Transport in Cells
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is diffusion?
The net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration down a concentration gradient.
Does diffusion require energy?
No, it is a passive process.
What three main factors affect the rate of diffusion?
Concentration gradient, Temperature, Surface area
How does surface area affect the rate of diffusion?
The larger the surface area, the quicker the rate of diffusion.
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
The higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy the particles will have, so the rate of diffusion is quicker.
How does a concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
The steeper the concentration gradient the quicker the rate of diffusion.
__________ diffuses into the blood from the lungs, down a __________ gradient.
Oxygen, concentration
________ ________ diffuses into the lungs from the blood, down a concentration _________.
Carbon dioxide, gradient
Give an example of a substance transported by diffusion in the kidney.
Urea diffuses from cells into blood plasma so it can be excreted in urine.
How are single-celled organisms adapted for diffusion?
They have a large surface area to volume ratio which maximises the rate of diffusion of molecules to meet the organism’s needs.
How is surface area to volume ratio calculated?
Surface Area = Number of Sides × (Side Length × Side Width)
Volume = Length × Width × Depth
Ratio = Surface Area:Volume
What four factors increase the effectiveness of a gas exchange surface?
Large surface area
Thin membrane (short diffusion distance)
Efficient blood supply (animals)
Ventilation (animals)
What is osmosis?
The net movement of water from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration through a partially permeable membrane, down a concentration gradient.
Does osmosis require energy?
No, it is a passive process.
What is meant when a solution is isotonic to a cell?
The water concentration inside the cell is the same as the water concentration outside the cell.
What is meant when a solution is hypertonic to a cell?
The water concentration inside the cell is higher than the water concentration outside the cell.
What is meant when a solution is hypotonic to a cell?
The water concentration inside the cell is lower than the water concentration outside the cell.
What may happen when an animal cell is placed in a very hypotonic solution?
Water moves into the cell by osmosis and the cell will burst.
What may happen when an animal cell is placed in a very hypertonic solution?
Water moves out of the cell by osmosis ans the cell will shrivel up.
How do plant leaves and stems remain rigid?
Turgor pressure.
Turgor pressure: Water moves in by _______, causing the ______ to swell and the cytoplasm to press against the ____ ____.
osmosis, vacuole, cell wall
A plant cell is placed into a hypertonic solution, complete the sentence:
Water moves out of the cell by _______ and the vacuole and _______ decrease in size. The cell membrane may pull away from the ____ ____, causing the cell to become __________.
osmosis, cytoplasm, cell wall, plasmolysed
A plant cell is placed into a hypotonic solution, complete the sentence:
Water moves into the cell by _______ and the ________ and cytoplasm increase in size. The cell membrane may push up against the ____ ____, causing the cell to become __________.
osmosis, vacuole, cell wall, turgid
What is active transport?
The movement of substances from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution against a concentration gradient.
Does active transport require energy?
Yes, it requires energy from respiration
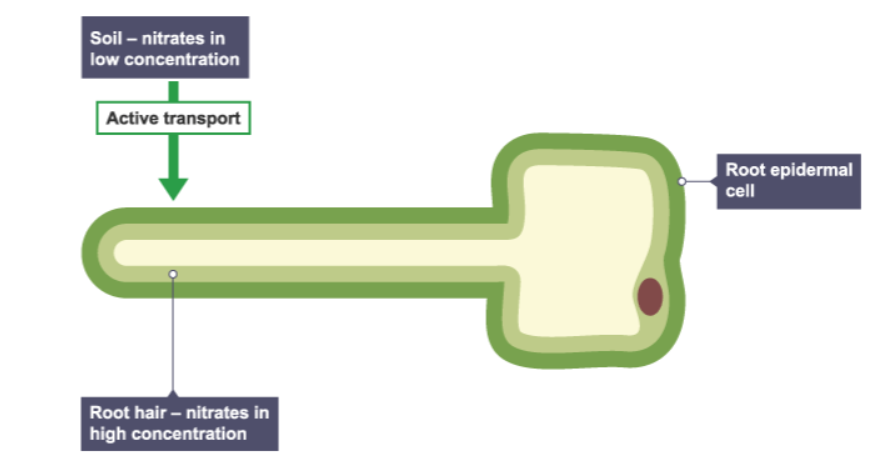
How do plant root hair cells use active transport?
Root hair cells use active transport to take up mineral ions from the soil.
Ions such as _________ and ________ are required for healthy growth in plants.
magnesium, nitrates
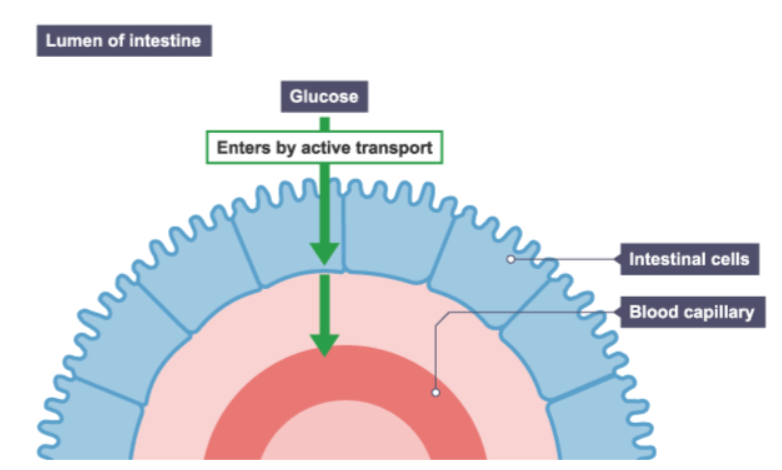
Active transport used to absorb the products of digestion. Complete the sentence:
Active transport is used to transport glucose from a ______ concentration in the ___ to a ______ concentration in the _____.
lower, gut, higher, blood
Glucose is transported to the tissues where it can be used in ___________.
respiration
Substances moved by diffusion: ______ _______, oxygen, _____ , food substances, wastes, eg ____
Carbon dioxide, water, urea
hat substance is moved by osmosis?
Water
Substances moved by active transport: ________ ____ into plant _____, _______ from the ___ into intestinal cells, from where it moves into the ______.
Mineral ions, roots, glucose, gut, blood
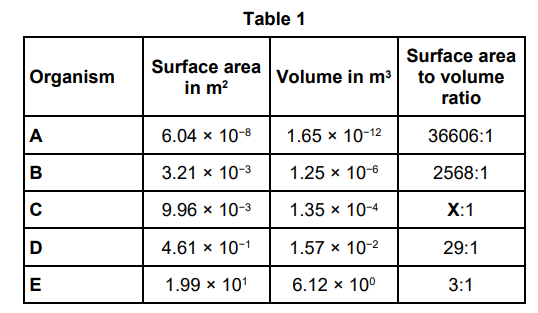
Table 1 shows information about five different organisms. Calculate value X in Table 1. Give your answer to the nearest whole number.
74
What is the relationship between the size of an organism and its surface area to volume ratio? Use Table 1.
As the size of an organism increases the surface area to volume ratio decreases.
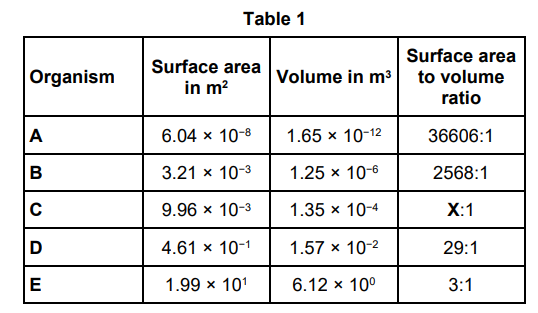
Organism B exchanges gases with the environment directly through its skin. Organism D exchanges gases with the environment using its respiratory system. Explain why organism D requires a respiratory system, but organism B does not require a respiratory system.
D has a smaller surface area to volume ratio than B so the diffusion distance is too large to meet the demands of the organism.
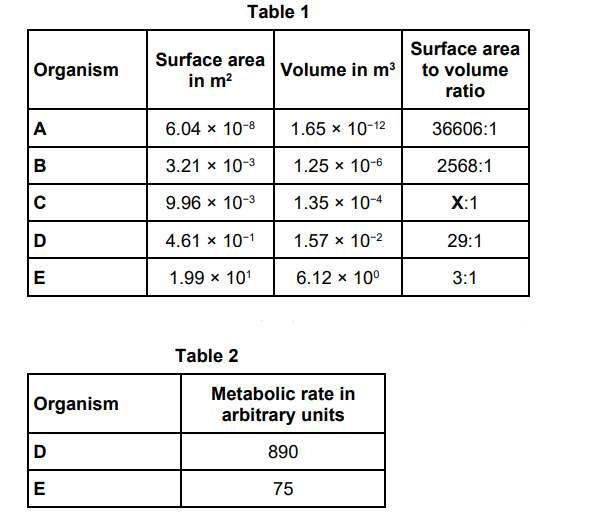
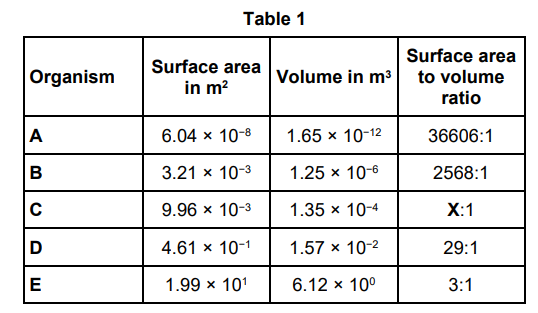
Table 1 is repeated below. Table 2 shows information about organism D and organism E. Organisms D and E both keep a constant body temperature (warm-blooded). Explain why the metabolic rate of organism D is greater than the metabolic rate of organism E. Use information from Table 1 and Table 2.
D has a larger surface area to volume ratio and so will lose heat more quickly per unit volume than E. D requires a greater rate of respiration as respiration is a large part of metabolism so it needs to generate more heat to keep itself warm.
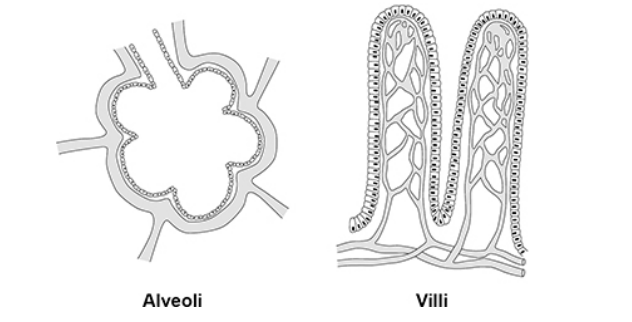
The figure below shows some alveoli and some villi. Describe how the alveoli and the villi are adapted to increase absorption.
Both alveoli and villi have a large surface area to maximise the rate of diffusion. They also have walls that are one cell thick to reduce diffusion distance. They both have a good blood supply to maintain a concentration gradient which increases the rate of diffusion. Villi have microvilli to further increase surface area and the cells of villi contain many mitochondria to provide energy for active transport.
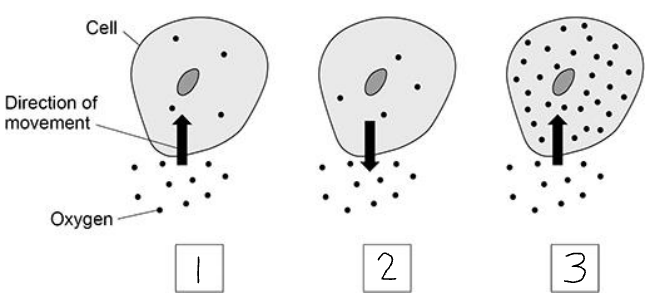
Which diagram shows oxygen moving by diffusion?
1
Plant cells use osmosis to absorb ________.
water
Plant cells use active transport to absorb __________.
mineral ions
Active transport moves substances against the concentration gradient and needs ________.
energy
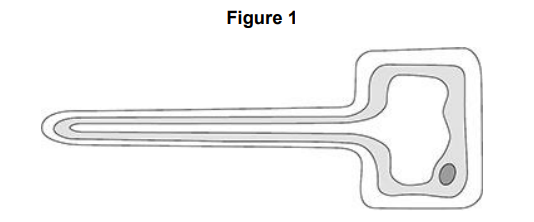
Figure 1 shows a specialised cell that absorbs substances from the soil. Name the type of specialised cell in Figure 1.
Root hair cell
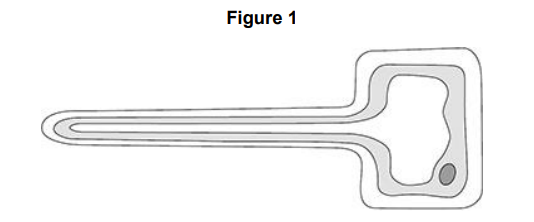
Figure 1 shows a specialised cell that absorbs substances from the soil. Describe how the cell in Figure 1 is adapted to increase the absorption of substances from the soil.
It has a large surface area and lots of mitochondria to provide energy for active transport.
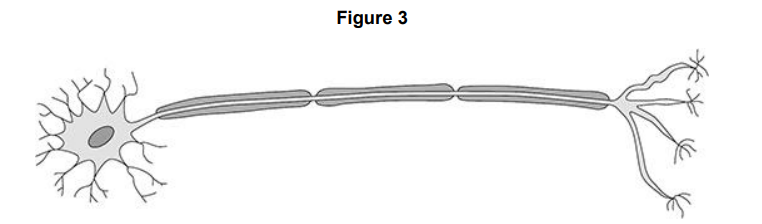
Figure 3 shows another specialised cell. Name the type of cell in Figure 3.
Nerve cell
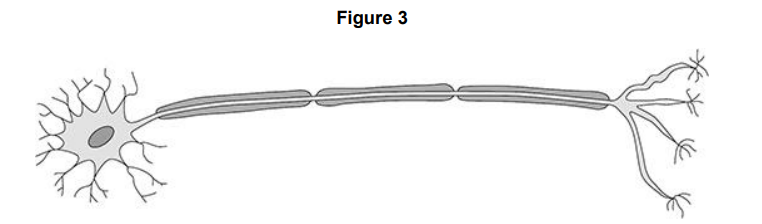
Figure 3 shows another specialised cell. Describe three features of the cell that helps it to carry out its function.
It is long, has insulation and has branches
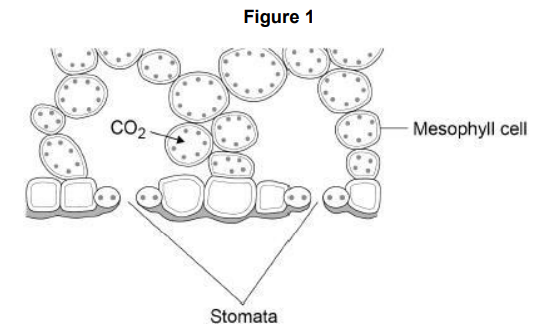
Figure 1 shows part of a leaf. Molecules of carbon dioxide diffuse from the air into the mesophyll cells. Which two changes will increase the rate at which carbon dioxide diffuses into the mesophyll cells?
Increased carbon dioxide concentration in the air, Increased number of stomata that are open
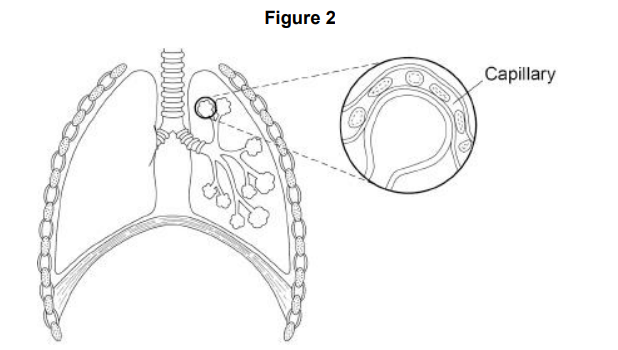
Diffusion also happens in the human lungs. Figure 2 shows the human breathing system. Explain how the human lungs are adapted for efficient exchange of gases by diffusion.
The lungs have many alveoli to provide a large surface area to volume ratio. The capillaries are thin which provides short diffusion distance for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The lungs are ventilated to bring in fresh oxygen and remove carbon dioxide to maintain a concentration gradient. There is a large capillary network around alveoli to remove oxygenated blood quickly and bring carbon dioxide to the lungs quickly to maintain a concentration gradient.
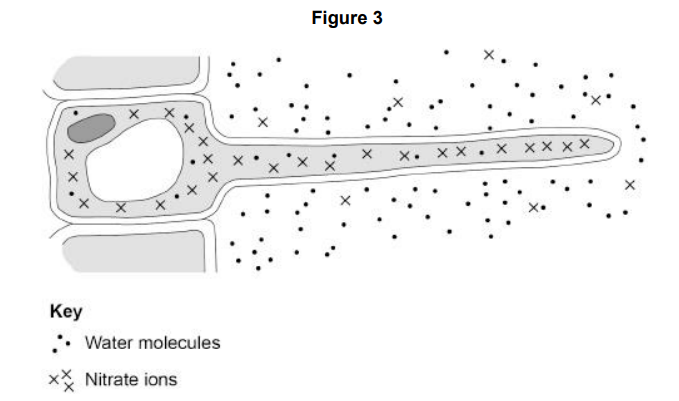
Figure 3 shows a root hair cell. Name the process by which water molecules enter the root hair cell.
Osmosis
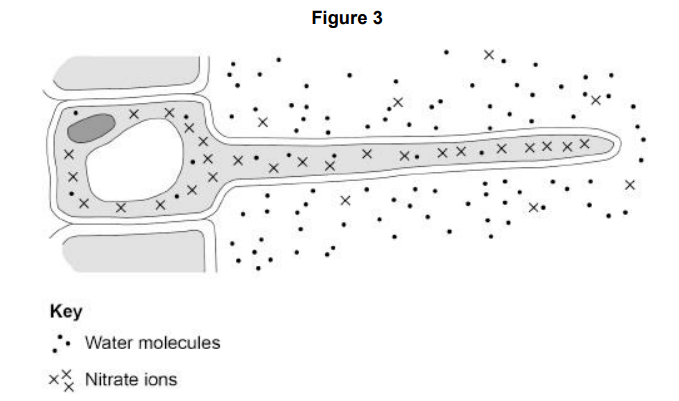
Figure 3 shows a root hair cell. Nitrate ions need a different method of transport into the root hair cell. Explain how the nitrate ions in Figure 3 are transported into the root hair cell. Use information from Figure 3 in your answer.
The root hair cell uses active transport to move the nitrate ions from a lower concentration in the soil to a higher concentration in the cell against a concentration gradient.The root hair cell has many mitochondria to provide energy for this process.