Pharmaceutical Stability Kinetics: Reaction Orders and Shelf-Life Estimation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Shelf-Life Estimation (t90)
Time within which product contains at least 90% of the labeled amount of active ingredient(s).
Accelerated stability studies
Studies determined via high temperature and high humidity.
Responsibility of the Pharmacist
Dispense oldest stock first and observe expiration dates.
Proper storage conditions
Store products under conditions stated in USP monographs and/or labeling.
Instability observation
Observe products for evidence of instability.
Repackaging responsibility
Properly treat/label products that are repackaged, diluted, or mixed with other products.
Dispensing requirements
Dispensing in proper container with proper closure.
Patient education
Informing/educating patients concerning proper storage and use of products, including the disposition of outdated or excessively aged prescriptions.
Expiration date considerations
Expiration date given at room temperature: What is the expiration extension if refrigerated?
Temperature effects on expiration
Expiration date for refrigerated temperature given: How long if left at room temperature?
Heating effects on expiration
Expiration date for room temperature given and it is desired to heat (autoclave): What is the % decomposition?
Kinetics
The study of the rate of chemical change and the way this rate is influenced by conditions of concentration of reactants, products, and other chemical species that may be present and by factors such as solvent, pressure, and temperature.
Reaction Kinetics
Kinetic data includes reaction order and reaction rate.
Reaction Order
The order of reaction refers to the way in which concentration of drug or reactants influences the rate of chemical reaction or process.
Rate of reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction is the velocity with which the reaction occurs.
Rate expression
If the amount of drug A is decreasing with respect to time, then rate of this reaction can be expressed as - dA/dt.
Concentration function
The rate of decrease in the concentration C of reactant A to form product B can be described as a function of time.
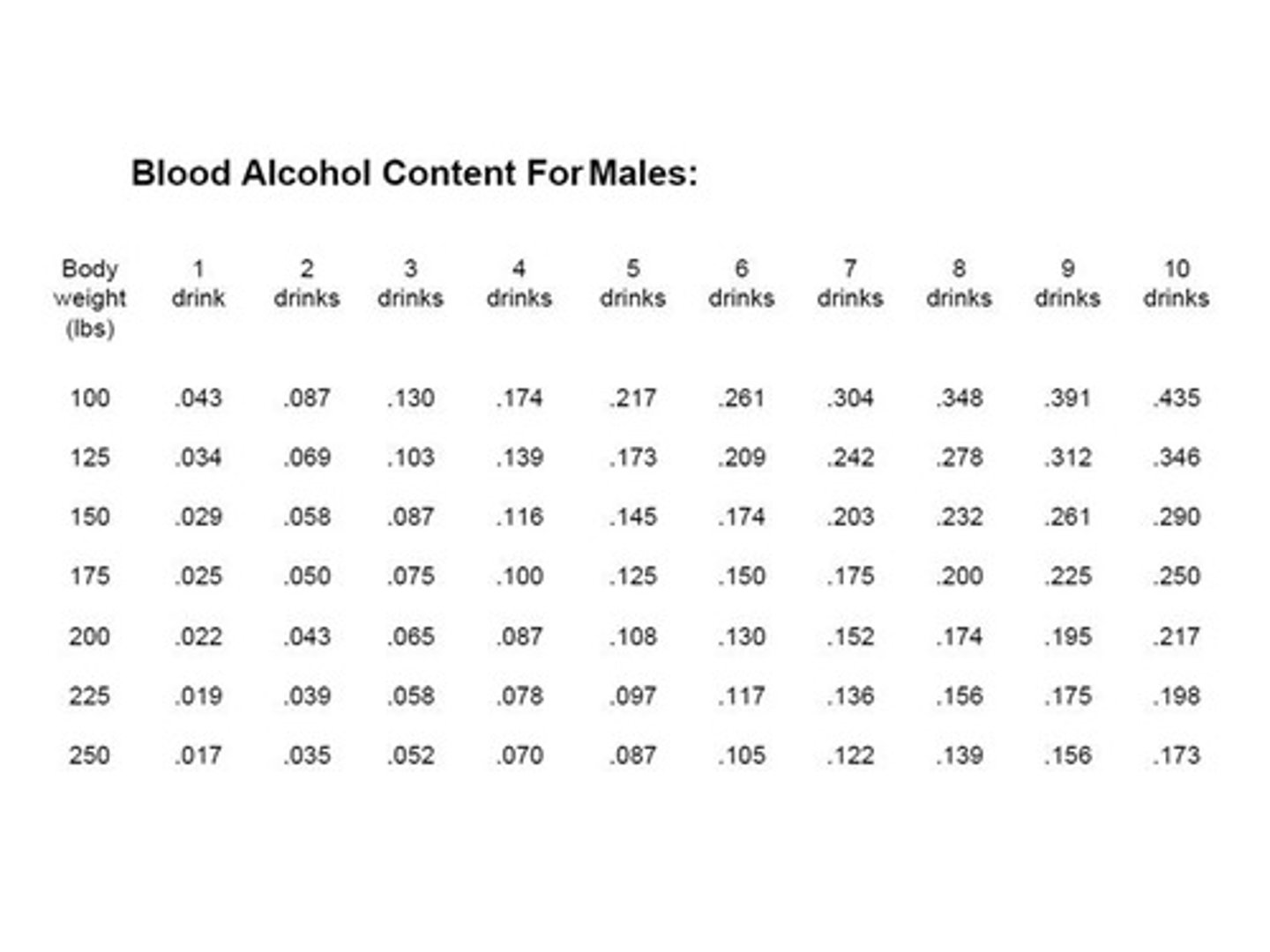
Blood Alcohol Content (BAC)
The concentration of alcohol in blood, usually measured as mass per volume.
First-Order degradation
[drug] decreases exponentially with time; rate of degradation is proportional to [drug]; plot of log [drug] or ln[drug] vs. time is linear; t 1/2 is constant regardless of [drug].
![<p>[drug] decreases exponentially with time; rate of degradation is proportional to [drug]; plot of log [drug] or ln[drug] vs. time is linear; t 1/2 is constant regardless of [drug].</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/befd17e2-c074-4656-a075-e79f89edcb93.jpg)
Zero-Order degradation
[drug] decreases linearly with time; rate of degradation is constant; rate of elimination is independent of [drug]; plot [drug] vs. time is linear; no true t 1/2.
![<p>[drug] decreases linearly with time; rate of degradation is constant; rate of elimination is independent of [drug]; plot [drug] vs. time is linear; no true t 1/2.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/99e307d3-1763-45af-b36d-f4c42cfd5aaa.jpg)
Rate equations
Rate = k C; C = Co e-kt; Rate = k; C = Co - kt.