Energy stored in a spring: Forces: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Elastic potential energy
The energy stored in when an object is stretched or compressed

Work done on a spring
Equal to the amount of elastic potential energy stored in a spring when it is elastically stretched
Elastic stretch
When an object returns to it original shape when the stretching force is removed

Inelastic (plastic) stretch
When an object does not return to it original shape when the stretching force is removed

Ee = 1/2 ke²
The equation linking elastic potential energy, spring constant and extension (or compression)
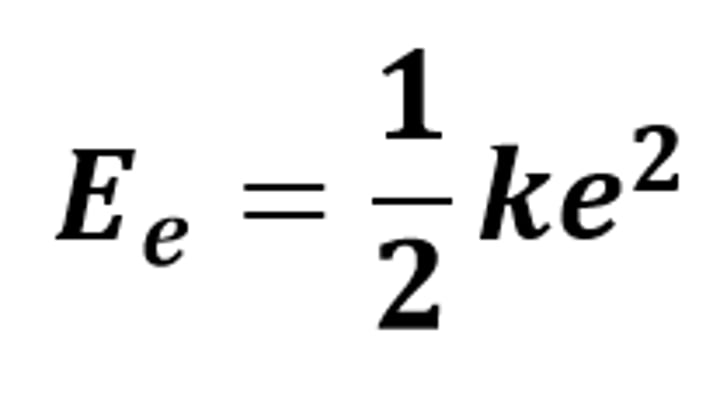
Ee
The symbol for elastic potential energy
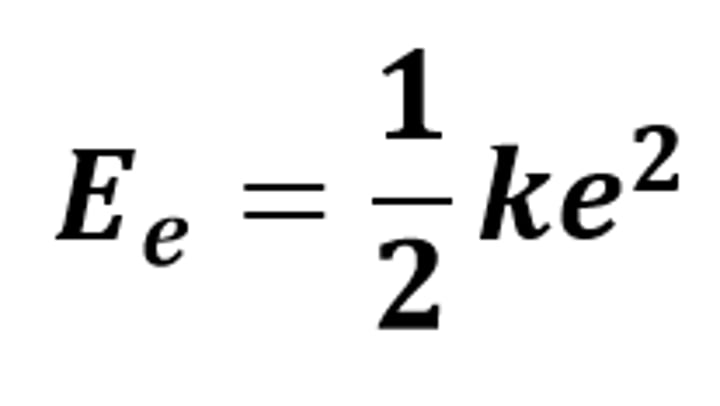
k
The symbol for spring constant
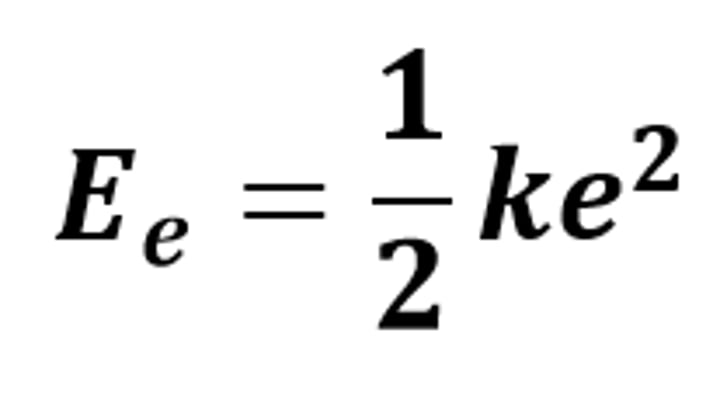
e
The symbol for extension (or compression)
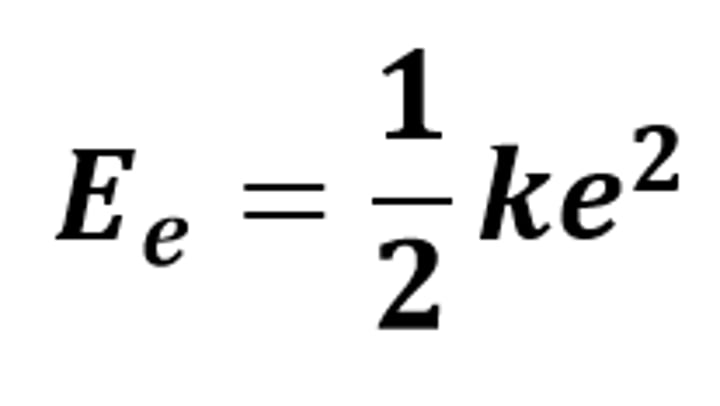
Joules (J)
The SI unit for energy

Newtons per metre (N/m)
The SI unit for spring constant
Metres (m)
The SI unit for extension

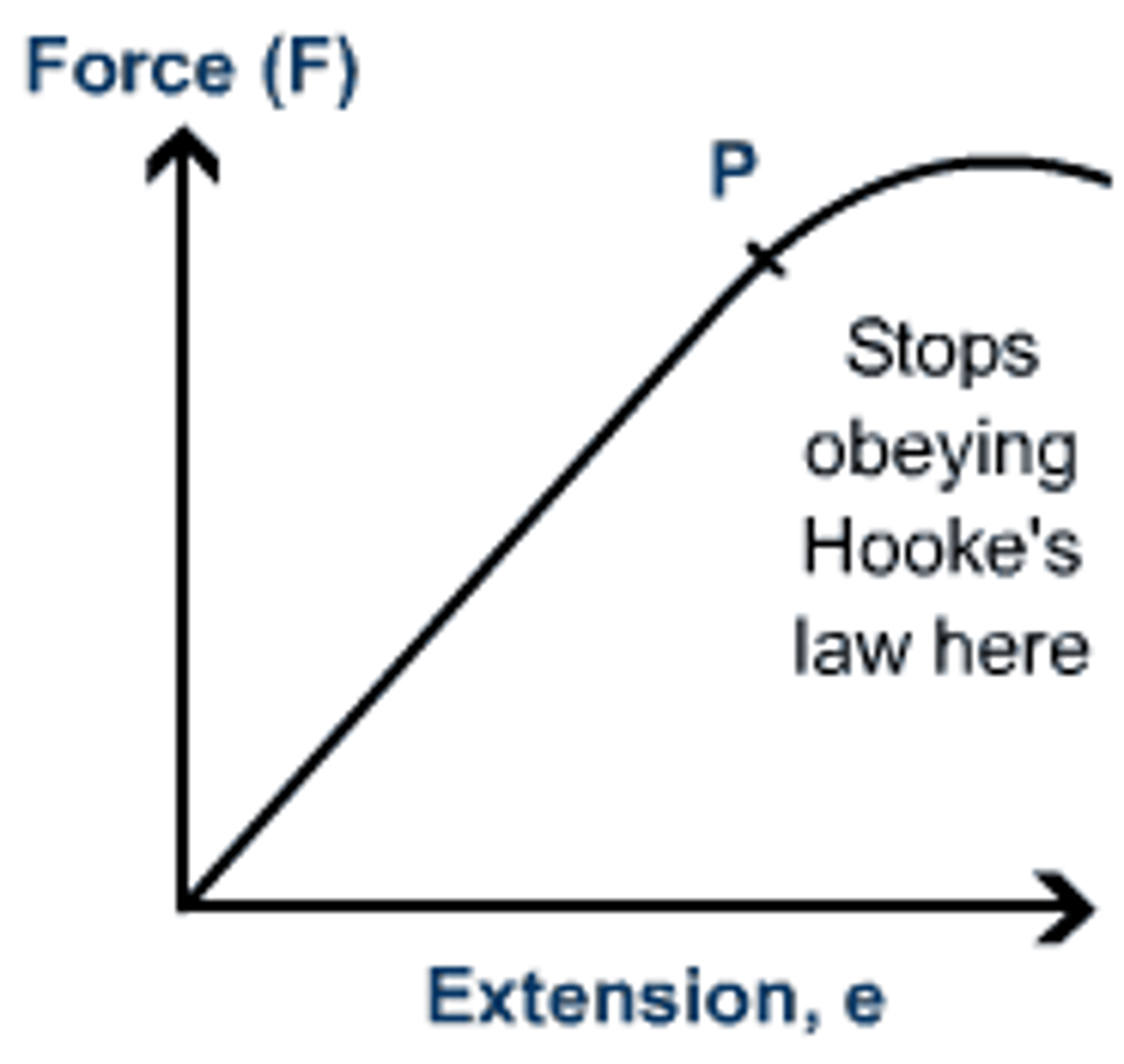
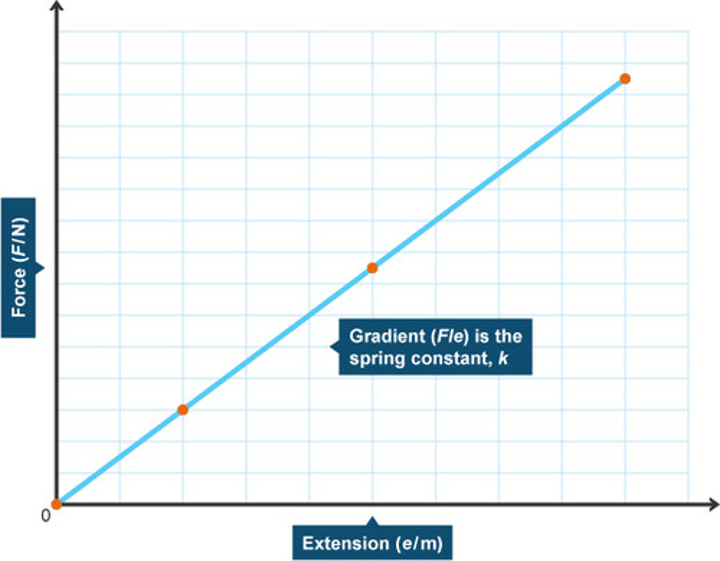
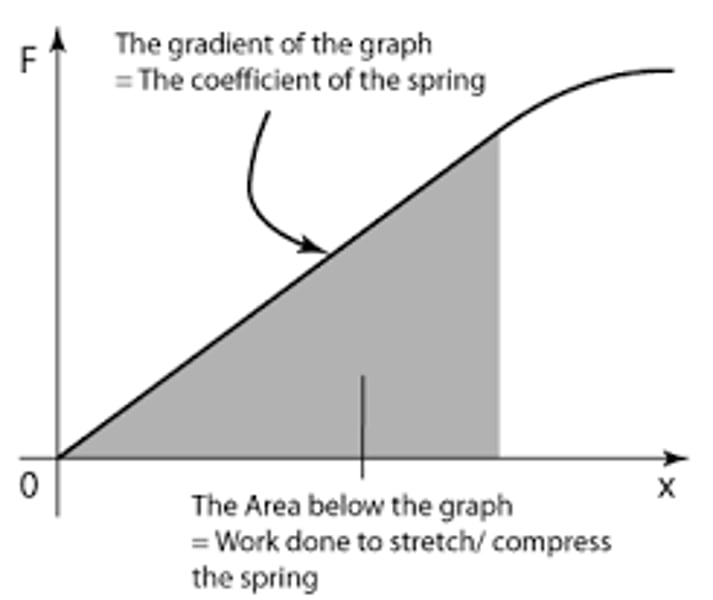
Force-extension graph
A graph of force against extension for an object being stretched
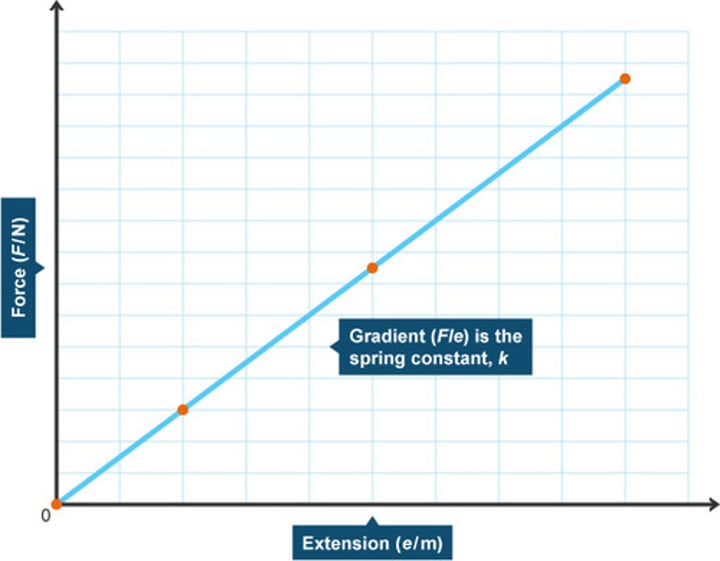
Significance of the gradient of a force-extension graph
Equal to the spring constant of the object being stretched when it is stretching elastically
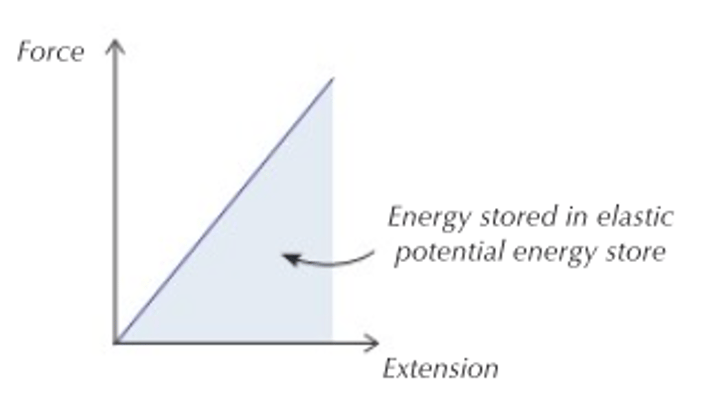
Significance of the area under a force-extension graph
Equal to the work done or the elastic potential energy stored by the object being stretched
Linear extension (on a force-extension graph)
Occurs below the limit of proportionality when the object is deforming elastically
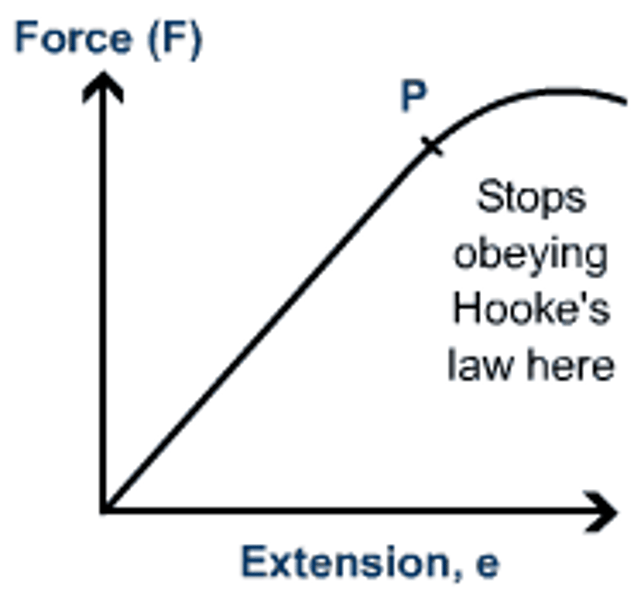
Limit of proportionality (on a force-extension graph)
The point at which the extension of the object changes from a linear to a non-linear extension
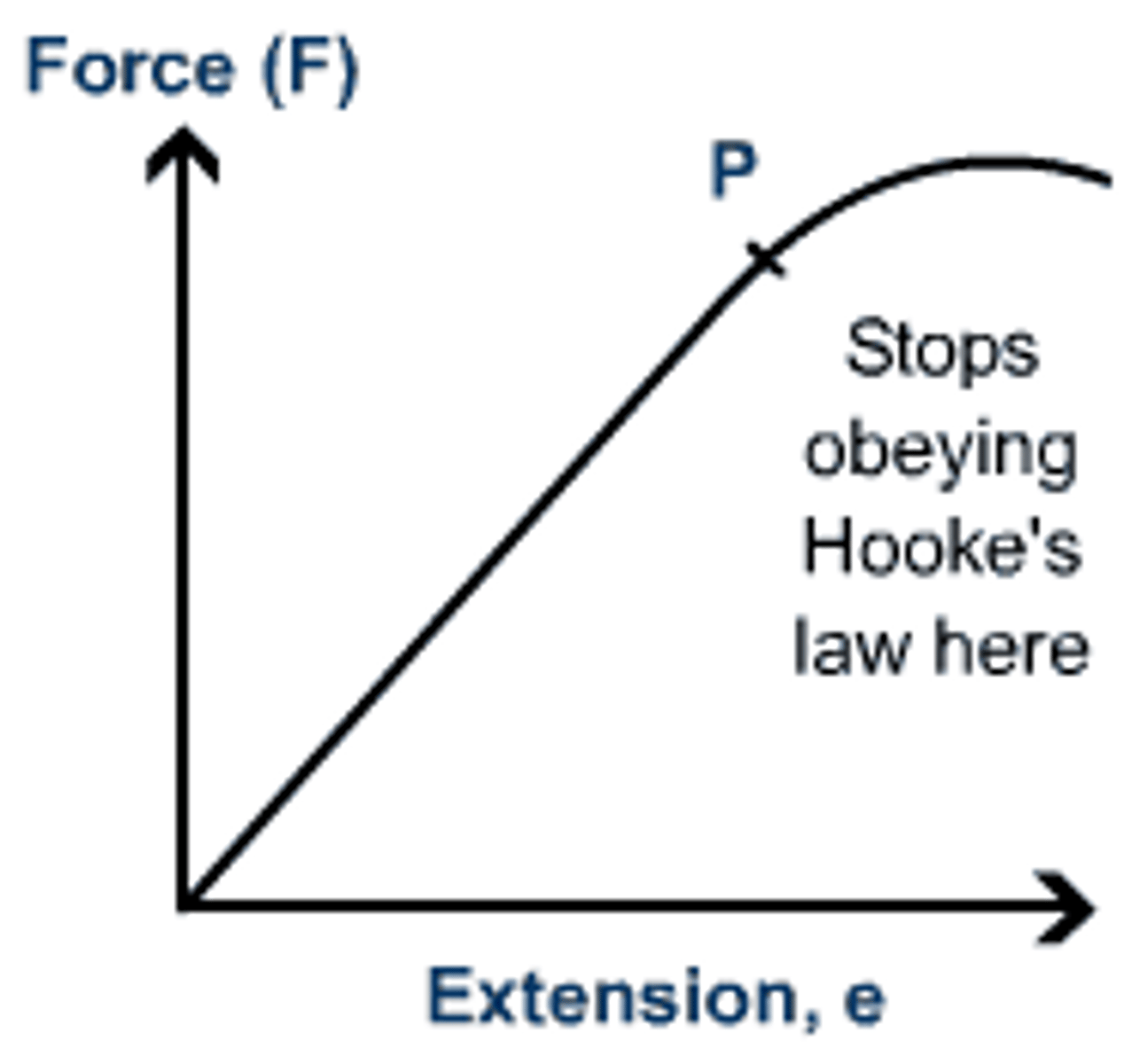
Non-linear extension (on a force-extension graph)
Occurs above the limit of proportionality when the object is deforming inelastically