3: Depreciation & asset valuation
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is depreciation?
The annual loss in value due to use, wear, tear, age, and technical obsolescence. Both a business expense that reduces annual profit and a reduction in the value of the asset
Represents an expense, a decline in the value of an item resulting from obsolescence and deterioration lessening the items productivity
What must a depreciable item possess?
A useful life of more than 1 year
A determinable useful life but not an unlimited life
A use in a business in order for the depreciation to be a business expense
What are examples of a depreciable item?
Machine/equitment
Livestock/breeding
Buildings, wells, ponds, barns
Fencing
NOT bare land :(
What is useful life?
Number of years the asset is expected to be used in the buisness
What is Cost?
The price paid for the asset including:
Taxes
Delivery Fees
Installation
Jargon: “Cash Boot” or “Boot”
What is salvage value?
The expected market value of the asset at the end of its assigned useful life
What is book value?
The current value of item (original cost less accumulated depreciation)
What are the 3 depreciation methods?
Straight line (SL)
Sum of the years digits (SOYD)
Declining balance (DB)
What is partial-year depreciation?
An asset purchased during the year should have the first year’s depreciation prorated according to the length it was actually owned
What are the equations used for Straight Line depreciation?

What is the equation used for Sum of the Years Digits (SOYD) depreciation?

What equation is used for Declining Balance annual depreciation?
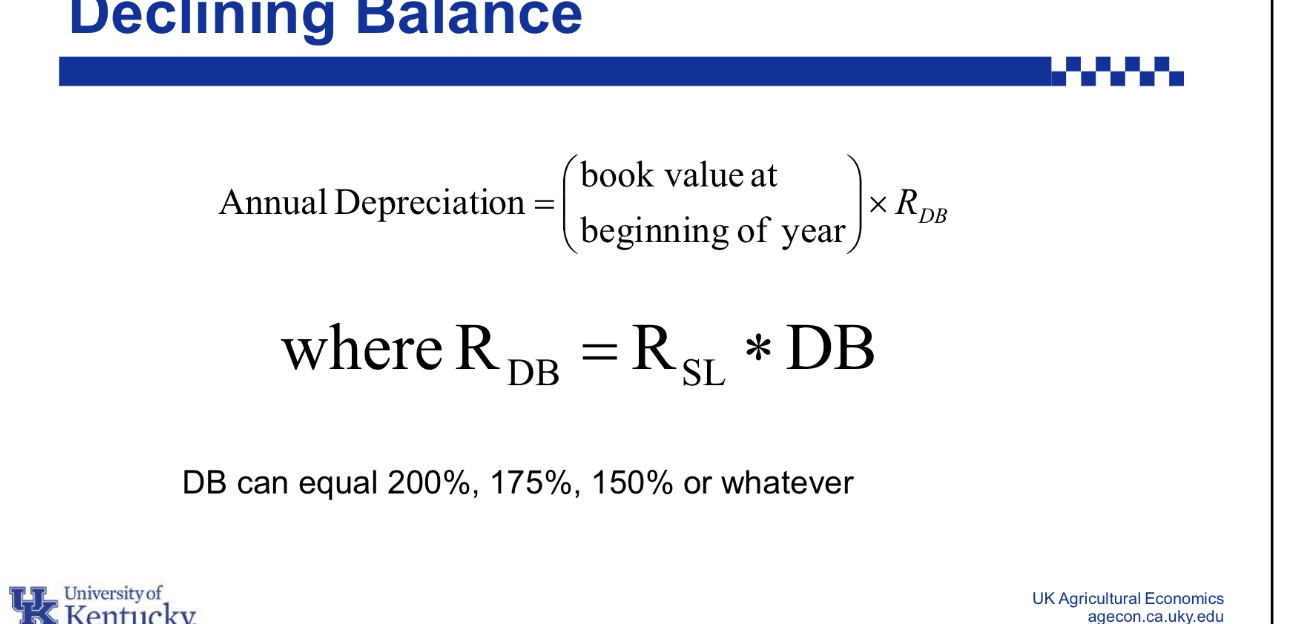
What is Rsl?
Rsl= annual straight-line percentage rate (100%/useful life)
What system does Income Tax Depreciation use?
MACRS
What does MACRS stand for?
Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System
Income tax depreciation must follow what?
Must follow IRS rules
What is income tax depreciation?
An annual deduction that allows businesses and investors to recover the cost of an asset over its useful life. This deduction accounts for the assets wear and tear
What falls under MACRS useful life class of 3-years?
Breeding hogs
Road tractors
What are you?
BEAUTIFUL AND SMART AND SO LOVING
What falls under MACRS useful life class of 5-years?
cars, pickups
Breeding cattle and sheep, dairy cattle
Computers
What falls under MACRS useful life class of 7-years?
Most farm machinery
Fence, grain bins, silos
Office furniture
What falls under MACRS useful life class of 10-years?
singlerpose agriculture and horticultural structures
What falls under MACRS useful life class of 15-years?
Water wells
Paved Lots
What falls under MACRS useful life class of 20-years?
General purpose buildings such as machine sheds/hay barns
What is MACRS used for?
same basic assumption for all depreciable property under MACRS
Implied salvage value $0 for all items
One-half year of depreciation allowed in the year of purchase regardless of purchase date
A system of property classes which fixes the useful life for each type of property
What is economic depreciation?
The decline in value due to an asset’s reduced ability to produce revenue now and in the future.
The only way to truly assess the “expense” of that particular asset in that year
What is tax depreciation?
An annual icomone tax deduction that allows a business or indicidual to recover the cost of certain property over its useful life. this spreads the cost over a period of time rather than deducting it all in the year of purchase. By lowering a taxpayer’s taxable income, it reduces their total tax liability
What are the 5 different asset valuations?
Market Value
Cost
lower of cost or market
Farm production cost
Cost less depreciation
What is tax liability?
Total amount of tax debt that an individual or business owes to the government. It is a tax obligation from all taxable activities such as earnings or sellings
What are the two most important asset valuations?
Market value and Farm production cost
What are examples of real property?
Land and a house
What are examples of personal property?
Vehicles and equitment
What is market value?
Current market price less selling costs
AKA: fair market value or net market price
Examples: Land, machinery, most assets
What is cost?
Original cost when purchased
Ex: Taxes
What is lower of cost or market?
Lesser of cost or market for a conservative estimate
Ex: Balance sheet
What is farm production cost?
Actual cost of item produced; production expenses incurred to date
same concept as “value of growing crop”
bridges two accounting periods (add up all expenses to 12/31/xxxx)
Ex: Winter wheat or cover crops: seeds, chemicals, fertilizer, fuel
What is cost less depreciation?
original cost less depreciation
Ex: same as “cost” but for depreciation assets
Think taxes
Why are depreciation assets important?
Accurate financial reporting: It provides a more accurate representation of an assets current value and the cost of using it in a business
Tax savings: Businesses can claim depreciation as an expense. This reduces their taxable income (reduces taxes owed)
Budgeting and planning: helps businesses understand the cost of their capital assets and planning for future replacements
What is a depreciation asset?
Depreciation is a non-cash accounting process that allocates the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life as it wears out, becomes obsolete, or loses value over time. It reduces the asset's "book value" on the company's financial statements and allows businesses to take tax deductions, lowering overall taxes owed. Common depreciable assets include machinery, vehicles, buildings, and office equipment, while land is generally not depreciable.