UNIT 1: MEASUREMENT AND SCIENTIFIC NOTATION
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Importance of SI units (UNIT 1)
The basis of the metric system. They are used to describe what type of measurement you are using and whether you are measuring a mass, rate of change, amount of time, amount of force, etc.
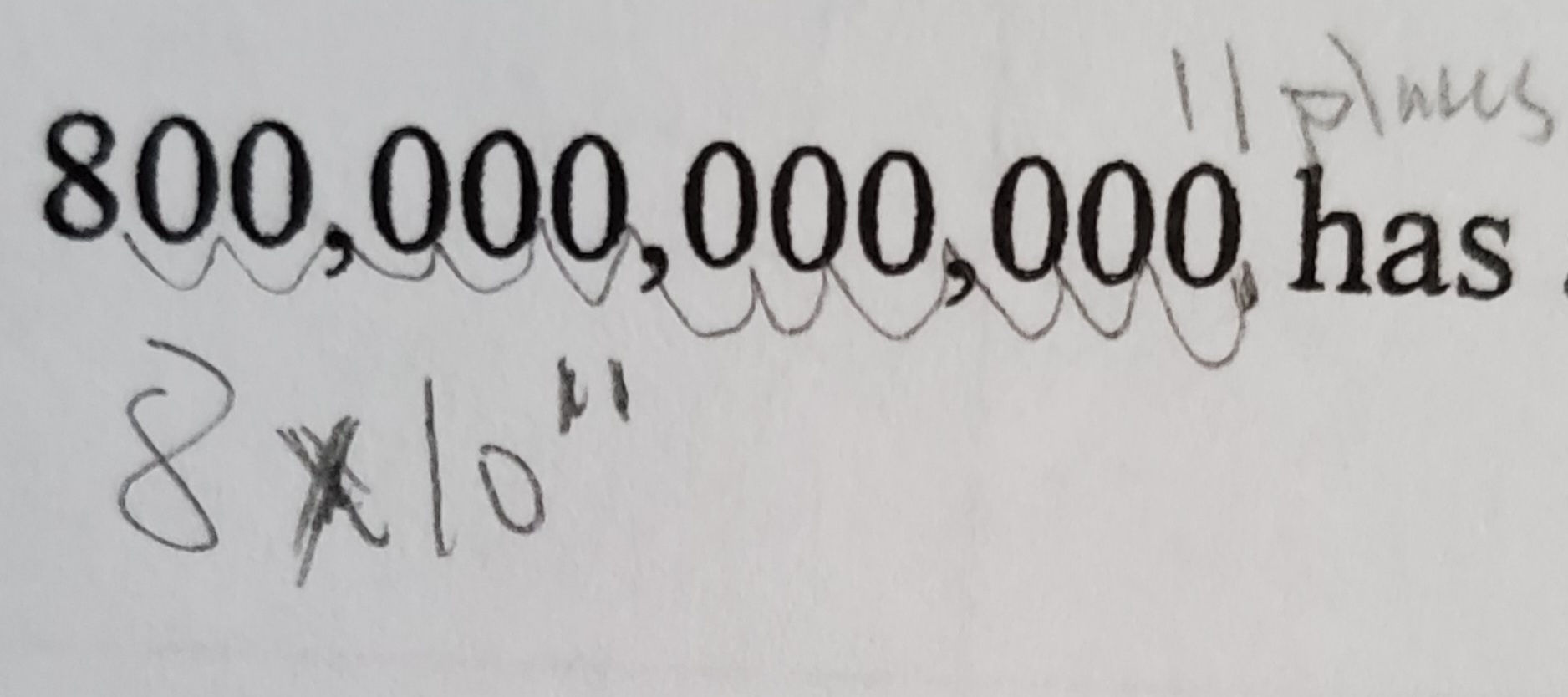
Scientific Notation (UNIT 1)
Used for describing numbers that are too large or too small
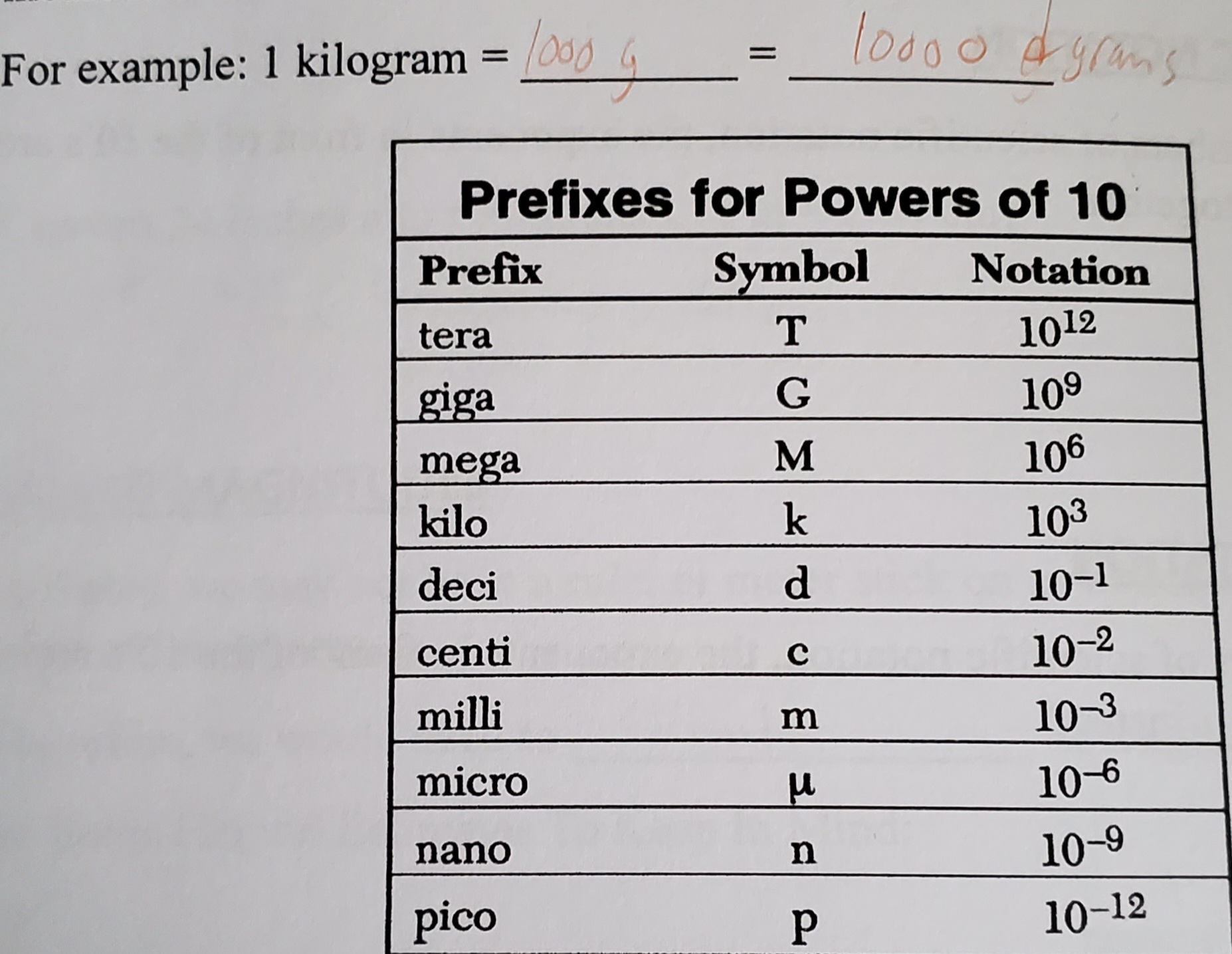
Prefixes for scientific notation (UNIT 1)
Each prefix has its own symbol and can be matched with any unit of measurement
Multiplying Scientific Notation (UNIT 1)
When multiplying numbers of scientific Notation, the exponents in front of the 10's are added together (EX. 10¹⁰ × 10⁶ = 10¹⁶)
Dividing Scientific Notation (UNIT 1)
When diving numbers of scientific Notation, the exponents in front of the 10's are subtracted instead (EX. 10¹⁰ ÷ 10⁶ = 10⁴)
Factor Label Method (UNIT 1)
Way of converting units into other units, or vice versa.
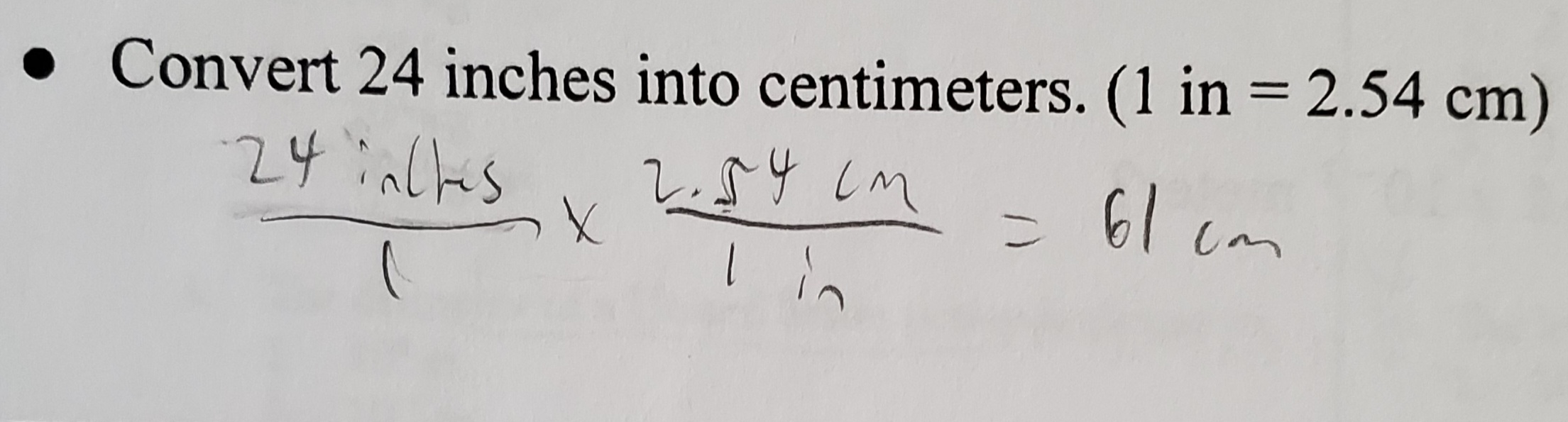
How to do Factor Label Method (UNIT 1)
Cross multiply the units with their conversions. If a unit in a numerator matches a unit in the denominator, the units cancel out

Estimating Magnitudes (UNIT 1)
At times, we may not have a ruler or meter stick on us to know the exact measurements of an object or area. Therefore, we need to estimate its length, width, height, or thickness
The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately… (UNIT 1)
10⁰ m