Chapter 2: Cells of the Nervous System (All About Neurons)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
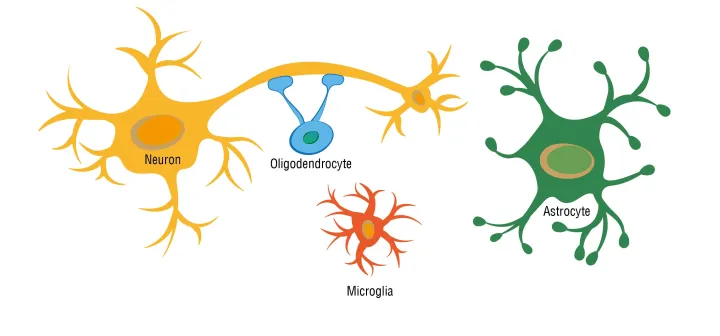
Neurons vs. Glial Cells
____ (the chocolate chips in a cookie)
information processing
senses changes in the environment
communicates and commands
vs.
__ (the dough in a cookie)
glue (holds everything together)
insulation
support
nourishment
housekeeping (gets rid of toxins)
Neurites
= tubes that expand out from the cell body
(general term for either axon or dendrite)
The Neuron Doctrine
“neurons communicate by contact NOT continuity” (Cajal)
= idea that says the nervous system is a bunch of INDIVIDUAL cells talking to each other instead of a single CONTINUOUS web
Cytosol
= Fluid of the cytoplasm, excluding organelles.
inside of the cell
potassium rich
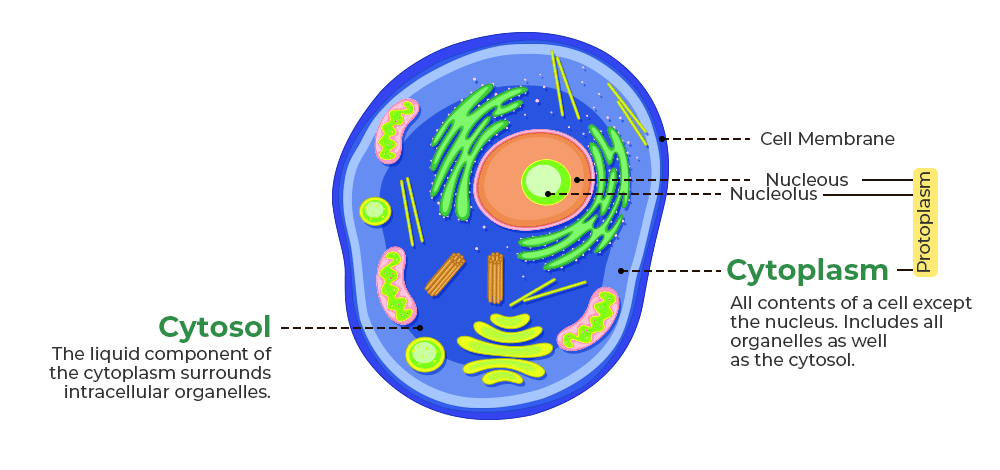
Rough ER
studded with ribosomes
protein synthesis and transport within the cell
the place where RNA bind to ribosomes to begin TRANSLATION into proteins

Smooth ER
functions:
protein folding (prep before send-off)
substance concentration control (ex. calcium)
NO ribosomes on its surface

Mitochondria
produce ATP
especially for maintaining membrane concentration differences
Neuronal Membrane
separates cytoplasm from outside fluid
protein pumps and channels line it (diff. composition depending on which region of the neuron
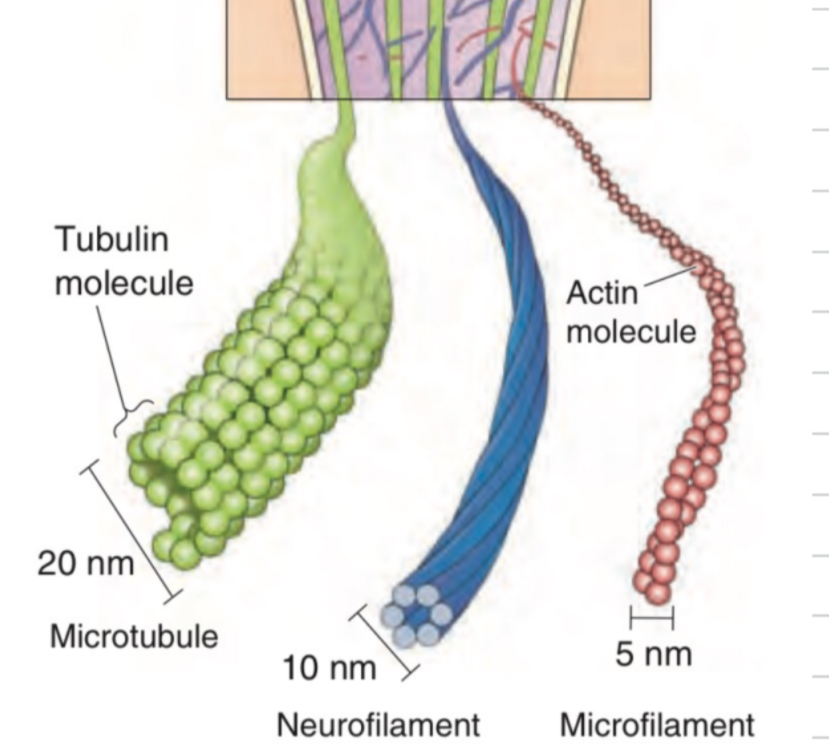
Cytoskeleton
= Network of protein filaments in the cell providing:
structure
cell division,
cell movement and transport
has 3 parts:
Microtubules
Neurofilaments
Microfilaments
Polymerization
= joining of proteins into a strand 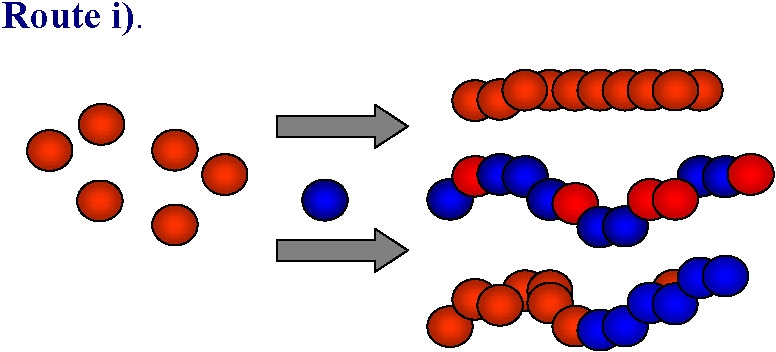
Microtubules
part of the cytoskeleton
Tubulin proteins
20 nm (BIG)
run along neurites (dendrites or axons)
constantly being built/broken down by MAPs (microtubule-associated proteins)
cell division
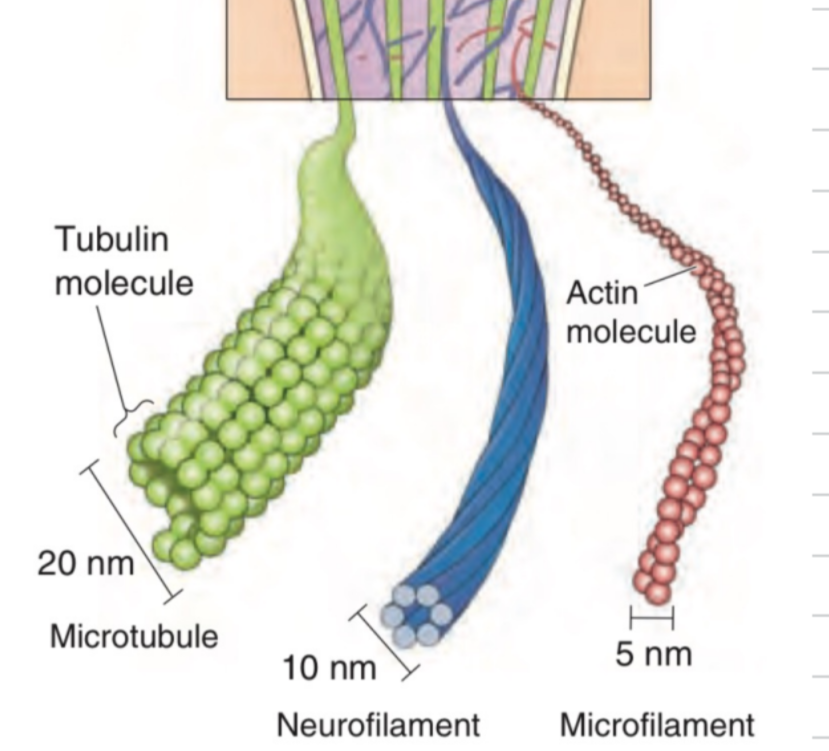
Neurofilaments
part of the cytoskeleton
long proteins in a tight coil
very strong
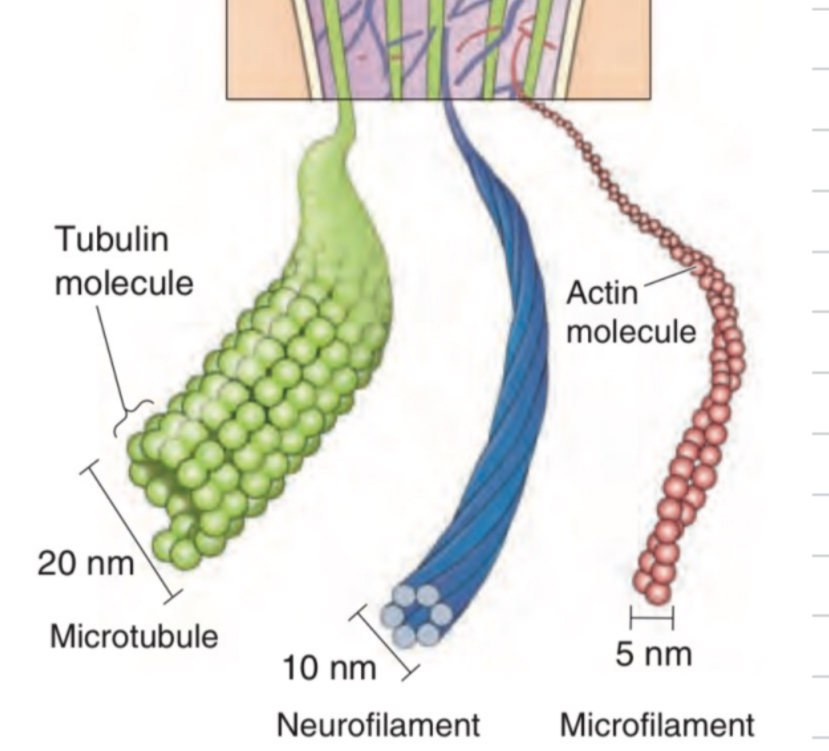
Microfilaments
part of the cytoskeleton
Actin proteins (in braids)
stringlike = more for cell signaling and movement
structure
constantly being built/broken down
Axon
no rough ER (so no protein synthesis)
membrane of this part of the neuron is made up of different protein channels (causes “telegraph wire” or information sending properties)
Innervation
when a neuron makes a synapse at another cell
Special Characteristics of Axon Terminal
microtubules (cytoskeleton) end before it
vesicles
dense proteins near synapse
has a LOT of mitochondria (needs a lot of ATP for the membrane pumps)
Synaptic Transmission
When info passes through the synapse
pre-synaptic (electric impulse) —> neurotransmitters in the synapse (chemical signal) to post-synaptic (electrical impulse)
Axoplasmic Transport
the flow of materials down the axon
since there are no ribosomes in axons or axon terminals, they depend on the soma from protein generation
Wallerian Degeneration
When axons die from being cut off from the soma (axoplasmic transport stopped = flow of material stopped)
Anterograde Transport
when kinesin proteins move material (in vesicles) by “walking” down the axon from soma to axon terminal
Retrograde Transport
When dynein proteins move material back up axon from axon terminal to the soma
Dendrites
Antennae of the neuron
have many receptor proteins to detect neurotransmitters
Dendritic Spines
Bumps on dendrites that receive special input
they recognize specific types or amounts of chemical synaptic activity
Stellate Cell
star shaped neuron
can be spiny or aspinous

Pyramidal Cell
a cell shaped like a pyramid
always spiny

Golgi Type I
classification of neurons by length
= long axons (from brain end to end)
Golgi Type II
classification of neurons by length
= short axons (local circuits)
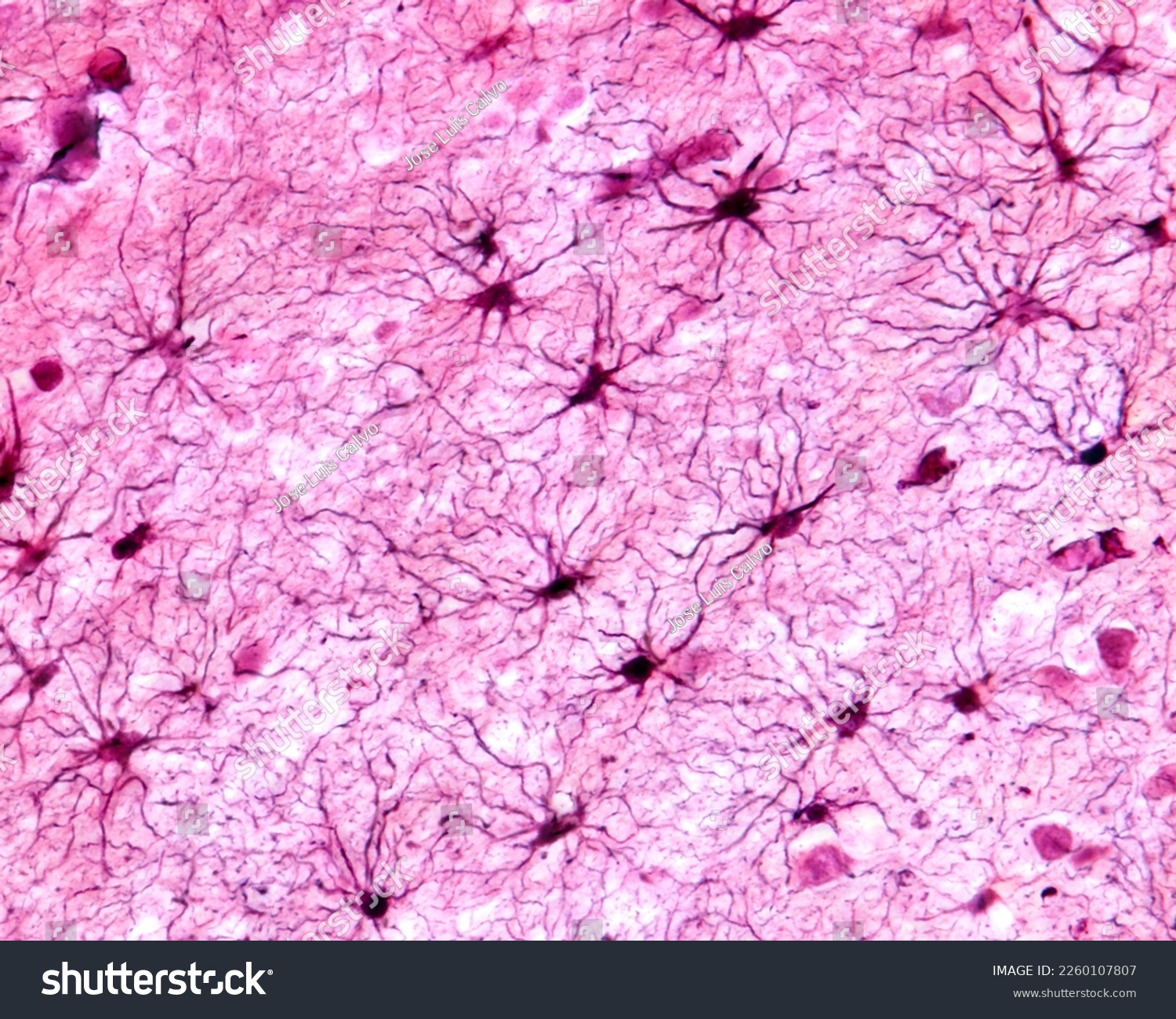
Astrocyte
a type of glial cell that fills space between neurons (influences neurite growth)
majority of CNS neurons
regulates chemicals (like K+ ions)
stops neurotransmitters from spreading beyond synapses (can even remove them from the synaptic cleft)
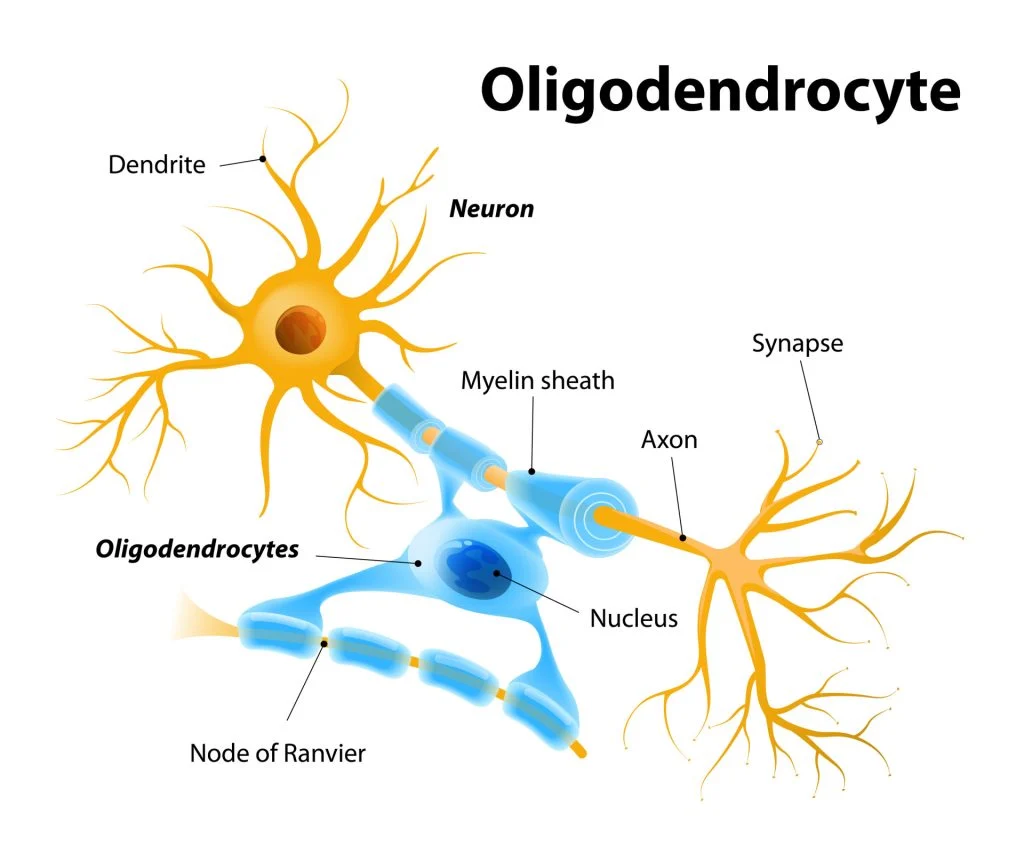
Myelinating Glia
a type of glial cell whose membrane wraps around axons for insulation
Oligodendroglial Cells
a type of myelinating glia
only in CNS
myelinates multiple axons
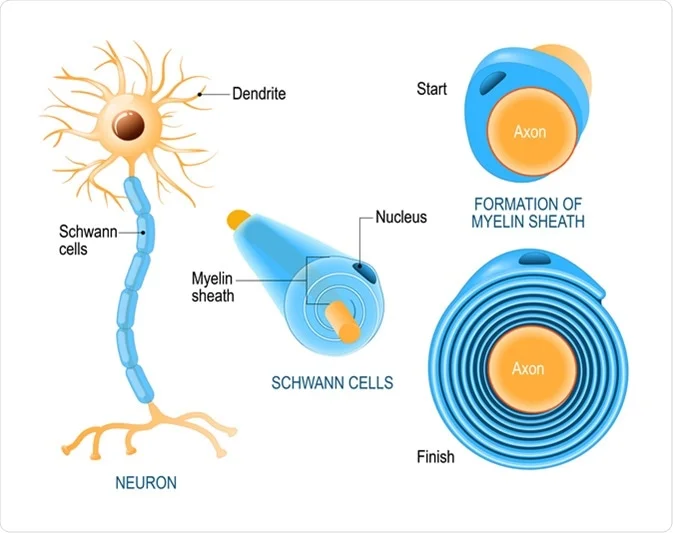
Schwann Cells
a type of myelinating glia
only in PNS
myelinates a single axon
regenerates (especially after a demyelinating disease)
Microglia
a type of glial cell that removes debris/toxins in the brain
“immune cells” of the brain
the “protectors” of the brain