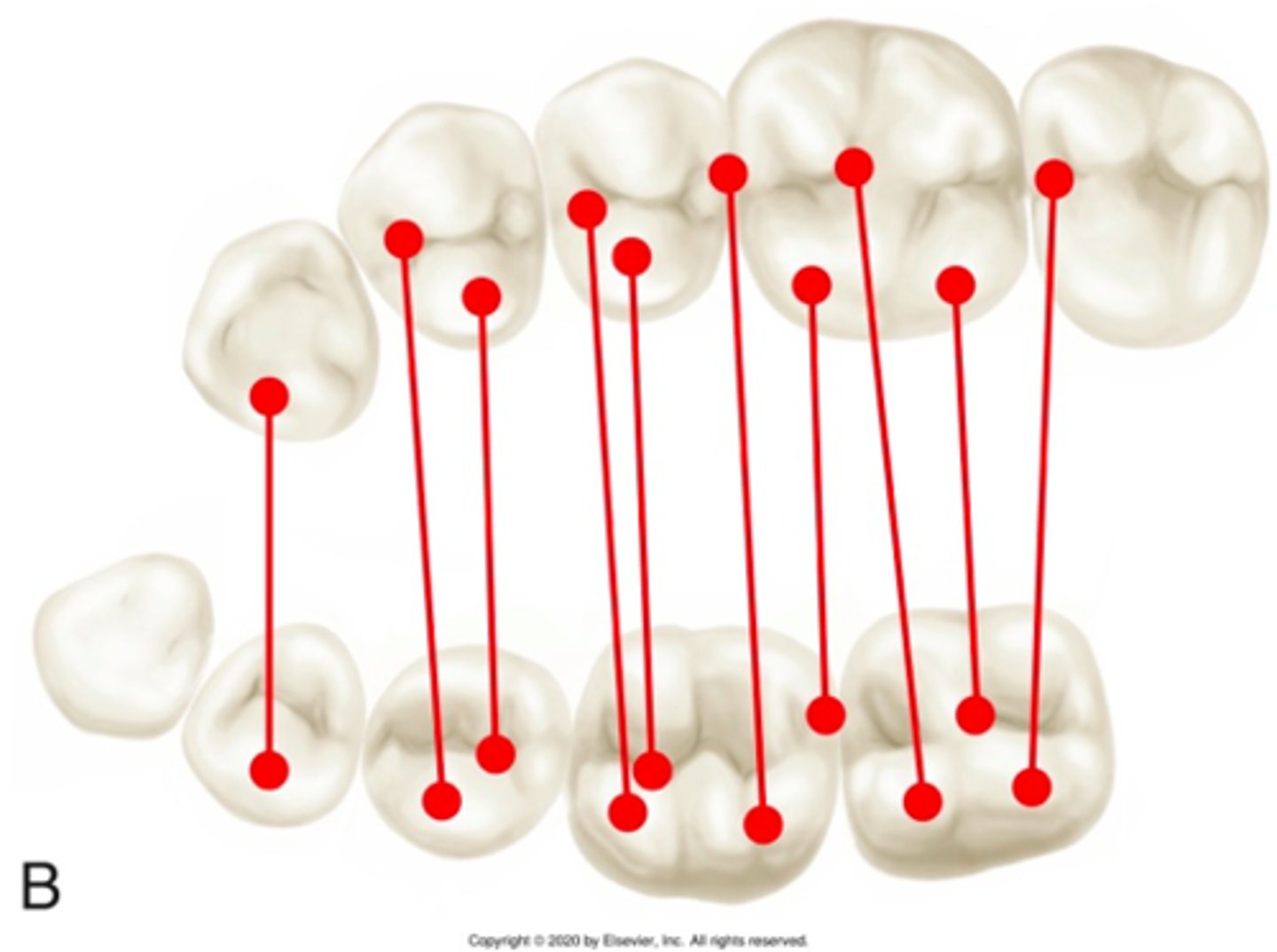

Occlusal plane
Define the following:
A line drawn through all the buccal cusp tips and incisal edges of the mandibular teeth.
Curved plane
Define the following:
Permits maximal utilization of tooth contacts during function.
Rotation and translation (3D activities), normally simultaneously
Which movements are involved in mandibular movement?
TMJ
What structure determines the movements of the mandible?
False
T/F: The maxilla moves during mandibular movement
Rotational movement
Define the type of movement:
- "The process of turning around an axis: movement of a body about its axis."
- Occurs when the mouth opens and closes within the condyles
Hinge axis
Define the type of movement:
- Transverse horizontal axis
- An imaginary line around which the mandible may rotate within the sagittal plane (GPTg)
Protrusive
Laterotrusive
Retrusive
What are the three types of mandibular movements?
Protrusive mandibular movement
Define the type of movement:
Any movement of the mandible from the intercuspal position that results in tooth contact.
laterotrusive movement
ID the mandibular movement:
During lateral movements one side of the arch will move laterally across their opposing teeth and the other side will move medially (towards the midline) across their opposing teeth
Right and left mandibular posterior teeth move across their opposing teeth in different directions
During lateral mandibular movements, how do the right and left mandibular posterior teeth move?
MIP
ID the mandibular movement/position
protrusive movement
ID the mandibular movement/position
laterotrusive movement
ID the mandibular movement/position
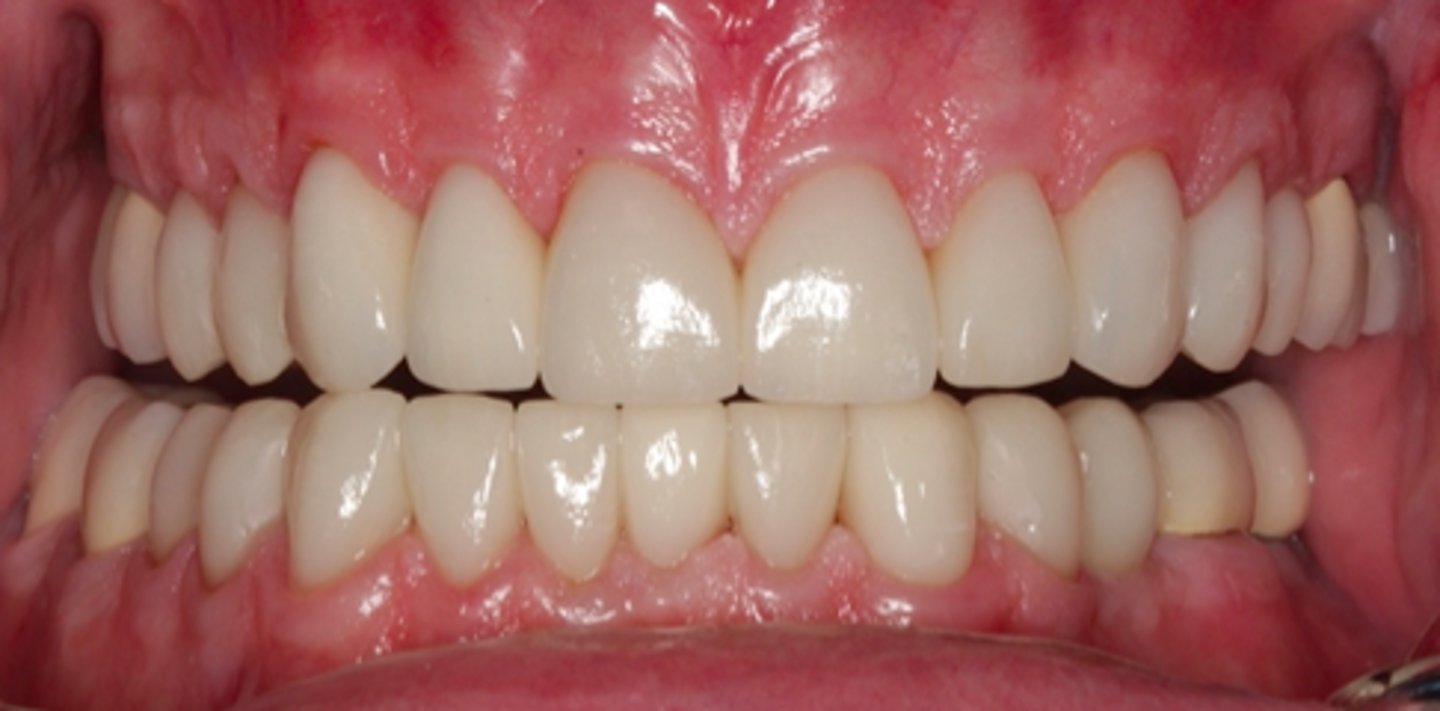
right
in this picture, which side participating in laterotrusive movement?
left
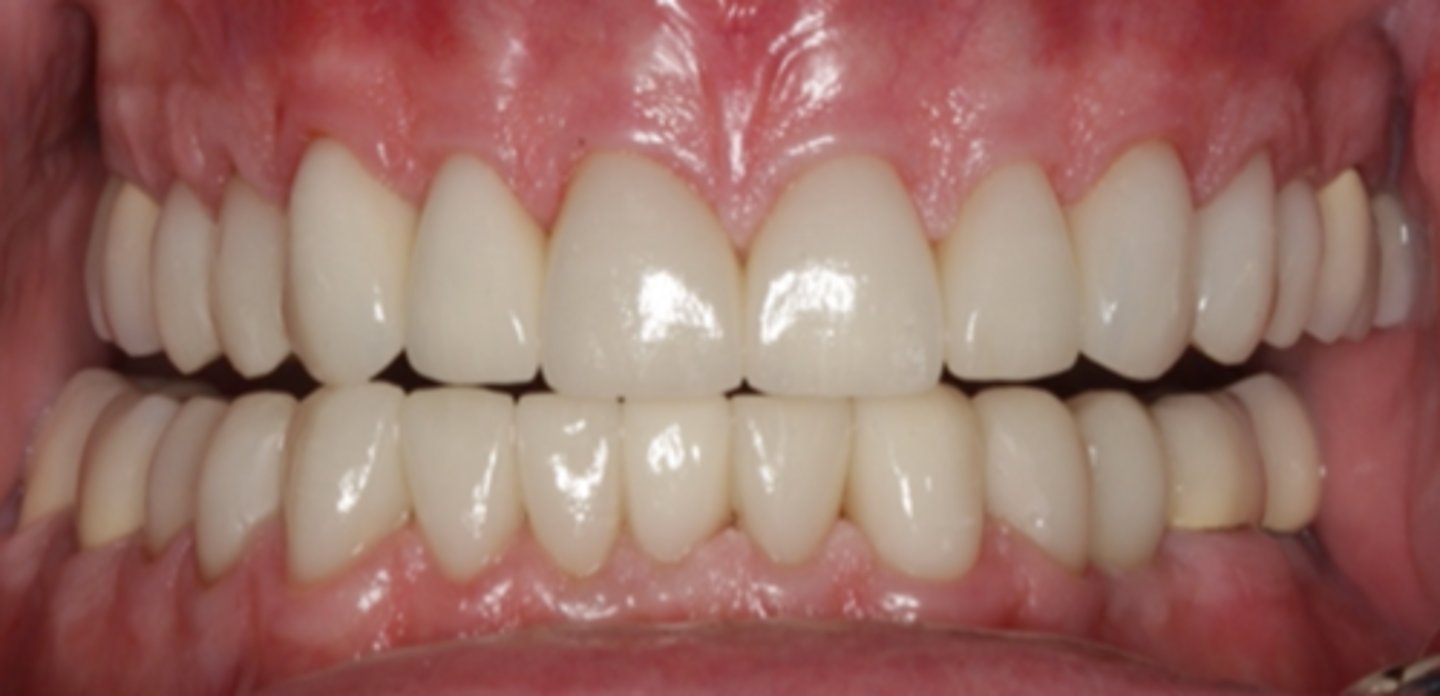
in this picture, which side participating in laterotrusive movement?
protrusive movement
Occurs when the mandible moves forward:
anterior teeth
which teeth predominantly come in contact during mandibular protrusive movement?
protrusive movement
ID the mandibular movement:
The incisal and labial edges of mandibular incisors slide against the lingual areas and incisal edges of the maxillary incisors
laterotrusive movement
canine guidance occurs during what mandibular movement?
This will let you restore a tooth so that it will have contact in MIP and not interfere during lateral movement
What is the importance of understanding cusp pathways?
occlusal interference
Define the following:
Any tooth contact other than the designated cusp pathway during mandibular movement
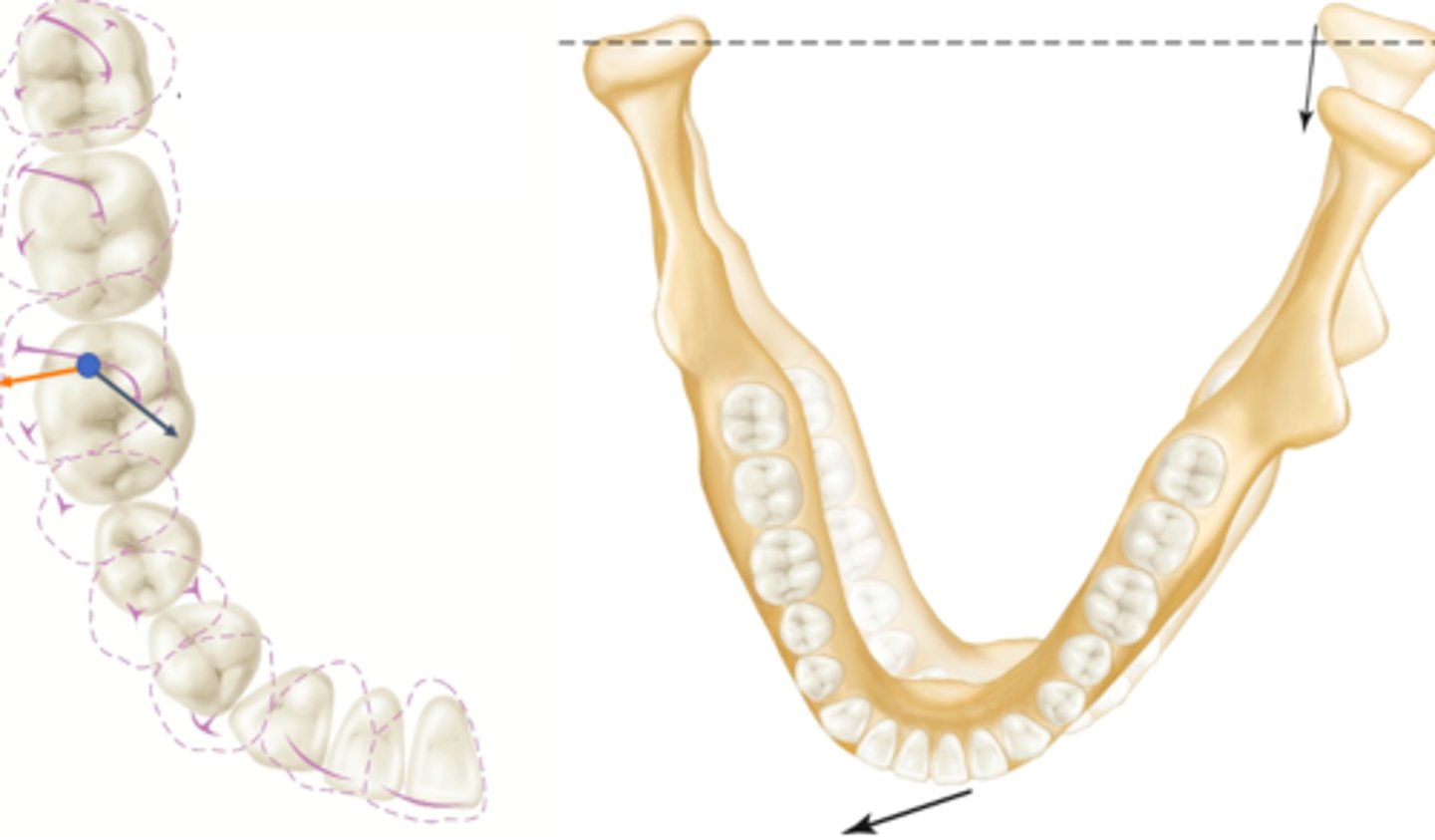
laterotrusive pathway for mandibular teeth
ID the cusp pathway:
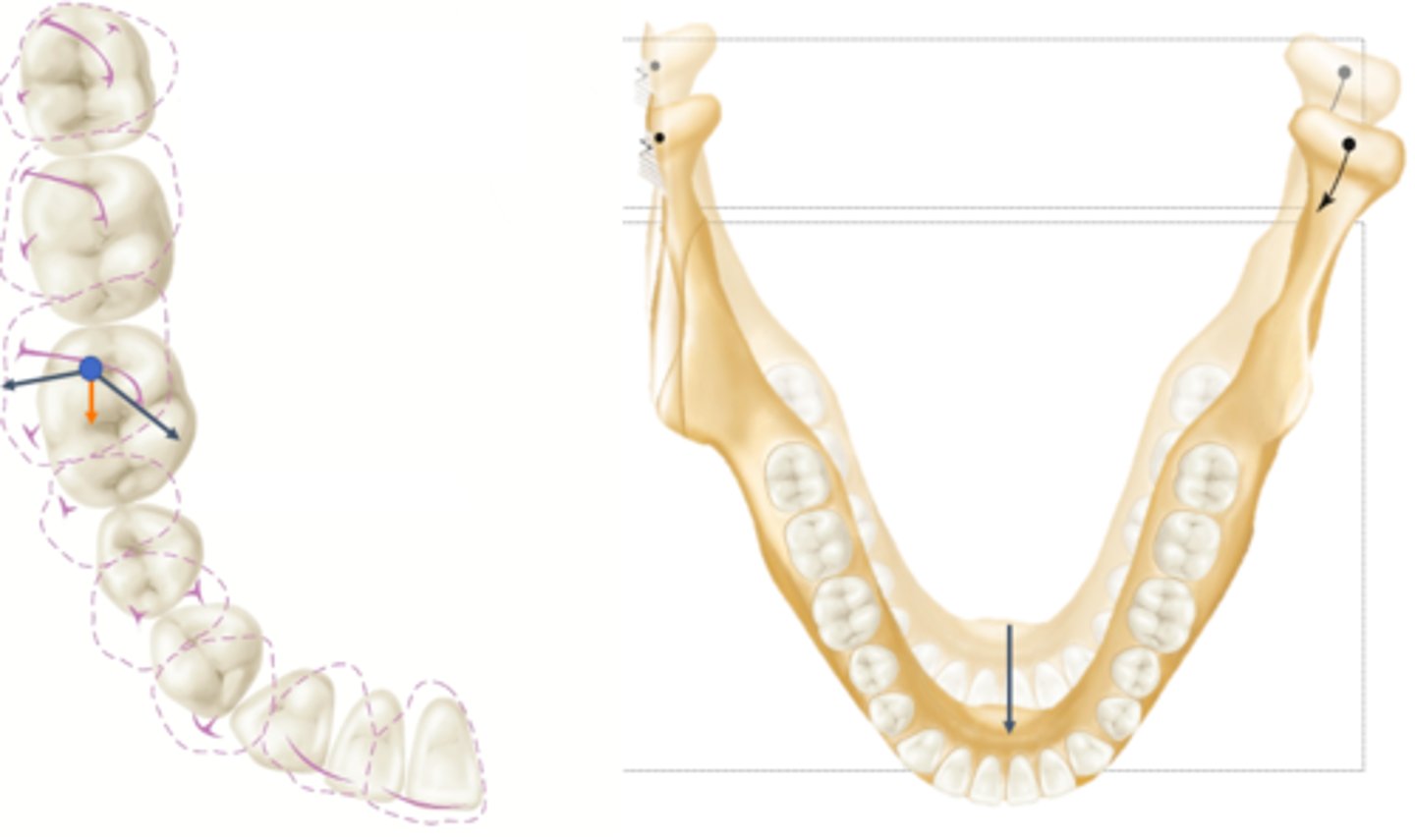
protrusive pathwayor mandibular teeth
ID the cusp pathway:
mandible
during occlusion, which jaw moves, maxilla or mandible?
Where the cusp heights should be and their height
The position and direction of ridges and grooves
When restoring a tooth it is important to know...
Obtain a normal occlusal anatomy, optimal occlusal contacts, and no interferences during eccentric movements
What is the goal when restoring a tooth?
Palatal cusps
What are the functional cusps of maxillary molars?
Buccal cusps
What are the functional cusps of mandibular molars?