Diabetes Intro
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
3 Primary Disorders of Glucose Metabolism
Sustained hyperglycemia, abnormal insulin secretion, insulin resistance
What is Diabetes?
A chronic, multi-system disorder of abnormal insulin production, impaired use of insulin, or both; being in a constant state of hyperglycemia
What are the 2 major risks from developing Diabetes?
Heart disease and Stroke
Causes of Diabetes
Genetics (Human leukocyte antigens), autoimmune disorders, environmental (virus, obesity)
Normal Glucose Metabolism Pathophysiology
Glucose levels rise from eating, etc.
Pancreas responds by secreting “Bolus” of insulin
Insulin decreases glucose level
Feedback loop occurs where kidneys maintain glucose homeostasis
Pancreas reduces insulin secretion and returns to basal rate
Liver resumes function as a store
Fasting Glucose Metabolism Pathophysiology
Insulin continues to be released at basal rate
cells still demand glucose or energy of some source
Liver provides energy in form of glycogen
Other sources like adipose or muscle tissue are broken down for energy creating fatty acids
Fatty acids affect pH
Ketones are produced as byproducts of fatty acid metabolism
Type ___ Diabetes has a higher association with Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR4)
1
How is T1D developed as an Autoimmune Disorder?
You already have a gene in your body that develops antibodies against insulin or specific pancreatic cells that make insulin, and some environmental factor triggers it at some point in your life
T or F: Insulin is continuously released into the bloodstream in small amounts
T
Insulin (hormone) is produced and secreted by the _________
Pancreas
Insulin must latch onto __________ in order for it to enter cells, leading to glucose breakdown for energy and lowered blood sugar
Glucose
What are the 3 main types of Cells that Insulin enters?
Adipose, Liver, Muscle
How does the Rise in blood insulin After a Meal work?
Gluconeogenesis is inhibited, dietary fat is deposited into adipose tissue, protein synthesis increases
How does the Fall in blood insulin Overnight work?
Glycogen from liver, protein from muscle, and fat from adipose tissue is released to maintain glucose homeostasis
T or F: If you don’t consume glucose, your body will get it from adipose, liver, and muscle tissue, which can lead to hyperglycemia and then DKA
T
What makes Liver Cells different from Adipose or Muscle Cells?
They are not insulin-dependent SO instead they have receptors that facilitate the uptake of glucose which converts to glycogen
What do Counter-Regulatory Hormones do to Blood Glucose?
They are released at night to work against insulin and therefore increase blood glucose
Counter-Regulatory Hormone Examples
Glucagon, Epinephrine, Growth Hormone, Cortisol
Glucagon stimulates the release of _________ that is stored
Glycogen
T or F: Counter-Regulatory Hormones increase blood glucose levels, even when they are already elevated, because of the expected drop in blood glucose at night
T
Diabetes Risk Factors
Family history, age, metabolic syndrome, obesity, physical inactivity, high blood pressure, Hispanic
What Labs are done for Diagnosing Diabetes?
HgB A1C > 6.5%, fasting glucose > 126, oral glucose tolerance test > 200 mg, random glucose level > 200 mg
Which lab is the best indicator for how a patient is managing/controlling their Diabetes?
HgB A1C
T or F: You must meet ALL Lab work criteria to be diagnosed with Diabetes
T
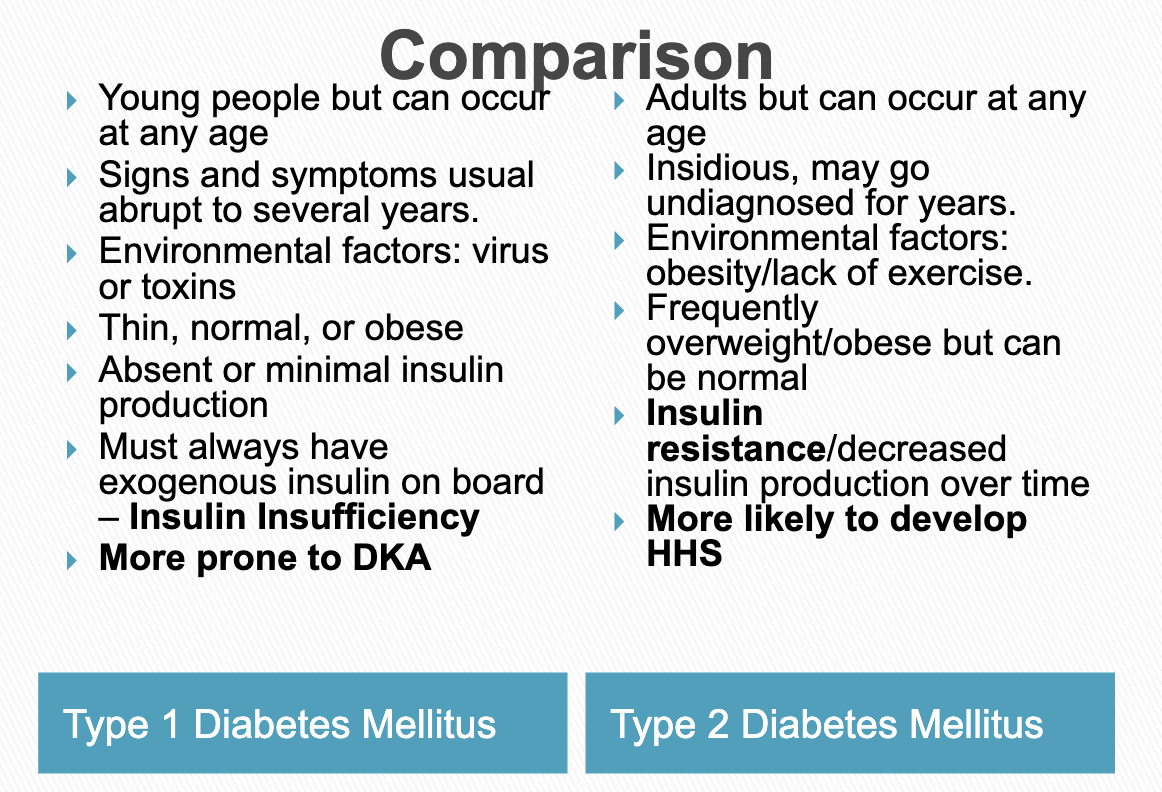
Type 1 Diabetes
A chronic, autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin from the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells; NOT reversible
Specific Characteristics of T1D
Onset is months to years, typically occurs in children, usually skinny, treatment is just insulin, only affected by pancreas
Type 2 Diabetes
A chronic condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough; reversible
Specific Characteristics of T2D
Onset is gradual over many years, typically occurs in older adults, usually obese, treatment is a combination, affected by pancreas / liver / muscle / and adipose tissue
4 main factors leading to T2D
Insulin resistance, decreased insulin production, abnormal glucose production, production of adipokines
What does the production of Adipokines lead to?
Chronic inflammation and (maybe) insulin resistance
Metabolic Syndrome Criteria
Central obesity, hyperlipidemia, high BP, hyperglycemia
Metabolic Syndrome increases the Risk for….. ?
T2D and Cardiovascular events
4 Main Diabetes Treatments
Insulin, drugs, nutrition, exercise
Rapid Acting Insulin → Onset, Peak, Duration
O: 10-30mins
P: 30mins-3hrs
D: 3-5hrs
Intermediate Acting Insulin → Onset, Peak, Duration
O: 1.5-4hrs
P: 4-12hrs
D: 12-18hrs
Long Acting Insulin → Onset, Peak, Duration
O: 0.8-4hrs
P: no peak
D: 16-24hrs
Rapid Acting Insulin is given as a _______, often in smaller amounts and given before meals (compensates for rise in glucose after a meal)
Bolus
Long Acting Insulin is given as a _______, often in larger amounts and given once at night (mimics body’s constant release of insulin)
Basal
The highest risk for hypoglycemia is at the ______
Peak
4 Complications from Insulin Therapy
Morning hyperglycemia, allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, hypertrophy
What is Lipodystrophy?
Loss of SQ fatty tissue from not rotating injection sites
What is Hypertrophy?
Thickening of SQ fatty tissue
3 Causes of Morning Hyperglycemia
Insulin Waning, Dawn Phenomenon, Somogyi Effect
How do we treat Morning Hyperglycemia?
Check blood sugars throughout the night
Why should patients NOT take more insulin before going to sleep to combat Morning Hyperglycemia?
It can cause hypoglycemia
What Psychological problems arise from Diabetes?
Stigma of being “handicapped”/”disabled”, family burden, religious obstacles (pork products), language barriers, poor health literacy
How do Diabetes Drugs affect the Pancreas?
Increase insulin production
How do Diabetes Drugs affect Adipose and Muscle Tissue?
Increase use/uptake of glucose, decrease insulin resistance
How do Diabetes Drugs affect the Stomach and Small Intestine?
Delay starch absorption, increase incretin activity, decrease gastric emptying
How do Diabetes Drugs affect the Liver?
Decrease hepatic glucose production
How do Diabetes Drugs affect the Kidney?
Decrease glucose reabsorption
What is the Main risk when treating Diabetes with Drugs?
Hypoglycemia
Goal for T1D
Maintain insulin dosing based on eating and exercise habits
Goals for T2D
Achieving healthy glucose / lipid / BP levels AND weight loss
What food groups should Diabetic focus on?
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fiber, alcohol
What is the PRIMARY treatment for Hypoglycemia?
15 mg of Carbs
How does Exercise affect blood glucose levels?
Decreases insulin resistance → low BS and weight loss, increases risk for hypoglycemia
Interventions for Diabetics prior to Exercising
Check glucose before and after, eat 15mg carb snack before and every 30 mins during exercise
What is the most IDEAL way to monitor Glucose?
Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) that monitors Q5 minutes via interstitial fluid
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Less severe: Headache, fatigue, drowsiness Severe: pallor, diaphoresis, tachycardia, shakiness, confusion, slurred speech, unconsciousness
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
Excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, sudden weight loss, headaches
_____________ gives you time to be treated while _____________ DOES NOT (is an emergency)
Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia
Nursing Interventions for Unconscious Hypoglycemic patient
Check BS, administer Glucagon or Dextrose, repeat BS check in 15 mins
Nursing Interventions for Conscious Hypoglycemic patient
Check BS, give 15 mg of simple carbs, repeat BS check in 15 mins
Diabetic Considerations for Sick Days
Notify provider, continue basal insulin and oral meds, monitor BS every 2-4 hours, stay hydrated, maintain carbohydrate needs with solid foods or fluids containing sugar (if not tolerating solids)
What does the presence of Ketones in the urine mean?
Indicates that fat and protein are being used to maintain glucose needs which can lead to DKA
Normal Fasting BS
Under 100
Normal Random BS
70-115
HgB A1C indicating Diabetes
6.5+
T1D vs. T2D