1.1 - 1.3 Monomers + Polymers, Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Monomers
Smaller, repeating molecules/units from which larger molecules (polymers) are made.
Polymers
Molecules made from many identical or similar monomer molecules.
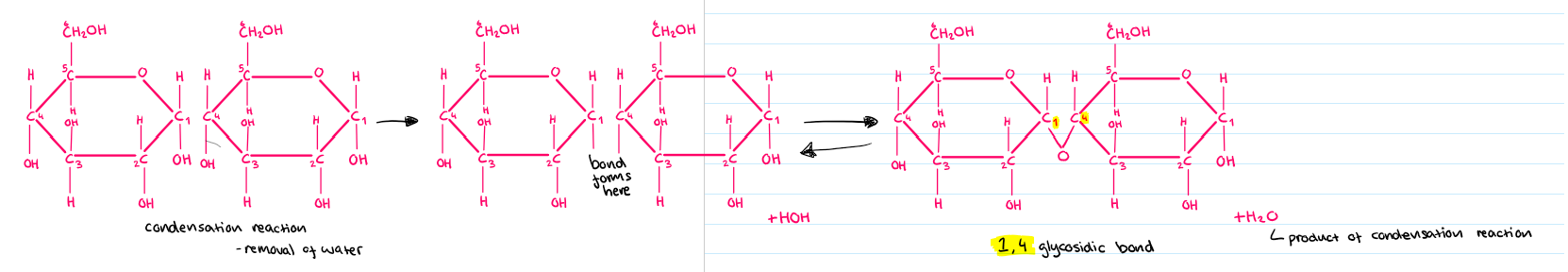
Condensation reaction
A reaction where two molecules join together, forming a chemical bond and releasing a water molecule.
Hydrolysis reaction
A reaction where two molecules are separated, breaking a chemical bond and using a water molecule.
Monosaccharides
The monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made; examples include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
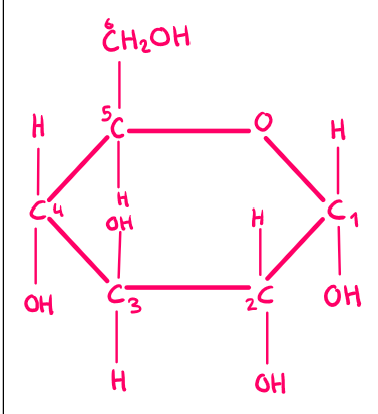
α-glucose
A form of glucose where the OH group is below carbon 1.
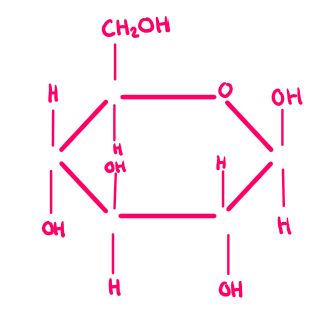
β-glucose
A form of glucose where the OH group is above carbon 1; isomer of α-glucose.
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates formed by the joining of two monosaccharides with a glycosidic bond through a condensation reaction.
Glycosidic bond
A type of bond that connects monosaccharides in disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Polysaccharides
Large carbohydrates formed by many monosaccharides joined together with glycosidic bonds through condensation reactions.
Starch
A polysaccharide of α-glucose that serves as an energy store in plant cells; can be unbranched (amylose) or branched (amylopectin).
Glycogen
A polysaccharide made of α-glucose that serves as an energy store in animal cells; contains both 1,4- and 1,6-glycosidic bonds, making it branched.
Cellulose
An unbranched polysaccharide of β-glucose that provides strength and structural support to plant and algal cell walls. When joined together with other cellulose molecules with hydrogen bonds → is called a microfibril
Has 1,4 glycosidic bonds and hydrogen bonds.
Benedict’s test
A biochemical test for reducing sugars that involves adding Benedict’s solution to a sample and heating it.
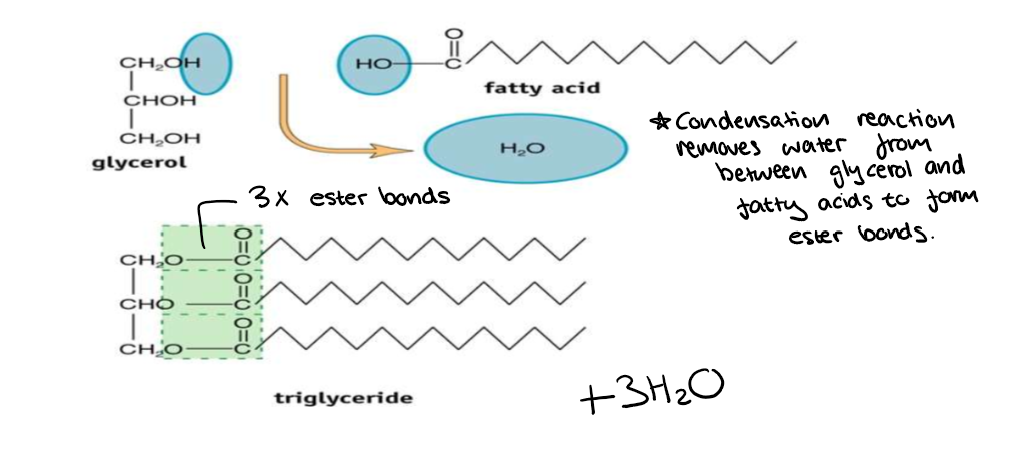
Ester bonds
Bonds formed between glycerol and fatty acids in triglycerides and phospholipids.
Lipid test
A test for lipids that involves adding ethanol to dissolve lipids, followed by water to form a milky white emulsion
What disaccharide is produced with glucose + glucose?
Maltose
What disaccharide is produced with glucose + galactose?
Lactose
What disaccharide is produced with glucose + fructose?
Sucrose
What is used for storage in animals?
Glycogen
What is used for storage in plants?
Starch
Describe the structure of glycogen
A polysaccharide of a-glucose joined by glycosidic bonds
Describe two differences between the structure of a cellulose molecule and a glycogen molecule
Cellulose is made up of B-glucose and glycogen is made up of a-glucose.
Glycogen has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds and cellulose has only 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
Why is starch a good storage molecule for plants?
It is insoluble in water so does not affect water potential.
Branched/ coiled nature makes molecule compact and good for storage.
Large molecule, so cant cross the cell membrane.
Branches ends allow for faster enzyme action and breakdown of starch into glucose for respiration.
What makes glycogen a good storage carbohydrate?
Very branched, so has more strand ends for faster hydrolysis.
Insoluble in water so does not affect osmotic balance of cell.
Compact
Forms a-glucose when hydrolysed and can be used in respiration.
Why do animals store carbohydrate as glycogen rather than starch?
Glycogen has a faster release of glucose for respiration from the additional strand ends (it is more branched than amylopectin).
Animals have a higher metabolic rate so therefore require more glucose for respiration as they need more energy.

How are amylose and amylopectin different?
Amylose has 1,4 glycosidic bonds → Amylopectin has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds.
Amylose is an unbranched polymer of a-glucose → amylopectin is a branched polymer of a-glucose.
Amylopectin
Is branched so that there are more ends for amylase to break down during hydrolysis to release glucose for respiration.
Amylose
Good for storage of glucose in starch due to its few branch ends (unbranched). It is highly compact.
What is formed by the condensation of a-glucose?
Glycogen and Starch
What is formed by the condensation of b-glucose?
Cellulose
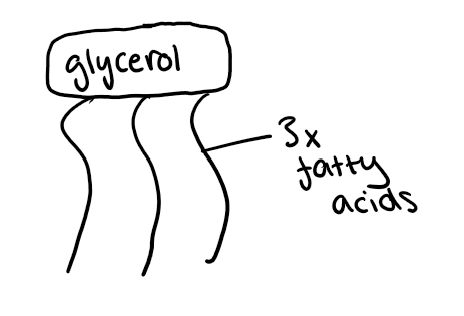
Structure of Triglycerides
Three fatty acids + glycerol
Structure of Phospholipids
Two fatty acids + glycerol + phosphate group
Structure of Steroids
four fused rings
Role of Lipids
long term energy store
lipids release more energy upon complete breakdown than carbohydrates do.
However not easily hydrolysed, so energy is released slowly → slower than carbohydrates.
Insoluble in water → no osmotic effect on cells so wont burst.
Waterproofing because its hydrophobic → repel water (waxy cuticle in plants)
Good heat and electrical insulator (myelin sheath)
Protection (layers around organs, act as shock absorber)
What happens when a triglyceride undergoes a condensation reaction?
Condensation reaction removes water from between glycerol and fatty acids to form ester bonds.
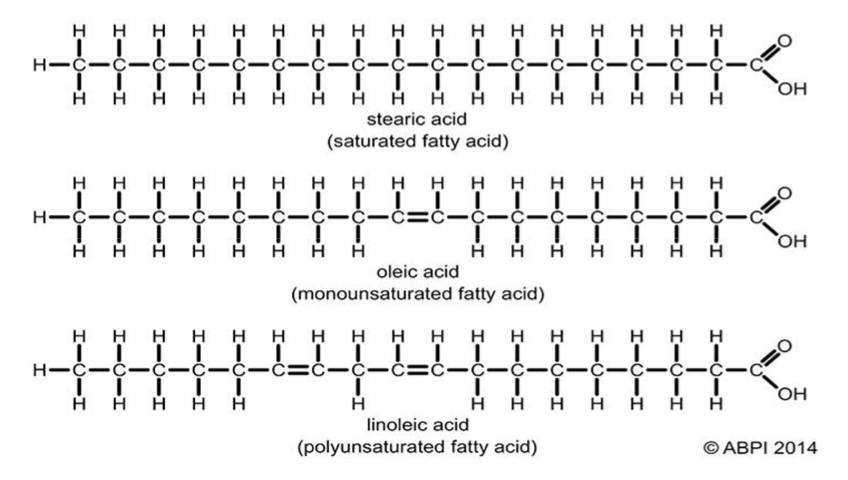
Differences between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated:
- have a maximum number of H atoms
Unsaturated:
- C=C double bonds
- weaker intermolecular bonds due to kinks from double bonds (less compact) → liquid at room temperature (has a lower mp)
What are fatty acids made up of?
Carboxyl group and variable group
Properties of phospholipid
Head is hydrophilic (phosphate group + glycerol) → polar
Tail is hydrophobic (fatty acids) → non polar
Similarities of structure and properties of triglycerides and phospholipids
both have ester bonds between glycerol and fatty acids
they both contain glycerol
both are insoluble in water
fatty acids can both be unsaturated or saturated
Differences of structure and properties of triglycerides and phospholipids
Triglyceride has 3 fatty acids and glycerol but Phospholipid has 2 fatty acids, glycerol and a phosphate group.
Phospholipids form monolayer on surface and triglycerides dont.
Triglycerides are hydrophobic/ non-polar and phospholipids have hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.