Nutrition Case Study - FINAL
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Hypercarotenemia
high carotenoid concentration in blood
Too many carrots or β-carotene supplements/pills
Vitamin D deficiencies
Osteomalacia: softening of bones in adults
Rickets: same thing in children
for both calcium absorption decreases
Who benefits from supplements? part 2
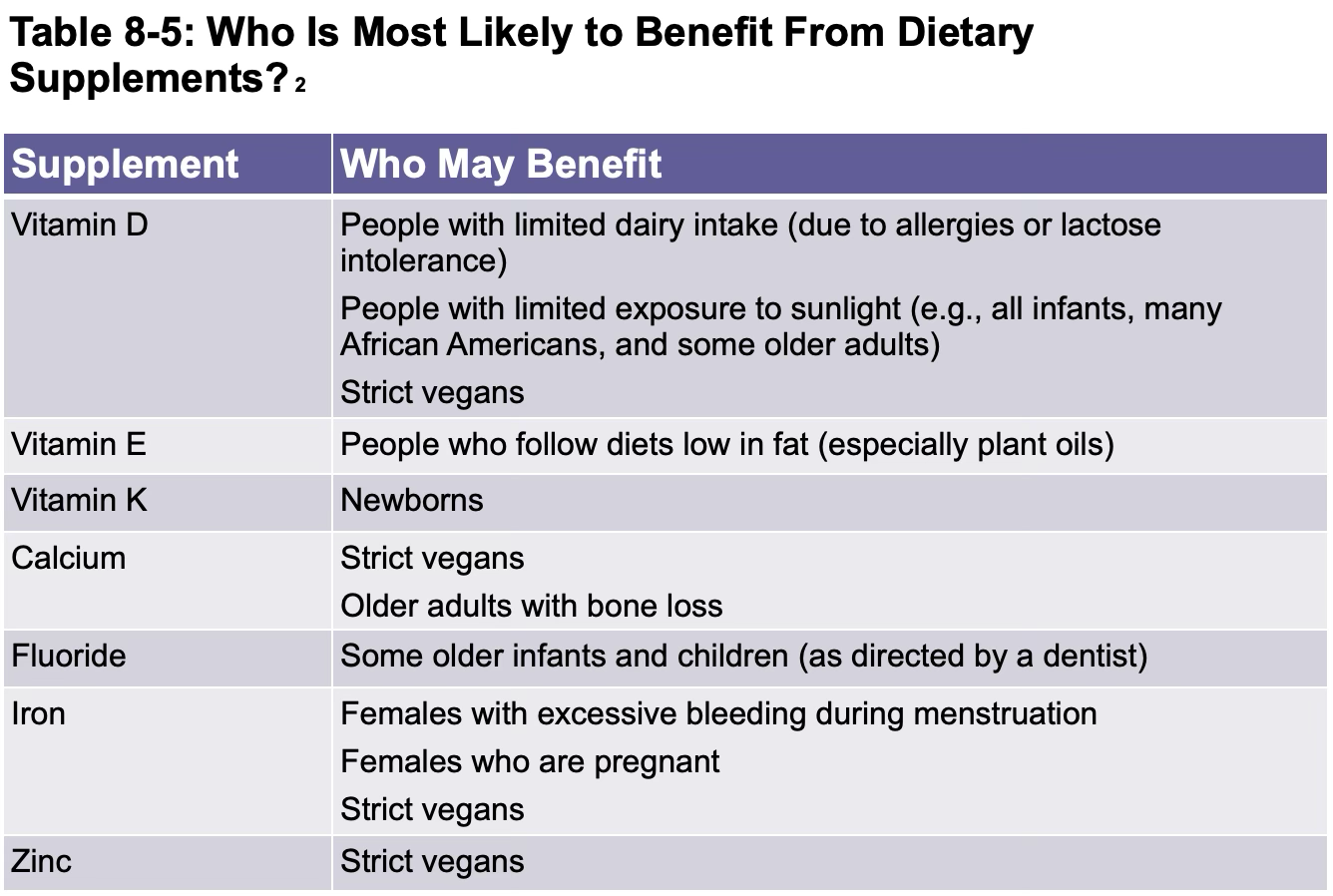
who benefits from supplements? part 1
Supplement | Who May Benefit |
Multivitamin/ mineral supplement | People on restrictive diets (< 1200 kcal per day), vegans, vegetarians People with suboptimal diets (for example, in cases of food insecurity or picky eaters) People with malabsorptive diseases People who take medications that interfere with nutrient absorption or metabolism Older adults (over 50 years of age) Females who are pregnant or those of childbearing age |
Various B vitamins | People who abuse alcohol |
Folic Acid | Females of childbearing age (especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding) |
Vitamin B-12 | Older adults Strict vegans |
Vitamin C | People who use tobacco |
Too much Vitamin E
can interfere with Vitamin K and anticoagulant medications
Vitamin K deficiency
In infants:
Vitamin K is administered by injection soon after birth
Infant’s gut at birth is sterile
GI tract doesn’t have bacteria
Can’t synthesize vitamin K needed for clotting if needed
In adults:
After long-term antibiotic use
Fat malabsorption
Maternal Folate Deficiency
Maternal folate deficiency (along with a genetic abnormality related to folate metabolism) has been linked to the development of neural tube defects in the fetus.
These defects include spina bifida (spinal cord or spinal fluid bulge through the back) and anencephaly (absence of a major portion of the brain).
Vitamin B-12 deficiency
common in vegans and older adults
Vitamin C
tobacco users need extra because of increased oxidation by tobacco smoke in the lungs
Too much Vitamin C
can be problematic for iron stores
stomach inflammation and diarrhea
kidneys rapidly excrete vitamin C
hyponatremia
TOO MUCH WATER
Sodium Deficiency
Groups at risk
Low sodium intake
Excessive perspiration
Persistent vomiting or diarrhea
Symptoms
Muscle cramps
Nausea
Vomiting
Dizziness
Shock
Coma
Potassium Deficiency
hypokalemia - low blood potassium
Causes
Chronic diarrhea
Vomiting
Laxative abuse
Diuretic use
Alcohol abuse
Eating disorders
Very low-calorie diets
Symptoms
Loss of appetite
Muscle cramps
Confusion
Constipation
Irregular heartbeat
chloride deficiency
lack of water, salt, fruits and veggies
Calcium deficiency
Tetany -
muscles become stiff or twitch involuntarily
Magnesium Deficiency
Deficiency causes:
Irregular heartbeat, weakness, muscle pain, disorientation, and seizures
Disruption in hormonal regulation of blood calcium by parathyroid hormone
Affects vitamin D activity
Magnesium loss caused by:
Heavy perspiration
Prolonged vomiting or diarrhea
Diuretic use
Alcohol use disorders increase urinary magnesium excretion
Iron Deficiency
Anemia
TOO much Zinc
Toxicity from zinc supplements and overconsumption of zinc-fortified foods
Interferes with copper metabolism
Intakes over 50 milligrams: diarrhea, cramps, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite
Intakes over 300 milligrams: depressed immune system function
Selenium Deficiency
Selenium content of foods:
Strongly dependent on selenium content of soil where plants are raised or animals graze
Low blood levels linked to increased risk of some types of cancer specifically prostate
Symptoms:
Muscle pain and wasting, heart damage, and thyroid dysfunction
Iodine Deficiency
Goiter: enlargement of thyroid gland caused by insufficient dietary iodine
During pregnancy—causes congenital hypothyroidism
Fluoride deficiency
cavaties?
Chromium deficiency
Deficiency symptoms:
Impaired glucose control
Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides
Osteopenia vs Osteoporosis
Osteopenia
Moderately low bone mineral density
Precursor to osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Severely low bone mineral density
Bones are porous, fragile, and susceptible to fracture