VM 528 Final Exam
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
The order of placental membranes between the fetus and the dam in the horse is:
Fetus, amnion, allantois, chorion, endometrium
The primary stimulus for relaxin secretion is:
PGF2a
Fetal placenta
Chorion
Collects embryonic wastes
Allantois
Shock absorber, protects fetus
Amnion
Fusion of allantois and chorion
Allantochorion
Regresses in mammals
Yolk sac
Mammary duct growth and branching is stimulated by:
estrogen
How many mammary glands does the bitch have?
8 to 12
What provides antibodies in the first few days postpartum to the neonatal calf?
Colostrum
Tactile stimulation of the teat promotes release of what?
Oxytocin
T/F: Lochia is abnormal and a sign that treatment is required
False
T/F: Steroid hormones from the mother past to the milk
True
The sterile heifer twin to a bull. It has incomplete development of the reproductive tract and male-like behavior.
Freemartin
Term for estrus
Heat
To give birth
Parturition
Male used to induce heat or receptivity in a female, but not to breed
Teaser
A period of anestrus induced by either long (ewe) or short (mare) photoperiods
Seasonal anestrus
A glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary that causes ovulation and subsequent development and maintenance of the corpus luteum. In the male, it causes Leydig cells to produce testosterone.
LH
For the spermatozoa to fuse with the oocyte cell membrane, which one of the following is true?
A. The sperm must be outside the zona pellucida
B. The sperm must be in the perivitelline space
C. The spermatozoa should have the acrosome intact
B.
Where does fertilization occur within the female reproductive tract?
Oviduct
What type of placentation does the mare have?
Diffuse
What hormone is responsible for reproductive behavior?
Estradiol
What type of placentation does the cow have?
Cotyledonary
What are the cardinal signs of pregnancy in cattle?
Amniotic vesicle
Fetus
Chorioallantoic membrane slip
Placentomes
How would you describe the fluid of pregnancy?
Anechoic
During what phase of spermatozoal transport do the sperm move into the isthmus and attach to the oviductal epithelium?
Sustained phase
What type of placentation does the bitch have?
Zonary
Place the events in the correct order in which they occur.
Sperm penetrate zona pellucida
Formation of pronuclei
Sperm is engulfed
Acrosomal reaction
Membrane fusion between sperm and oocyte
Hyperactive activity
Sperm nucleus decondensation
Capacitation
Sperm bind to zona pellucida
Capacitation
Hyperactive activity
Sperm bind to zona pellucida
Acrosomal reaction
Sperm penetrate zona pellucida
Membrane fusion between sperm and oocyte
Sperm is engulfed
Sperm nucleus decondensation
Formation of pronuclei
Which one of the following female species has the longest estrous cycle?
A. Sow
B. Cow
C. Bitch
D. Llama
C.
Indicate which one of the following female species is a seasonally polyestrus long-day breeder?
A. Cow
B. Mare
C. Ewe
D. Bitch
B.
During ‘consummation’ period, which female species is characterized by clitoral exposure by labial eversion?
Mare
During the ‘courtship’ period, which female species is characterized by making mounting attempts with other females?
Cow
Which one of the following factors DOES NOT play a role in sperm retention of the ejaculate in the female trac:
A. Anatomical region where the sperm are deposited
B. Whether the female is primiparous or multiparous
C. Immunological reaction in the female tract
D. Physical characteristics of the ejaculate
B.
In which one of the following female species the sperm can maintain its fertilization capacity the longest?
A. Bitch
B. Cow
C. Mare
D. Woman
A.
The process whereby spermatozoa are formed. It consists of proliferation (mitosis), meiosis and differentiation.
Spermatogenesis
Animals that display estrous cycles uniformly distributed throughout the year without marked seasonal influence
Polyestrous
Young female cattle up to the birth of first calf or in the lactation following the first calving
Heifer
An animal in the early stages of development that has not taken an anatomical form that is recognizable as a member of a species
Embryo
A peptide synthesized by neurons in the hypothalamus and released by nerve terminals in the posterior lobe of the pituitary. It is also produced by the corpus luteum. It causes contractions in smooth muscle in the male and female reproductive tract and regulates luteolysis
Oxytocin
A decapeptide released from terminals of neurons in the surge and tonic centers of the hypothalamus that causes the release of gonadotropins from the anterior lobe of the pituitary.
GnRH
Erection of the penis involves:
Penile vasodilation, high penile blood pressure
Ejaculation involves contraction of the (choose all that are correct):
A. Bulbospongiosus muscle
B. Retractor penis
C. Ischiocavernosus muscle
A. C.
In which species does the embryo migrate extensively during the period of maternal recognition?
Horse
When the male and female pronuclei fuse, the embryo at this stage is called the:
Zygote
T/F: Low progesterone maintains pregnancy.
False
Match the hormones/process with the relevant information regarding maternal recognition.
CL lifespan similar for cycle and pregnancy
Movements of conceptus
hCG
Interferon tau
Reroutes PGF2a
Bitch
Mare
Woman
Ruminants
Sow
T/F: The blastocyst expand and contracts helping the embryo to hatch from the zona pellucid
True
The first differentiation event in the early embryo refers to the:
Trophoblast and inner cell mass cells form
Interferon-t (IFN-t) is the hormone secreted by the conceptus to prevent luteolysis in:
Cow
Castrated male horse
Gelding
Technique of artificial insemination in which the semen is deposited into the uterus using a pipette to penetrate and bypass the cervix
Transcervical insemination
A steroid hormone produced by corpora lutea and the placenta that is required for the maintenance of pregnancy
Progesterone
A glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary in response to GnRH. It promotes follicular development in the female and Sertoli cell function in the male.
FSH
Specific behavior in the female that promotes copulation, e.g. lordosis, tail deviation and backing toward males
Receptivity
In the dog, what are the dark bands at the margins of the placenta where it attaches to the endometrium called?
Marginal hematomas or pigmented zone (PZ)
In the horse, what two fetal membranes fuse and are attached to the endometrium?
The allantois and the chorion
Are the cotyledon of the bovine placenta convex or concave? Those of the ewe’s placenta?
The cow’s placental cotyledon is convex and the ewe’s is concave.
What is the order of the membranes between the endometrium and the fetus in the mare?
Endometrium
Chorion
Allantois
Amnion
Fetus
What are the contents of the umbilical cord?
Wharton’s jelly, 2 arteries, 1 vein, 1 allantoic duct
What artery provides most of the blood supply to the equine or ruminant mammary gland?
A branch of the external iliac artery, the external pudendal a.
What lymph nodes drain the canine and feline mammary glands? What about horses or ruminants?
Dog/Cat: axillary (and accessory axillary in cats) drains the cranial mammary glands; sternal lymph node can also drain the cranial mammary glands. Caudal mammary glands drained by the superficial inguinal lymph nodes (=mammary lns)
Horses/Ruminants: Superficial inguinal LN (mammary)
How does venous blood drain from the udder of ruminants?
External pudendal vein; milk vein
Which domestic species have two openings at the end of each teat?
Mares and sows
What type of placenta does the cow have?
Cotyledonary and epitheliochorial
What two functions does the acrosomal reaction have regarding fertilization?
Reaction enables spermatozoa to penetrate the zona pellucida
It modifies the equatorial segment so that it can later fuse with the plasma membrane of the oocyte
T/F: Release of acrosomal enzymes allows the spermatozoon to digest its way through the zona pellucida
True
What is the correct oder of the placental membranes between fetus and dam in the cow?
Fetus, amnion, allantois, chorion, endometrium
What happens if a pregnancy is lost after maternal recognition of pregnancy has occurred?
The interestrus interval will be longer than normal
T/F: in the cow, maternal recognition of pregnancy must occur before day 7
False - day 17
What is the average gestation length of bovine?
Ranges from 270-292 days
What is the least invasive placenta type?
Microcotyledonary, epitheliochorial placentation
What hormone does the endometrial cups of the mare secrete?
eCG
Which species is CL dependent for the entire gestation?
Caprine - goat
What are the 3 P’s of parturition?
Presentation, Position, Posture
What is normal fetal orientation position for parturition?
Dorsosacral
The ability of a single cell to give rise to a complete, fully formed individual
Totipotent
What are some clinical sign that suggests the bitch is close to parturition?
Nesting, temperature drop, panting, digging, seclusion, food refusal
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of lochia?
A. Blood-tinged fluid
B. Occurs for days after parturition
C. Malodorous/fetid
D. Physiologically normal in all species
C.
What provides antibodies for the first few days of the neonate’s life?
Colostrum
What influences when the blastocyst hatches?
Growth and fluid accumulation within the blastocyst
Production of enzymes by the trophoblastic cells
Contraction of the blastocyst
What gives rise to the chorion and amnion?
The trophoblast, primitive endoderm, and mesoderm
T/F: Maternal recognition of pregnancy must occur prior to luteolysis
True
In what species does the conceptus make extensive contact with the endometrial surface to initiate and complete maternal recognition of pregnancy?
Equine
What is the functional unit of the placenta?
Chorionic villus
Type of placenta where the endometrial epithelium transiently erodes and then regrows, causing intermittent exposure of the maternal capillaries to the chorionic epithelium.
What species is it found in?
Syndesmochorial
Ruminants
What are 4 hormones produced by the placenta that play a role in gestation?
Progesterone
Estradiol
Lactogen
Relaxin
What two major events do the endocrine changes cause to initiate parturition?
Removal of the myometrial progesterone block = myometrial contractions begin
Increased reproductive tract secretions, particularly by the cervix
T/F: Oxytocin stimulates relaxation of the myometrium
False - contraction
What are the 4 major events during the puerperium?
Myometrial contractions and expulsion of lochia
Endometrial repair
Resumption of ovarian function
Elimination of bacterial contamination of the reproductive tract
What is the difference between milk secretion and milk ejection?
Alveolar cells produce the milk that is then secreted into alveolar lumina passively
Milk ejection is an active mechanism that requires contraction of myoepithelial cells
What ligament links ovary to the end of uterine horn?
Proper ligament of the ovary
What is the method of sexing mice and rats?
Anal genital distance
What signals the physiological events associated with parturition?
Fetal mass approaches the inherent space limitations of the uterus = causes ACTH to be secreted by the fetal pituitary
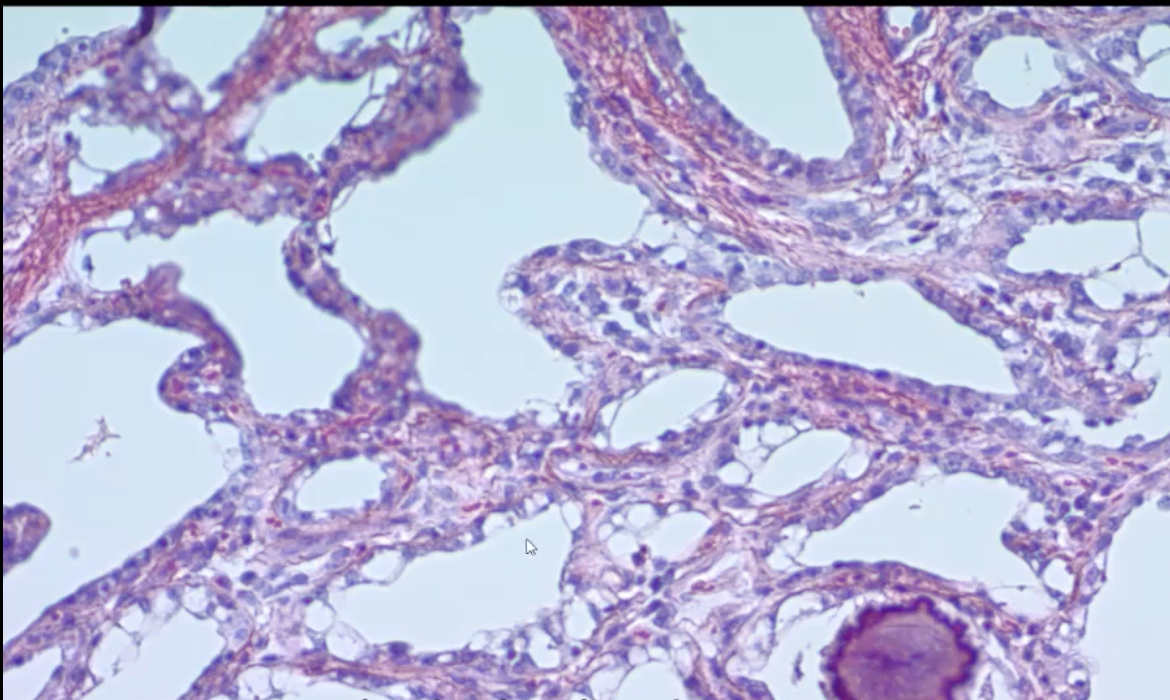
What structure is this from?
Mammary gland - alveoli and corpora amylacea
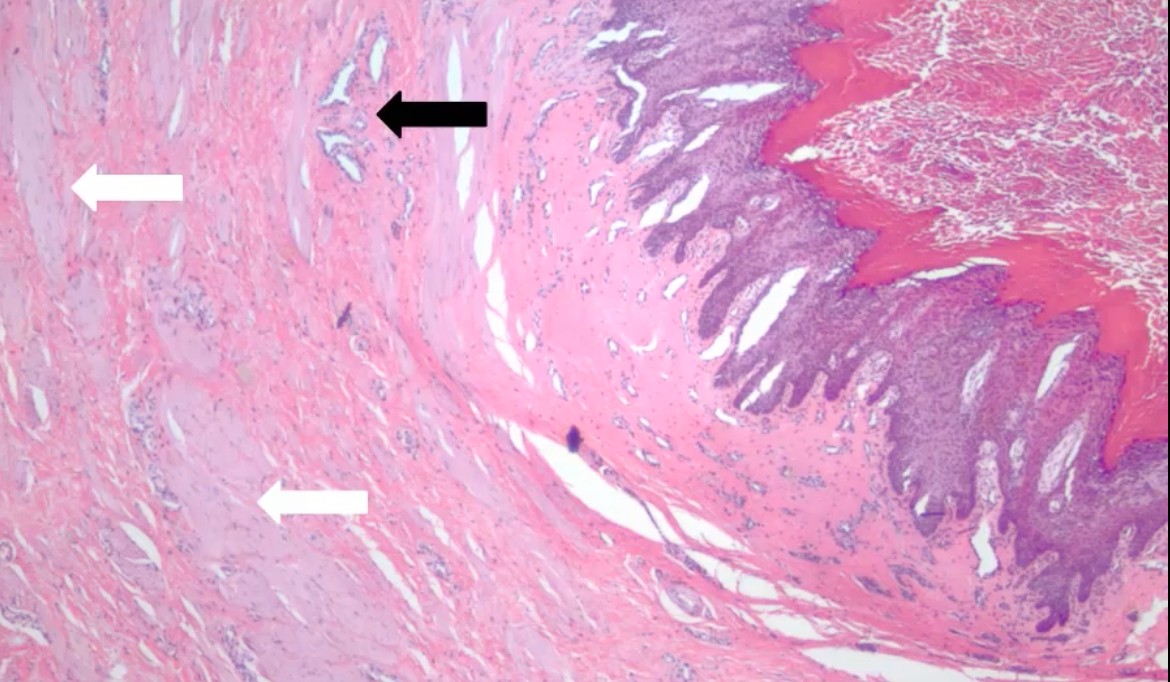
Label the black and white arrows
White - Smooth muscle bundle of teat canal
Black - small glands for secretions
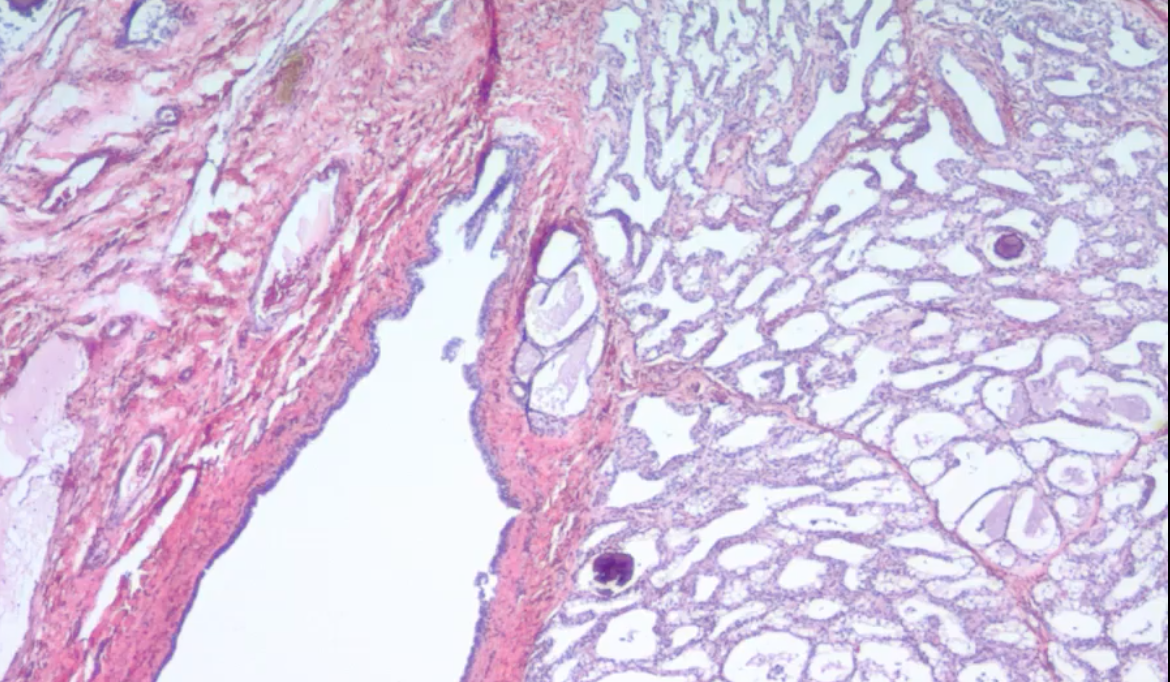
What duct is this? Where does it drain?
Interlobular duct - drains into teat cistern and and collects milk from smaller ducts
In the mammary gland, what does estrogen stimulate?
Ducts and branching