G4 - River Landscapes
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
What is erosion?
The process that wears away the river bed and banks.
Types of erosion
Hydraulic action
Abrasion
Attrition
Solution
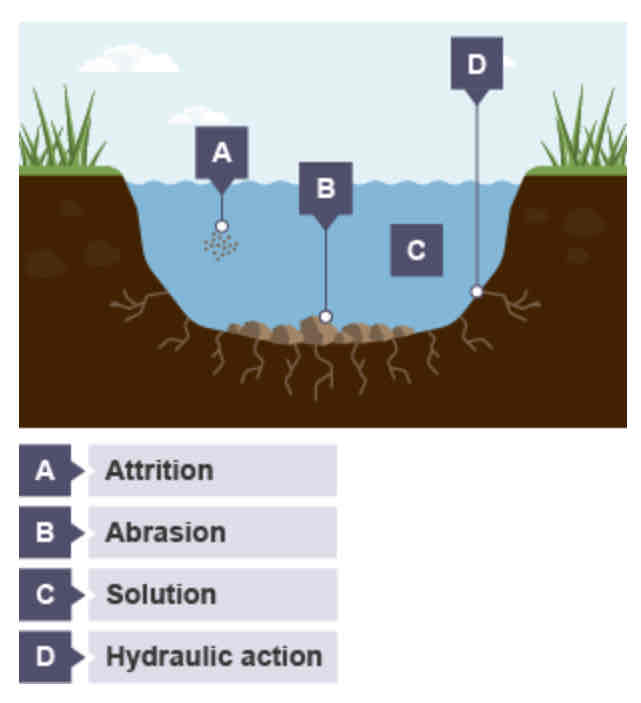
Hydraulic action
This is the sheer power of the water as it smashes against the river banks. Air becomes trapped in the cracks of the river bank and bed, and causes the rock to break apart.
Abrasion
When pebbles grind along the river bank and bed in a sand-papering effect.
Attrition
When rocks that the river is carrying knock against each other. They break apart to become smaller and more rounded
Solution
When the water dissolves certain types of rocks, eg limestone.
What is transportation?
When the river picks up sediment and carries it downstream in different ways.
Types of transportation
Traction
Saltation
Suspension
Solution
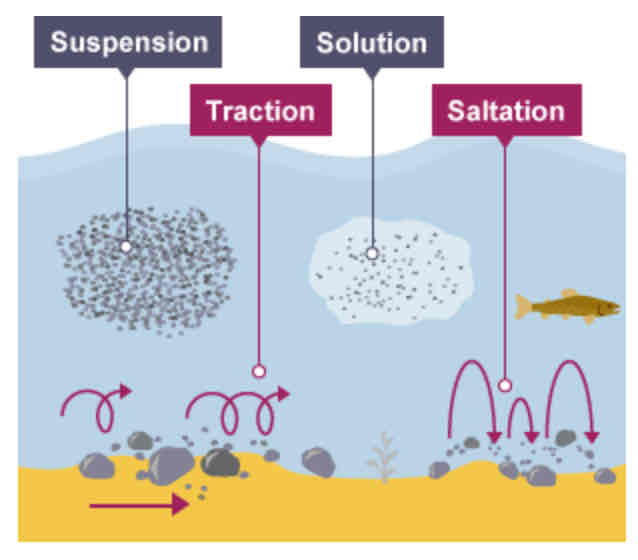
Where is traction most common?
Near the source of a river, as here the load is larger.
Saltation
Pebbles are bounced along the river bed.
Where is saltation most common?
Near the source of the river.
Suspension
Lighter sediment is suspended (carried) within the water.
Where is suspension most common?
Near the mouth of the river.
Solution
The transport of dissolved chemicals.
Where is solution most common?
Varies along the river depending on the presence of soluble rocks.
What is deposition?
When the river loses energy, it drops any of the material it has been carrying.
What factors lead to deposition?
shallow water
at the end of the river's journey, at the river's mouth
when the volume of the water decreases
Drainage basin
The area of land around the river that is drained by the river and its tributaries.
What are the key words when labelling a river?
Drainage basin
Watershed
Source
Mouth
Confluence
Tributary
Channel
Dark wizards snatched many concerning thugs continuously.
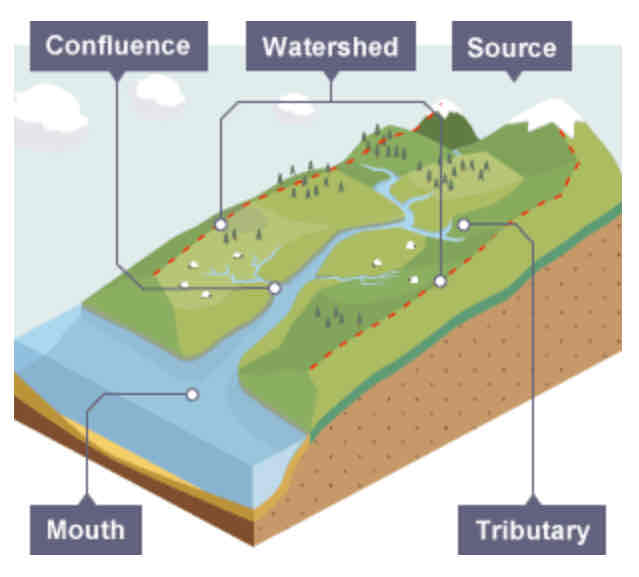
Source
Where a river begins.
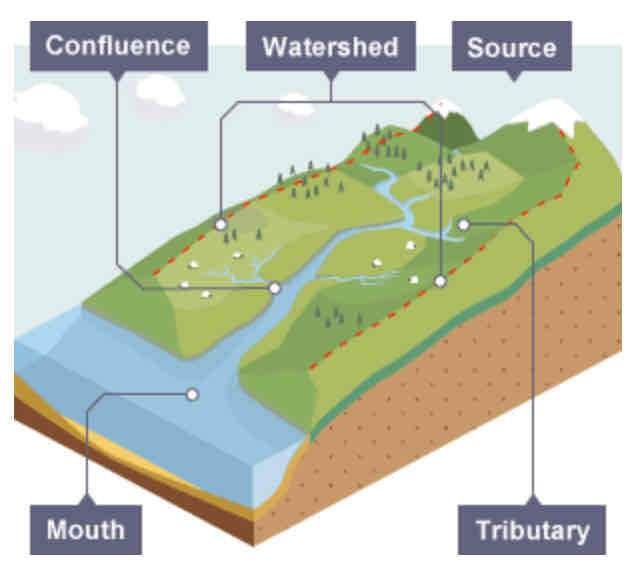
Mouth
Where a river meets the sea.
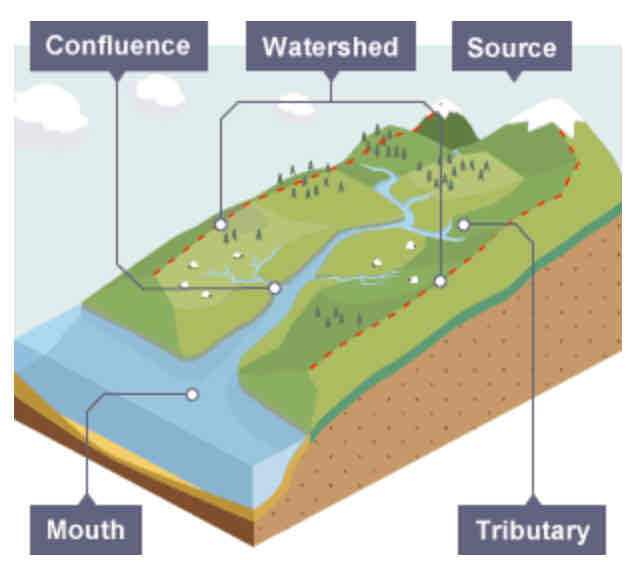
Confluence
The point at which two rivers meet.
Tributary
A small river or stream that joins a larger river.
Channel
Where the river flows.
What is a long profile?
A section/line of the course of a river drawn from source to mouth.
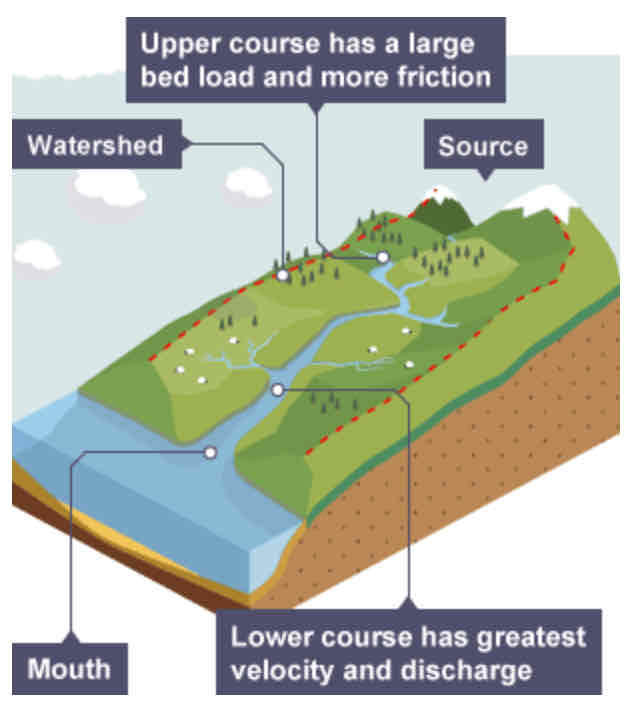
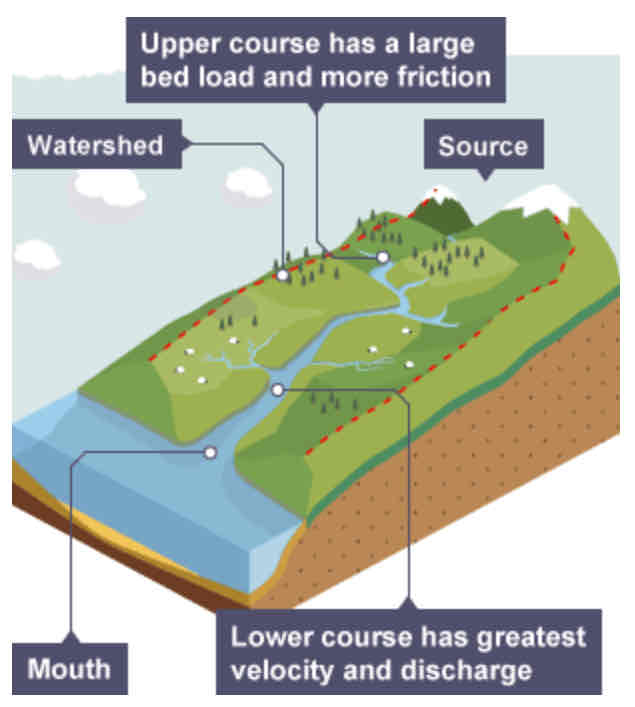
What does a long profile show?
It shows how the river changes over its course.
What is the terrain like in the upper course?
Often an upland area.
What is the load like in the upper course?
The river's load is large in the upper course, as it hasn't been broken down by erosion yet.
What is the terrain like in the lower course?
The land is a lot flatter.
What is the load like in the lower course?
The river's load is fine sediment, as erosion has broken down the rocks.
What is a cross profile?
A cross-section of the valley and channel of a river, at a certain point along the river’s course.
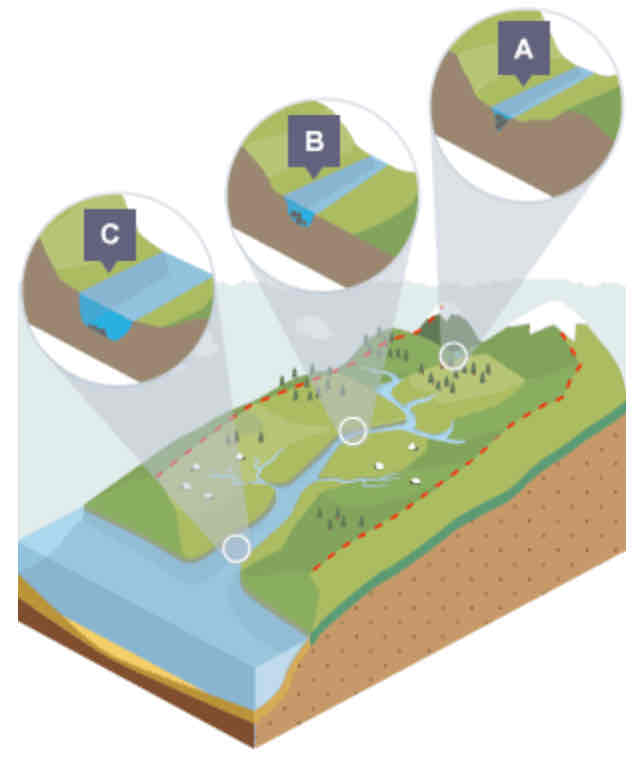
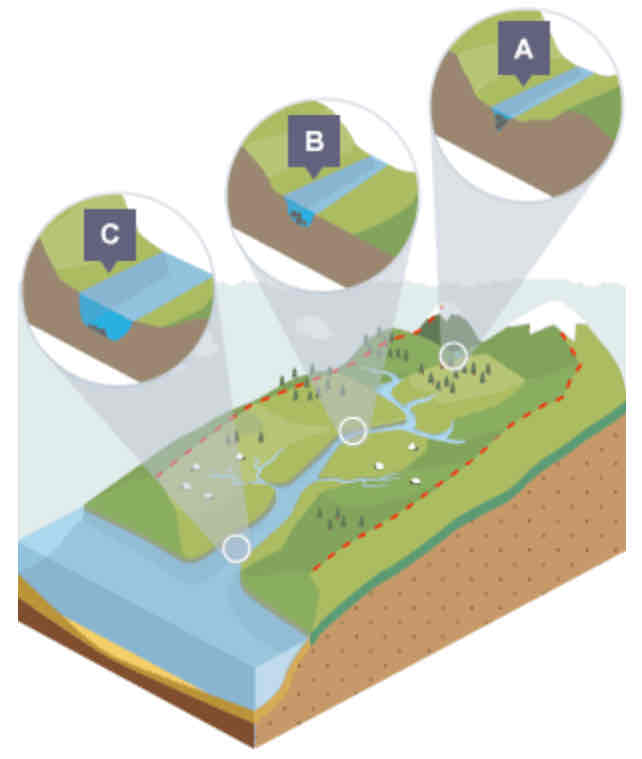
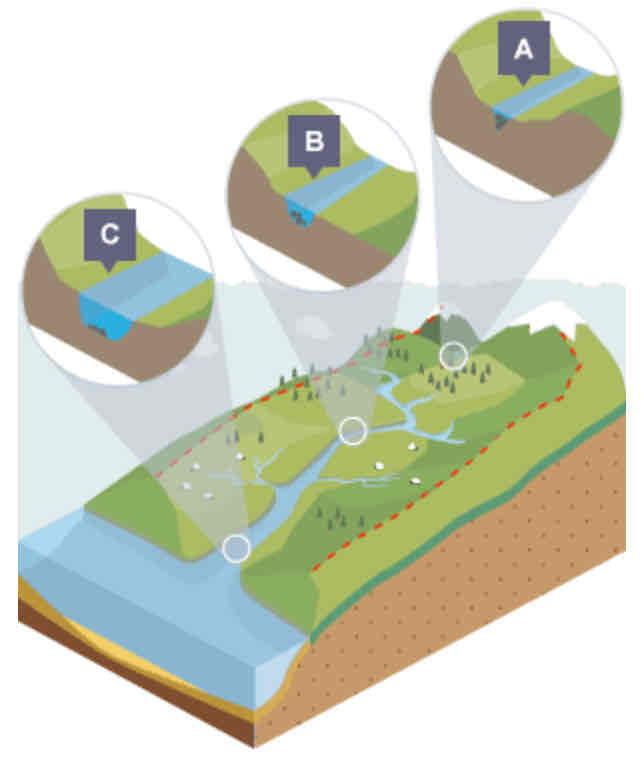
What is shown in the cross profile at point A?
In the upper course…
Not a lot of water in channel
Channel is shallow and narrow as a result
Some increase in vertical erosion
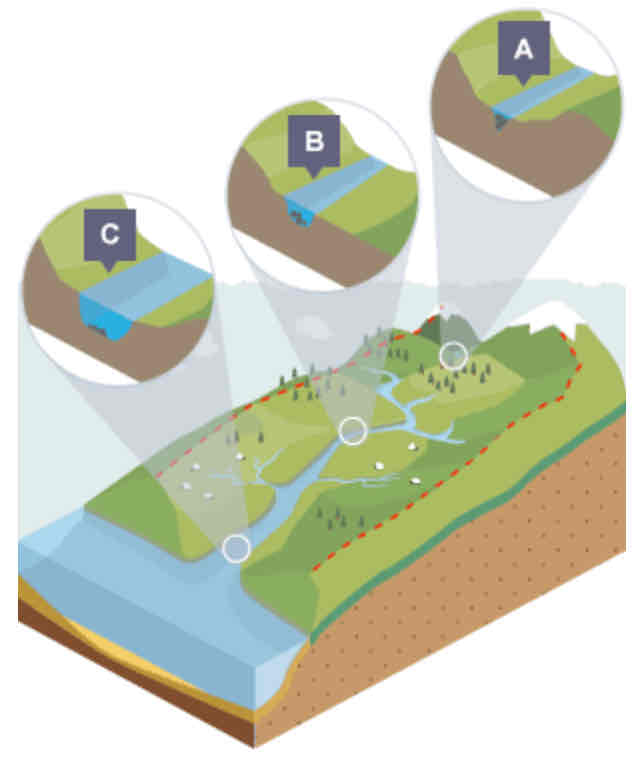
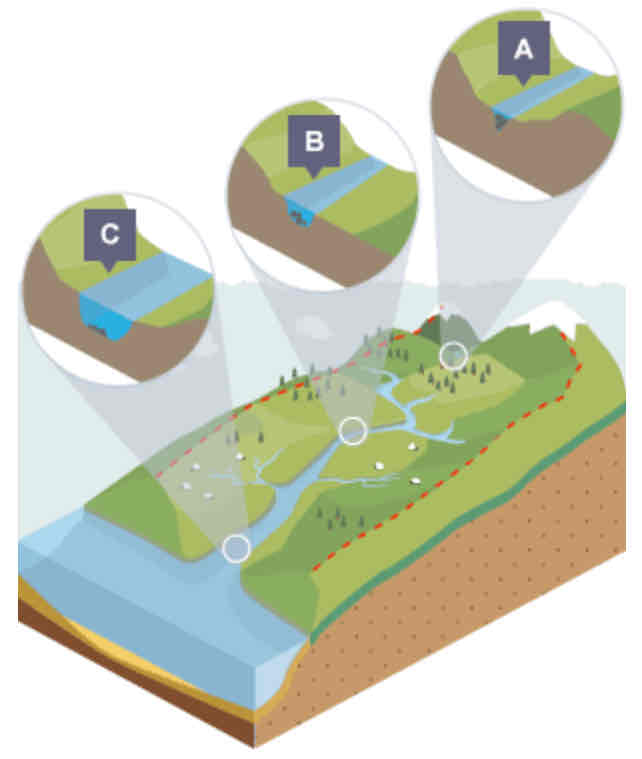
What is shown in the cross profile at point B?
In the middle course…
Some vertical erosion
More lateral erosion
Channel is wider and deeper as a result
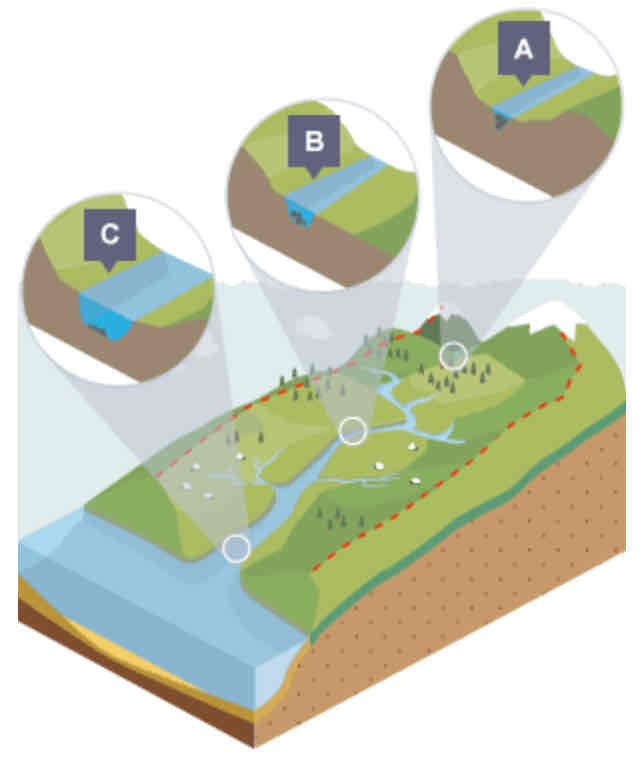
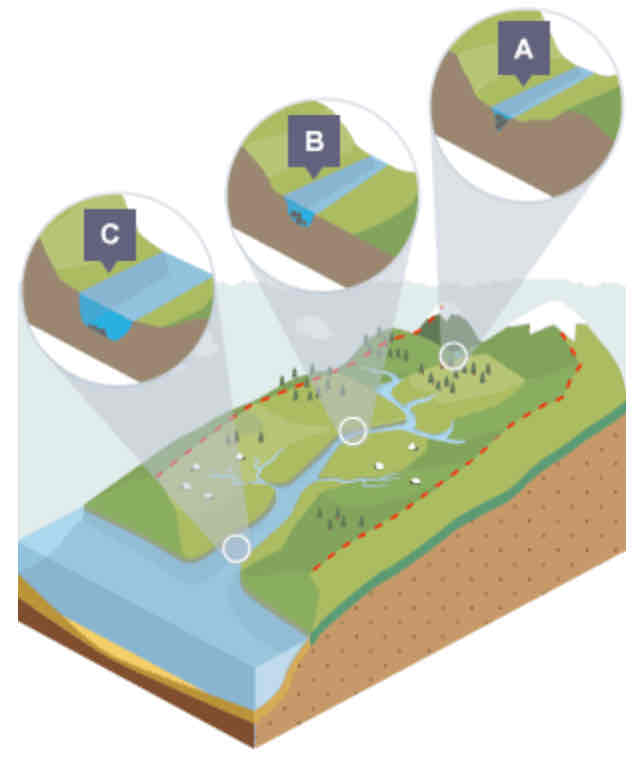
What is shown in the cross profile at point C?
In the lower course…
Lot less erosion
Only some lateral erosion
Channel is at its widest and deepest
What creates different river landforms?
Erosion
Deposition
Where are the erosional features usually found?
Upper course
What are the landforms found in the upper course?
Waterfalls
Gorges
Interlocking spurs
What is a waterfall?
A suden drop along the river course.
Where does a waterfall form?
When there are horizontal bands of resistant rock (hard rock) positioned over exposed, less resistant rock (soft rock).
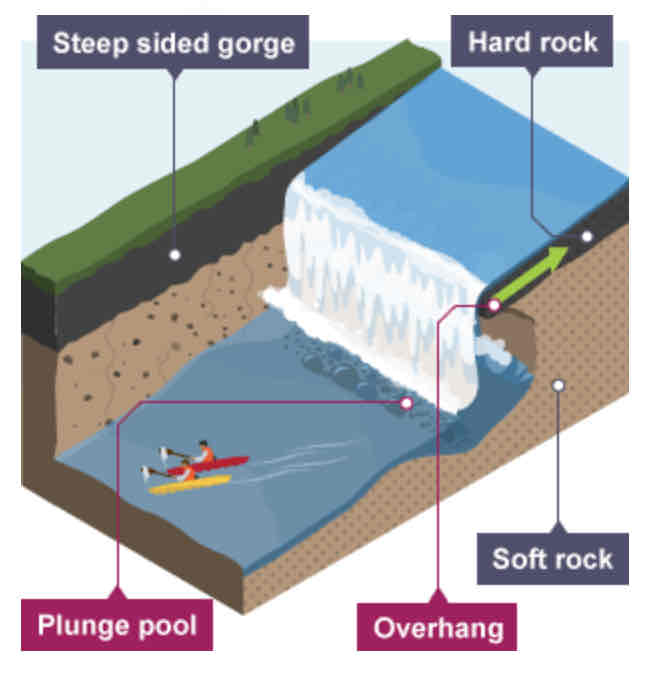
Waterfall formation: step-by-step (6)
The soft rock is eroded quicker than the hard rock, creating a step.
As erosion continues, the hard rock is undercut, forming an overhang.
Abrasion and hydraulic action erode to create a plunge pool.
Over time this gets bigger, increasing the size of the overhang until the hard rock is no longer supported and it collapses.
This process continues and the waterfall retreats upstream.
A steep-sided valley is left where the waterfall once was. This is called a gorge.
What is a gorge?
A deep, narrow passage that usually has a river running through it.
What kind or erosion is usually found in the upper course?
Vertical erosion / gravitational erosion
Vertical erosion
Land is eroded in a downwards direction due to gravity.
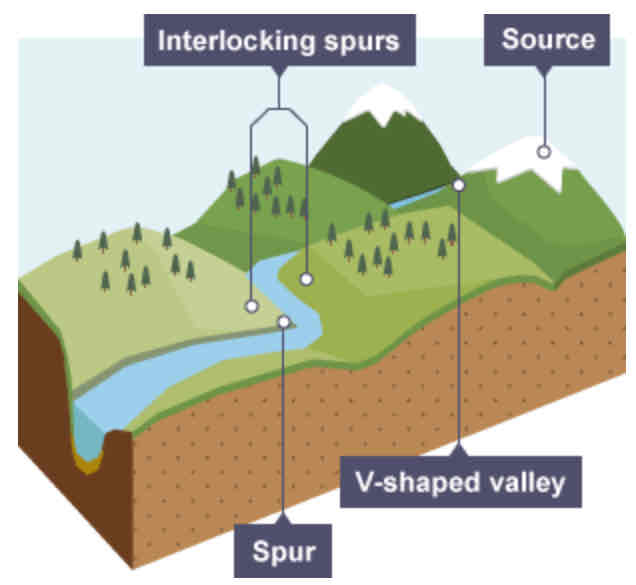
How do interlocking spurs form?
The river cuts down into the valley due to vertical erosion. If there are areas of hard rock which are harder to erode, the river will bend around it. This creates interlocking spurs of land which link together like the teeth of a zip.
What are the landforms found in the middle course?
Meanders
Slip-off slopes
River cliffs
Oxbow lakes
What is a meander?
A bend in the river.
The energy of the river increases/decreases in the middle course.
Explain why.
increases
Because it gains more water, and therefore more energy.
What type of erosion causes the river to become deeper?
Vertical erosion
In the upper course, vertical erosion forms a __-______ valley.
V-shaped
What type of erosion causes the river to become wider?
Lateral erosion
Why is the river wider in the middle course?
increased lateral erosion
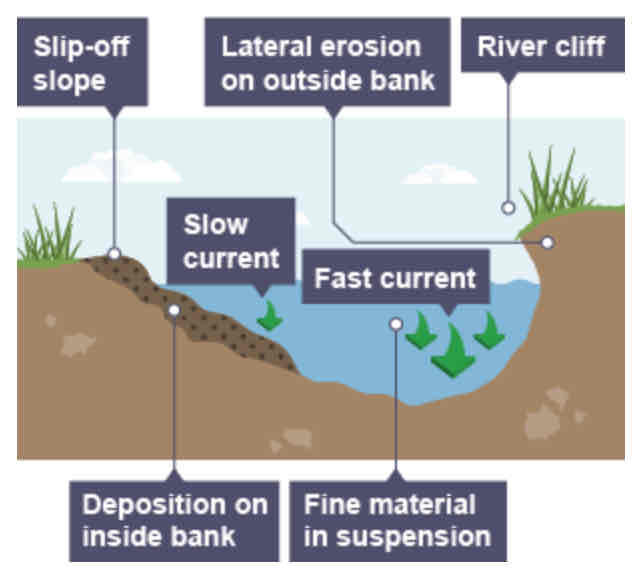
Slip-off slope formation: step-by-step (4)
As a river goes around the bend, most of the water is pushed towards the outside, so increased speed and erosion.
Lateral erosion on outside bend causes an undercutting of the bank, forming river cliff.
Water on the inner bend is slower, so water slows down and deposits the eroded material, forming a gentle slip-off slope of sand and shingle.
How does a meander form?
Continuous erosion on the outer bend and deposition on the inner bend forms a meander. This is because the after is fastest flowing on the outside bend, and therefore the rate of erosion is greatest there.

Does the shape of a meander stay the same?
No - due to erosion on the outside of a bend and deposition on the inside, the shape of a meander will become more curved.
How does an oxbow lake form?
As the meander becomes more curved, erosion narrows its neck, and the meanders move closer together. When there is a very high discharge (eg. flood), the river cuts around the neck, taking a new, straighter and shorter route. Deposition will occur to cut off the original meander, leaving a horseshoe-shaped oxbow lake.
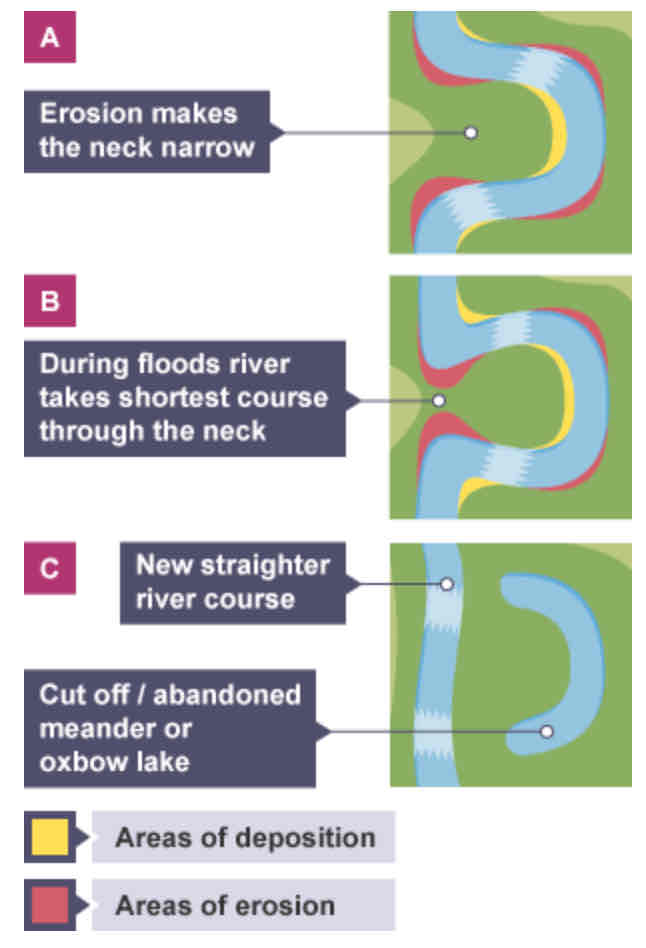
Do oxbow lakes last forever?
No - eventually they get filled with sediment.
What landforms occur in the lower course?
Floodplains
Levees
Estuaries
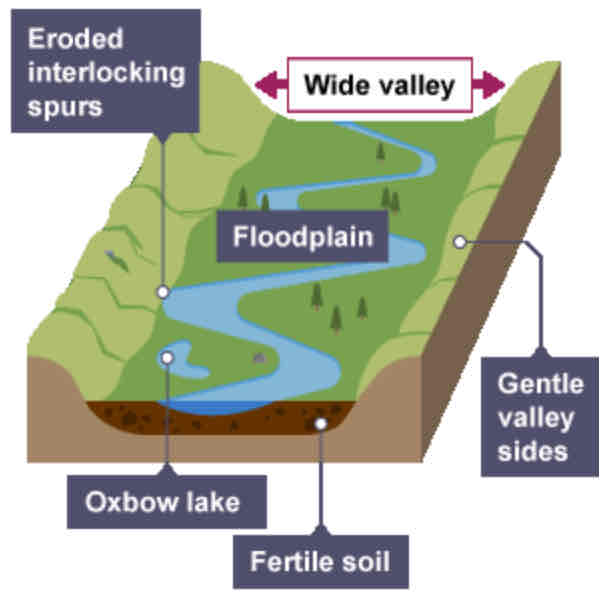
What is a floodplain?
An area of low-lying land next to a river which is prone to flooding. It is covered in water when a river bursts its banks.
What processes cause floodplains to form?
Erosion
Deposition
How does a floodplain form?
Erosion removes any interlocking spurs to create a wide, flat area on either side of the river
During a flood, material carried by river is deposited (as river loses speed and energy).
Over time, the height of the floodplain increases as material is deposited on either side of the river.
What are the benefits of floodplains?
Made up of alluvium, so they are very fertile and can be used for agriculture.
What is alluvium?
The sediment deposited by rivers. Also known as silt.
Why are floodplains wide?
Because of meanders shifting along the valley.
When do levees occur?
In the lower course, when there is an increase in the volume of water flowing downstream and flooding occurs.
Levees formation: step-by-step
Sediment that has breen eroded further upstream is transported downstream.
When the river floods, the sediment spreads out across the floodplain.
When a flood occurs, the river loses energy.
The largest material is deposited first on the sides of the river banks.
The smaller material is deposited further away.
After many floods, the sediment build is up to increase the height of the river banks, so that channel can carry more water (greater discharge) and flooding is less likely o occur in the future.
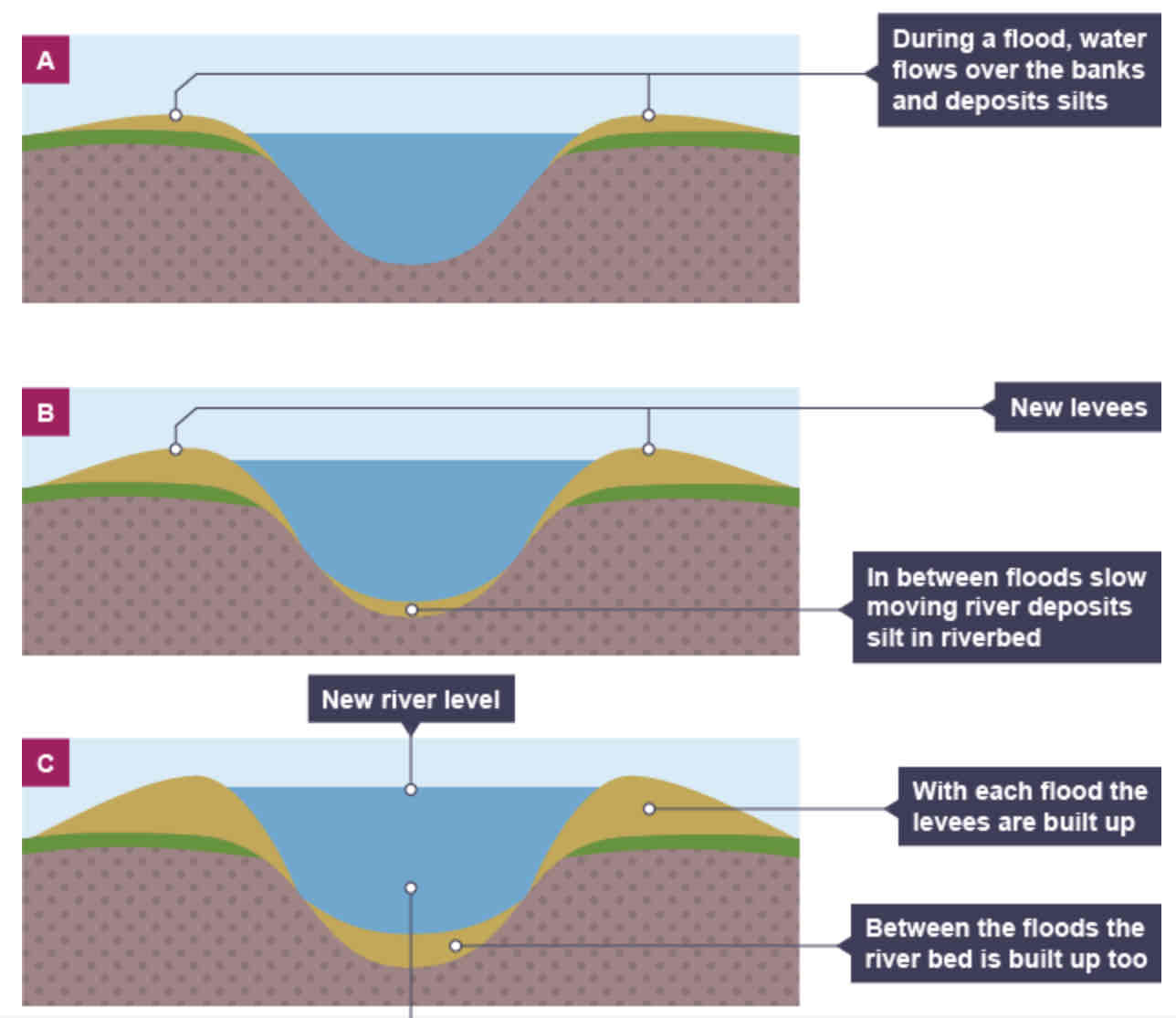
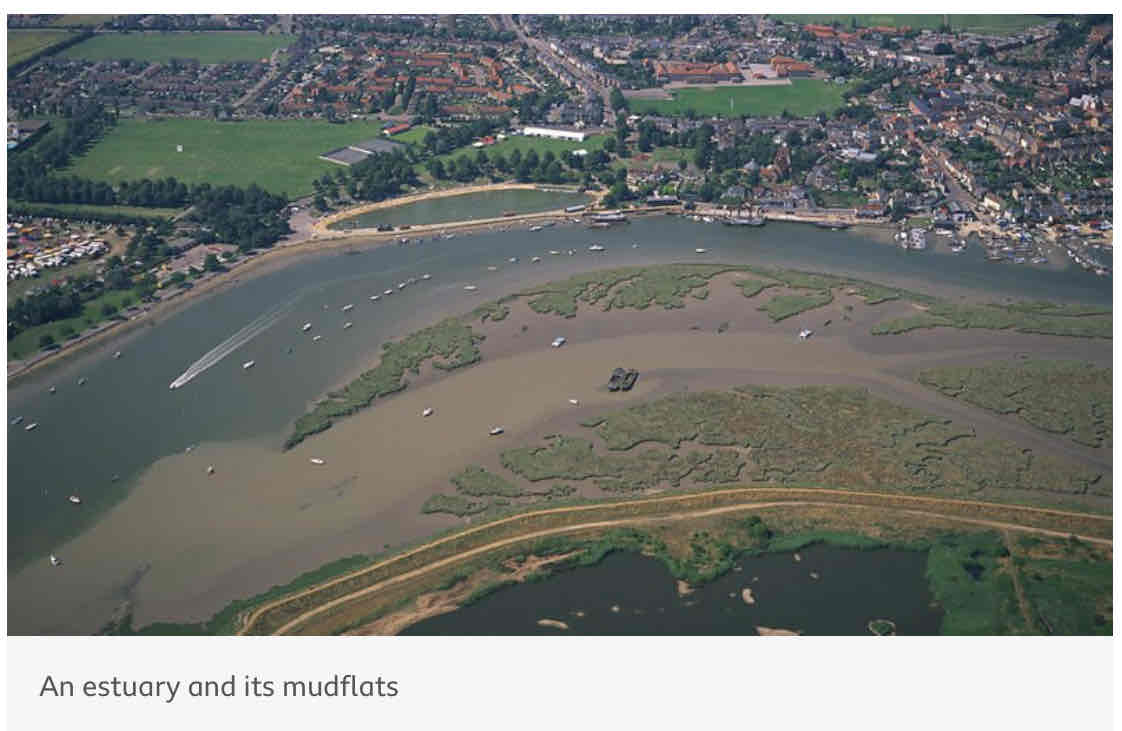
What is an estuary?
The open mouth of the river where it meets the sea.
The river at an estuary is _____.
tidal
What happens to the estuary when the sea retreats?
The volume of water in the estuary is reduced. As there is less water, the river deposits silts to form mudflats, which are an important habitat for wildlife.

What is the case study for river processes?
The River Tees
River Tees - Location
Located in the North of England. The source is located in the Pennines and it flows east to its mouth, where the river joins the North Sea.
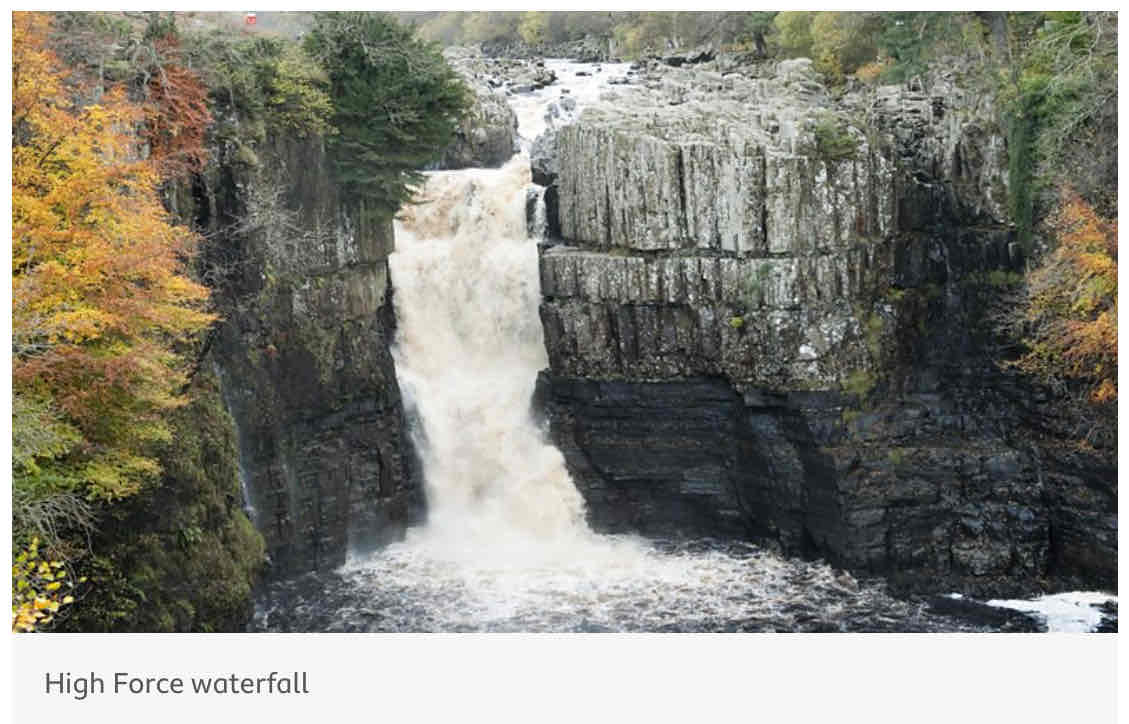
Upper Course of River Tees - key features (5)
Hard impermeable ricks
V-shaped valley
‘High Force’ waterfall
Area of hard rock: Whinstone (at the top of waterfall)
Area of soft rock: sandstone and shale

Middle Course of River Tees - key features (1)
Meanders near Barnbard Castle
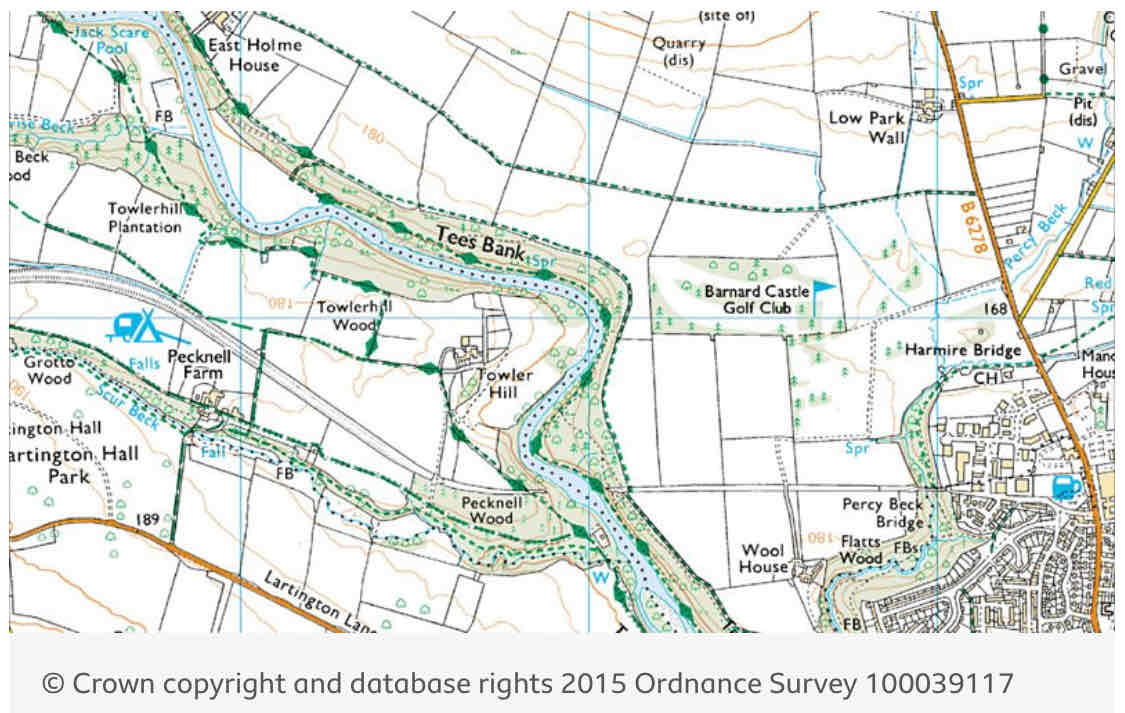
Lower Course of River Tees - key features (3)
Oxbow lakes, levees and much larger meanders near Yarm.
Very large estuary with mudflats and sandbanks, supporting area’s wildlife.
Sites such as Seal Sands are protected areas.

When does flooding occur?
When a river bursts its banks and overflows onto the surrounding land.
What are the 2 categories which flood causes fit into?
natural/physical
human
Physical Flooding Causes
Saturated soil
Heavy rainfall
Relief
Geology
How does saturated soil cause flooding?
The land around the river becomes saturated during prolonged periods of rainfall.
This means more rainfall cannot be soaked up, and surface run-off occurs into the river.
How does heavy rainfall cause flooding?
Heavy rainfall beans a smaller chance for infiltration, so ti runs into the river. The faster the water reaches the river, the more likely it will flood.
How does relief cause flooding?
A steep valley is more likely to flood than a flatter valley becase the rainfall will run off into the river more quickly.
How does geology cause flooding?
Permeable rocks allow water to pass through pores and clacks, whereas impermeable rocks do not. If a valley is made up of impermeable rich, there is a higher chance off flooding as there is an increase in surface run-off.
Human Flooding Causes
Deforestation
Urban land use
How does deforestation cause flooding?
Trees and plants intercept and absorb water, thereby reducing flood risk. Deforestation increases the flood risk as the water will flow into the river rather than being intercepted.
How does urban land use cause flooding?
When an area surrounding a river is built on, there is an increase in the amount of tarmac and concrete, which are impermeable surfaces. Drains and sewerage take water directly the river, increasing flood risk.
What is a hydrograph?
A graph to show how a river responds to a period of rainfall.
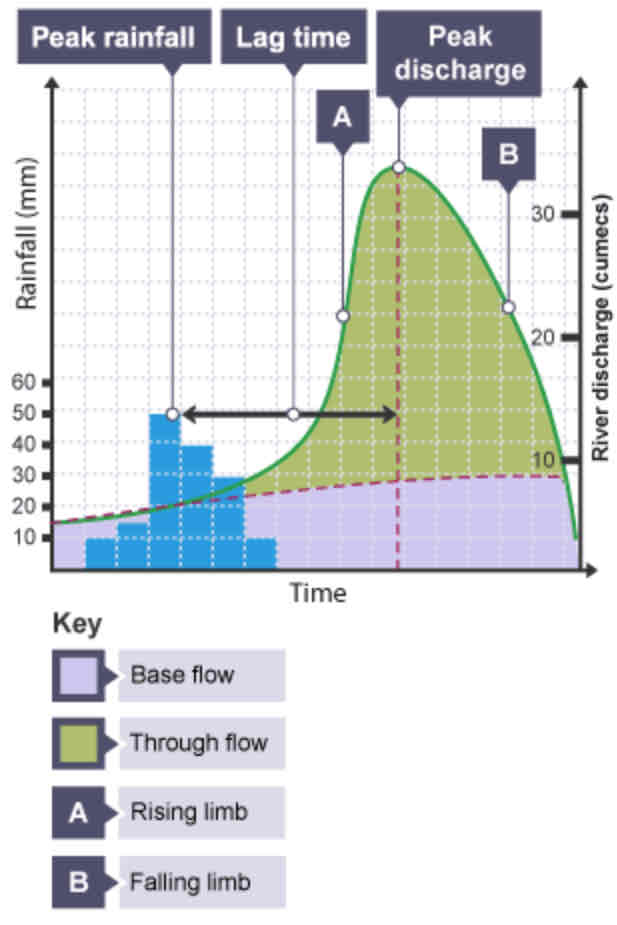
What is discharge?
The volume of water in a river passing a point in a given time. Measured in cumecs (cubic metres per second).
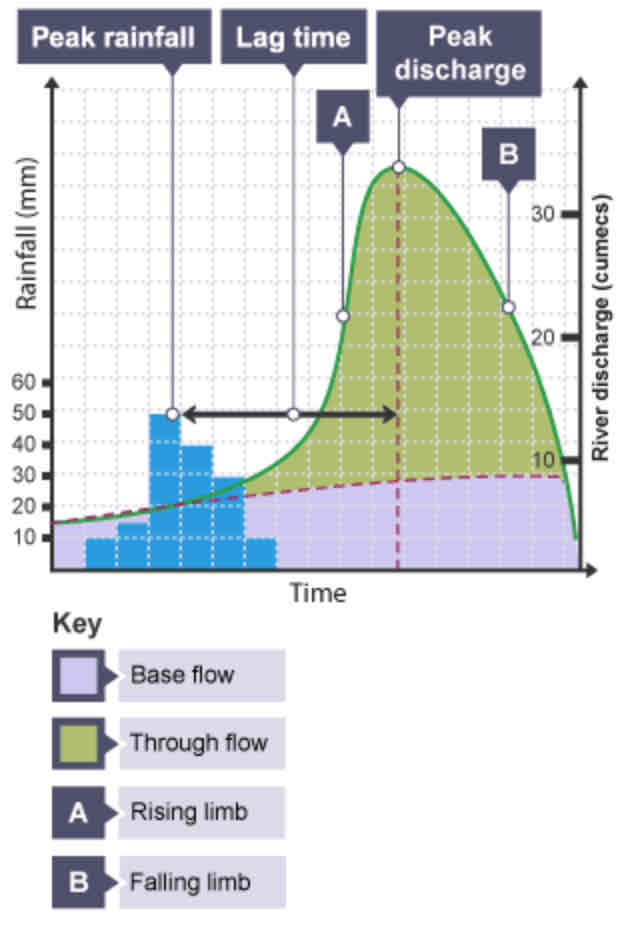
What does the peak rainfall show?
The maximum amount of rainfall (mm).
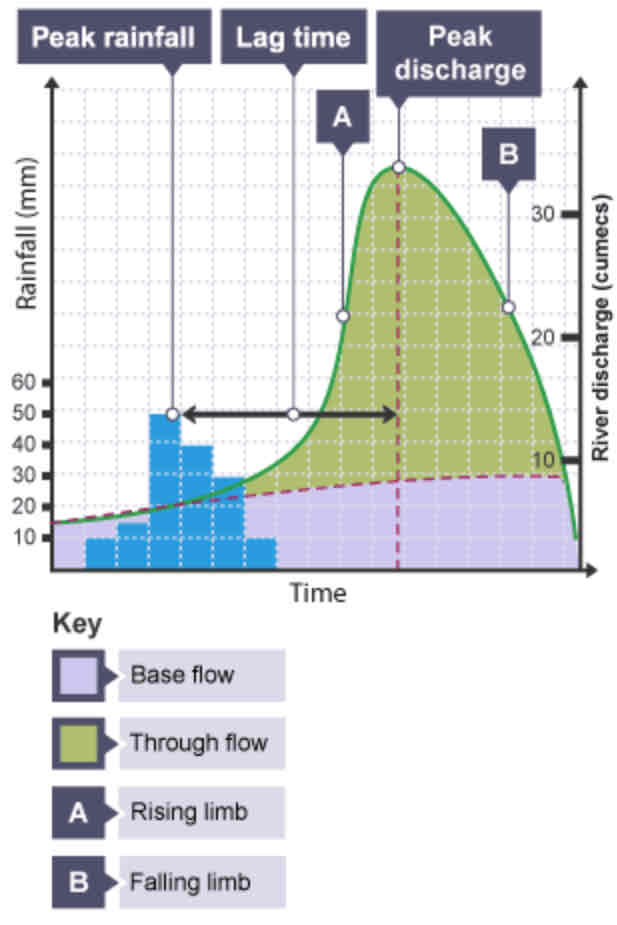
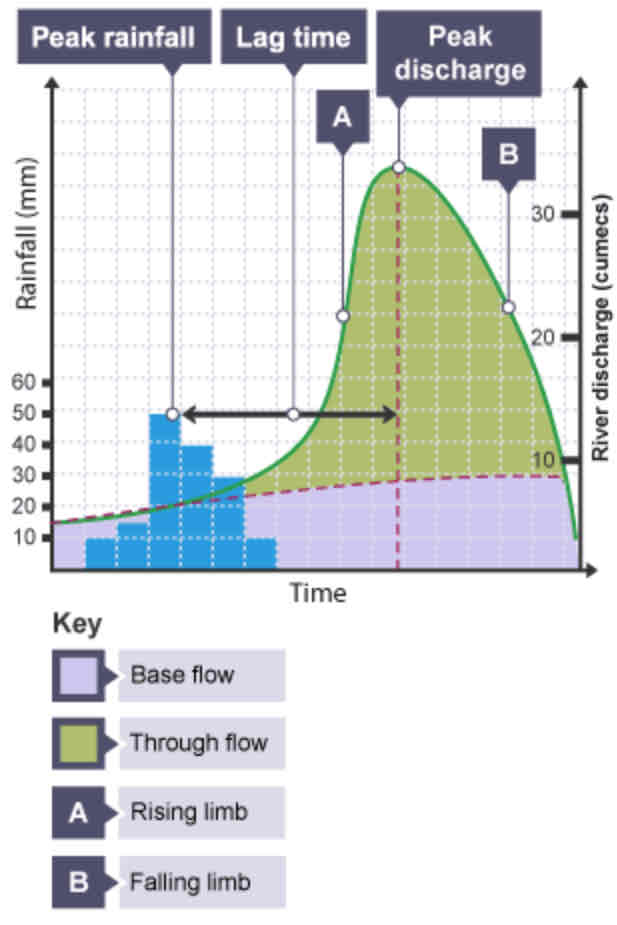
What does the lag time show?
The time taken between the peak rainfall and peak discharge.
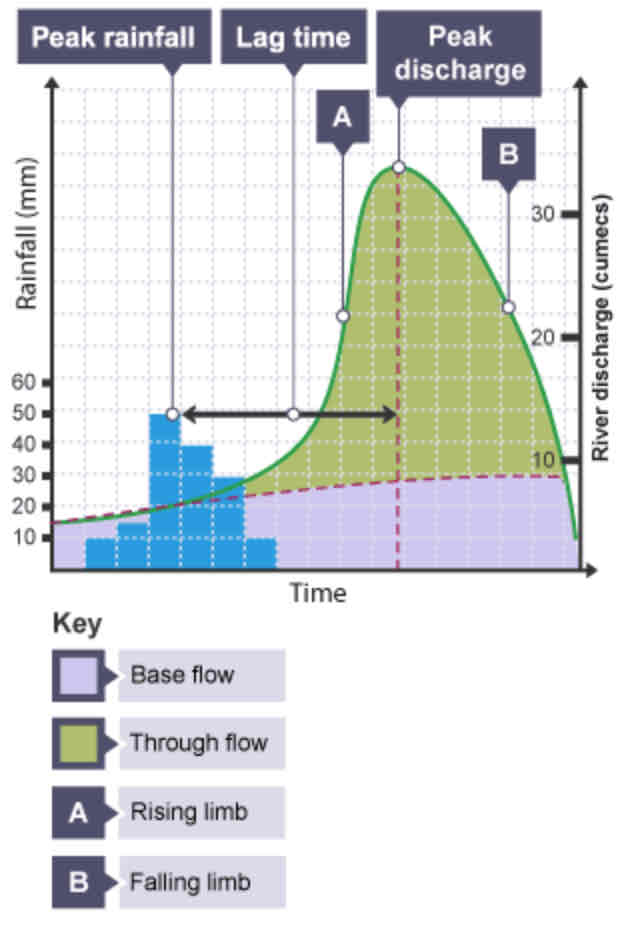
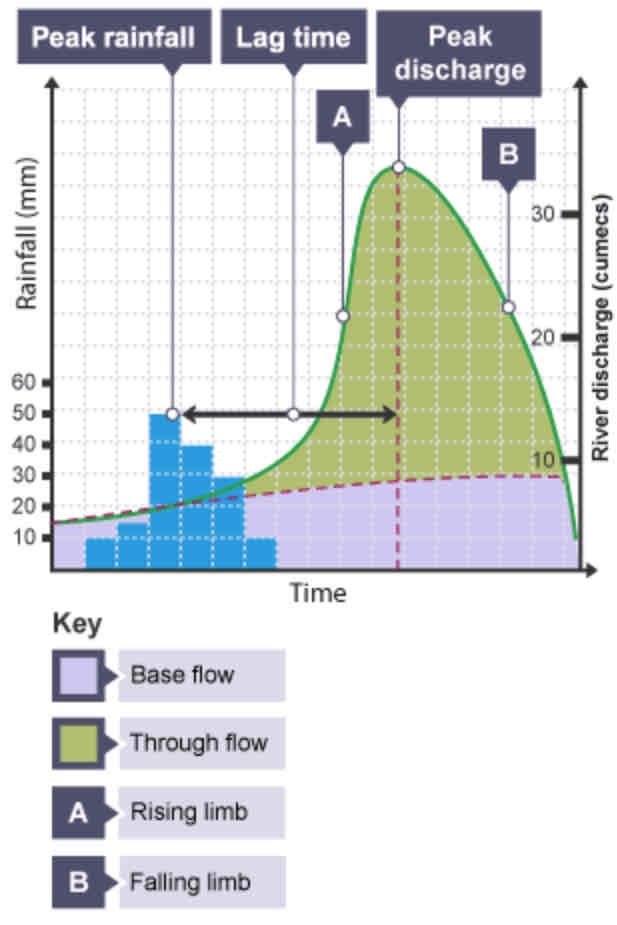
What does the falling limb show?
The return of discharge to normal/base flow on a hydrograph.
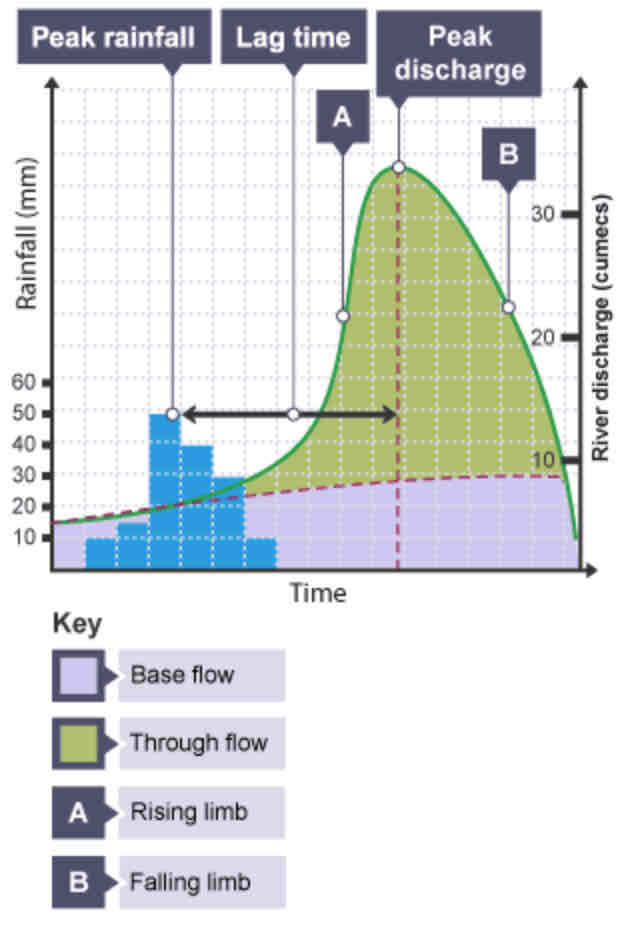
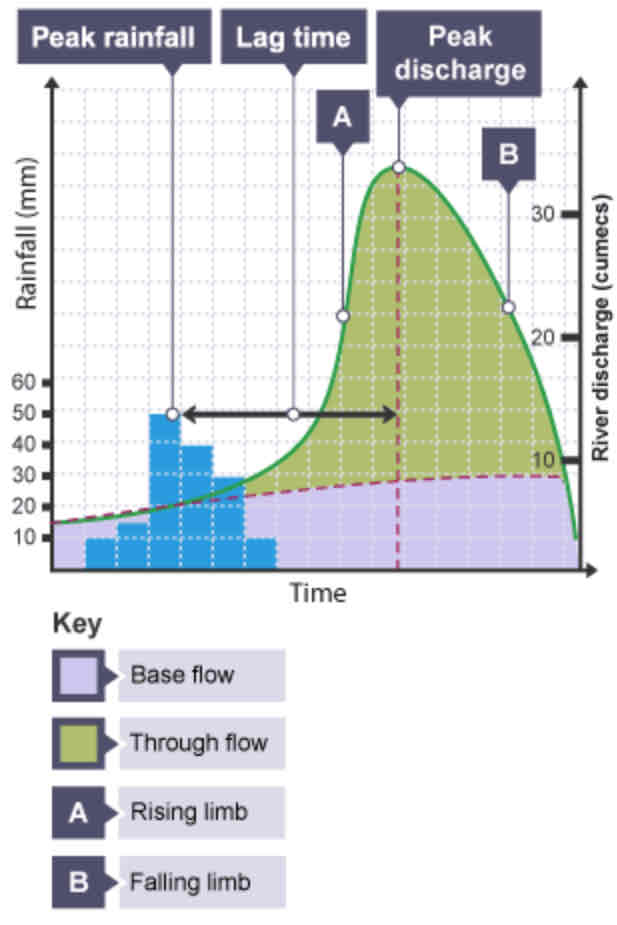
What does the base flow show?
The normal discharge of the river.
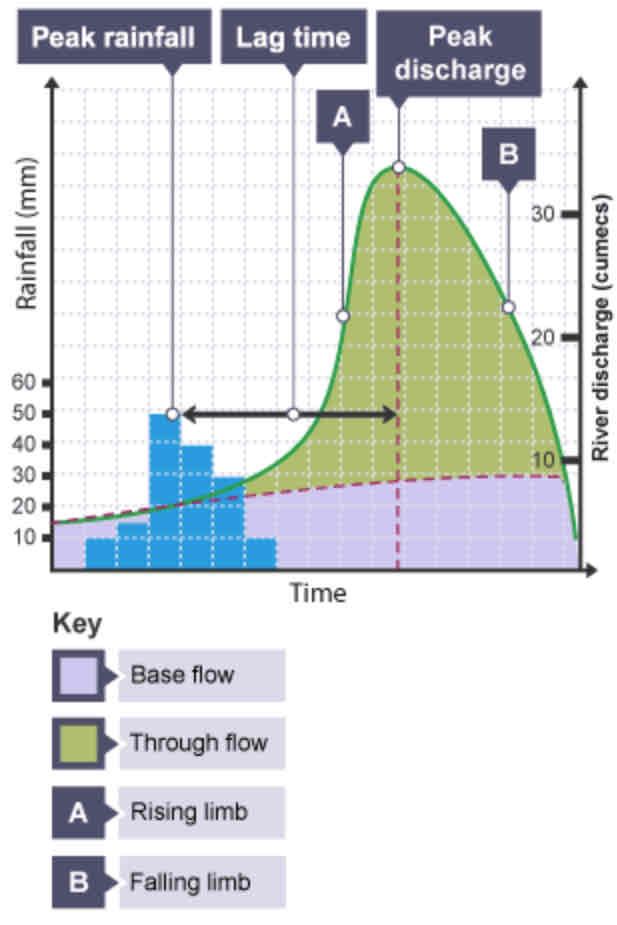
A short/long lag time means a greater change for flood.
Explain why.
Short
Because the water reaches the river more quickly, so there is a greater chance for flood.
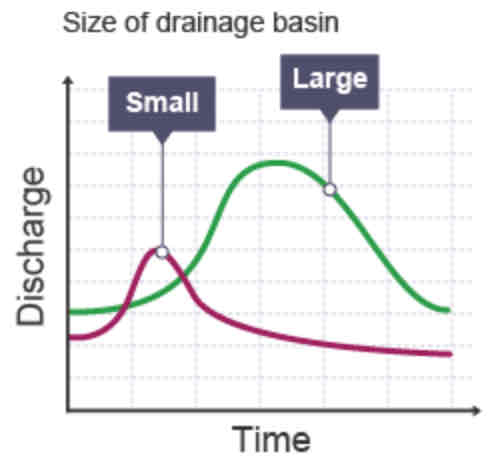
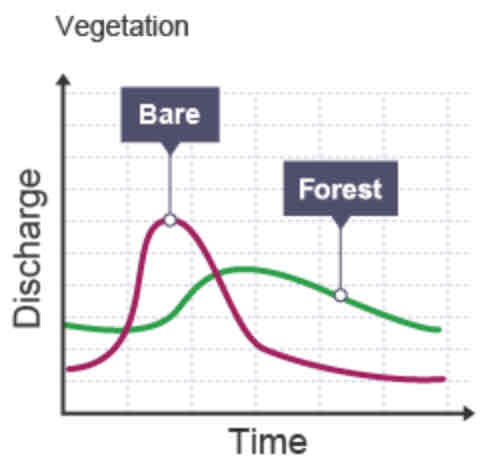
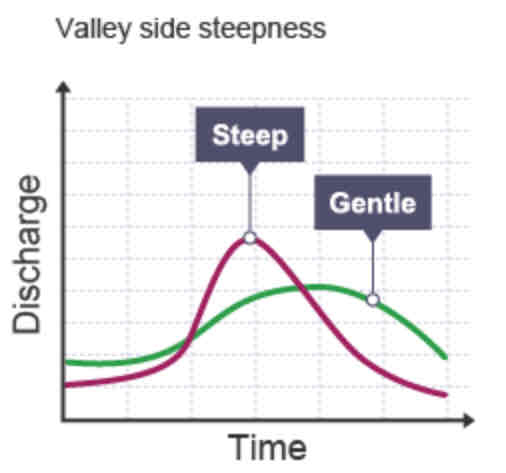
Which factors influence lag time?
Size of drainage basin
Vegetation
Valley side steepness
Soil type
How does the size of Drainage basin affect the lag time?
Graph
How does vegetation affect the lag time?
Graph
How does the Valley side steepness affect the lag time?
Graph
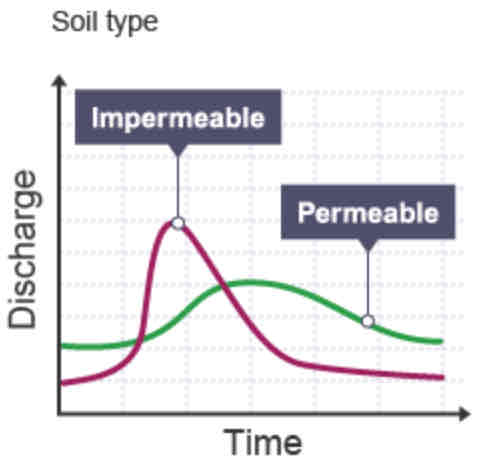
How does the Soil type affect the lag time?
Graph
What can flooding damage?
Homes
Businesses
Infrastructure
Communications
What is hard engineering?
Building man-made (artificial) structures, which try to control rivers.
What are examples of hard engineering strategies for rivers?
Dams and reservoirs
River straightening and dredging
Embankments
Flood relief channels
How do dams control flooding?
Trap water, which builds up behind it, forming a reservoir. This water can be released in a controlled way.
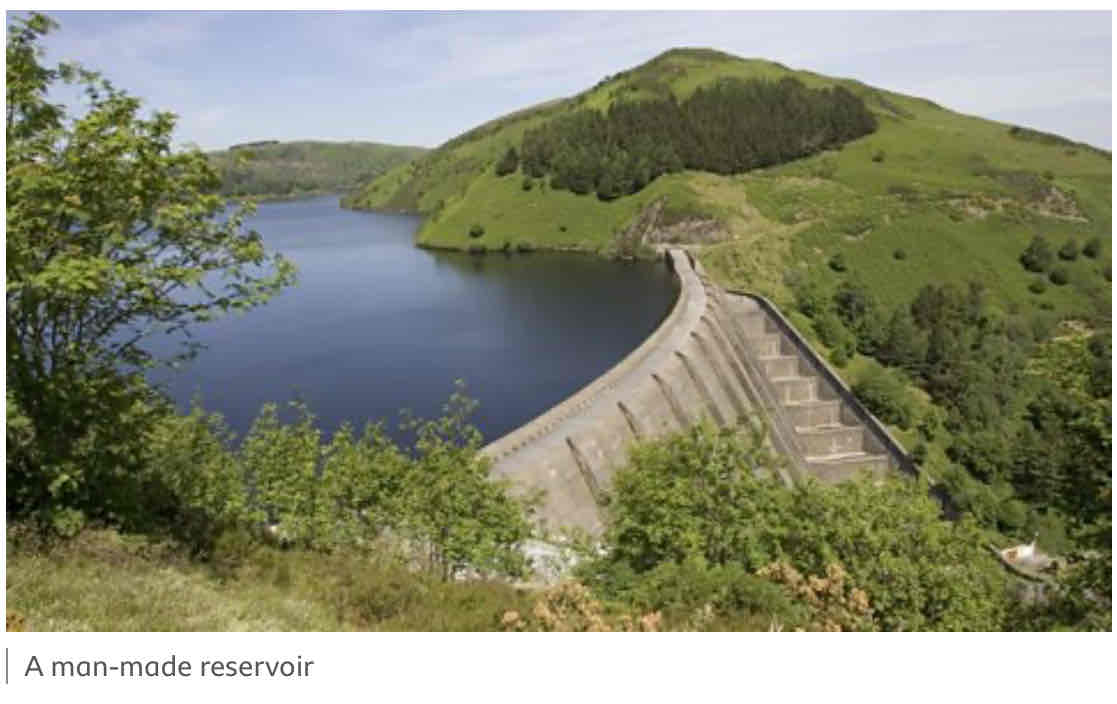

Advantages of Dams and Reservoirs (2)
Can be used to produce electricity by passing the after through a turbine within the dam
Reservoirs can attract tourists