Psychology 2e: Chapter 2
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
deductive reasoning
results are predicted based on a general premise
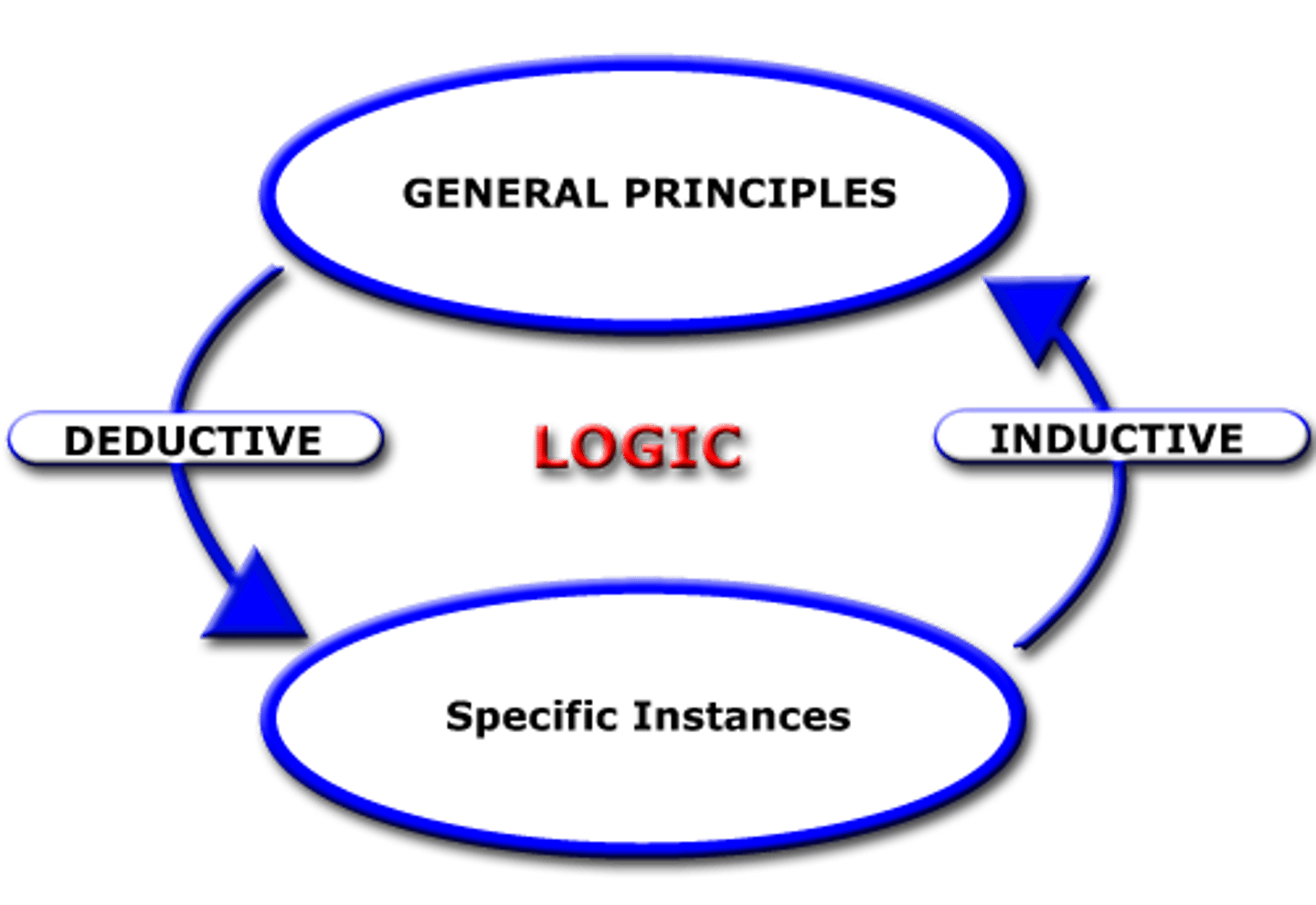
inductive reasoning
conclusions are drawn from observations
Theory
well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena
Hypothesis
a tentative, testable statement or prediction about what has been observed
Approaches to Research
Clinical or case studies; Naturalistic Observation; Survey; Archival Research; Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Research
clinical or case studies
Focus on one individual. The studied individual is typically in a extreme or unique psychological circumstance that differentiates them for the general public. Also for a lot of insight into a case. Difficult to generalize results to the larger population.
observer bias
when observations may be skewed to align with observer expectations
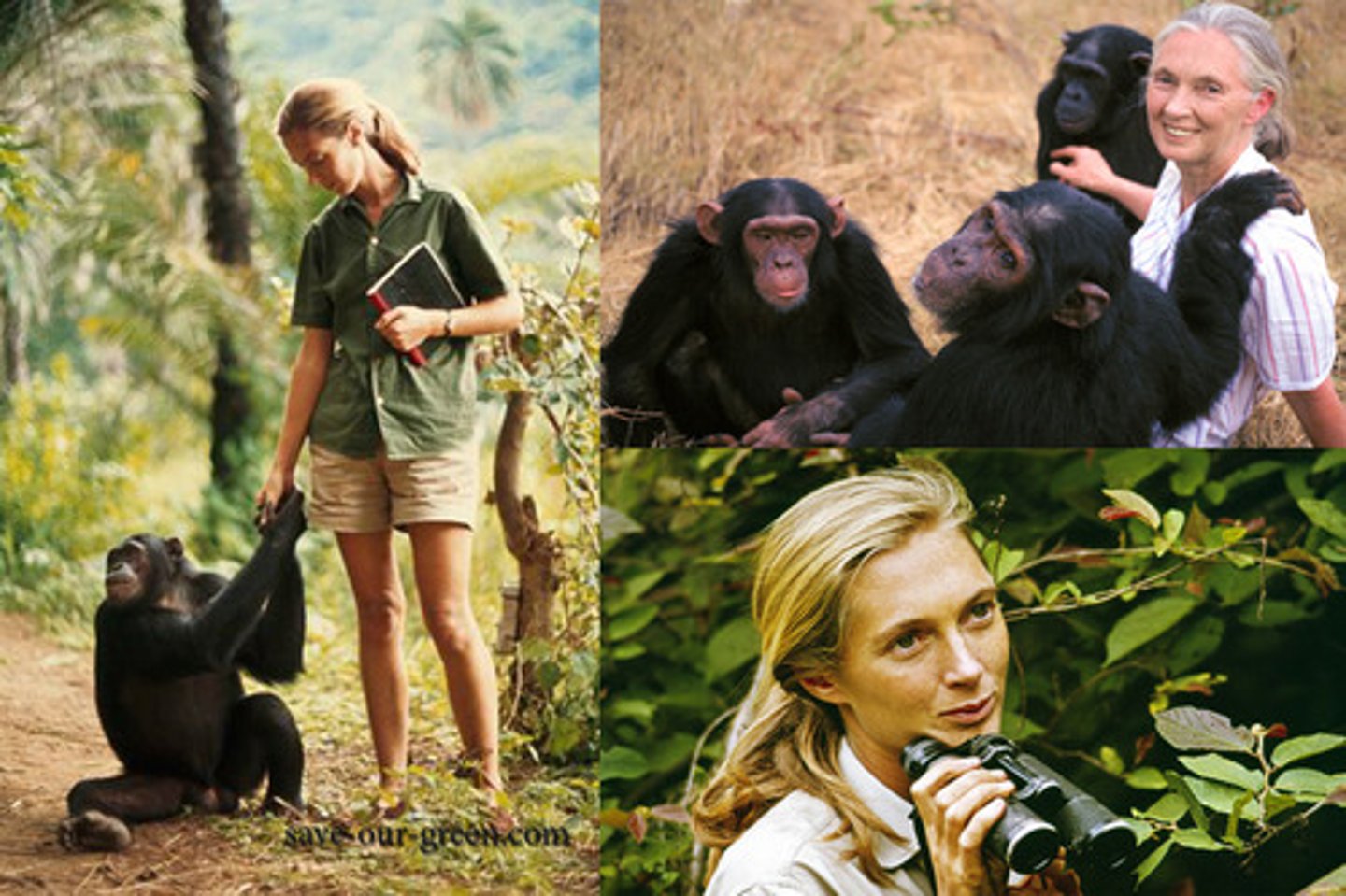
Jane Goodall
made a career of conducting naturalistic observations of chimpanzee behavior

archival research
Uses past records or data sets to answer various research questions, or to search for interesting patterns or relationships
Cross-sectional Research
compares multiple segments of a population at a single time
Longitudinal
Studies in which the same group of individuals is surveyed or measured repeatedly over an extended period of time.
attrition
reduction in number of research participants as some drop out of the study over time
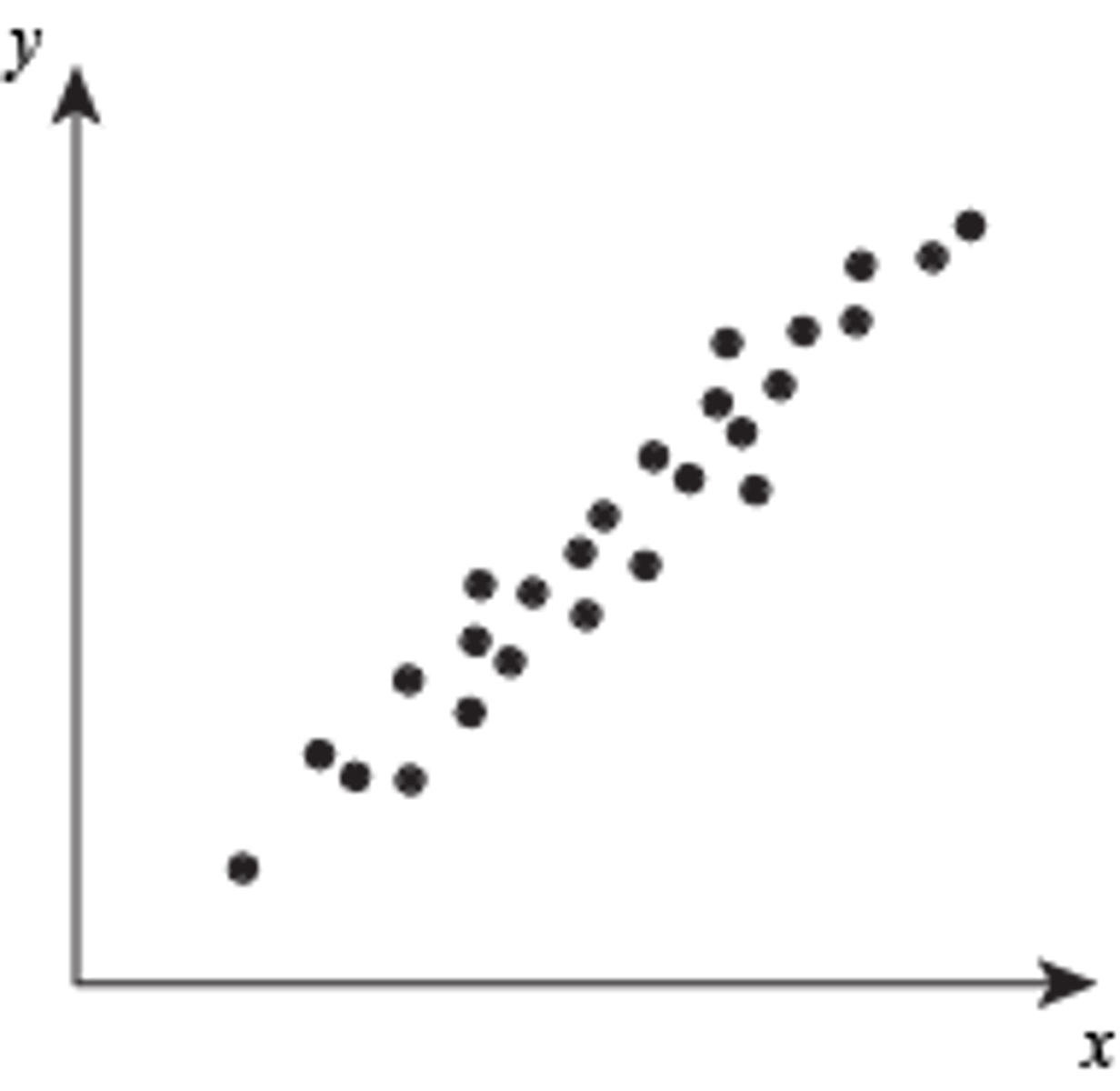
Correlation
relationship between two variables
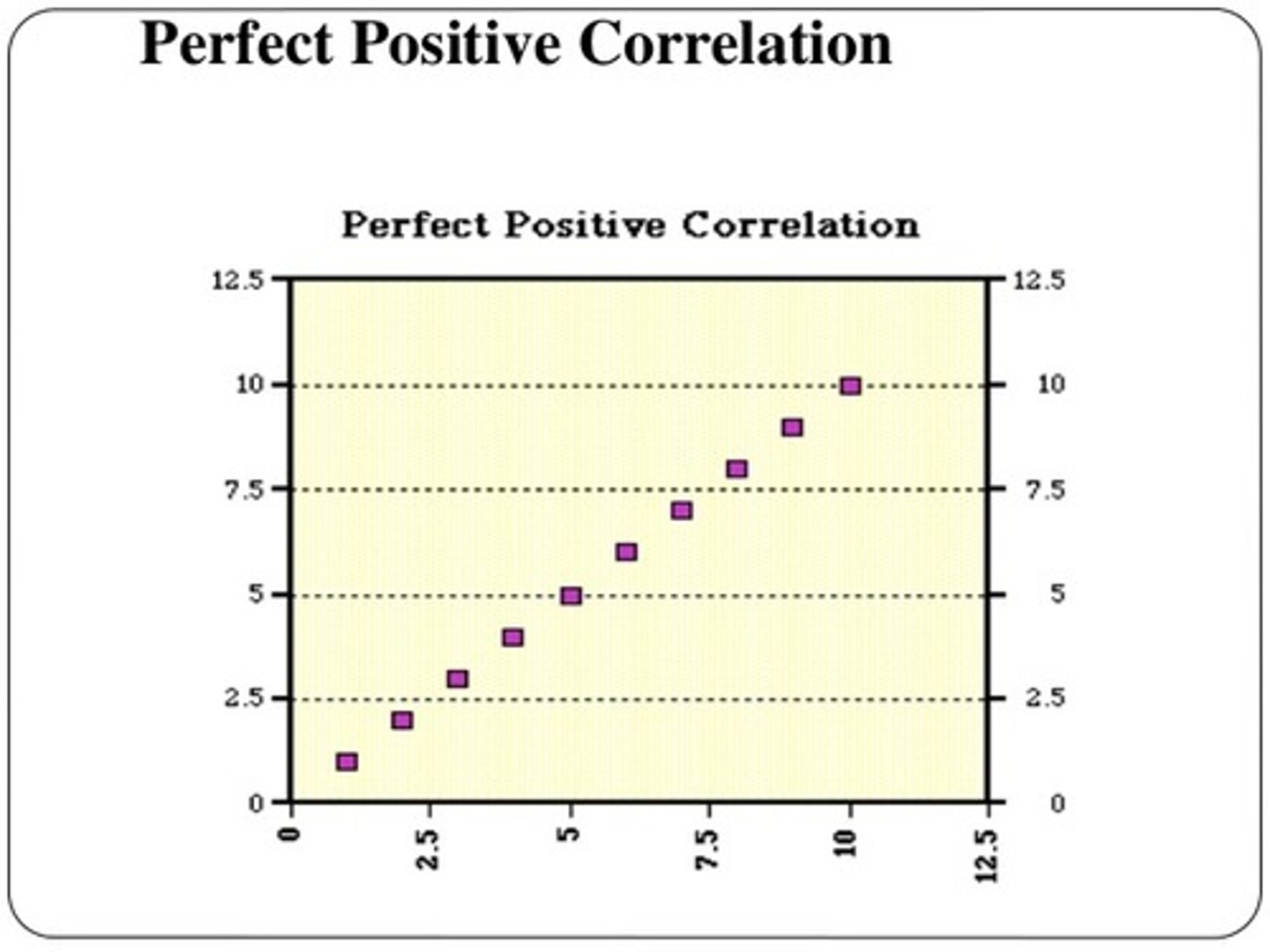
correlation coefficient
number from -1 to +1, indicating the strength and direction of the relationship between variables, and usually represented by r
positive coorelation
Two variables change in the same direction, both becoming either larger or smaller.
negative coorelation
Two variables change in different directions, with one becoming larger as the other becoming smaller, a negative correlation is not the same thing as no correlation
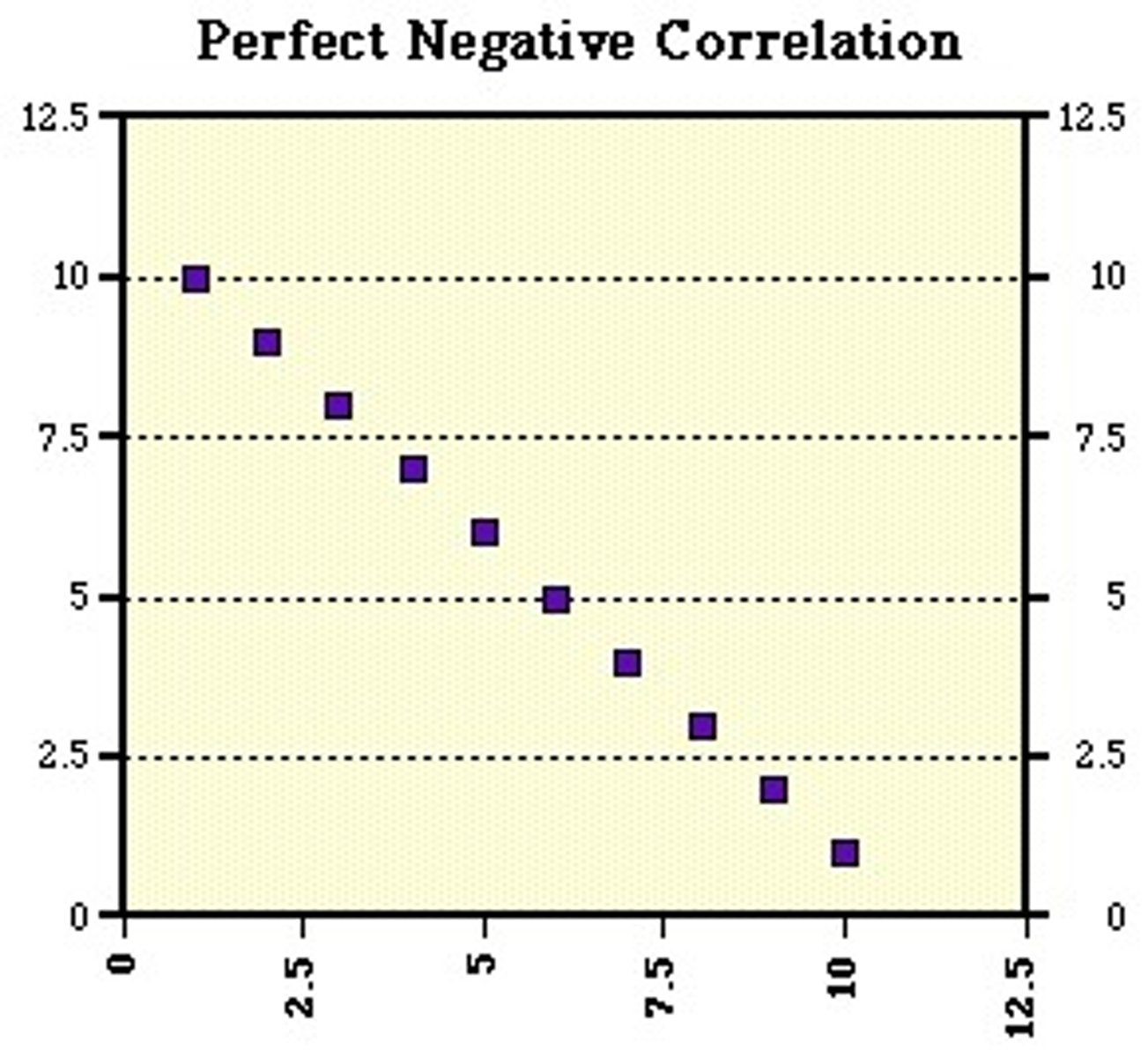
cause-and-effect relationship
changes in one variable cause the changes in the other variable; can be determined only through an experimental research design
confounding variable
unanticipated outside factor that affects both variables of interest, often giving the false impression that changes in one variable causes changes in the other variable, when, in actuality, the outside factor causes changes in both variables
illusory correlation
seeing relationships between two things when in reality no such relationship exists
confirmation bias
tendency to ignore evidence that disproves ideas or beliefs.
experimental group
The participants that experience the manipulated variable (group designed to answer the research question).
control group
Participants that do not experience the manipulated variable.
operational definition
description of what actions and operations will be used to measure the dependent variables and manipulate the independent variables
Experimenter bias
researcher expectations skew the results of the study
Participant bias
participant expectations skew the results of the study.
Single-blind study
experiment in which the researcher knows which participants are in the experimental group and which are in the control group
Double-blind study
experiment in which both the researchers and the participants are blind to group assignments
placebo effect
people's expectations or beliefs influencing or determining their experience in a given situation
independent variable
Variable that is influenced/controlled by the experimenter. Ideally this should be the only important difference between the experimental and control group.
dependent variable
variable that the researcher measures to see how much effect the independent variable had
Participants
subjects of psychological research
Sample
subset of individuals selected from the larger population
Population
Overall group of individuals that the researcher is interested in.
Random Sample
subset of a larger population in which every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected
random assignment
method of experimental group assignment in which all participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either group
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC)
Committee of administrators, scientists, veterinarians, and community members that reviews proposals for research involving non-human animals.
deception research
purposely misleading experiment participants in order to maintain the integrity of the experiment
Debriefing
when an experiment involved deception, participants are told complete and truthful information about the experiment at its conclusion
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
committee of administrators, scientists, and community members that reviews proposals for research involving human participants
Statistical analysis
determines how likely any difference between experimental groups is due to chance