Material science 1
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcard Deck: Materials Science Exam Review (Based on Callister 10th ANZ Edition)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
What is the difference between an atomic structure and a crystal structure?
Atomic structure describes the arrangement of particles inside a single atom where as in an crystal structure the multiple atoms are ordered together in a neat geometric pattern.
Chapter 3: Structure of Crystalline Solids (3.1-3.15)
-
What is a crystal structure?
The manner in which atoms, ions , or molecules are spatially arranged in a crystalline material.
What is the coordination number?
the number nearest neighbour atoms/ions that surround the central atom
What is the formula for unit cell length BCC?
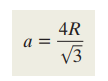
What is the formula for unit cell length FCC?
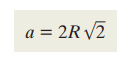
Unit cell volume FFC
Vc=a3
What are the three common crystal structures and the amount of atoms in them?
FCC (Face centered Cubic)
Atoms per unit cell = 4BCC (Body Centered Cubic)
Atoms per unit cell = 2HCP (Hexagonal Close-packed)
Atoms per unit cell = 6
Volume unit cell HCP
a = unit cell length
c = unti cell height
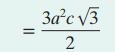
What is the most efficient crystal structure?
FCC
Difference between crystal system and crystal structure?
Crystal system refers to unit cell geometry; crystal structure includes lattice type and atomic positions
What is the formula for Atomic Packing Factor (APF?)

What is a unit cell?
The smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice.Wha
What is polymorphism?
The ability of a material to exist in more than one crystal structure.
Unit cell length HCP
a = 2R
What is anisotropy?
Directional dependence of properties.W
What is the miller index?
A notation to describe crystal planes and directions.
Chapter 12: Structure & Properties of Ceramics
-
What is the coordination number in ceramic structures dependent on?
The ratio of cation to anion radii.Wh
What is a glass?
An amorphous non-crystalline solid.
What is a defect structure?
The arrangement and concentration of point defects in ceramics.W
Why are ceramics brittle?
Because of strong ionic/covalent bonds that restrict dislocation motion.
What is a frenkel defect?
a type of point defect where a cation leaves its regular position and takes a intersitial position
What are shottky defects?
A type of point defect where equal amounts of cations and anions are missing from the crystal lattice, mainting electrical neutrality.
Ns=N*exp(-Qv/2kT)
Why are ceramics unable to cunduct electricity?
Ceramics are unable to conduct electricity because of their structure. The strong covalent/ionic bonds do not allow free electron movement thus leading to no current.
Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids
-
What are the 4 main types of crystal imperfections?
Point defects
Line defects
Interfacial defects
Bulk defects
What is a vacancy?
A missing atom in a lattice site
What is a self interstitial?
An atom positioned in the interstitial siter of its own lattice.Wha
What is a dislocation?
A linear defect around which some atoms are misaligned
WHat are the types of dislocations?
Edge dislocation
Screw dislocation
Mixed dislocation
Define what a edge dislocation is
It is a linear defect where an extra half plane of atoms is inserted into the lattice distorting the structure of the lattice
Define what a screw dislocation is
It is a disloaction formed by shear stress where the lattice is shifted in two opposite directions
What is a grain boundary?
An interfacial defect between two grains of different orientation.
Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties of Metals
-
What is stress?
Force applied per unit are (Pa)
What is shear stress?
The stress caused by parralell motion
What is strain?
Deformation per unit length
Explain tensile strength
It is the ability to withstand plastic deformation and determines when necking occurs
Explain plastic deformation
Plastic deformation is the permanent deformation caused by stress
Explain the stress-strain relation ship and each region a metrial undergoes
The stress-strain relationship describes how a material deforms under applied stress and is usually shown by a stress strain curve.
The stages of deformation with increasing stress are:
The Elastic region
Here the material elastically deforms, stress and strain are proportional (Hookes Law applies here)Plastic region
In this region the material can no longer withstand the stress applied to it and starts to permanently plastically deform.Necking region
After reaching the limit of plastic deformation the material starts thinning out (Think of an elastic band)The cross-sectional area reduces and deformation is focussed in one spot ‘‘neck’’
Fracture
The material breaks
What is youngs modulus?
Ratio of stress to strain in the elastic region
What is yield strength?
The stress at which plastic deformation begins.
What is tensile strength
Maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched.
What is ductility?
The percent elongation of a material under stress.
What is toughness?
The ability to absorb energy up to fracture
Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms
-
What is slip?
Plastic deformation by dislocation motion
What are common strengthening mechanisms?
Grain size reduction
Solid solution strengthening
Strain hardening
Precipitation hardening
What is strain hardening?
Increase ins trength due to plastic deformation
What is the Hall-Petch relationship?
Where strength increases with decreasing grain size.
Chapter 8: Failure
-
What is fatigue?
Failure under cyclic stress.
What is creep?
Time-Dependent deformation under constant stress
Waht is fracture toughness
Resistance to fracture when a crack is present
What are the three stages of creep strain
primary creep
secondary creep
terrtiary creep
What is brittle fracture?
The sudden fracture with little or no plastic deformation
Chapter 9: Phase Diagrams
-
Define what a binary isomorphous system is and draw its phase diagram
when there is complete liquid and solid solubility
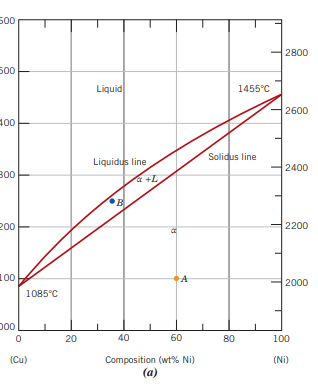
What is a phase diagram?
A map showing phase stability as a function of temperature and composition
In a phase diagram, alpha, L and alpha + L regions are used, what are they?
The alpha region represents a solid solution phase. The L region shows the liquid phase. Alpha + L means coexistence.
Formula for mass fraction liquid phase
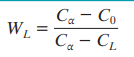
What is the eutectic point?
The lowest temperature at which liquid can coexist with two solids.
What is a eutectoid transformation?
A transformation into two phases, eg austenite into cementite and pearlite
What is the lever rule.
A method used to calculate phase fractionsWha
What is solid solubility?
The extent to which one solid dissolves in another
What are the main microstructures of iron-carbon alloys?
Ferrite
Austenite
Cementite
Pearlite
Bainite
Martensite
What is ferrite?
Soft ductile Fe-C alloy with BCC structureWh
What is austenite?
High tougness FCC structure Fe-C alloy
What is cementite?
Hard brittle Fe-C structure, high in Carbon wt%
What is pearlite?
A eutectoid mixture of alternating layers of ferrite and cememtite
medium strength medium ductility
What is bainite?
Fine mix ferrite and cementite, forms at lower temps
What is martensite?
Highest strength structure
Formula for mass fractio alpha phase
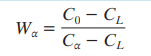
How does cooling rate affect microstructure?
Rapid cooling → Fine microstructure , higher strength
Slow cooling → Coarse microstructure, lower strength
Sort microstructures by strength
Martensite
Bainite
Pearlite
Ferrite
Chapter 10: Phase Transformations
-
What is nucleation?
The initial formation of a new phaseW
What is the difference between Homo- and Hetero genous nucleation?
Homogenous nucleation refers to a nuceli forming anywhere while heterogenous nucleation refers to a nuclei forming at defects or grain bounderies
What is growth?
The increase in size of a new phaseW
What is the critical free energy G* and its formula?
The energy barrier that must be overcome for a nucleus of size r* to grow
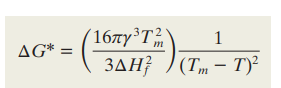
What is the TTT diagram?
Time Temperature Transformation diagram for phase changes
What are the main phases of iron ?
Austenite
High tempFerrite
Room temp up to 900 celsiusCementite
Pearlite
Martensite
Bainite
Chapter 14: Polymer Structures
-
What are the types of polymer structures?
Linear
Branched
Crosslinked
Networked
What are the 3 classifications polymers fall under when it comes to stress strain behaviour?
Brittle
Plastic
Highly elastic
What is tacticity?
Arrangement of side groups in a polymer chain
What is crazing?
Crazing is the formation of microvoids and fine thread like fibrils under stress. These fibrils bridge the gap between voids and create a reenforcement.
What is injection molding?
A process where molten polymer is injected into a moldWh
What are thermoplastics
Polymers that can be reheated and reshapedW
What are thermosets
Polymers that harden permanently when heated
Chapter 21: Optical Properties & Liquid Crystals
-
What is birefringence?
Property of having different refractive indices for different light polarizations
What is transmittance?
Fraction of incident light that passes through a material
What is a nematic liquid crystal?
These are molecules that are both liquid and solid and inbetween. They are aligned in the same direction without long-range positional order
What is fluorescence
Immediate emission of light after absorption Wha
What is phosphorescence
Delayed light emission due to trapping in metastable states
How does band gap affect optical properties?
Larger gaps mean transperent in visible. Smaller gaps mean visible light gets absorbed
What is photoconductivity’?
This is the increase in electrical conductivity due to light exposure