4.2 Epithelial Tissue
What are the 5 functions of epithelial tissue?
Protection, immune defense, secretion, transportation, and sensation
Apical
The apex, or facing the surface of the cell.
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are the 5 functions of epithelial tissue?
Protection, immune defense, secretion, transportation, and sensation
Apical
The apex, or facing the surface of the cell.
Basal lamina
Made of glycoproteins and collagen, lies below the epithelium layer and provides an attachment site.
Reticular lamina
Made by underlying connective tissue, is below the basal lamina and attaches to it. Made of reticular fibers and ground substance.
Basement membrane
Basal and reticular lamina. Anchors underlying blood vessels in place and provides a barrier between epithelia and further underlying tissues.
Tight junction
Hold cells closely together, space in between is impermeable to movement of macromolecules.
Anchoring junction
Help stabilize epithelial tissues, includes desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, and adherens.
Gap junction
Small pores, formed by protein channels, allows substances to flow freely between each cell's cytoplasm.
Squamous
Flattened
Cuboidal
Boxy
Columnar
Tall, rectangular
Microvilli
Finger-like, increases surface area for absorption.
Cilia
Propel substances through hollow organs.
Simple
One single cell layer
Stratified
More than one cell layer
Pseudostratified columnar
Single layer or irregularly shaped and sized columnar cells.
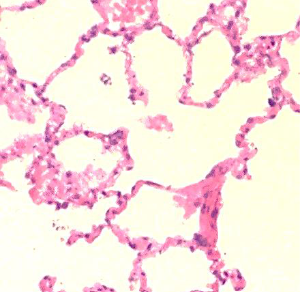
Simple squamous epithelium function
Fried egg appearance, allows for diffusion, filtration, and secretes a lubricating substance.
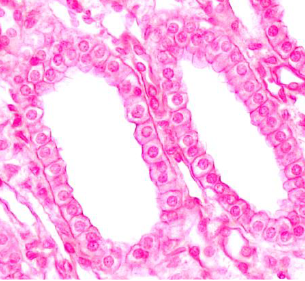
Simple cuboidal epithelium function
Large central nucleus, absorption, secretion, and potentially diffusion.
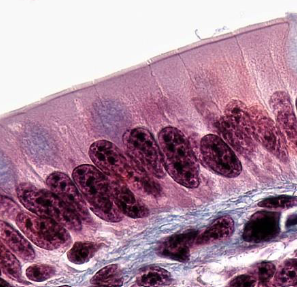
Simple columnar epithelium function
Cilliated or smooth, absorption, secretes mucus and enzymes.
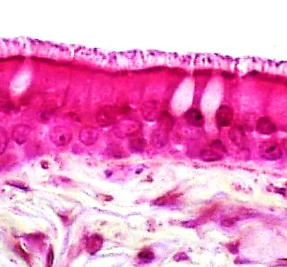
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium function
Nuclei have varied heights, secretes mucus; ciliated tissue moves mucus.
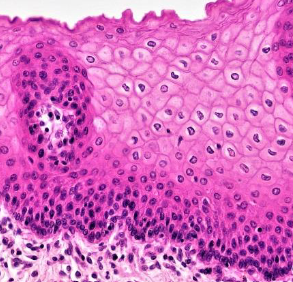
Stratified squamous epithelium function
Protects from abrasion.
Stratified cuboidal epithelium function
Rare, protective tissue.
Stratified columnar epithelium function
Apical is columnar, basal layer is cuboidal, secretes and protects.
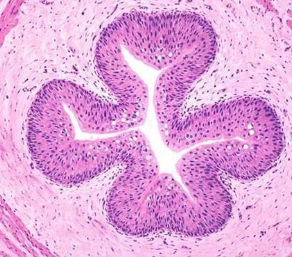
Transitional epithelium function
Dome-shaped, allows for the urinary organs to expand and stretch.
Simple squamous location
Lung air sacs, lining of the heart and blood vessels, kidney tubules and lymphatic vessels.
Simple cuboidal location
Gland ducts, segments of renal tubules, respiratory passages, and the thyroid.
Simple columnar location
Ciliated tissues in larger bronchioles, uterine tubes, and uterus; smooth in the digestive tract and bladder.
Pseudostratified columnar location
Ciliated tissues line the bronchi, trachea, and much of the upper respiratory tract (nasal cavity).
Stratified squamous location
Lines esophagus and mouth.
Stratified cuboidal location
Sweat, salivary, and mammary glands, and ducts.
Stratified columnar location
Male and female urethrae, cornea of the eye and some gland ducts.
Transitional location
Lines bladder, urethra, and the ureters
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Apical cellular layers consist of dead cells, lack nuclei, and covered with keratin.
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Apical layers are alive and retain nuclei.
Gland
Made of epithelia, produces and releases chemical substances.
Endocrine
A method of release into the bloodstream via hormones.
Exocrine
A method of release onto the outside of the body.
Merocrine (Eccrine)
Secretions are enclosed in vesicles and move to the apical surface and released by exocytosis. Found in salivary and sweat glands.
Apocrine
Secretion accumulates near the apical portion and that portion is thin pinched off and released. Found in axillary areas.
Holocrine
The entire gland cell ruptures and explodes. An example is sebaceous glands which secrete sebum.
Unicellular glands
Single cells scattered about, such as goblet cells.
Multicellular (Serous glands)
Form secretory surface that secretes directly into an inner cavity such as the abdomen and chest.
Goblet cells
Common unicellular exocrine gland, found in digestive and respiratory tracts (among columnar epithelial cells). Responsible for secreting mucus.