
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
endosymbiosis theory
Lynn Margulis’ theory
two different cell types combined (bacterial cell taken up inside an archaea cell)
chloroplasts
mitochondria
evidence of endosymbiosis theory
Look inside the cases of endosymbiosis and check what the DNA looks like (linear or circular)
Chloroplasts and mitochondria have their own DNA and its a single circular chromosome
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes have differences in their cell membranes;
If one cell takes up another, the cell that was taken up (will be present in membrane) within the cell that was doing the taking up
Chloroplasts and mitochondria both have double membranes (the composition of the intracellular membrane is much more like a prokaryote membrane)
The outer membrane has the characteristics of a eukaryotic cell membrane
endosymbionts; mitochondria
different types of cells have different numbers of mitochondria; usually correlates with the energy requirement of the cell
main function: production of ATP—> ‘powerhouse of the cell’
outer membrane: tends to match in composition with eukaryotic cell
inner membrane: prokaryotic-like membrane
contains special characteristics that are specific to mitochondria
convoluted shape: increases the surface area of the inner membrane
important because the more SA the more space the mitochondria has to carry out the reactions to generate energy
different enzyme complexes in this membrane (e.g. ATP synthase)
circular chromosome: genes that are encoded on this chromosome encode key requirements for energy production
most of the mitochondria is constructed using genes that are in the nucleus
over the period of evolution, the original cell that was endosymbiot would have had a complete genome with all the information needed to make mitochondria, but over the evolutionary time, many of these genes have been transferred to the nucleus
endosymbionts; chloroplasts
main function: photosynthesis
found in plant cells
gives the cell green colour pigment chlorophyll
within the chloroplasts there are enzymes which fucntion to produce sugar
sugar isn’t enough to produce energy by itself
It is a substrate that can be used by other processes such as by the mitochondria to convert the sugar into energy sources such as ATP
has an outer and inner membrane
has its own circular DNA chromosome
has thycoloid membranes where photosynthesis is carried out
nucleus
Contains all of the genetic material except for the endosymbose organelles' (e.g. Mitochondria and chrloroplasts)
Nucleolus; darker fragment
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is made here (a component of ribosomes)
Nuclear pore complex:
The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane that blocks access to the nucleus except through the nuclear pores
Controls transport of things into and out of the nucleus
ribosomes
Closely associated with the nucleus
mRNA is transcribed within the nucleus and then transported out of the nucleus to the ribosomes
Job: synthesise proteins based on the information carried by the mRNA
DNA -> mRNA -> protein
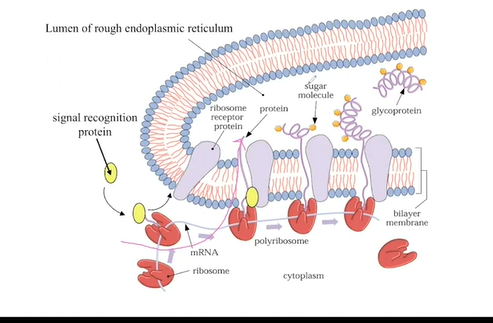
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Proteins enter the ER using signal sequence of amino acids
Wrapped around the nucleus
Very closely associated with the nucleus because it is very closely associated with the production of proteins
Inside of the ER: lumen
Rough ER: has ribosomes attached
Smooth ER: no ribosomes attached
biosynthetic factory: lipids, glycoproteins etc.
smooth ER
functions
metabolism of carbohydrates
lipid production
phospholipid production
rough ER
functions
when the ribosomes translate mRNA to a protein, it can be directly transported into the cell
processes result in the production of sugar molecules or lipids is protected from the rest of the cytoplasm
allows for the production of more
complicated products
the endomembrane system
A system of internal, membrane-bound compartments within the cell that can form physical links to exchange components
Nuclear envelope (nucleus)
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosome and vacuoles
Continuous system
Pieces of the endomembrane can break off into vesicles (little spherical compartments)
Can go to the plasma membrane and fuse and cause the contents to go outside the cell, or can travel to specific locations within the cell and deposit their material there, or go to the Golgi Apparatus
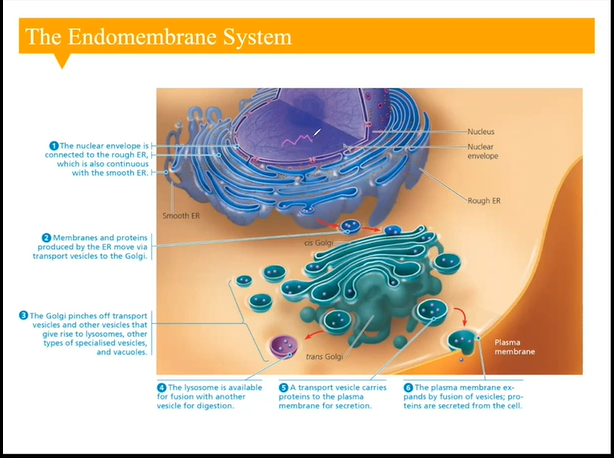
endomembrane system; golgi apparatus
‘The postal service’
Broken into two areas:
Cis golgi; next to (same side) as the ER
Trans golgi: far side (opposite) as the ER
Not continuous with the ER
Breaking off of materials is thus necessary into the vesicles so they can travel from the ER to the golgi apparatus and deposit the contents inside the luma
Contents can then be modified
Once the contents have matured, a new vesicle can then be formed to transport this material to other parts of the cell (fuse with another organelle or outer plasma membrane)
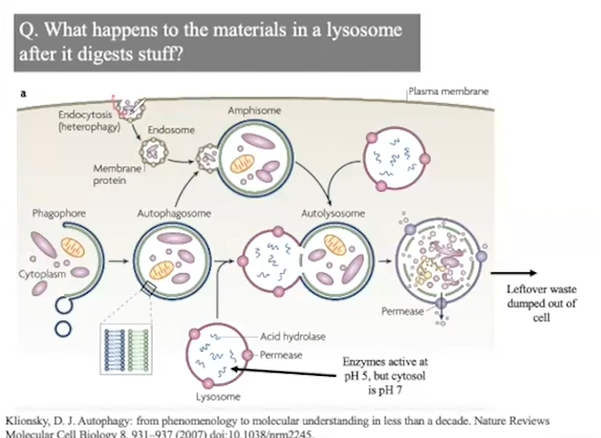
endomembrane system: lysosomes
‘Waste recycling centre’
Vesicles full of hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes
A highly acidic environment
Phagocytosis: 'food' from outside the cell is engulfed
Macrophages are white blood cells that engulf bacteria
Autophagy: breaking down damaged organelles for recycling
A human liver cell recycles half its macromolecules each week
endomembrane system: vacuoles
can control large spaces within the cell
Storage compartments
Can contain food or water
Provide good example of why eukaryote cells want compartments
E.g. acid hydrolase enzymes can digest cell components; it would not be good for the cell if these got out and moved freely throughout the cell, or these enzymes would digest the cell itself
endomembrane system: cytoskeleton
unique to eukaryotes
support and motility
three different support structures summary:
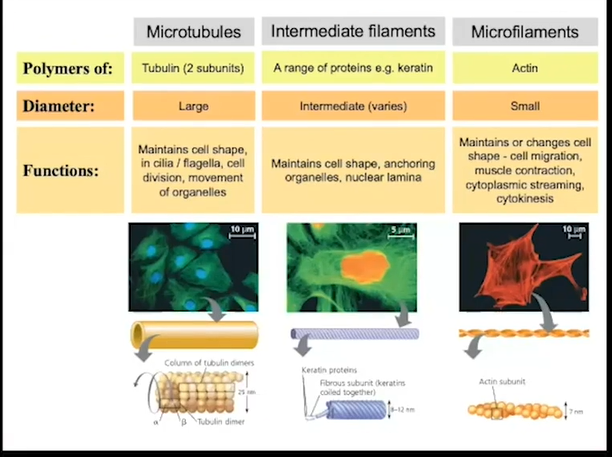
endomembrane system; cytoskeleton; support structures; microtubules
Formed by sets of a dimer (two proteins that always go together)
Dimer; each side of the dimer will have different properties
The alpha side is able to grow in length
The beta side is less prone to being able to group
The side of the microtubule that can grow quickly is the + side
The side of the microtubule that cannot grow as quickly is called the - side
The - side of the microtubule starts at the microtubule organising centre (centrosome--> type)
Then these molecules are able to rapidly grow or contract based on the local concentration of tubulents
endomembrane system; cytoskeleton; motility
Microtubules in cilia and flagella
More rigid structures that can be used for motility
Flagella:
One or a few tails that propel the cell forward
Cilia:
Many cilia (shorter than flagella) cover the cell, beat back and forth
9 + 2 configuration
radio spokes that connect the fixed parts of the flagella
dynein; protein used for movement
One side of the dynein is fixed and the other side can move
One side will move up and then the other side will move up, creating a angulating motion