Comprehensive Anatomy & Physiology: Body Structures, Homeostasis, and Medical Terminology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of organisms.
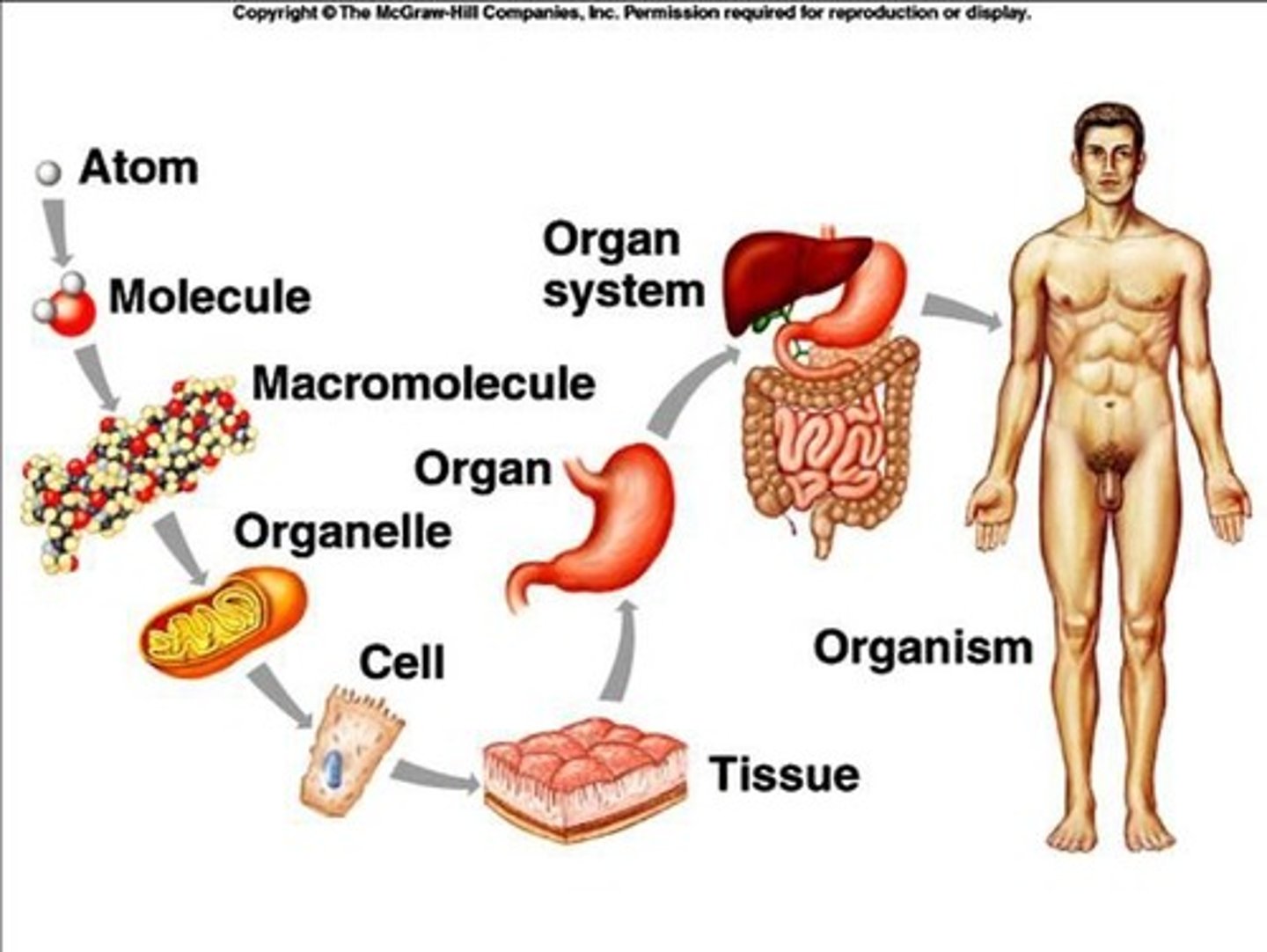
Physiology
The study of the functions of living organisms and their parts.
Homeostasis
A stable internal environment maintained by physiological systems.
Cell
The smallest unit of an organism capable of performing all of the basic functions of life.
Tissue
A mass of similar cells and extracellular matrix forming a discrete region of an organ and performing a specific function.
Organ
A structure composed of 2 or more tissue types working together to carry out a particular function.
Organ system
A group of organs with a unique collective function, such as circulation, respiration, digestion.
Gross anatomy
The study of structures that can be seen with the unaided eye.
Microscopic anatomy
The study of structures requiring a microscope to view.
Cytology
The study of cells.
Histology
The study of tissues.
Epithelial tissue
One of the four principal tissue types that covers body surfaces and lines cavities.
Nervous tissue
One of the four principal tissue types that transmits impulses and processes information.
Connective tissue
One of the four principal tissue types that supports and binds other tissues.
Muscle tissue
One of the four principal tissue types that is responsible for movement.
Autoregulation
Automatic response by a cell, tissue, organ or organ system to a change in its environment.
Extrinsic regulation
Regulation by the nervous or endocrine system.
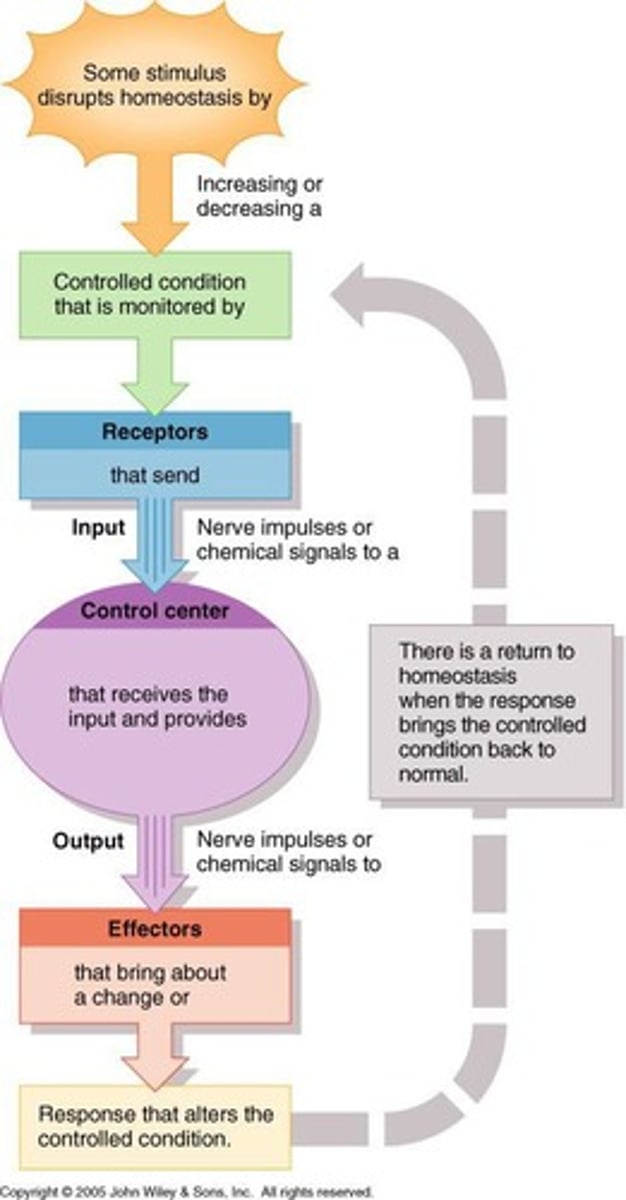
Negative feedback
A stimulus is producing a response that opposes the original stimulus.
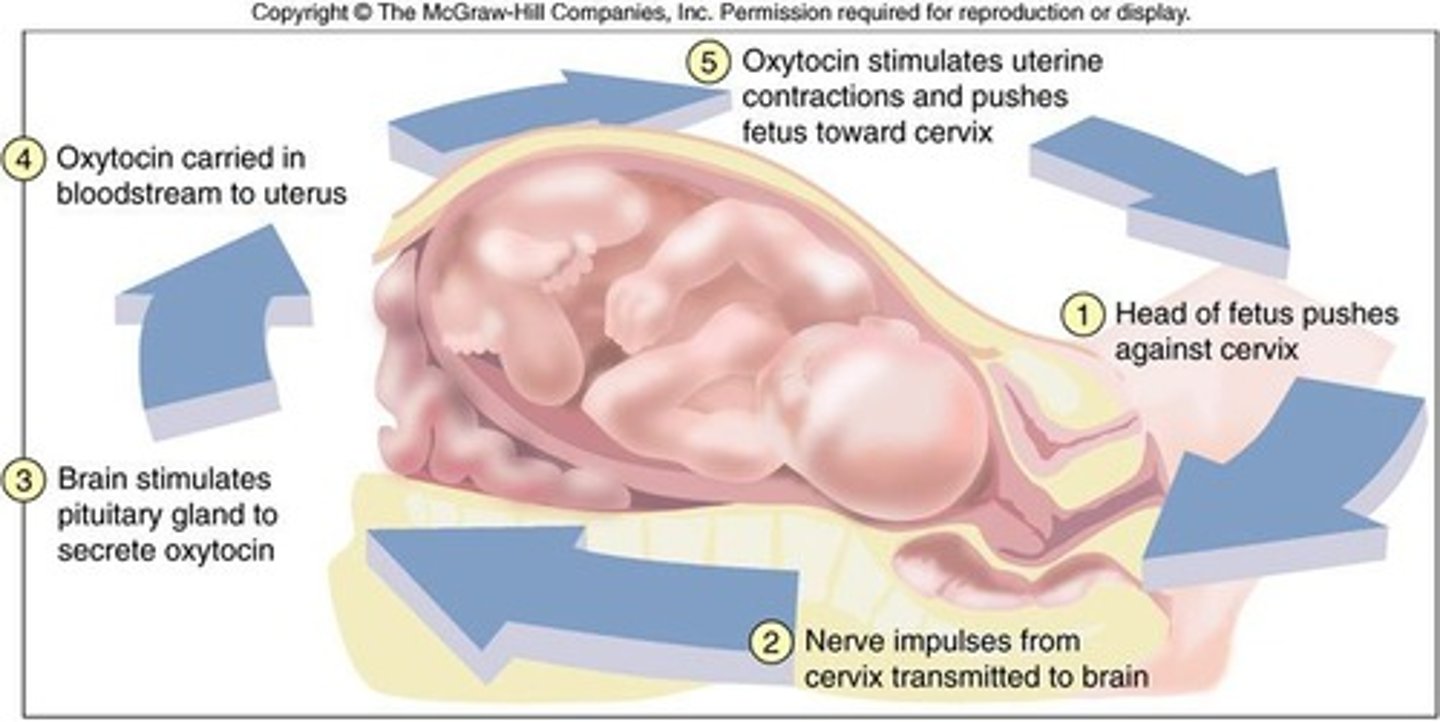
Positive feedback
An escalating cycle that reinforces the initial stimulus instead of opposing it.
Integrating center
A control center able to process and communicate.
Effectors
A cell or organ able to respond to the control center and effect some change.
Receptors
A sensor able to perceive a stimulus or change.
Positive feedback loop
Parturition.
Supine position
Lying on the back.
Prone position
Lying on the stomach.
What happens when the body fails to maintain homeostasis?
Death
Why is positive feedback helpful in blood clotting?
Positive feedback is suitable because without it bleeding would not stop.
Why is the anatomical position important?
Provides a standard and precise frame of reference, ulna and radius are uncrossed
Anterior
toward the front of the body
Posterior
toward the back of the body
Medial
toward the midline of the body
Lateral
away from the midline of the body
Superior
closer to the top of the body
Inferior
closer to the bottom of the body
Proximal
situated closer to the point of origin or attachment
Distal
situated away from the point of origin or attachment
Superficial
closer to the body surface
Deep
further within the body
Ipsilateral
on the same side
Contralateral
on the opposite side
Planes
frontal, sagittal, transverse
Sagittal Plane
results in left and right portions
midsagittal plane
results in exact right and left portions
Frontal Plane
also called coronal plane, results in anterior and posterior portions
Transverse Plane
also called transaxial or horizontal plane, results in inferior and superior portions
Serous membranes
membranes that secrete a lubricating film of fluid similar in composition to blood serum
Peritoneum
the membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity
Greater omentum
a fatty fold of the peritoneum that hangs like an apron from the inferior anterior margin of the stomach
Mesentery
a double layer of peritoneum that suspends the intestines from the dorsal abdominal wall and supplies them with blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.