PATHOLOGY EXAM 2
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
morsicatio buccarum
biting trauma on buccal mucosa
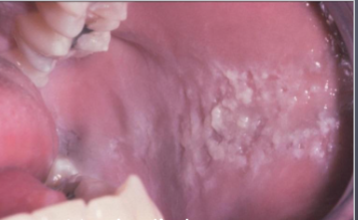
morsicatio linguarum
biting trauma on lateral border of tongue
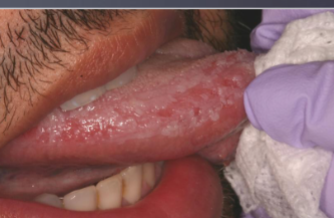
traumatic granuloma with stromal eosinophilia (TUGSE)
deep chronic ulceration with slow resolution
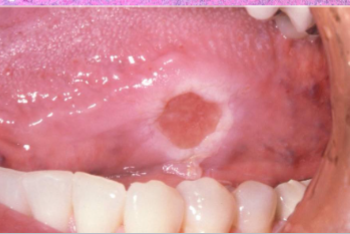
incisional biopsy and removal of trauma
what is the treatment for this?
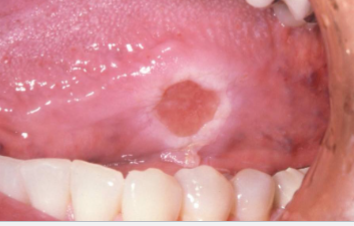
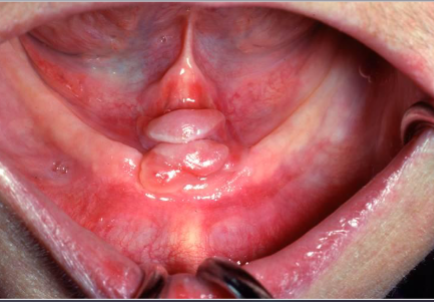
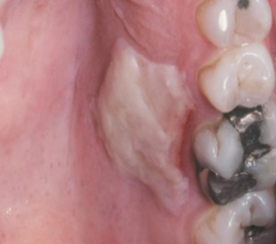
epulis fissuratum
a benign fibrous hyperplasia caused by irritation, often seen in edentulous (no teeth) patients.
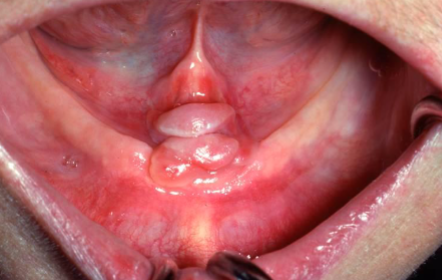
ill fitting denture
what is the most likely cause of this lesion
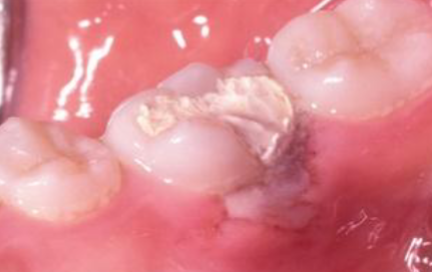
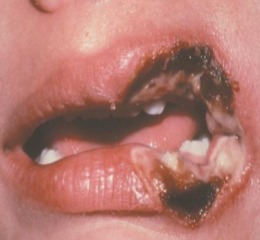
chemical burn (aspirin)
resulting from placing aspirin next to toothache
phenol burn
chemical burn (hydrogen peroxide burn)
chemical burn (phenol peel)
chemical burn (formocresole necrosis)
thermal burn
caused by contact with hot beverages and food
electrical burns
caused by contact with electricity
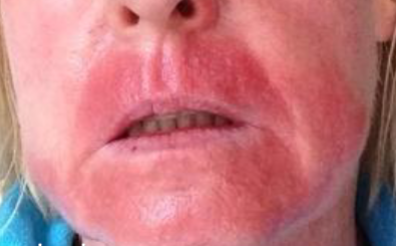
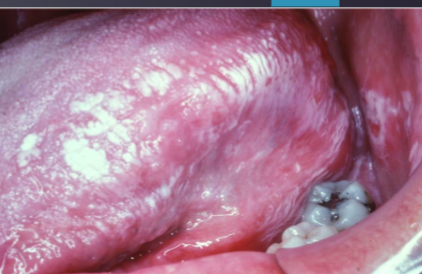
contact stomatitis
topical allergic reaction
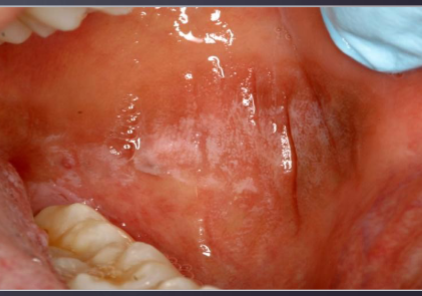
mouth wash, toothpaste, candy, gum (contact stomatitis)
what coulld be the cause of this lesion
cinnamon
most common flavoring agent that causes contact stomatitis
chemo therapy mucositis
begins few days- weeks after CHEMOTHERAPY
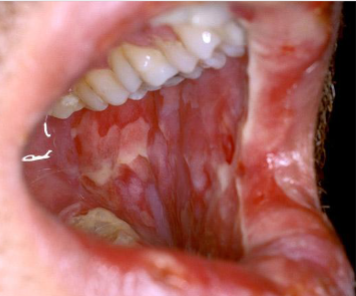
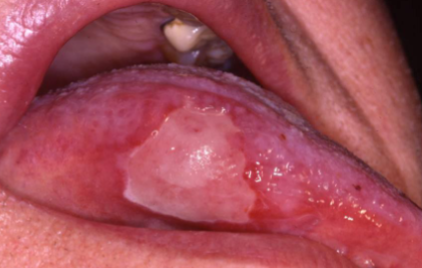
radiation mucositis
occurs after radiation therapy
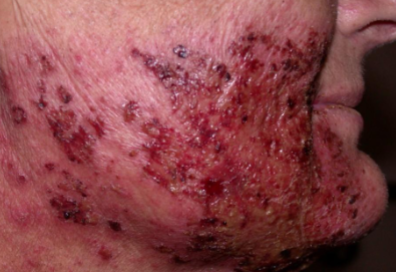
radiation dermatitis
occurs after radiation therapy
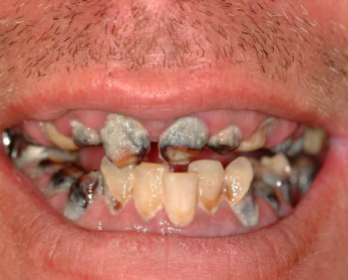
radiation caries
occurs after radiation
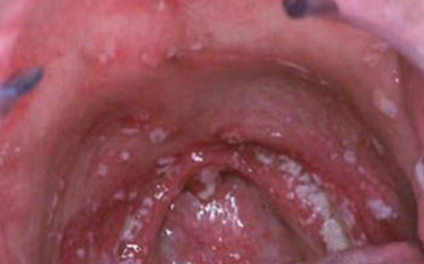
candidiasis
occurs after radiation
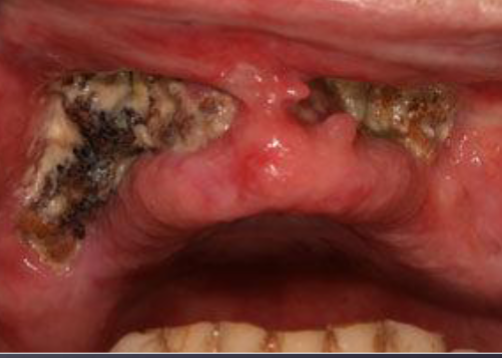
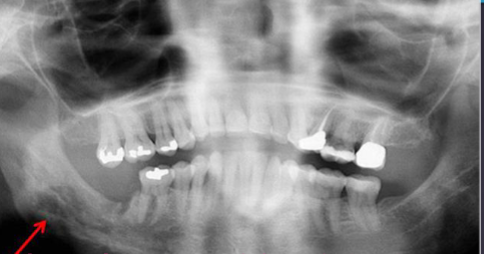
osteoradionecrosis
occurs 4m to 3yrs after radiotherapy
> 60 Gy
radiation dose that increases risk of osteoradionecrosis
fistula associated with osteoradionecrosis
osteoradionecrosis
ill defined radiolucency occurs after radiation therapy

mandible
most common location of osteoradionecrosis
before treatment begins
best time for dental treatment of radiation patients
MRONJ
current/previous treatment with antiresorptive medication and ho history of radiation therapy
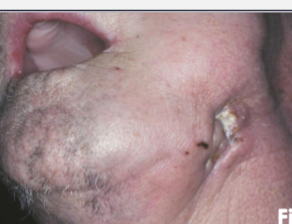
cocaine osetonecrosis
bone necrosis associated with cocaine use, often affecting the nasal cavity
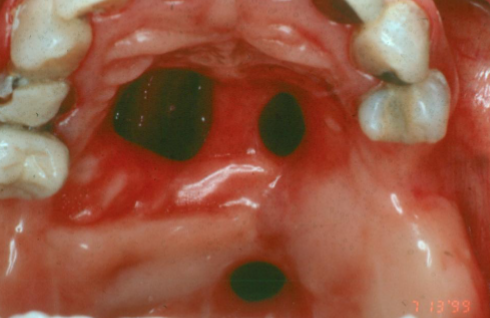
anesthesia necrosis
necrosis/ ischemia from epinephrine
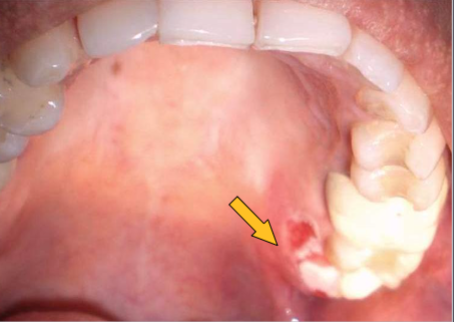
petechiae
minute hemorrhage (1-2 mm)
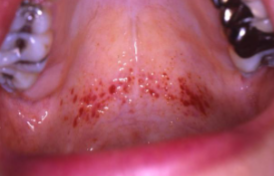
pupura
a larger area of hemorrhage (max 1 cm) under the skin or mucous membranes
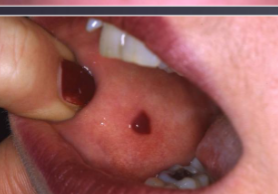
ecchymoisis
any hemorrhage over 2cm, often referred to as a bruise.
hematoma
accumulation of blood within tissues producing a mass
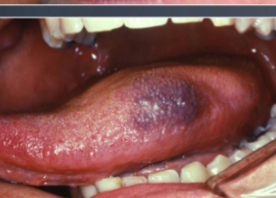
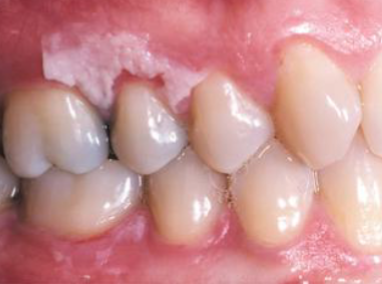
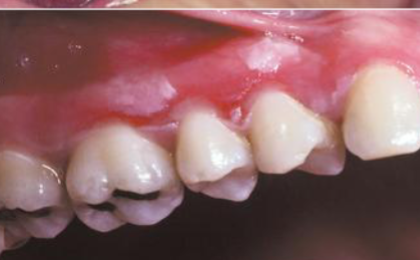
amalgam tattoo
what is the most likely cause of this blue/gray lesion
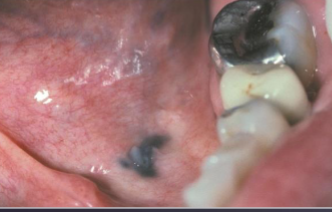
lead poisoning/ plumbism
what caused the black marginal ridges
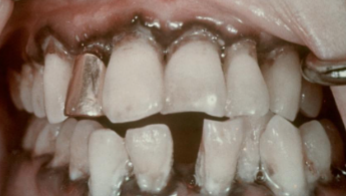
silver poisoning/ argyria
diffuse gray discoloration of skin, gray marginal gingiva
mercury poisoning/ acrodynia (pink disease)
a condition characterized by pink or red skin rash, irritability, and pain in the extremities
sequestrum
a piece of necrotic bone that has become separated from healthy bone
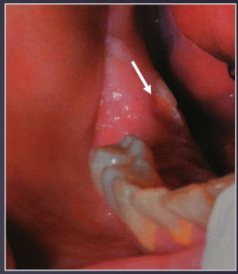
antral pseudocyst
dome shaped, faintly radiopaque lesions arising from maxillary sinus
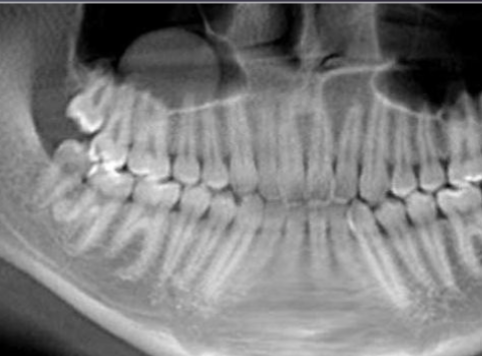
surgery
how would you treat this?
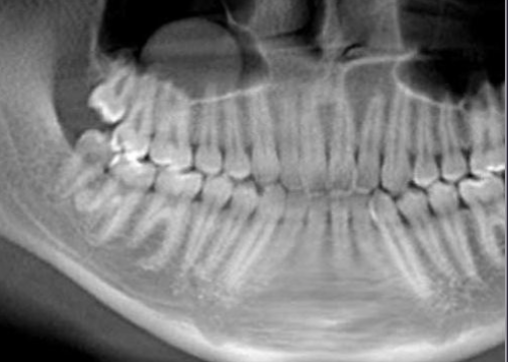
cervicofacial emphysema
rapid onset of facial swelling and pain
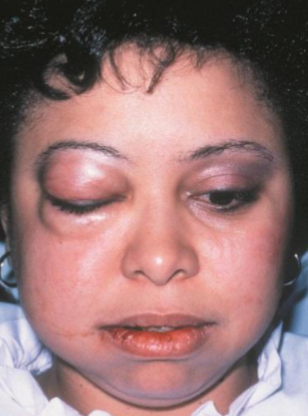
ephelis (freckles)
benign focal increase in MELANIN deposition, INCREASES with UV
actinic lentigo
what is this lesion
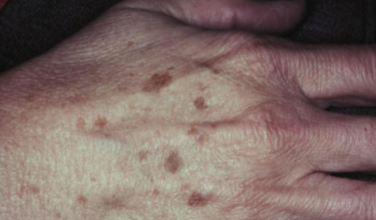
actinic lentigo
benign brown macule, caused increase in MELANOCYTES, does NOT change with UV
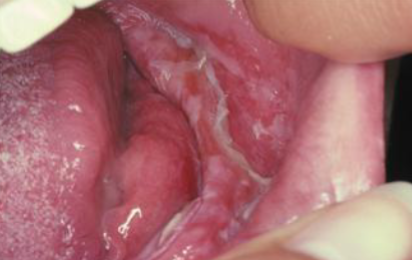
melanocanthoma
benign ACQUIRED dark melanosis of mucosa
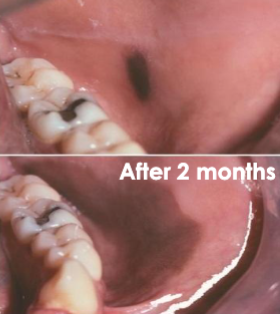
trauma (ex: toothbrush)
what is the cause of this lesion
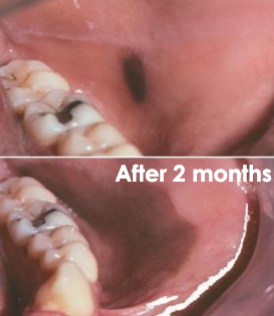
labial melanotic macule
benign focal increase in MELANIN deposits, NO change with UV
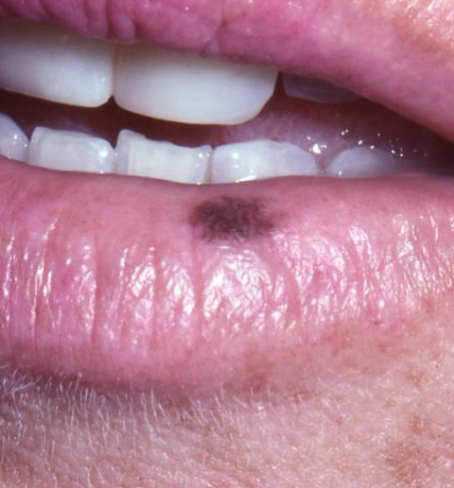
oral melanotic macule
a benign, localized area of increased MELANIN in the oral mucosa
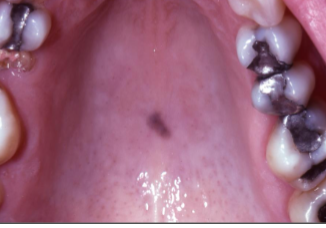
melanocytic macule
what is this lesion
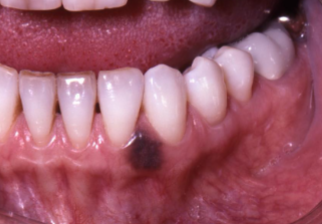
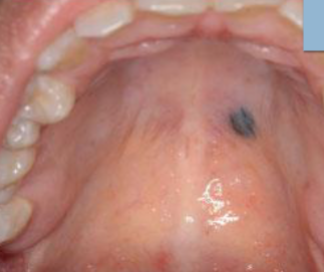
acquired melanocytic nevus
develops during childhood, most common on HARD PALATE or GINGIVA
acquired melanocytic nevus
what is this lesion?
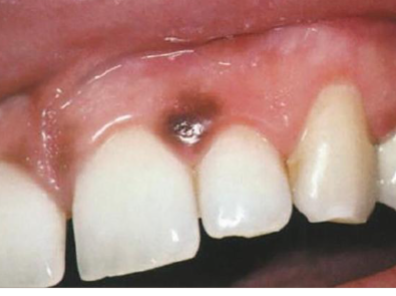
acquired melanocytic nevus
benign localized proliferation of nevus cells (no dendritic processes) that develops during childhood or young adulthood
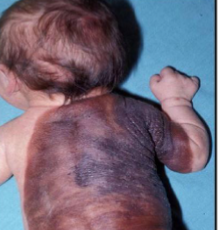
congenital melanocytic nevus
a type of nevus present at birth, characterized by pigmented lesions that may vary in size and can carry a RISK of MELANOMA
melanoma
what is the concern with congenital nevus?
removal for esthetic reasons or definitive diagnosis
what is the treatment for melanocytic nevus
blue nevus
macular/dome shaped blue/black lesion smaller than 1cm
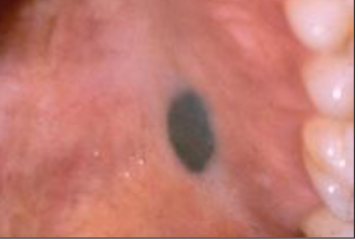
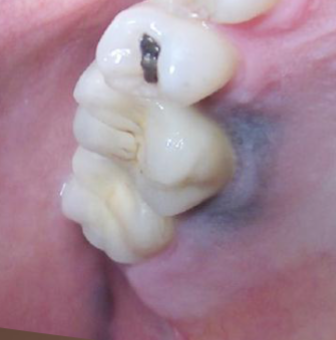
amalgam tattoo
what is the most likely diagnosis
blue nevus
what is the most likely diagnosis
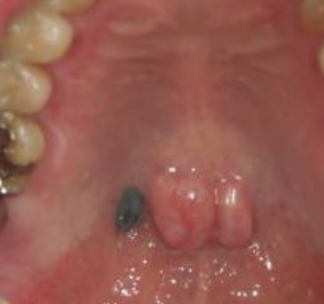
palate
most common site of BLUE NEVUS in ORAL CAVITY
tyndall effect (melanin granules scatter short wavelengths (blue))
why do blue nevus appear blue?
melanoma
malignant neoplasm of MELANOCYTES
melanoma
3rd most common skin cancer
melanoma
most deadly skin cancer
oral
what kind of melanoma has the worst prognosis
melanoma
blue/black CHANGING lesion with asymmetrical broders
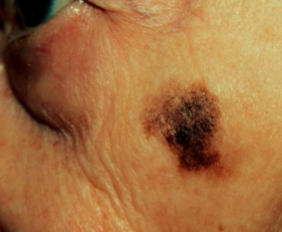
melanoma
what is the most likely diagnosis
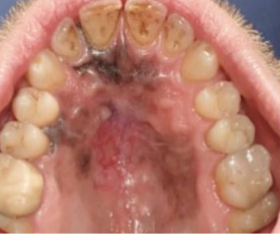
melanoma
what is the most likely diagnosis
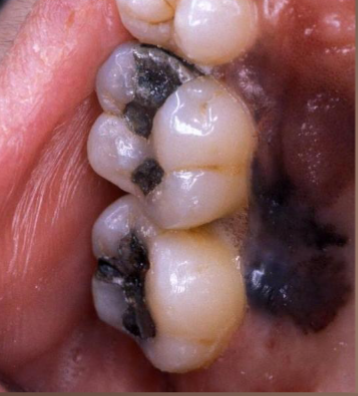
papillary tip melanossi
brown discoloration of fungiform papillae, more common in DARKER SKIN individuals

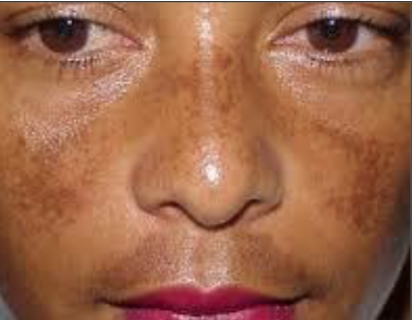
melasma (cholasma)
ACQUIRED hyperpigmentation of face and neck, gets DARKER with UV
melasma (cholasma)
hyperpigmentation of sun exposed skin
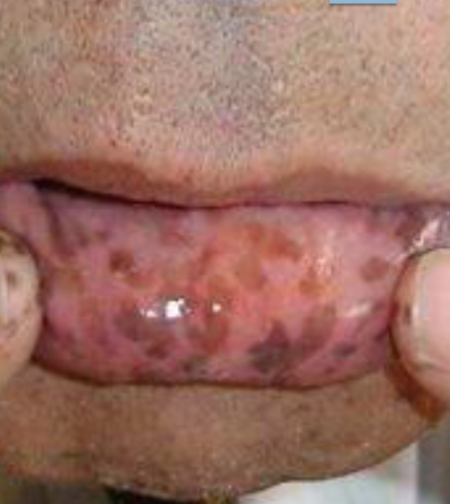
peutz-jehgers syndrome
freckle like brown lesions on lips, buccal mucosa, tongue, and extremities
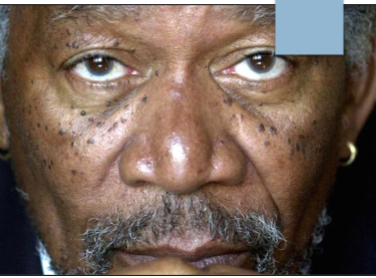
peutz-jeghers syndrome
autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by freckle-like lesions and INTESTINAL POLYPS (risk of cancer)
seborrheic keratosis
acquired, benign proliferation of epidermal BASAL cells
seborrheic keratosis
what kind of lesion are these
hormonal therapy
potential cause of melasma
gigantism
increased growth hormone BEFORE closure of epiphyseal plates
acromegaly
increased growth hormone AFTER closure of epiphyseal plates
gigantism/acromegaly
presents with enlarged mandible, prognathism, MACRODONTIA
dwarfism
caused by decrease in growth hormone
dwarfism
presents with delayed eruption of teeth and MICRODONTIA
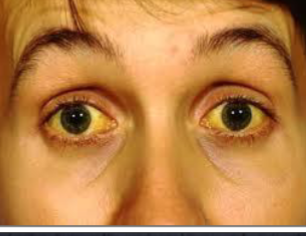
jaundice
excess billlirubin in bloodstream
amyloidosis
a disease characterized by the abnormal accumulation of amyloid proteins in organs and tissues, death imminent
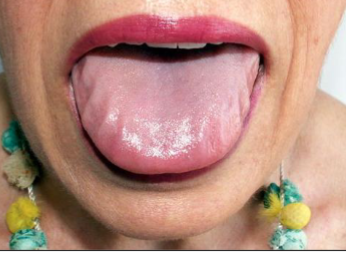
primary amyloidosis
presents with thick lips and macroglossia
crohn’s disease
a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation in the digestive tract, resulting in abdominal pain, diarrhea, and malnutrition
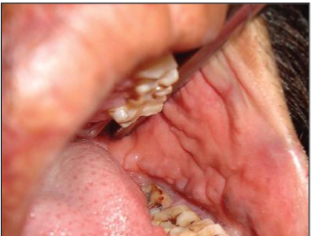
crohn’s disease
oral lesions can PRECEDE GI lesions
crohns disease
oral lesions with COBBLESTONE appearance
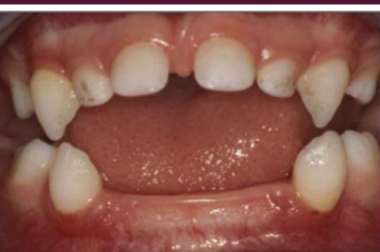
hypophosphatasia
caused by DECREASED alkaline phosphatase enzyme
hypophosphatasia
presents with LACK OF CEMENTUM and PREMATURE LOSS of teeth
hypophosphatemia (vit D resistant rickets)
large pulp horns and multiple none vital teeth without caries or trauma causing
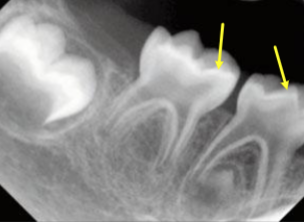
hypophosphatemia
characterized by low serum phosphate and low calcium
iron deficiency anemia
presents with angular cheilitis, atrophic tongue, glossitis, and potentially candidiasis
iron deficiency anemia
what is the most likely cause
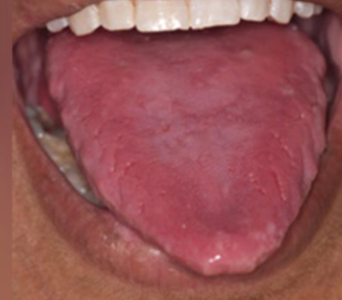
plummer-vinson syndrome
a condition associated with iron deficiency anemia, characterized by dysphagia due to ESOPHAGEAL WEBS, kaoilonychia (spoon like nails), atrophic glossitis
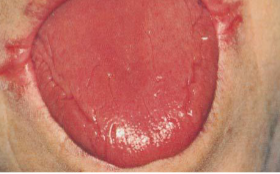
hyperthyroidism
presents with excessive perspiration, tongue tremor, bulging eyes, glossopyrosis (burning tongue), goiter and weight loss
hypothyroidism
presents with cold intolerance, thick tongue, weight gain, dry skin, constipation, and hair loss
cretinism (congenital hypothyroidism)
IN CHILDREN large protruding tongue, delayed development/eruption of teeth, intellectual diaability
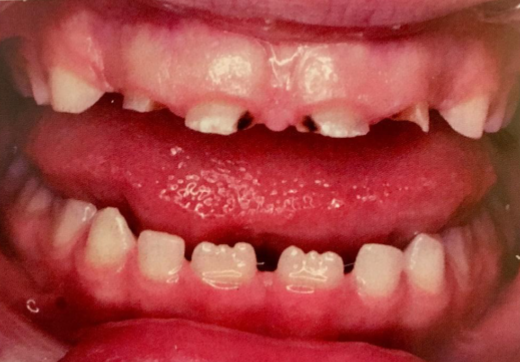
regulate calcium levels
function of parathyroid hormone
hyperparathyroidism
LOSS of trabecular bone pattern and lamina dura
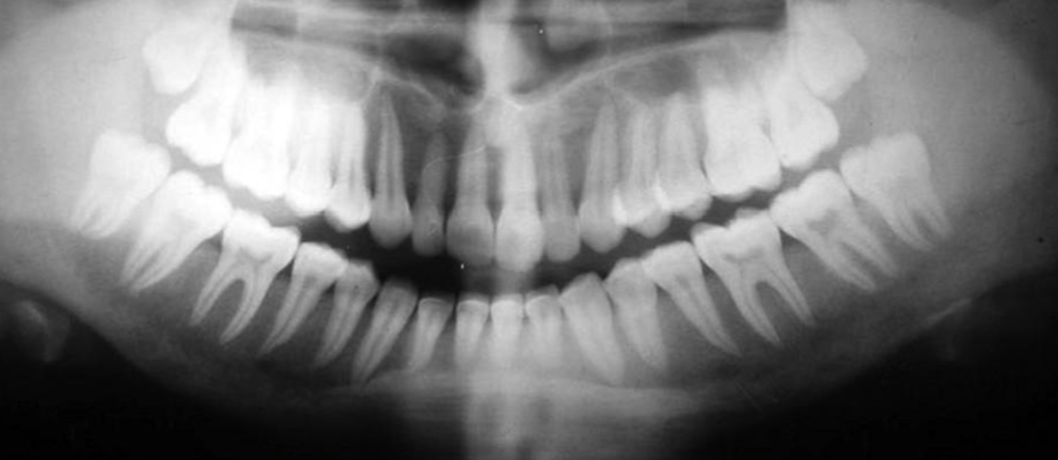
addison’s disease
insufficient production of corticosteroid (decreased cortisol)