STP 420 Exam 2
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Conditional Probablity
P(A|B) = P(A n B)/P(B)
Long Run Probability
As the number of trials increases, the average of the results will get closer and closer to the expected value. (Law of large numbers)
General Addition Rule
P(A u B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A n B)
Special Addition Rule
P(A u B) = P(A) + P(B) when independent
Expected Value
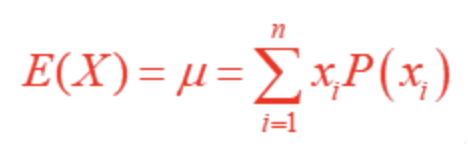
Var[X]
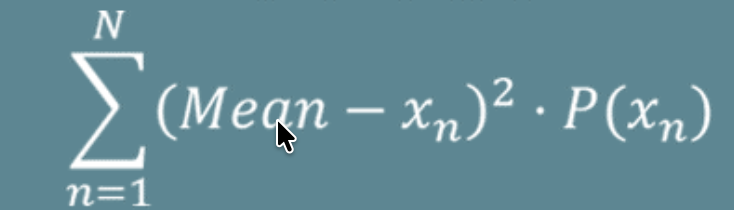
Properties of E[X]
E[c] = c
E[g1(x) + g2(x)] = g1E[x] + g2E[x]
E[cg(x)] = cE[g(x)]
Properties of Var[x}
Var[c] = 0
Var[X + Y] = Var[X] + Vary[Y] only if X and Y are independent
if dependent: Var[X] + Var[Y] + 2psqrt(Var[X])sqrt(Var[Y])
Var[aX + b] = a²Var[X]
CLT Requirements
We can assume a normal distribution of a sample if:
population is normally distributed
sample size is sufficient (n >= 30)
Confidence Interval Requirements
Check CLT
Za/2
a = 1 - confidence level
90% confidence: 1 - .90 = 0.1 => 0.1/2 = 0.05
z0.05 = 1.96
Margin of Error
za/2*(sd/sqrt(n))
Confidence Interval
point estimate ± margin of error
Necessary sample size for confidence level with certain margin of error
n = ((za/2)²(sd)²)/(E)²
round up for integer value