Ch. 14 Soils
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is soil composed of?
Soil is composed of living organisms, water, mineral matter, humus and air.
What is humus?
Humus is a dark, jelly-like substance that is rich in nutrients. It forms when dead plants and leaves decay on top of the soil in a process called humification. Living organisms then mix this material through the soil. Humus helps bind soil together, and increases the fertility of soil.
What is mineral matter?
Mineral matter comes from bedrock that has been broken down by the processes of weathering and erosion. It helps nourish plants that grow in the soil.
Describe how bedrock, climate and relief influence how soil forms.
Bedrock provides minerals for soil, with hard rocks breaking down slowly and soft rocks quickly. Climate affects weathering and soil types: cold areas form thin soils, hot areas form deeper ones, wet areas experience leaching, and dry areas have hard, impermeable soil. Relief influences soil too, with highlands having wetter, less fertile soils and lowlands having deeper, more fertile soils.
How can human activity affect the quality of soil?
Human activity impacts soil quality and composition. Practices like ploughing, irrigation, and fertiliser use can enhance soil fertility. However, removing vegetation and overusing soil depletes its nutrients, reducing fertility and potentially leading to soil erosion.
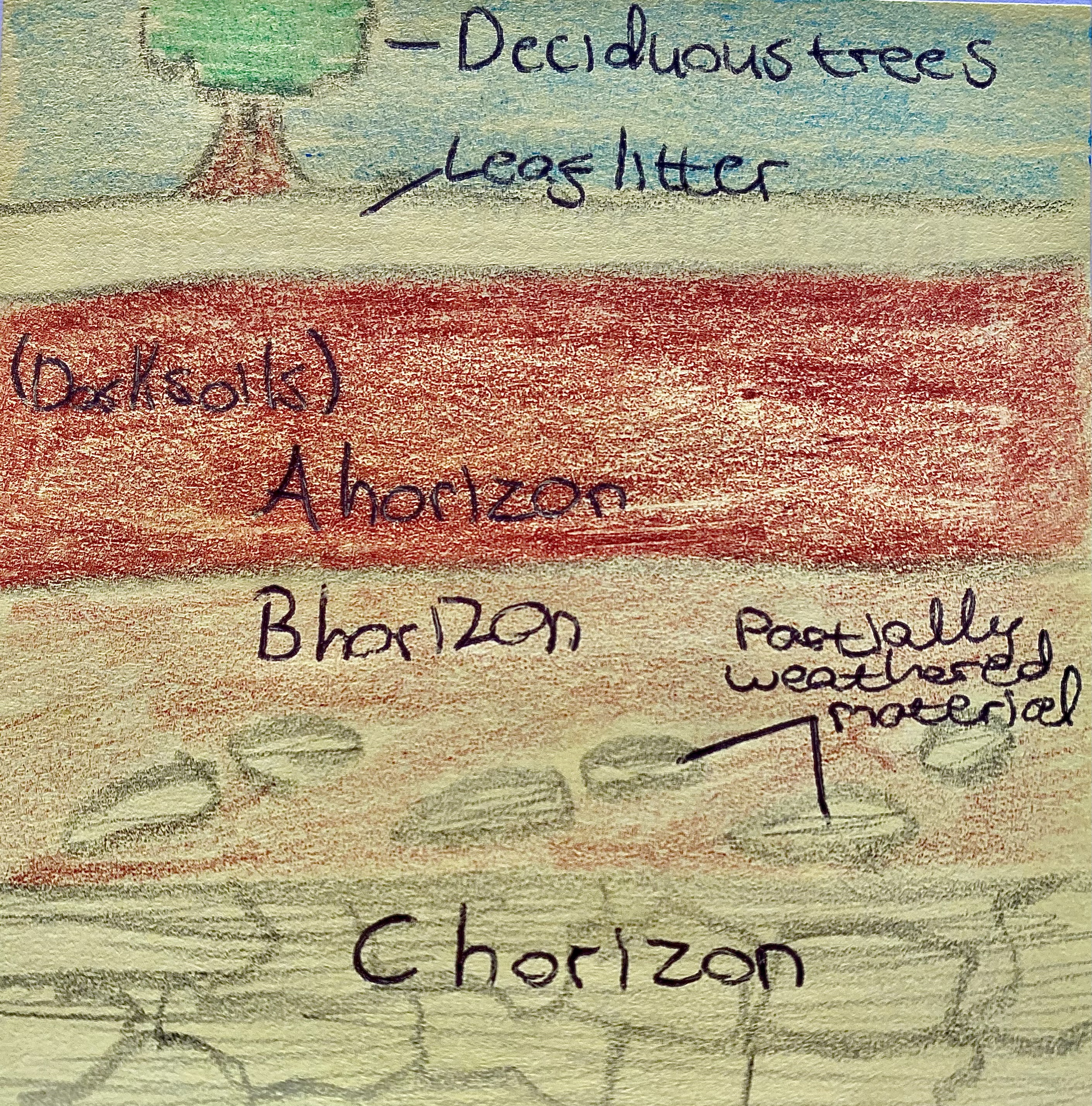
Describe the soil profile for brown soils with a diagram.
Brown soils, or brown earths, form in well-drained lowland areas once covered by deciduous forests, where leaf litter creates rich humus. They develop in regions with moderate rainfall, preventing leaching and keeping nutrients in the A horizon. This makes the soil fertile, ideal for crops and grazing. Brown earths are common in Ireland’s midlands, south, and east.
Describe 4 points on how human activity impacts soils.
Overgrazing by animals removes plant cover, exposing soil to wind and rain, which leads to soil erosion.
Overcropping and monoculture deplete soil nutrients, reducing fertility and causing erosion, especially where farmers can’t afford fertilisers.
Deforestation for wood and farming leaves soil bare and weakens it, increasing the risk of erosion from weather and poor farming practices.
Climate change causes extreme weather like floods and droughts, leading to soil erosion and desertification in areas like the Sahel in Africa.
Give 3 causes of desertification and the definition.
Desertification is the process where fertile land becomes dry and barren, turning into desert. It is causes by factors including climate change, overgrazing and deforestation.
Climate change causes less rain, making areas like the Sahel drier and drier, killing plants and leaving nothing but desert.
Overgrazing of soil causes erosion, exhausting the soil and leading to crop failure.
Deforestation causes desertification as it strips a protective layer of tree and leaves the soul venerable to erosion.
Give 3 solutions to desertification.
Planting trees – Trees protect the soil from erosion and help retain moisture.
Improving farming methods – Using crop rotation, compost, and less intensive grazing keeps soil healthy and fertile.
Water management – Building small dams or using drip irrigation helps conserve water and reduce land drying out.