Chapter 3 micro
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Phase-Contrast Microscopy
Light-dark pattern of specimen light refraction, leading to better understadning of 3-D resolution and true cell shape
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Electrons pass through a fixed, stained cross-section of a specimen in order to get high resolution is not very detailed
Light Microscopy
Specimens are stained to appear dark against a light background, and typically resolution is not very detailed.
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Electrons are scattered across a stained surface of a speicmen, providing high resolution of detail and shows very good 3-D approximation
Fluorescent Microscopy
Specimens appear dark, except for the cell parts that have been fluorescently dyed.
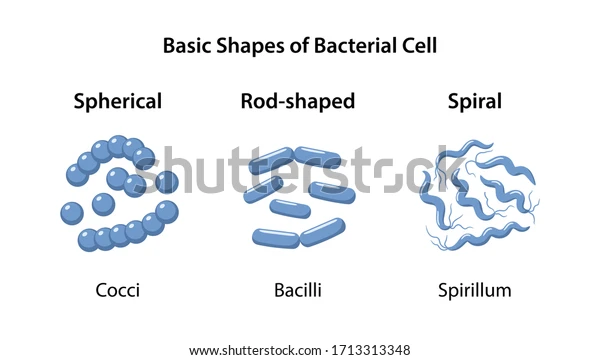
What does a coccus cell look like?
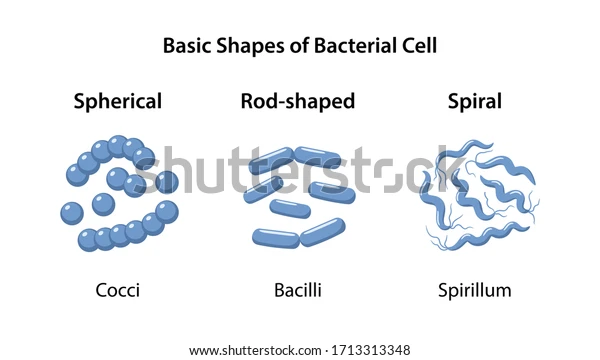
what does a bacillus (rod) look like?

what does a vibrio (curved rod) look like ?
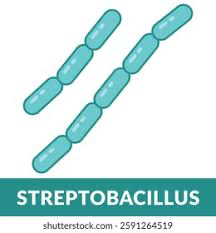
what does streptobacillus look like?
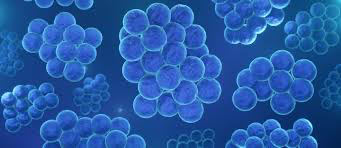
What does Staphylococcus look like?
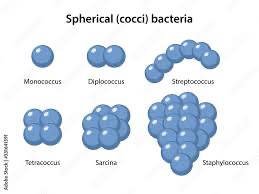
What does Diplococcus look like?
spirilla or a spirochete
A spiral-shaped bacterium is named either a ___ or _____ depending on the particular organisms characteristics.
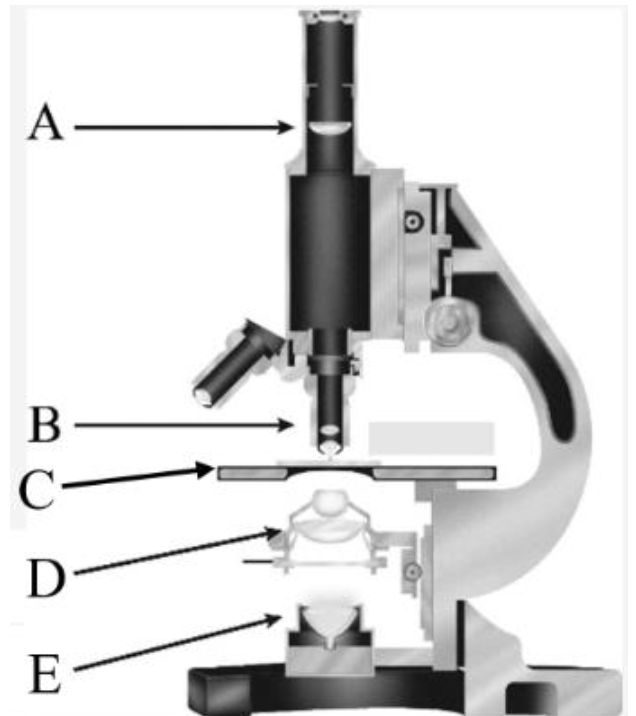
Eye piece/ Fixed eye piece lens
What is A?
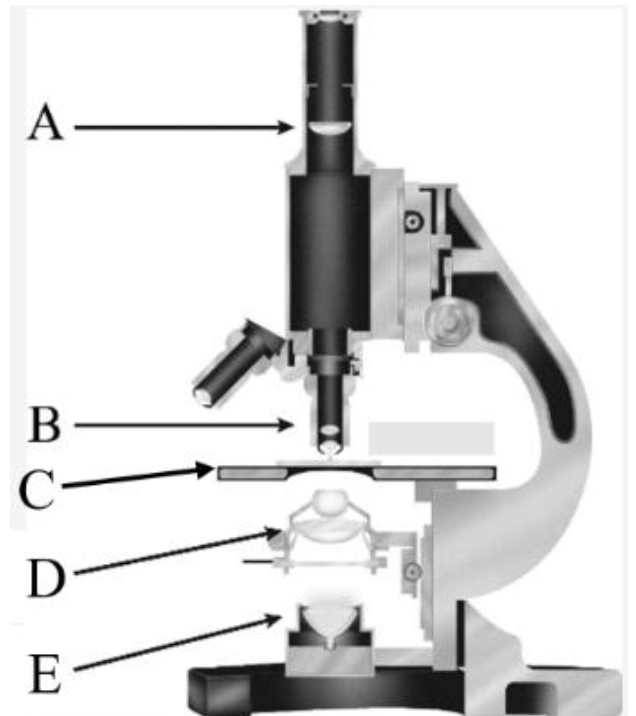
Objective lens
What is B?
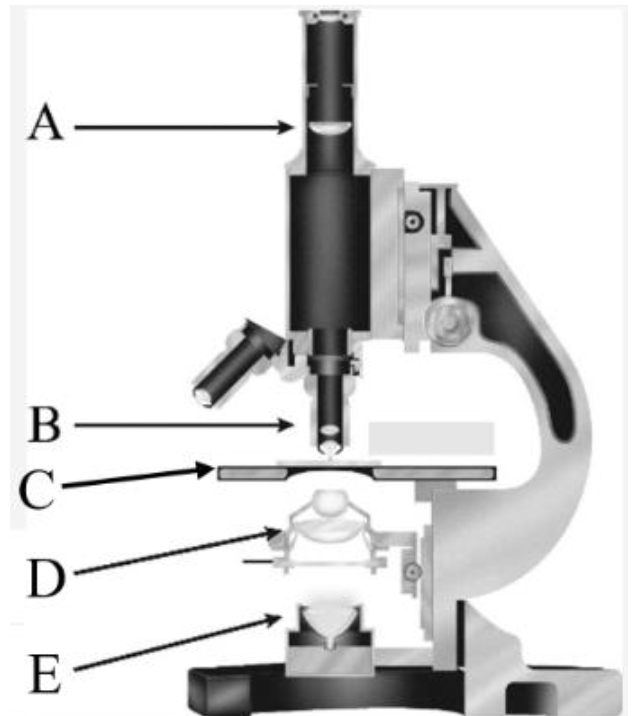
Stage
What is C?
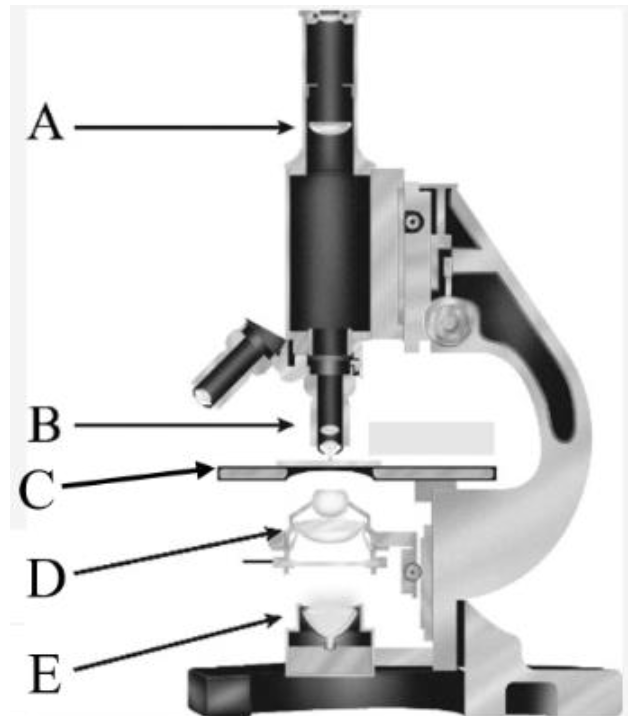
Condenser
What is D?
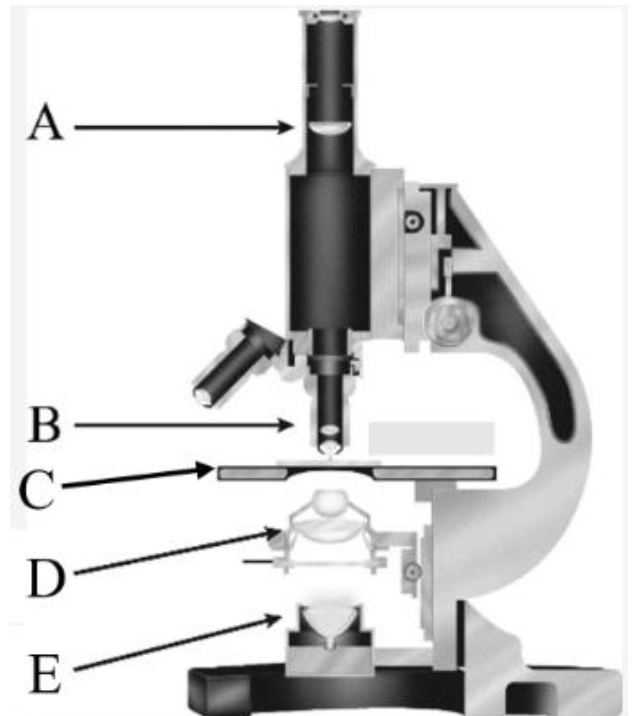
Light Source
What is E?
heat fixation
The process of using heat to kill and adhere/ stabalize bacterial cell sample to a slide is called _____ _____
10x, Objective Lenses
A standard Brightfield Compound Light Microscope typically has a fixed, or set, lens magnification in the eyepiece at ______ power, and a set of revolving lenses called _________ ____ that have different magnification powers.
200x (20 times 10 gives you 200)
For example, if you are viewing a specimen using the 20x objective lens, the total magnification would be?
purple
A Gram-positive cell will stain ______ color when a Gram stain procedure is performed
thick, lacks
A Gram-positive cell has a ____ layer of peptidoglycan and (circle one:) lacks/contains an outer membrane.
pink (sometimes reddish)
A Gram-negative cell will stain ____ _______ color when a Gram stain procedure is performed.
thin, contains an outer membrane
A Gram-negative cell has a _____ layer of peptidoglycan and (circle one:) lacks/contains an outer membrane.
If something has a differential function, it means there will be a color distinction between different groups of organisms, usually based on a physical characteristic difference or in terms of the ability to perform different biochemical functions.
If something, like a staining procedure or a particular type of growth medium for bacteria, has a “Differential” Function, what does that mean?
For example, a Gram stain groups bacteria into two groups based on the differences in the structure of their cell wall.
Primary Stain – stains all cells the same color, regardless of the cell wall structure, Gram-positive is purple and Gram-negative is purple
What is the function of crystal violet? And what are gram gram-negative/positive colors after each procedure?
Mordant – binds to the primary stains and intensifies the color of
the primary stain. Forms a water-insoluble compound with the
primary stain,Gram-positive is purple and Gram-negative is purple
What is the function of Grams Iodine? And what are gram gram-negative/positive colors after each procedure?
Decolorizer – removes color from the Gram-negative cells; however,
It traps the color in the Gram-positive cells by dehydrating the
Multiple layers of peptidoglycan, Gram-positive bacteria are purple and Gram-negative is colorless
What is the function of Ethyl Alcohol? And what are gram gram-negative/positive colors after each procedure?
Counterstain – imparts color back into the Gram-negative cells to
allow for a color distinction between the two cell types, Gram-positive bacteria are purple and Gram-negative bacteria are pink
What is the function of safrinin? And what are gram gram-negative/positive colors after each procedure?
Ethyl alchohol (decolorizer)
Which reagent in the Gram Stain procedure is considered the “Differential Step”?
Brownian motion
_______ ________ is bacterial cell movement due to the bombardment of water molecules, and the cell is NOT actually moving itself.
flagella, cillia, energy
True motility is when cells use a structure called ______ or _____ to physically move themselves, and this has an ____ cost for the cells to use these structures.