Audition and Touch Quiz
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Mechanoreceptors
Type of receptors our ears are
Mechanoreceptor
A sensory neuron that responds to mechanical stimuli; usually produce pressure, stretch, or vibration
Amplitude
Loudness
Frequency
Pitch
Pinna
Functions to funnel sound
Ear canal
Transport waves to tympanic membrane
Semicircular canal
Gives us our sense of balance
Endolynph
Thick viscous fluid in the ear
Cochlea
The snail shaped structure of the inner ear that contains the auditory transducing mechanisms
Base for tectorial membrane
Basilar membrane
Tonotopic organization
Base: High frequency; Higher: Low frequency
Auditory pathway
Auditory nerve→Cochlear nucleus→Superior olivary nuclei→Inferior colliculi→Medial geniculate nucleus→Auditory cortex
Organization of auditory cortex
High frequency: Medial; Low frequency: Lateral
Auditory association cortex
Where sound goes once it reaches auditory cortex
Organization of auditory association cortex
Anterior deals with complex sounds, Posterior deals with sound localization
Pitch
A perceptual dimension of sound; corresponds to the fundamental frequency
Loudness
A perceptual dimension of sound; corresponds to intensity
Tympanic membrane
The ear drum
Ossicle
One of three bones of the middle ear
Malleus
Hammer - the first of three ossicles
Incus
The anvil - second of three ossicles
Stapes
The stirrup - third of three ossicles
Oval window
An opening in the bone surrounding the cochlea that reveals a membrane which the stapes bangs against sending fluid vibrations
Hair cell
Receptive cell of the auditory apparatus
Basilar membrane
A membrane in the cohclea of the inner ear
Core region
Primary auditory cortex located on a gyrus on the dorsal surface of the temporal lobe
Belt region
The first level of auditory association cortex; surrounds the primary auditory cortex
Parabelt region
Second level of auditory association cortex; surrounds the belt region
Cochlear implant
An electronic device surgically implanted in the inner ear that can stimulate the basilar membrane
Two sensations of touch
Nociception and Thermoception
Nociception
The body's physiological process of detecting and converting noxious stimuli into a neural signal, which may or may not lead to the conscious experience of pain
Thermoception
is the sense of heat and cold, which allows organisms to perceive temperature and react accordingly
Meissners corpuscle
Fast acting
Perception of motion across skin
Fine texture by moving fingers
Small receptive field
Merkel’s disk
Slow acting
Perception of motion across the skin
Handgrip control
Small receptive field
Ruffini’s corpuscle
Slow acting
Perception of skin stretch
Large receptive field
Pacinian corpuscle
Fast acting
Perception of fine details
Texture and shape perception
Large receptive field
Pathways to the brain
Fine touch/vibration and Pain & Temperature
Fine touch and vibration pathway
Dorsal column of spinal cord, medulla, medial lemniscus, ventral posterior nuclei of thalamus, primary somatosensory cortex
Pain and temperature pathway
Dorsal column of spinal cord, spinothalamic tract, ventral posterior nuclei of thalamus, primary somatosensory cortex
Phantom limb pain
The perception of pain in a limb that is no longer present and is common after an amputation
Phantom limb pain cause
Brain and spinal cord rewire after an amputation
2PD Discrimination
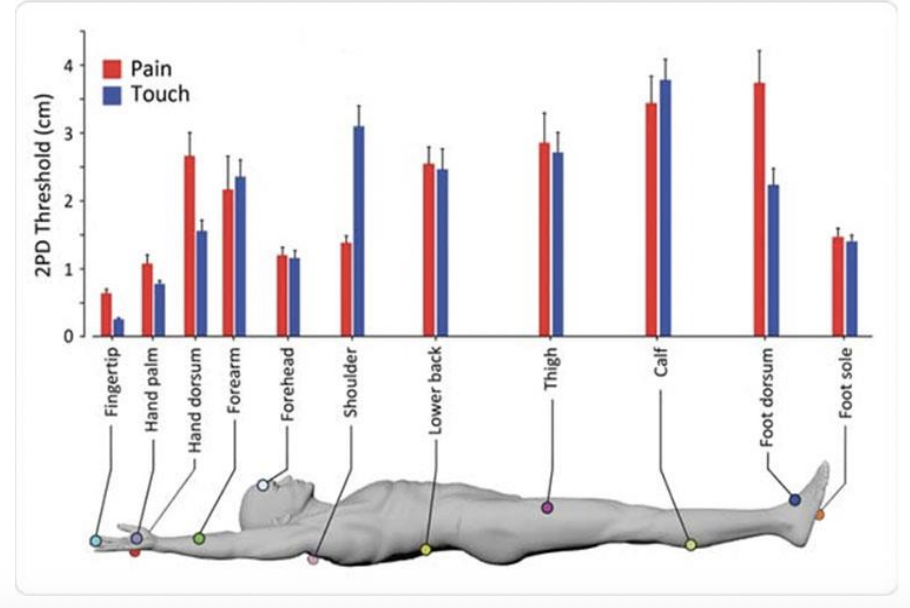
Sensory homunculus
A visual map of the body that represents how sensory input is processed in the brain’s somatosensory cortex
Binaural differences
Hearing between both ears
Duplex theory
Interaural timing differences (ILD) and interaural level differences (ILD)
Posterior semicircular canal
Head tilt
Lateral semicircular canal
Horizontal
Anterior semicircular canal
Vertical
Ampullae
Base of each canal
Otolithic organ function
Gives us sensation for lateral head movement
Composition of otolithic organs
Made up of utricles and saccules