Higher Biology - Unit 2 - Metabolism and Survival
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/92
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
1
New cards
Define metabolic pathways
sequence of reactions controlled by enzymes that change one metabolite to another
2
New cards
Fill in the blanks: Metabolic pathways can have ________ ______ , _________ ______ , and ___________ _______
Reversible steps, irreversible steps and alternative routes
3
New cards
What is the result of an anabolic reaction within metabolic pathway
Anabolic reactions **build up** large molecules from small molecules and require energy (large to small)
4
New cards
Give an example of an anabolic reaction
Protein synthesis / protein to amino acids
5
New cards
Give an example of a catabolic reaction
Aerobic respiration / Food indigestion
6
New cards
Give an example of how metabolic pathways can be closely linked between each other.
The energy generated by aerobic respiration (catabolic) is used for protein synthesis (anabolic)
7
New cards
Define alternative routes
Alternative routes through a metabolic pathway can exist which bypass stages
8
New cards
Define the purpose of the cell membrane
It controls the flow of materials which enter and exit the cell
9
New cards
Explain the mitochondrion’s membrane
The mitochondrion has a double membrane (inner and outer)
10
New cards
What two molecules make up the membrane
Proteins and phospholipids
11
New cards
What is the purpose of pores embedded in the cell membrane
They allow diffusion of specific molecules across the membrane
12
New cards
What is the purpose of pumps embedded in the cell membrane
To transport molecules against the concentration gradient
13
New cards
What is the purpose of enzymes embedded in the cell membrane
To speed up the rate of biochemical reactions
14
New cards
Define the activation energy
Energy required to initate a reaction - Enzymes decrease it
15
New cards
What effect does adding enzymes to a reaction have on the activation energy needed
It lowers the activation energy
16
New cards
Explain an enzymes induced fit
An induced fit occurs where the active site of the enzyme is changed slightly to better fit the substrate after the substrate binds.
17
New cards
What are two benefits of an induced fit
The active site comes into closer contact with substrate molecules, increases the chance of the reaction taking place
18
New cards
Define the affinity
The tendency for a molecule to bind to an enzyme
19
New cards
What does a low affinity indicate
the product has less of an attraction, this indicates the enzyme and substrate have separated
20
New cards
Define a competitive inhibitor
Binds at the active site preventing the substraye from binding
21
New cards
Define a non-competitive inhibitor
Binds away from the active site so changes the shape of the active site preventing the substrate from binding
22
New cards
Explain the effect of a feedback inhibitor
The end product in the metabolic pathway reaches a critical condition. This slows down the reactions in the pathway
23
New cards
Metabolism
All chemical reactions that occur within an organism
24
New cards
Define metabolic rate
The quantity of energy consumed by an organism per unit of time is called its metabolic rate
25
New cards
Compare bird and mammal metabolic rates to reptiles, amphibians and fish
Birds and mammals have higher metabolic rates
26
New cards
Describe a bird and mammals circulatory system
These organisms have a complete double circulatory system
27
New cards
What is a complete double circulatory system
A double circulatory system is a system in which there is no mixing off oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Blood can also be pumped at a higher pressure
28
New cards
Describe advantages of double circulatory systems
More advanced
29
New cards
Where does the citric acid cycle take place
The matrix of the mitrochondria
30
New cards
Describe an amphibian and reptiles circulatory system
These organisms have an incomplete double circulatory system
31
New cards
Why are systems described as incomplete
Because there is only one ventricle and some mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood occurs
32
New cards
Describe a fish circulatory system
These organisms have a single circulatory system
33
New cards
What circulatory system is this
A complete double circulatory system
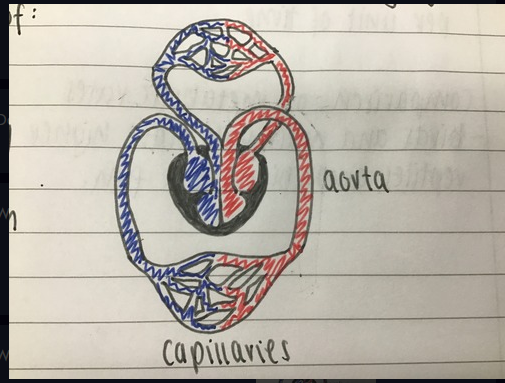
34
New cards
What circulatory system is this
An incomplete double circulatory system
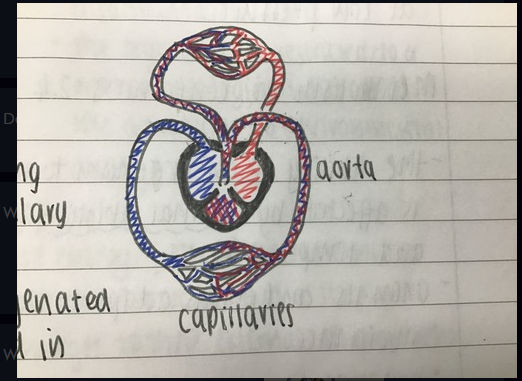
35
New cards
What circulatory system is this
A single circulatory system
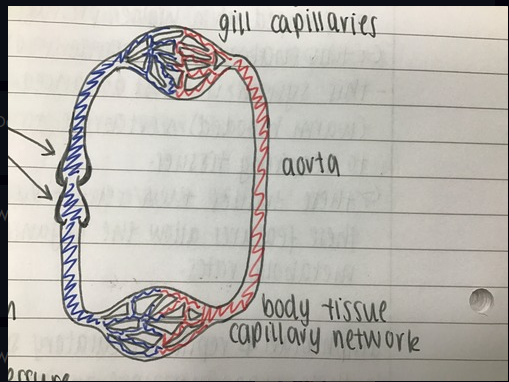
36
New cards
Define conformers
Organisms whose internal environment is dependent on their external environment.
37
New cards
Define regulators
Maintains their internal enviroment regardless of external enviroment
38
New cards
What is a conformers advantange?
Low metabolic cost - saves energy
39
New cards
What is a conformers disadvantage?
Restricted to a narrow ecological niche
40
New cards
What is a regulators advantage?
Wide range of ecological niche
41
New cards
What is a regulators disadvantage?
High metabolic cost
42
New cards
Define homeostasis
When an organism maintains a constant internal environment regardless of the external environment
43
New cards
What is the purpose of the hypothalamus
The temperature monitoring centre of the brain
44
New cards
Define thermoregulation
The process of maintaining your core internal temperature.
45
New cards
Describe the process of sweating
Body heat is used to evaporate water in sweat this cools the skin
46
New cards
Describe the process of vasodilation
Blood capillaries in the skin dilate increasing blood flow to the skin, this increases the heat loss by radiation
47
New cards
What are the body’s thermoregulatory responses to heat the body up
Shivering, vasoconstriction of blood vessels, increase in metabolic rate and action of hair erector muscles
48
New cards
Describe the process of shivering
Rapid involuntary contraction of skeletal muscles which generate heat
49
New cards
Describe the process of vasoconstriction
Blood capillaries in the skin constrict this decreases blood flow to the skin and decreases heat loss by regulation
50
New cards
Describe the process of hair erector muscles
muscles in the skin contract, hair stands up which traps an insulating layer of air between the hair and skin
51
New cards
What are the body’s thermoregulatory responses to cool the body down.
Sweating, Vascodilation, Decrease in metabolic rate
52
New cards
Describe the process of sweating
Body heat is used to evaporate water in sweat, this cools the skin
53
New cards
Describe the process of vasodilation
Blood capilaries in the skin dialate increasing blood flow
54
New cards
Describe how decreased metabolic rate cools the body
Metabolic reactions generate heat.
55
New cards
Define cellular respiration
A series of metabolic pathways that releases energy from food.
56
New cards
What is the key role of ATP in cells
To transfer energy to cellular processes which require energy
57
New cards
Define fermentation
In the absence of oxygen, fermentation takes place. This does not generate ATP after glycolysis
58
New cards
What is more efficient fermentation or aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is more efficient and results in more ATP being produced
59
New cards
What happens in fermentation in animals
Pyruvate is converted to lactate in a reversible reaction (glucose - pyruvate - lactate)
60
New cards
What happens in fermentation in plants
Pyruvate is converted to ethanol and CO2 in an irreversible reaction (glucose - pyruvate - ethanol + CO2)
61
New cards
What is osmoregulation
The control of water concentration in the blood
62
New cards
Define oxaloacetate
Substance that combines with the acetyl group in citric acid cycle to form citrate
\
\
63
New cards
Explain the function of dehydrogenase enzymes
Enzymes which remove hydrogen from its substrate
64
New cards
Define homeostasis
Maintenance of a steady state in the cells of a living organism
65
New cards
Define aestivation
Dormancy in a response tp high temperatures or drought
66
New cards
Describe dormancy
Where animals in response to adverse conditions try to survive.
67
New cards
Describe Migration
During a period of adverse conditions the organism will avoid this by migrating
68
New cards
Define consequential dormancy
Dormancy that occurs in response to the onset of adverse conditions
69
New cards
Give an example of dormancy
Hibernation, aestivation
70
New cards
Define daily torpor
period of reduced activity with organisms with high metabolic rates.
71
New cards
Define extremophile
Organism that lives in an environment with extreme abiotic conditions
72
New cards
Define hibernation
Response by an animal to avoid adverse conditions by reduction of metabolic rate
73
New cards
Name techniques used to study long distance migration
Tagging, radio observation,capture and release, direct observation
74
New cards
The ability to migrate is either _______ or ______
innate or learnt behaviour
75
New cards
Define innate behaviour
Unlearned instinctive behaviour
76
New cards
Define learned behaviour
Behaviour of an individual organism not common to all members of its species and which is acquired by experience
77
New cards
Define predictive dormancy
Dormancy that occurs before the onset of adverse conditions
78
New cards
What are the three domains of life?
Bacteria, Archaea,Eukaryota
79
New cards
Define Lag Phase
Little to no change in number of microbites.
80
New cards
Define exponential phase
Growth phase of microorganisms involving a rapid geometric increase in numbers
81
New cards
Describe Stationary Phase
(Secondary substances made) Nutrients in culture become depleated and toxic metabolites are produced
82
New cards
Define death phase
Lack of nutrients are in the culture medium
83
New cards
Define secondary metabolite
Substance produced during stationary phase of growth of a culture of microorganisms
84
New cards
Define sterile
Not containing contaminating microorganisms
85
New cards
Define viable cell count
Number of live cells from total cell count
86
New cards
What is an example of a eukaryote microorganism
Algae, yeast and slime moulds
87
New cards
What is an example of a bacteria microorganism
E. Coil and staphylococcus aureus
88
New cards
What is an example of a archaea microorganism
Methanogens and thermophiles
89
New cards
How can sterility be controlled
steam and filters are used. This reduces competition with desired micro-organisms for nutrients and reduce risk of spoilage
90
New cards
How can temperature be controlled
Water jackets and a thermostat are used to monitor and control temperature, this keeps enzymes at their optimum temperature
91
New cards
How can oxygen levels be controlled
Air inlets and paddles are used for aeration, this allows aerobic respiration to occur
92
New cards
What two methods must you use to improve the strain when working with microoganisms
Mutagenesis and Recombiant DNA
93
New cards
What are the two types of Mutagenic agents
radiation and chemical