Dental Occlusion Q2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
occlusion is the statis relationship between
the incisal or masticating surfaces of the maxillary or mandibular teeth or tooth
occlusion is the act or process of
closure or being closed or shut
articulation is the place of union or junction between
two or more bones of the skeleton
articulation is the static and dynamic contact relationship between
the incisal/occlusal surfaces of the teeth during function
articulator
a mechanical instrument that represents the temporomandibular joints and jaw to which the maxillary and mandibular casts may be attached to simulate some/all mandibular movements
what are the three determinants of occlusion
posterior and anterior determinants and neuromuscular system
posterior determinants
TMJs w their surrounding tissues
anterior determinants
teeth and their guidance- occlusion or articulation
neuromuscular system
include muscle of mastication, nervous system, skeletal tissue, skeletal arrangements around TMJ
harmony
stable occlusal condition
stable occlusal condition
even and simultaneous contact of teeth, directing occlusal forces through long axis of tooth, and damaging horizontal movements are directed to anterior teeth (farthest from fulcrum and force vectors)
articular disc is interposed between the…
squama of the temporal bone and the condyle of the mandible
the TMJs are coupled, what does this mean
no movement can occur in one joint w/o some movement in the other joint
what are the two compartments of the TMJ of which each accomplishes different types of movement
superior and inferior cavity
ginglymoarthrodial
TMJ- a hinge joint with a moveable socket
the rotating/hinging movements the TMJ provides in one plane classifies it as what type of joint
ginglymoid joint
TMJ provides gliding movements which classifies it as what type of joint
arthrodial joint
which compartment does rotation occur of the TMJ
disc on the articular surface in the inferior cavity
what compartment does the free sliding movement (translation) occur of the TMNJ
between the surfaces in the superior cavity
compound joint requires the presence of
at least 3 bones
TMJ is made up of how many bones
2
the articular disc serves as a ________ bone and is considered as a third bone
non-ossified
what are the extracapsular ligaments of the TMJ
external lateral/temporomandibular, sphenomandibular, stylomandibular ligaments
external lateral/temporomandibular ligament funx
prevents from posterior dislocation of the joint
sphenomandibular ligament
primary passive support of mandible + muscles of mastication
stylomandibular ligament
limits opening and protrusion movements of jaw
the articular disc is composed of
dense fibrous connective tissue; no blood vessels or nerve fibers
the sagittal plane of the articular disc can be divided into 3 zones, rank them according to greatest to least thickness
posterior border> anterior border> intermediate zone
from an anterior view, is the articular disc thicker medially or laterally
medially
TMJ has what types of cartilage
fibrocartilage and secondary cartilage
fibrocartilage has what type of collagen
type I and II
secondary cartilage
intra-membranous ossification; forms after bone formation
what actions does the mandible undergo to engage the maxilla for occlusion
hinge and gliding action
transverse horizontal axis (terminal hinge axis)
an imaginary line around which the mandible may rotate within the sagittal plane
what is the average rotation angle/measurement of incisal opening, when does this occur
12 degrees/20-25 mm; centric relation
what determines the properties of terminal hinge position, is this reproducible
ligaments and TMJ; yes
what tooth is where the joints are in centric occlusion/point of initial contact
2nd molar
centric relation (CR) definition
restricted to a purey rotary movement (rotation) about the transverse horizontal axis; condyle dependent
centric occlusion (CO) definition
occlusion of opposing teeth when the mandible is in centric relation; may/may not coincide w maximal intercuspal position
maximal intercuspal position (MIP) definition
complete intercuspation of opposing teeth, regardless of condylar position
long centric/freedom in centric
CO to MIP slide w no vertical dimension change and no interferences
interocclusal rest space is when the mandible is at rest position with the teeth separated by ______ mm
2-4
if CO and MIP are vertically different, there is a greater __________ risk
pathological
during CO there is no…
muscle funx- jaw hinges w/o lateral pterygoid
centric stop
opposing cuspal fossae contacts that maintain the occlusal vertical dimension between opposing arches
in occlusion, a particular supporting cusp makes contact w a _________ on the opposing teeth
centric stop
during cusp to marginal ridge contact it is one tooth contacting how many teeth
2 teeth
during cusp to fossa contact it is one tooth contact how many teeth
1
supporting cusp in normal occlusion…
the lingual cusp of the upper posterior teeth and the buccal cusps of the lower posterior teeth
non-supporting cusp in normal occlusion…
buccal cusps of the upper posterior teeth and the lingual cusps of the lower posterior teeth
dipod and tripod cusp tip contact location
lateral to cusp tip
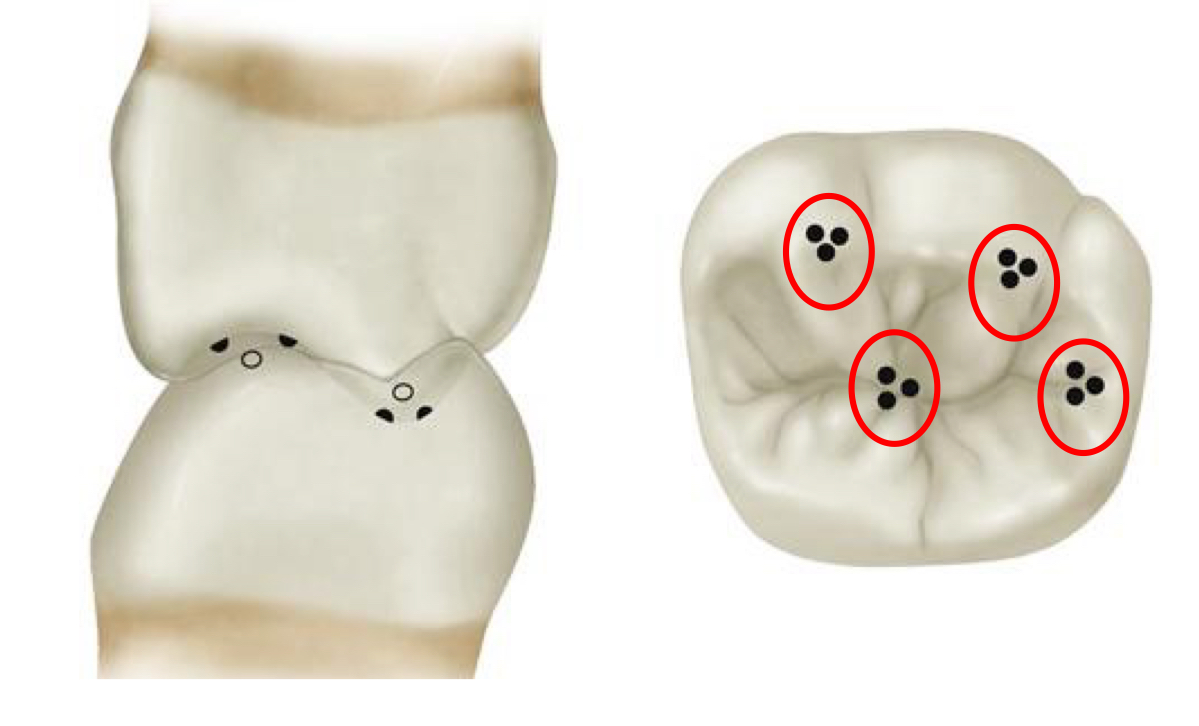
tripod
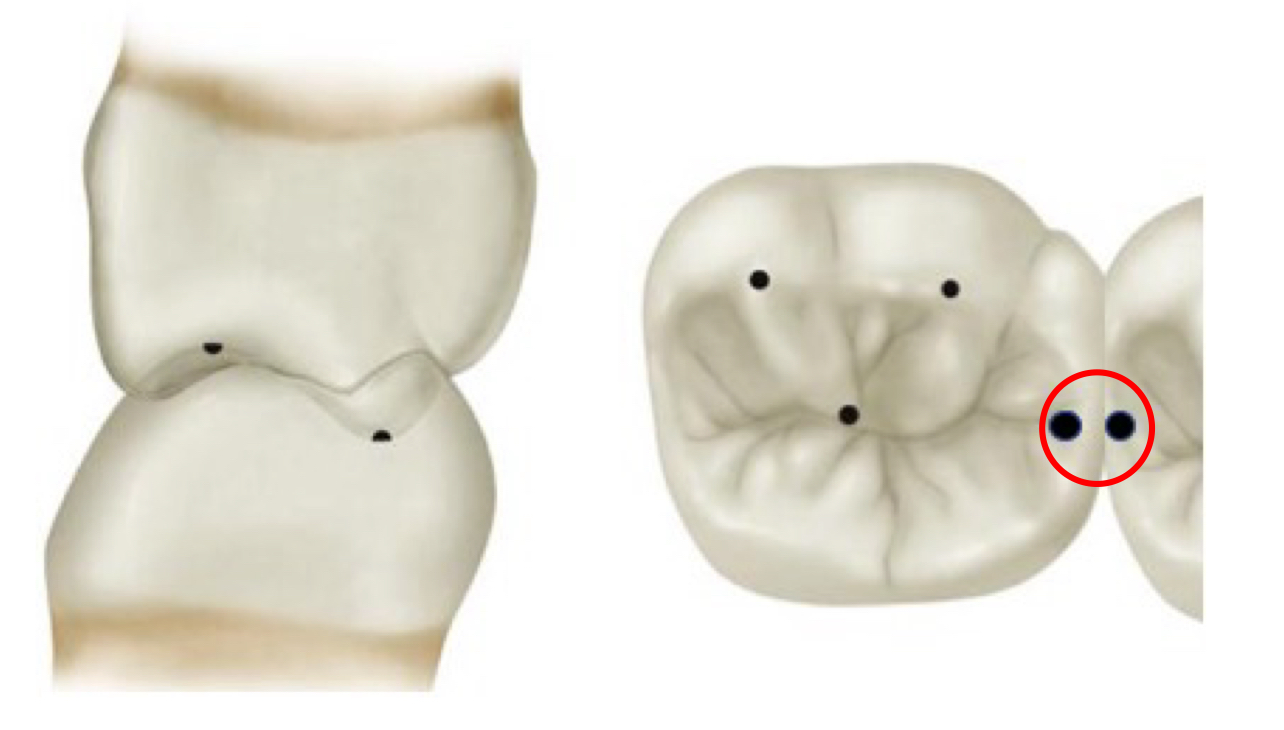
dipod
dipod and tripod cusp tip lateral forces are balanced to…
zero; net force is vertical in long axis
two-to-two-tooth MI contacts
cusp fossae and cusp marginal ridge relationships
tooth-to-tooth MI contacts
all cusp fossae relationships
advantages to tooth to two tooth MI contacts
vertically directed forces, commonly occuring/easy to restore, efficient protections against super eruption
disadvantages to tooth to two tooth MI contacts
greater interproximal food impactions risk, uneven adjacent MR heights may not allow appropriate design
excursive movements occur when the…
mandible moves away from maximum intercuspation
working-side
the side toward which the mandible moves in a lateral excursion
non-working side (balancing)
the side of the mandible that moves toward the medial during lateral excursion
protrusive movement
mandibular forward movement anterior to centric relation
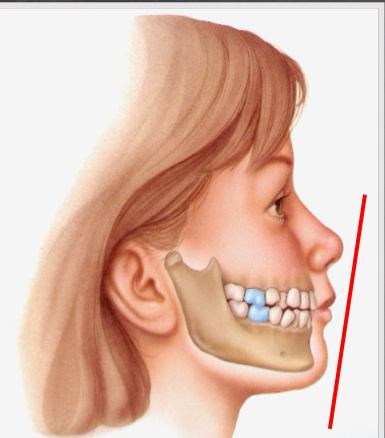
class I
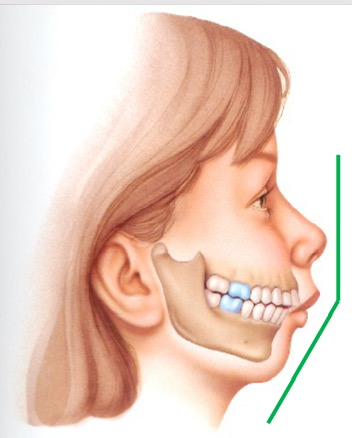
class II
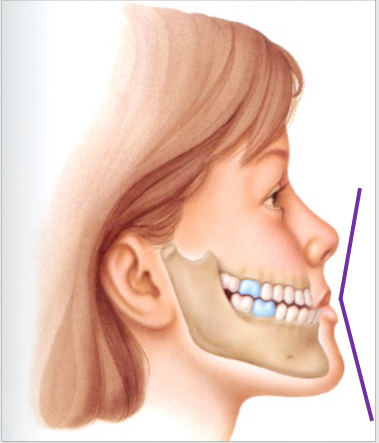
class III
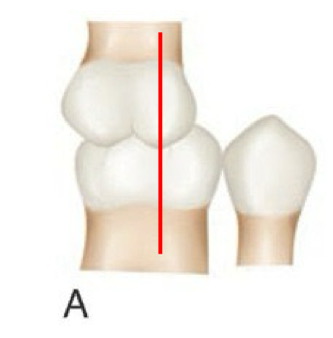
angle class __ molar relationship
I; maxillary first molar MB tip is aligned w mandibular first molar MB facial groove
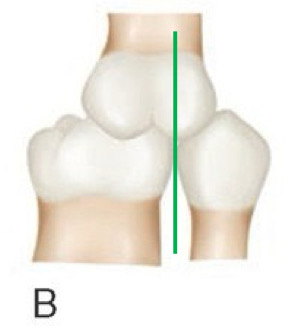
angle class __ molar relationship
II; maxillary first molar MB tip is anterior to mandibular first molar MB facial groove
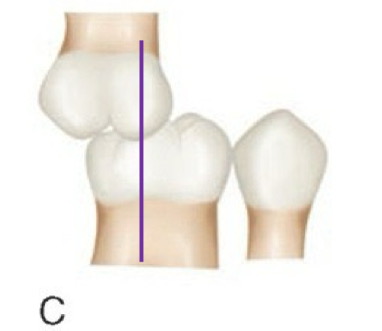
angle class ___ molar relationship
III; maxillary first molar MB tip is posterior w mandibular first molar MB facial groove
what do you need to mount the maxillary cast
facebow/earbow
what do you need to mount the mandibular cast
bite reg
face bow/hinge bow
records the spatial relationship of the max arch to some anatomic reference point(s)
purpose of facebow/earbow
transfer establishes the relationship between the upper teeth and pts head