Force and Motion (Terms)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
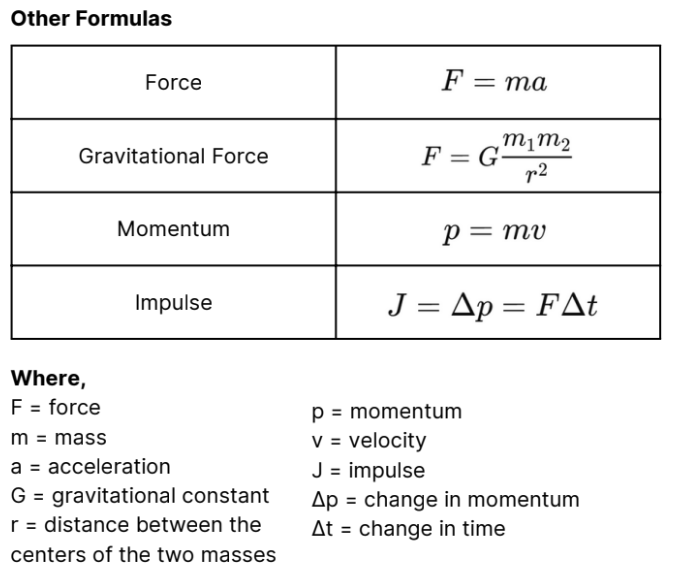
It is a push or pull that can cause an object to
accelerate, decelerate, or change its shape.
Force
It means it has both magnitude (how strong
the force is) and direction.
Vector Quantity
“An object at rest will remain at rest unless a force is acted
upon it.” or “An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in
motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the
same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced external
force.”
1st Law of Motion: Law of Inertia
“The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the
net force acting upon it and inversely proportional to its
mass.”
This can be expressed with the formula F=ma, where F is the
force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
2nd Law of Motion: Law of Acceleration
“For every action, there’s an equal and opposite reaction.”
This law means that forces always occur in pairs. If one body
exerts a force on another, the second body exerts an equal
and opposite force on the first.
3rd Law of Motion: Law of Interaction
It is a way of measuring how fast something is
moving. It tells you how far an object has traveled in a
certain amount of time. It is a scalar quantity.
Speed
Similar to speed but it contains both how fast the
object is and the direction of the object. It is a vector
quantity.
Velocity
It is the measure of how quickly an object’s
speed changes over time.
Acceleration
It is the change in position of an object from
its initial point to its final point in a specific direction. It is a
vector quantity.
Displacement
The total length of the path traveled by an object,
regardless of direction.
Distance
The size or length of a vector, representing the
quantity's size without considering its direction. A scalar
quantity.
Magnitude
A quantity that has only magnitude and no direction.
Scalars are represented using only a number and a unit.
Examples: Speed, distance, mass, temperature, energy.
Scalar Quantity
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
They are represented using arrows to show their direction
and magnitude.
Examples: Displacement, velocity, acceleration, force.
Vector Quantity
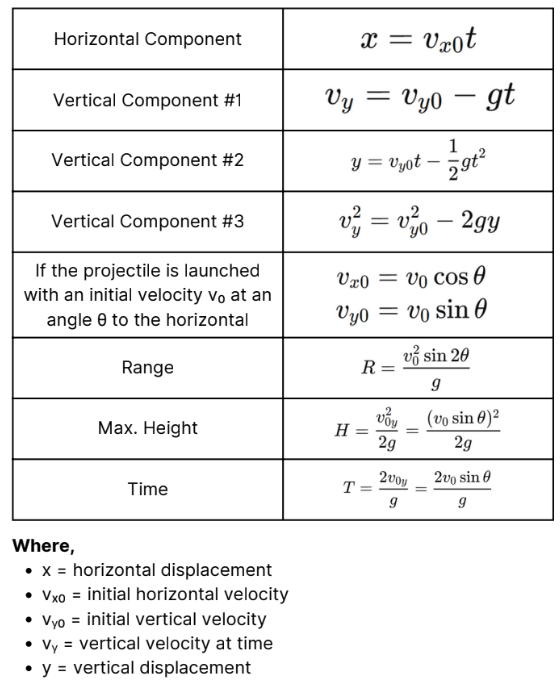
Formulas 1.0
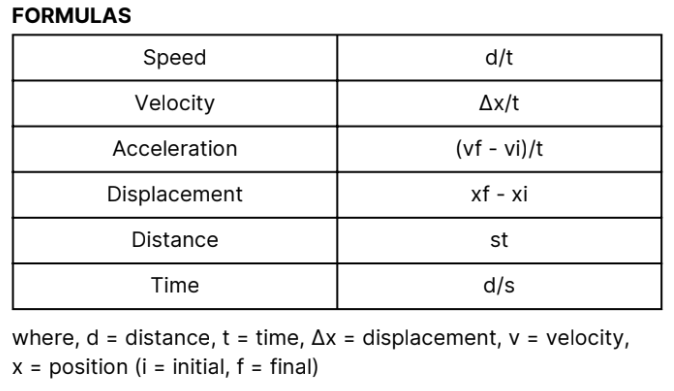
Formulas 1.0 (Triangle)
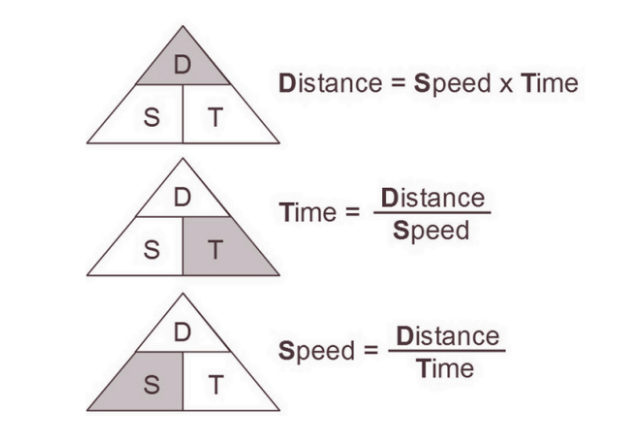
Formulas 2.0
Kinematic Equations for Uniformly Accelerated Motion
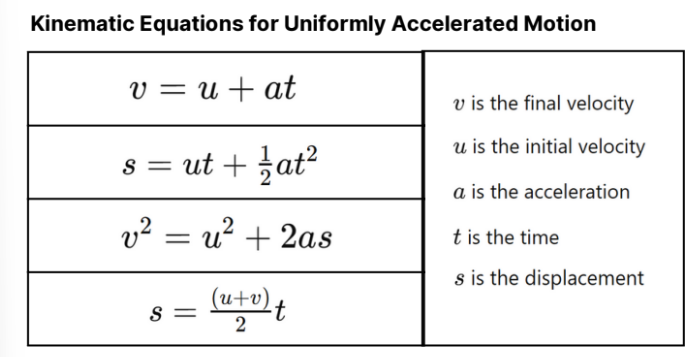
Motion of an object along a straight line with uniform velocity
as it covers equal distance in interval line.
Uniform Motion
One dimension with constant acceleration.
Objects involved are moving in a straight line whose
acceleration does not change over time.
The velocity of the body which is moving in straight lines
changes at a constant time.
Equal change in velocity in equal intervals of time.
Uniformly Accelerated Motion
This is the resistive force that opposes the relative
motion or tendency of such motion of two surfaces in contact. It
acts parallel to the surfaces and opposite to the direction of
motion or intended motion.
Frictional force
This force prevents relative motion between
two surfaces that are not moving relative to each other. It
must be overcome to start moving an object. (Ex.: Prevents a
stationary object from sliding down an inclined plane.)
Static Friction
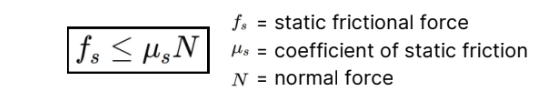
This force acts on moving
objects and opposes the motion. (Ex.: Opposes the motion of
a sliding object, such as a sled moving over snow.)
Kinetic (Dynamic) Friction

This is the support force exerted by a surface
perpendicular to an object resting on it. It arises from the
contact between two surfaces and prevents objects from
"falling" into the surface they rest upon. The normal force is
crucial in balancing the forces acting on an object, ensuring
that the object remains in equilibrium.
Normal Force
When an object rests on a horizontal surface
without any additional vertical forces, the normal force (N)
equals the gravitational force (mg) acting on the object.
Flat Surface

When an object rests on an inclined plane
making an angle θ\thetaθ with the horizontal, the normal force is
a component of the gravitational force perpendicular to the
surface.
Inclined Plane
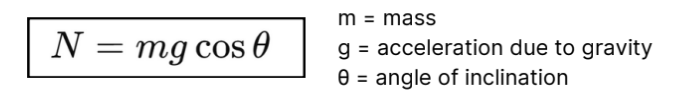
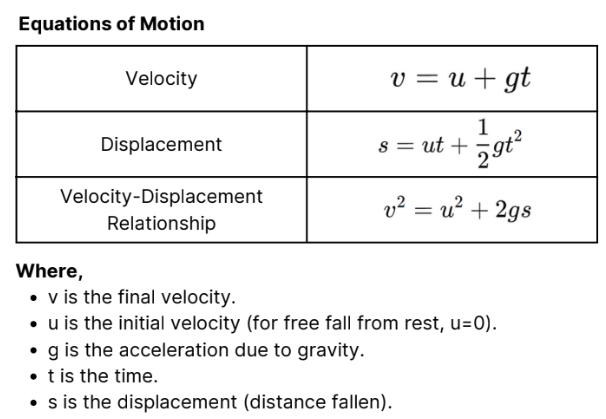
This refers to the motion of an object under the influence of
gravity alone, with no other forces acting on it. In a vacuum,
where air resistance is negligible, all objects fall at the same rate
regardless of their mass.
Free fall
Near the surface of the Earth, the acceleration due to gravity
is approximately?
g = 9.8 m/s²
Formulas 3.0
This describes the motion of an object that is
launched into the air and is subject to gravity. The path followed
by a projectile is called its trajectory, which is typically a
parabola.
Projectile motion
Velocity in the horizontal direction
(vx) remains constant.
Horizontal Component
Motion in the vertical direction is
influenced by gravity.
Vertical Component
The horizontal distance the projectile travels.
Range(R)
The peak vertical position of the
projectile.
Maximum Height (H)
The total time the projectile is in the air.
Time of Flight (T)
Formulas 4.0