Amazon rainforest carbon and water
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What are the annual yearly temperatures in the Amazon
25-30 degrees
how many GT/year of water is precipitated
13
How many GT per year of water is evaporated
7.2
What percentage of precipitation is recycled by evapotranspiration
50-60%
What percentage of rainfall is intercepted by trees
10%
what percentage of evaporation comes from intercepted rainfall
25%
How is convectional rainfall increased
Evaporation produces latent heat, which increases rainfall
How much water is evaporated annually?
8 trillion tonnes
How much water is lost annually to surface runoff
5.5 Gt
What is NPP
The amount of carbon retained in an ecosystem after respiration.
What is the NPP of the amazon
2500/g/m2/year
How much carbon is stored in the rainforest
100 billion tonnes
How much carbon does the amazon absorb per year
2.4 billion tonnes
the TRF is a carbon…
Sink - meaning it takes in more carbon than it releases
How much carbon is stored in above ground trees
180 tonnes per hectare
How much carbon is stored in the soil
200 tonnes per hectare
What proportion of global fossil fuels are absorbed by TRF
1/5
What are the 4 physical factors affecting the water cycle
rock porosity
Rock permeability
Relief
Temperature
How big is the amazon rainforest
6 million km
How many countries does the Amazon cover?
9
How much rain is there in the amazon year round?
2000mm
Why is there lots of surface run off in the amazon
High rates of rainfall, soil cant take all of it in - saturated overland flow
What is the NPP of the tundra
under 200g/m2/year
What does having a high NPP actually mean for the amazon
It indicates a rapid rate of biomass production - lots of growth, and so showing that the Amazon is a vibrant ecosystem with lots of growth.
How does temperature affect the water cycle?
High temperatures = frequent and intense convectional rainfall
Very high rates of evapotranspiration mean lots of recycling of water (50% of rainfall is returned by evap…)
Leeching is
Removal of minerals from soil by water moving down
Impact of relief on the water cycle in the amazon
Majority lowland, allows water to infiltrate more in gentle relief. Through flow main movement of water - some overland flow. Steeper areas near the feet of mountains have more overland flow.
Impacts of rock permeability on the amazon rainforest water cycle
Ancient shield rock is impermeable (metamorphic rock) - little percolation, and minimal storage capacity
Impacts of rock porosity on the water cycle
In areas with limestone (porous rock), rock can store rainwater & slow run-off rates.
Physical factors affecting flows and stores of the carbon cycle?
Temperature
Vegetation
Organic matter in soil
Mineral composition of rock
How does temperature affect the carbon cycle?
High temperatures allow for rapid nutrient cycle, and high biomass totals. Higher temperatures are catalysts for proccesses - decomposition and respiration, increasing the amount of carbon present
How does vegetation affect the carbon cycle
Carbon is transferred via photosynthesis, terrestrial to atmospheric relationship
Allows the TRF to become a carbon sink
How do the mineral composition in rocks impact the carbon cycle?
Generally, the ancient shield of igneous and metamorphic rocks (not carbonate, so no impact)
West Amazon has outcrops of limestone - store carbon
How does organic matter affect the carbon cycle
Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) in the soil - promoted by humidity and temperatures. Nutrients released to the soil very fast, for uptake by trees. Decomposition releases CO2 into the atmosphere
What fraction of the rainforest has been lost since 1970
1/5
What are the main reasons for deforestation?
Cattle pasture
Housing
Soybean farming
Logging
Roads
Impacts of deforestation on rainfall (madeira drainage basin)
Less trees, less uptake from roots and less transpiration, meaning less rainfall and water storage in the atmosphere
Removing trees decreases atmospheric humidity
Low albedo of forest trees (dark green colour absorbs suns insolation.) Ground becomes more reflective, reducing temperatures as heat cannot be retained - reducing convectional rainfall.
What is the estimated decrease in rainfall if deforestation continues?
20%
Impacts on runoff from deforestation:
Less interception and water storage within trees, and so more rain reaches the ground & faster. The intense rain reduces infiltration time, intensifying overland flow (shorter lag times)
In April 2014, what happened in the Madeira river?
Flooding
How high were discharge levels following the flood?
20m above normal
What are discharge levels?
The volume of water flowing through a river or stream at any given time
How many people were evacuated due to flooding?
68,000 families
What was the cause of flooding?
Deforestation in the upper basin (Bolivia and Peru), turning land into ranching and subsistence farming.
How is flood risk further enhanced due to deforestation
Deforestation leaves soil weaker and more vulnerable to erosion
Excess debris leads to sedimentation in rivers, reducing their discharge capacity and increasing flood risk
After deforestation, what percentage of rain goes straight to rivers rather than infiltrating?
50%
How much have rates of surface run off been increased
27 times
What is the above ground carbon biomass of grassland (the replacement of trees)?
16.2 tonnes per hectare , 1/11 of what it previously was.
What is the above ground carbon content of soy cultivation?
2.7 tonnes per hectare (almost 90x less)
How does deforestation impact carbon content in soils
Less leaf litter means a smaller carbon inout into soil
Pre deforestation, how much carbon was absorbed by photosynthesis
30.4 tonnes per hectare
10 years after deforestation, how much carbon was absorbed by photosynthesis
12.3 tonnes per hectare
post deforestation, how much carbon is stored in above ground biomass
12 tonnes per hectare
How are decomposers affected by deforestation
Soils with less carbon support less decomposers (need CO2), and so any leaf litter present is broken down slower and reduces carbon flow from soil to atmosphere
How does deforestation increase carbon transferred to the atmosphere
Slash and burn farming (mass combusting trees) emits excess amounts of CO2.
How is the nutrient cycle impacted by deforestation
Biomass is the principal store of carbon. Decomposition by fungi and bacteria mean as soon as leaves have fallen, nutrients are released for uptake, and the soil lacks nutrients. When the forest is removed, the nutrients are mainly removed and so minimal nutrients remain, explaining why it is difficult to regenerate a felled forest.
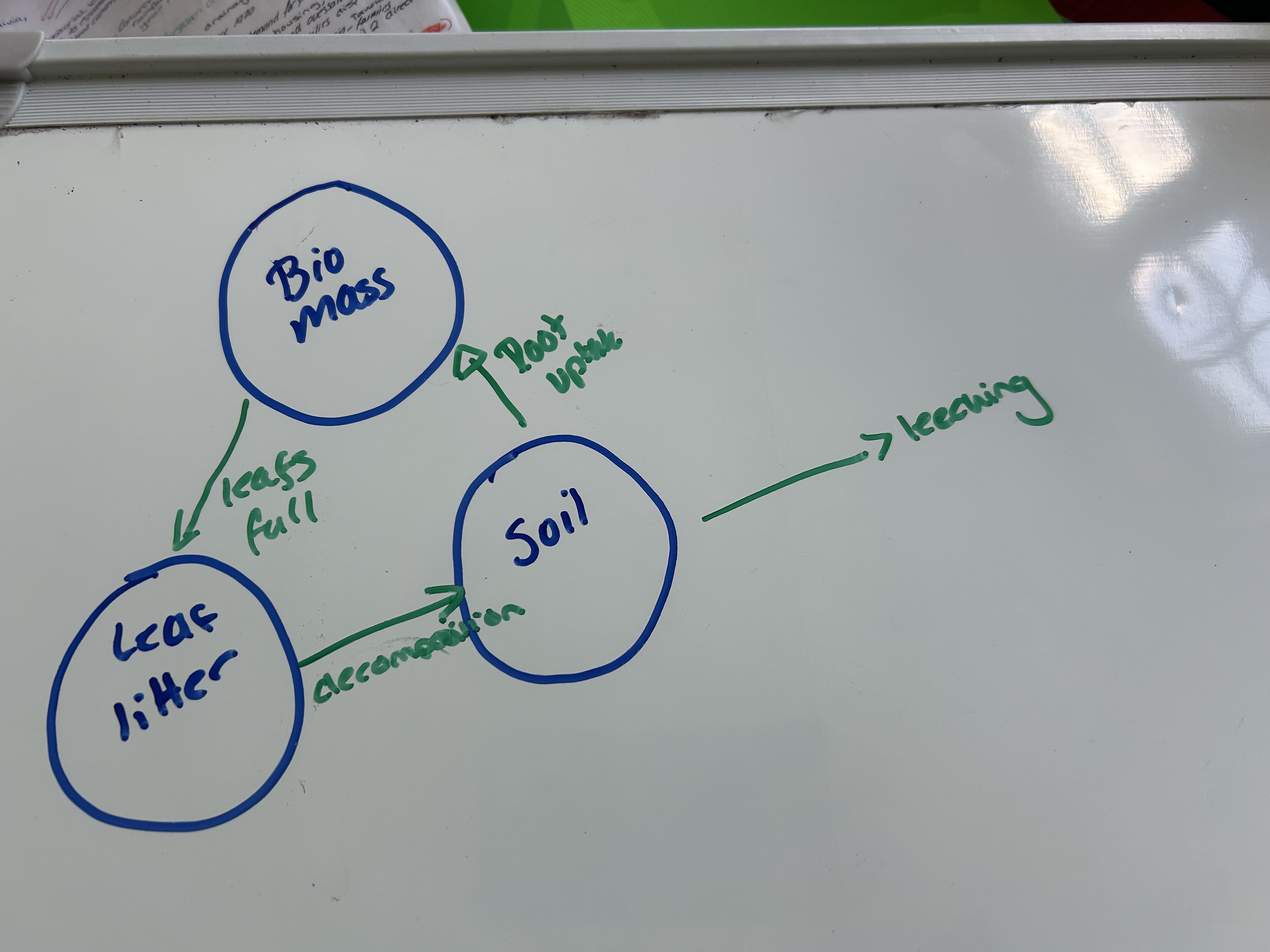
Nutrient cycle before deforestation (diagram)
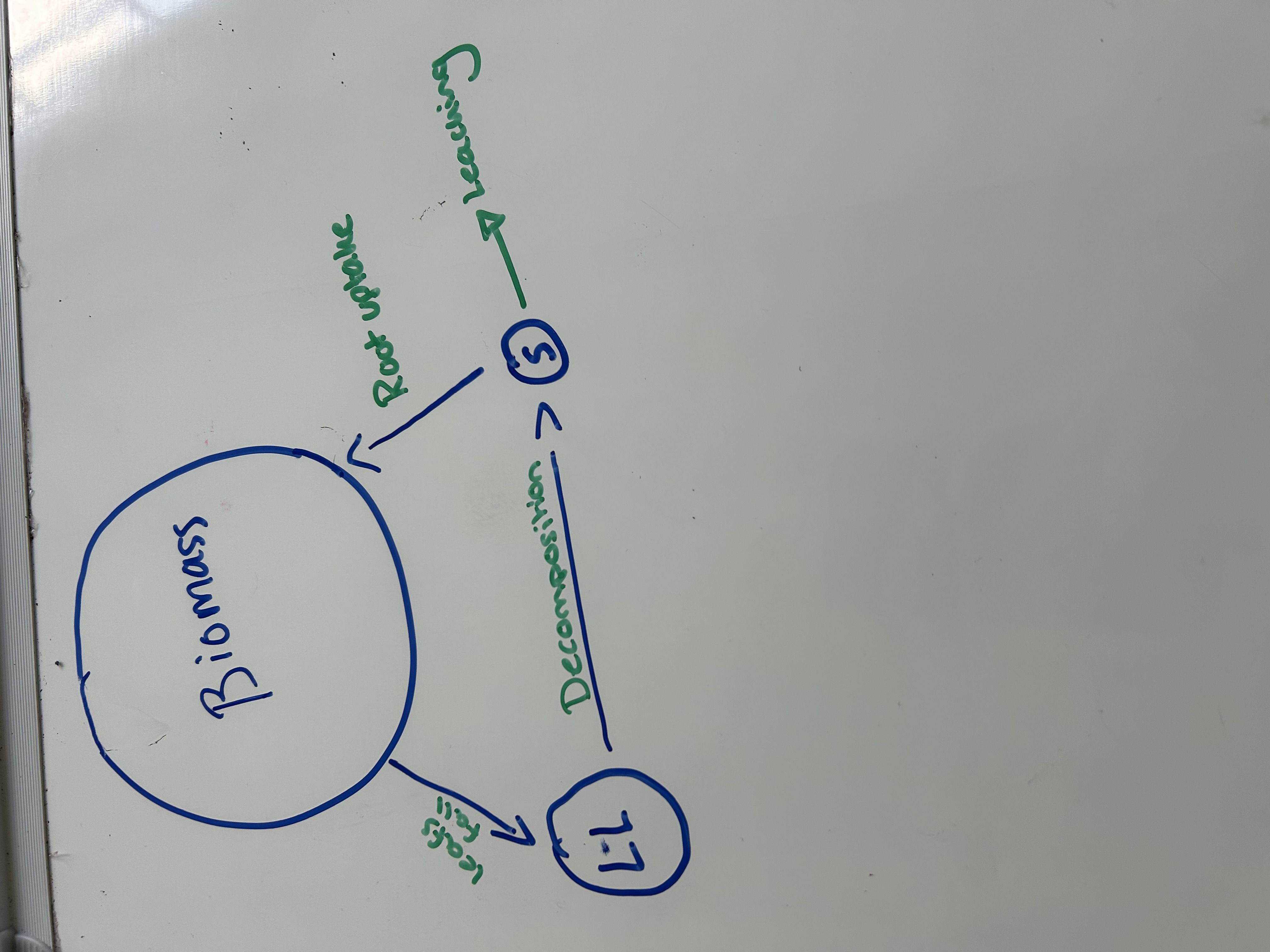
Nutrient cycle after deforestation (diagram)
What are the three types of managements in the TRF
Protecting remaining forest through legislation
Reforestation projects
Improving agricultural techniques
In what year did the Brazilian government establish conservation areas
1998
What percentage of the Brazilian amazon is national parks (Banning farming)
44%
What is a limitation of protecting forest through legislation
Brazil can only monitor what is going on in their area of the Amazon, as it is a transboundary area. Therefore, other countries are not able to be controlled by them.
How big is Parica
1000km3
What is the 4th most affected reigon by deforestation in the amazon
Parica
What is the Parica project
20 million fast growing seedlings have been planted, with the aim of growth in 25 years. Financial assistance is given to farmers owning smallholders. This timber will eventually be felled and sold
What are the limitations of the parica project
A monoculture is maintained in the forest, and so biodiversity is not improved. The trees are felled after 25 years, not letting them grow to full carbon sink potential. Farmers are only interested when there is a monetary incentive.
Who are the Suruí
A tribe native to western amazon (brazil)
How do the Suruí help reforest?
By planting native seedlings in deforested areas around their villages. In time, these trees give them food crops and timber as well as income through selling timber.
In what year did the surui join the REDD scheme
2009W
What is the REDD scheme?
Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation - essentially, the UN pays people who reforest areas with carbon credits, and large corporations who have exceeded their carbon allowance purchase the tribes carbon credits with real money
What is shifting cultivation
Due to low soil fertility, an area cleared for cultivation can only be used for a few years till it is abandoned and farming moves somewhere else.
What happends to abandoned areas of land after cultivation
Used for cattle ranching
How bad is the quality of land after cultivation
They can only support one cow per hectare
What agricultural techniques are used to help soil quality
Diversification (or rotational cropping) - alternating the crops planted every few seasons.