Physiology Exam 3 Lecture 10C [Renal Anatomy and Glomerular Filtration: Cabeza]
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
Role of the Kidney
Purify the blood
General way Kidneys do their function
Step one: Remove all dissolved material from plasma
Step two: Only take up what you want
Step three: Return the plasma with the good stuff
Body fluids
Total body water: 60% of body weight
Intracellular Water: 40% of body weight
Extracellular water: 20% of body weight
- Interstitial water= 15% body weight
- Plasma = 5% of body weight
Any fluid intake and output is from the
Plasma
The interstitial fluid must then equilibrate with the plasma and then the intracellular fluid must equilibrate with the interstitial fluid
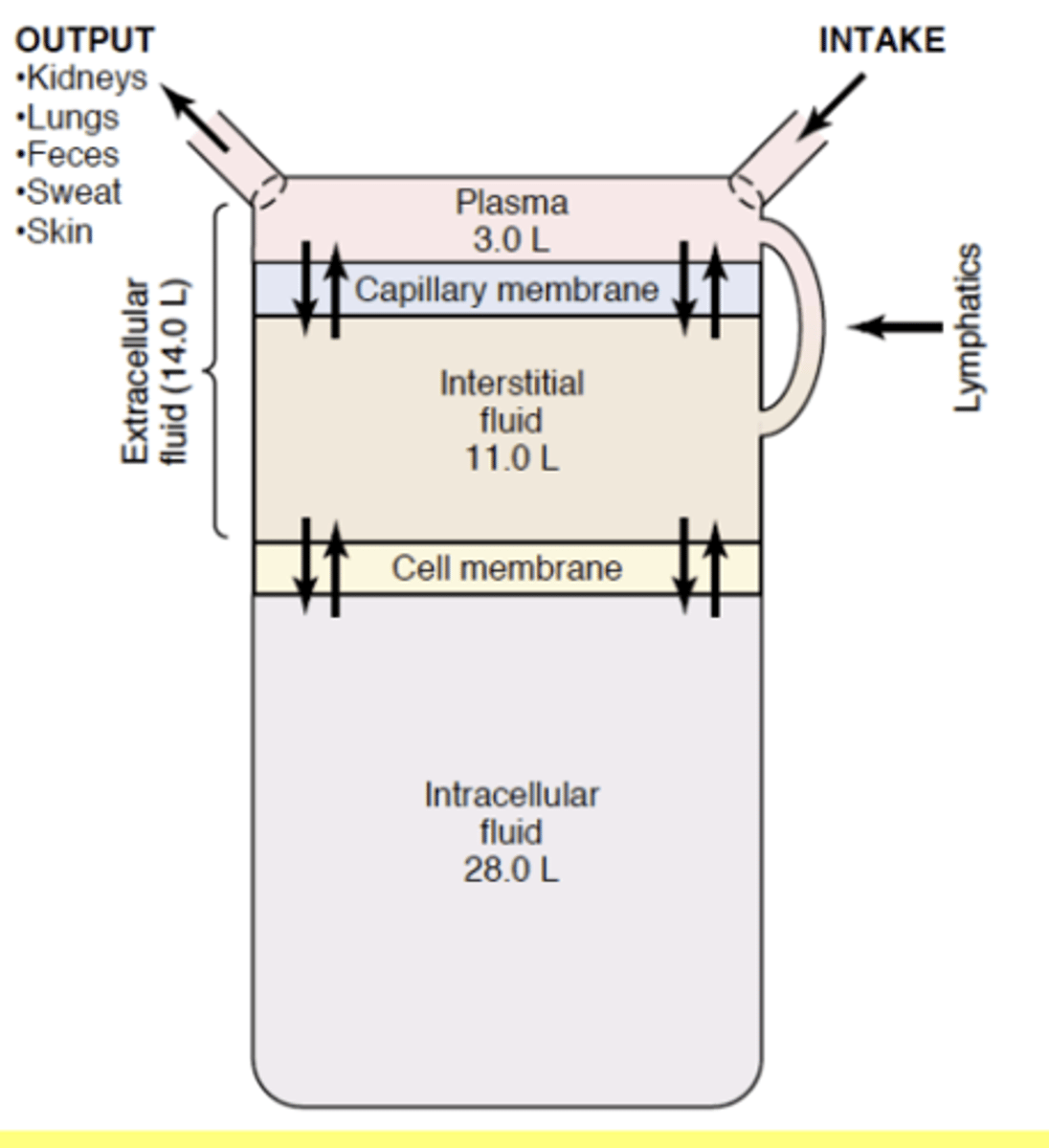
Major corporeal fluid intake
GI (30 min to equilibrium)
Major corporeal fluid removal
Kidneys, lungs, and skin
The major cation in the plasma is
Na+
The major anion in the plasma
Cl
and
Bicarbonate
Major cation in the interstitial fluid
Na
Major anion in the interstitial fluid
Cl
and
Bicarbonate
Plasma has a lot of proteins and interstitial fluid
does not
Intracellular fluids major cation
K+
Intracellular fluids major anion
Phosphate
Hyponatremia
Plasma Na less than 135 mEq/L
- Increase in ICF volume - cell swelling
- Over-hydration/lack of Na+/vomiting/excessive sweating
Hypernatremia
Plasma Na over 145 mEq/L
- Decreased ICF volume - cells shrinking
- Drinking seawater-soy sauce/ inadequate water intake/excessive loss of water
Hypokalemia
Plasma K less than 3.5 mEq/L
- Cell hyperpolarization
- Excessive alcohol.diarrhea/diarrhea/diuretics/ excessive sweating
Hyperkalemia
Plasma K+ over 6 mEq/L
- Cells excitability increased - especially heart
- Kidney disease/diuretics/high intake of K in foods
Note:
Not normally a problem with working kidneys
SUMMARY: Body water is mainly
inside cells
SUMMARY: Extracellular water is in the
interstitial space of in plasma
SUMMARY: Major changes to body water are the result of
water ingestion, urine production, sweating, and breathing
SUMMARY: The major cation/anion in intracellular water is
K+/PO4
SUMMARY: The major cation/anion in extracellular water (plasma, interstitial fluid) is
Na/Cl
SUMMARY: Changes to extracellular Na and K
can be very dangerous
Kidneys work at high
arterial pressures
Renal artery
Branch off the aorta coming into the kidney
Renal vein
Blood flow back to the vena cava from the kidney
ureter
From each kidney: travels down the abdomen to the urinary bladder.
Derek Note:
Just your friendly little Piss carrier
Urinary bladder
Stores piss
When its time to empty the urinary bladder
Empties through the urethra
Kidneys are located within
the rib cage which offers some protection
From the Pyramid into the kidney we call it the
Medulla
All the pyramids collect into
the renal papilla which lead to a urine draining area and exits through the renal pelvis and down the ureter
The business end of the kidneys
The Nephron
Two kinds of nephrons
Cortical nephrons
- 80% of all nephrons
Juxtamedullary nephrons
- 20% of all nephrons
Juxtamedullary nephron
Long loop that connects into the collecting duct
Cortical nephron
Short loop that connect into the collecting duct
Parts of the nephron (general)
Glomerulus
- Afferent arteriole
- Efferent arteriol
Bowman's capsule
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Loop of Henle
Distal tubule
Collecting duct
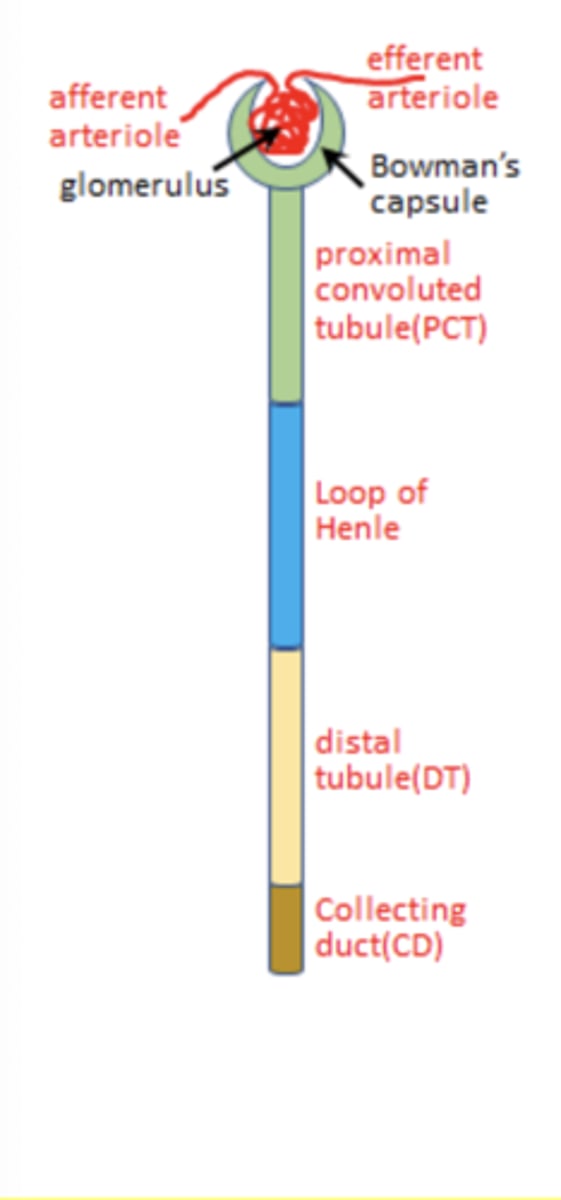
Parts of the nephron
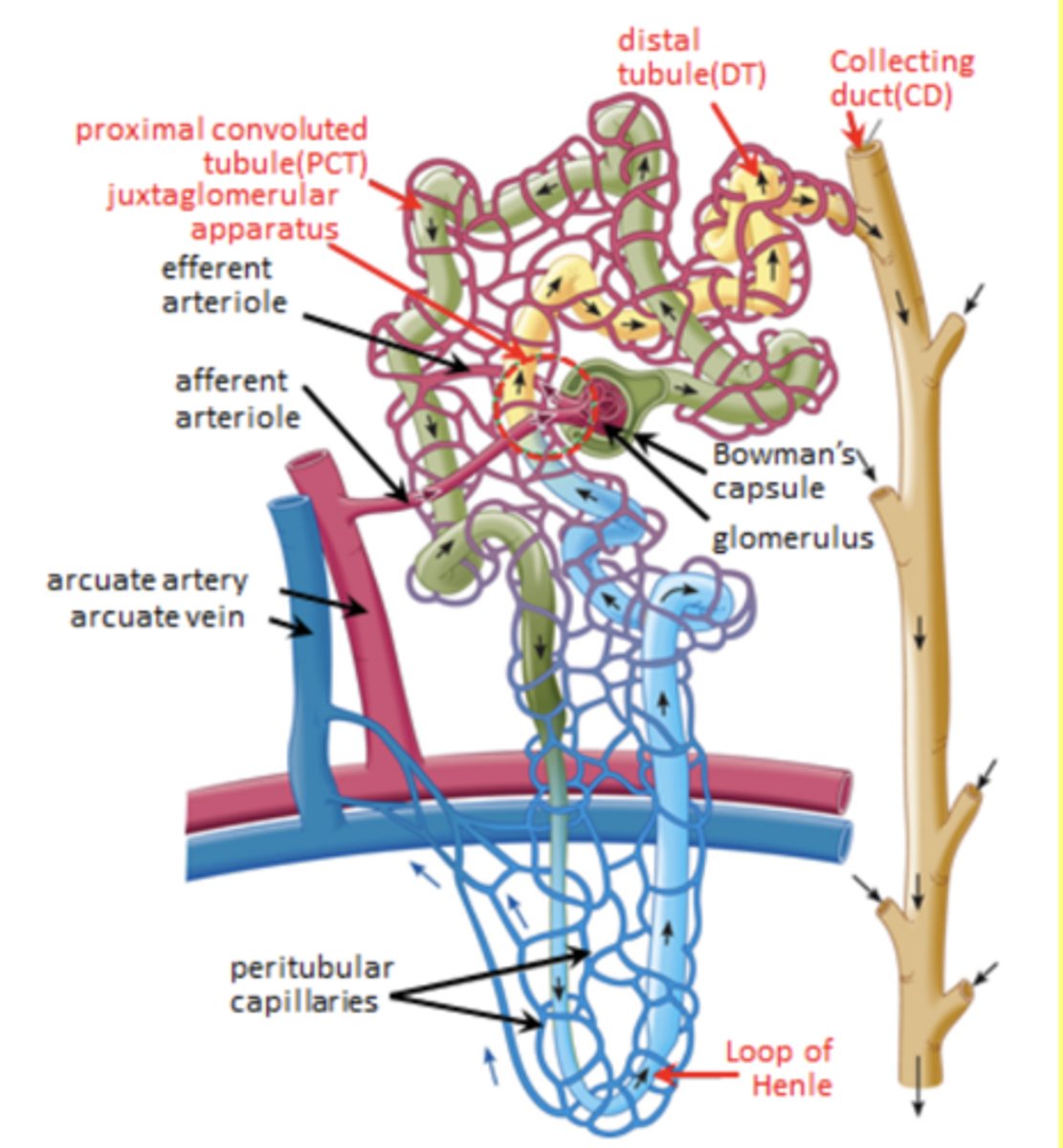
Loop of henle's job
Make urine dilute
Juxtaglomerular apparatus role
Feedback auto-regulation of glomerular filtration rate
Bowman's capsule/glomerulus =
glomerular filtration
SUMMARY: The renal system works at higher
arterial pressures than most other organs
SUMMARY: The functional unit of the kidneys are the
nephrons
SUMMARY: Two types of nephrons
Cortical nephrons: Have short loop of henle and make up 80% of the nephrons
Juxtamedullary nephrons: Have long loop of henle and make up 20% of the nephrons
SUMMARY: The different part of the nephron do very different jobs and have a complicated spatial position:
1. Bowman's capsule
2. Proximal convoluted tubule
3. Loop of Henle
4. Distal convoluted tubule
5. Collecting ducts
SUMMARY: The juxtaglomerular apparatus sits between
the distal convoluted tubule and the glomerulus
Basic function of the kidneys
Glomerular filtration:
- 5% of our plasma is filtered into the proximal tubule every minute by glomerular filtration. At this rate we would lose our entire blood volume in 20 minutes
Tubular reabsorption
- Substances that we need back such as water, glucose, amino acids, peptides, essential ions or minerals are almost entirely reabsorbed from the proximal tubule back into the blood
Tubular secretions
- Excretory products such as urea and protons to maintain acid-base balance are secreted into the ducts for elimination in urine
Glomerular filtrations begins the process of
renal reulation
Important materials from the filtrate are
reabsorbed
Some wastes or excress materials are
secreted
Water balance is
critically regulated by the kidney
Filtration of the plasma takes place at
Bowmans capsule
Reabsorption primarily takes place at the
proximal convoluted tubule
- Amino acids, glucose, fatty acids, etc
Regulation of excess materials primarily is dealt with at the
distal convoluted tubule
- Potassium secretion and some sodium reabsorption
TIP: Almost all the regulation (excluding the glomerular apparatus) takes place at the
distal end
Water balance requires the concerted actions of the
loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, and the collecting ducts
- Highly regulated process at the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting ducts
We filter 125mL/min of blood volume into nephrons. Since plasma volume is only 2.8L, we would lose our entire blood volume in 22 minutes.
We are saved by our bodies ability to
reabsorb essentially everything that is important to us
Substance reabsorption rates (%): Water
Reabsorbed: 99
Excreted: 1
Substance reabsorption rates: Sodium
Reabsorbed: 99.5
Excreted: 0.5
Substance reabsorption rates: Glucose
Reabsorbed: 100
Substance reabsorption rates: Urea
Reabsorbed: 50
Excreted: 50
Substance reabsorption rates: phenol
Reabsorbed: 0
Excreted 100
SUMMARY: The renal system basically accomplished 4 main functions
1. Glomerular filtration
2. Reabsorption of needed materials
3. Excretion of unwanted materials
4. Regulation of water balance (homeostasis)
SUMMARY: Bowman's capsule is responsible for the
glomerular filtration
SUMMARY: the proximal convoluted tubule is primarily responsible for the
reabsorption of needed materials
SUMMARY: The distal convoluted tubule regulates the
secretion of K and the uptake of Na
SUMMARY: The loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubules and the collecting ducts work in concert to regulate
water balance
SUMMARY: Actions at the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting ducts are
highly regulated
The Filtration of the blood plasma occurs at the
Bowman's capsule/glomerulus
The juxtaglomerular apparatus helps to
regulate how the glomerulus works
- Are we filtering to much or not enough plasma
The Glomerular capillaries are operating under _______ and are still only one cell thick
high pressure
The endothelial layer of the glomerular capillaries has a lot of finestra that are basically holes that allow for
the leakiness properties of these capillaries
In order to give the capillaries strength they are surrounded by a specialized cell called a
podocyte
Podocyte
foot structures in contact with capillary endothelium to create a regulated filtration barrier
Three primary filtration layers of the glomerular capillaries
1. Fenestrated endothelium: Provides pores that line the capillary
2. Glomerular Basement membrane
3. Filtration slits between podocyte foot structures
The glomerular basement membrane has what kind of charge
Negative
Derek Note:
- Like my attitude while I do this at 8:30pm when I'd rather be asleep
The negative change of the basement membrane allows for
repelling of negative charged proteins and forcing them to be retained in the plasma
- Makes the kidney not have to deal with these proteins (they keep their asses in the plasma like good little boys)
Fenestrated endothelium is very
leaky and acts like a sieve
Glomerular basement membrane is very
negatively charged and prevents proteins from going through
Filtration slits are controlled by the
podocytes and determine filtration rate by changing the filtration constant
Glomerular Filtration Rate
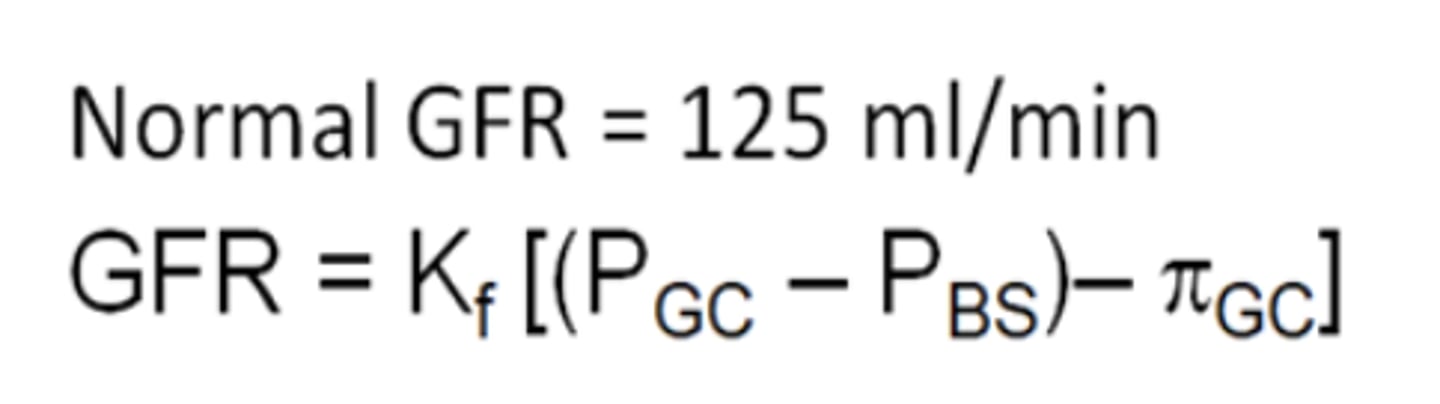
Glomerular Filtration Rate: Kf
Filtration coeffiecient
Glomerular Filtration Rate: PGC
Glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
Glomerular Filtration Rate:PBS
Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure
Glomerular Filtration Rate: πGC
Glomerular capillary oncotic pressure
Glomerular filtration rate: Why is there no oncotic pressure of Bowmans capsule (interstitial fluid)
because of that negative basement membrane not allowing for any proteins to get in.
Change GFR by
Changing the permeability (podocyte slits)
Change the pressure
Small changes in MAP
do not lead to large changes in GFR because of the myogenic regulation of the blood vessels entering the glomerulus
SUMMARY: Glomerular filtration takes place in
Bowman's capsule
SUMMARY: The glomerulus consists of three barriers
1. fenestrated glomerular capillaries (very leaky)
2. Glomerular basement membrane - highly negatively charged to prevent proteins from leaving the capillary
3. Podocytes- maintain capillary stability and control the filtration slits that primarily regulate the filtration coefficient
SUMMARY: The primary pressures for glomerular filtration are
capillary hydrostatic pressure
Bowman's capsule hydrostatic pressure
Capillary oncotic pressure
SUMMARY: Most of the hydrostatic and oncotic pressure
Do not vary much (under physiological conditions) and so the filtration coefficient is the main factor determining rate of filtration
The distal tubule interacts with the arterioles
To form a network of cells that create a feedback system
Monitors nephron function to allow compensation through changes in afferent and efferent arteriole pressures
Three cell types of the network of cells that create the feedback system from the distal tubule and arterioles
Mesangial cells
Macula densa
Granular cells
Mesangial cells have 4 major functions at the glomerulus
1. Physically support the capillaries
2. Adjust contractions based on blood pressure
3. Remove proteins adhering to glomerular filter
4. Provide part of immune responses at the glomerulus
Macula densa cells primarily
respond to changes in the level of Na+ in the distal tubule
High Na: Too high GFR
Low Na: Too low GFR
NOTE:
These cells are a physical part of the distal tubule
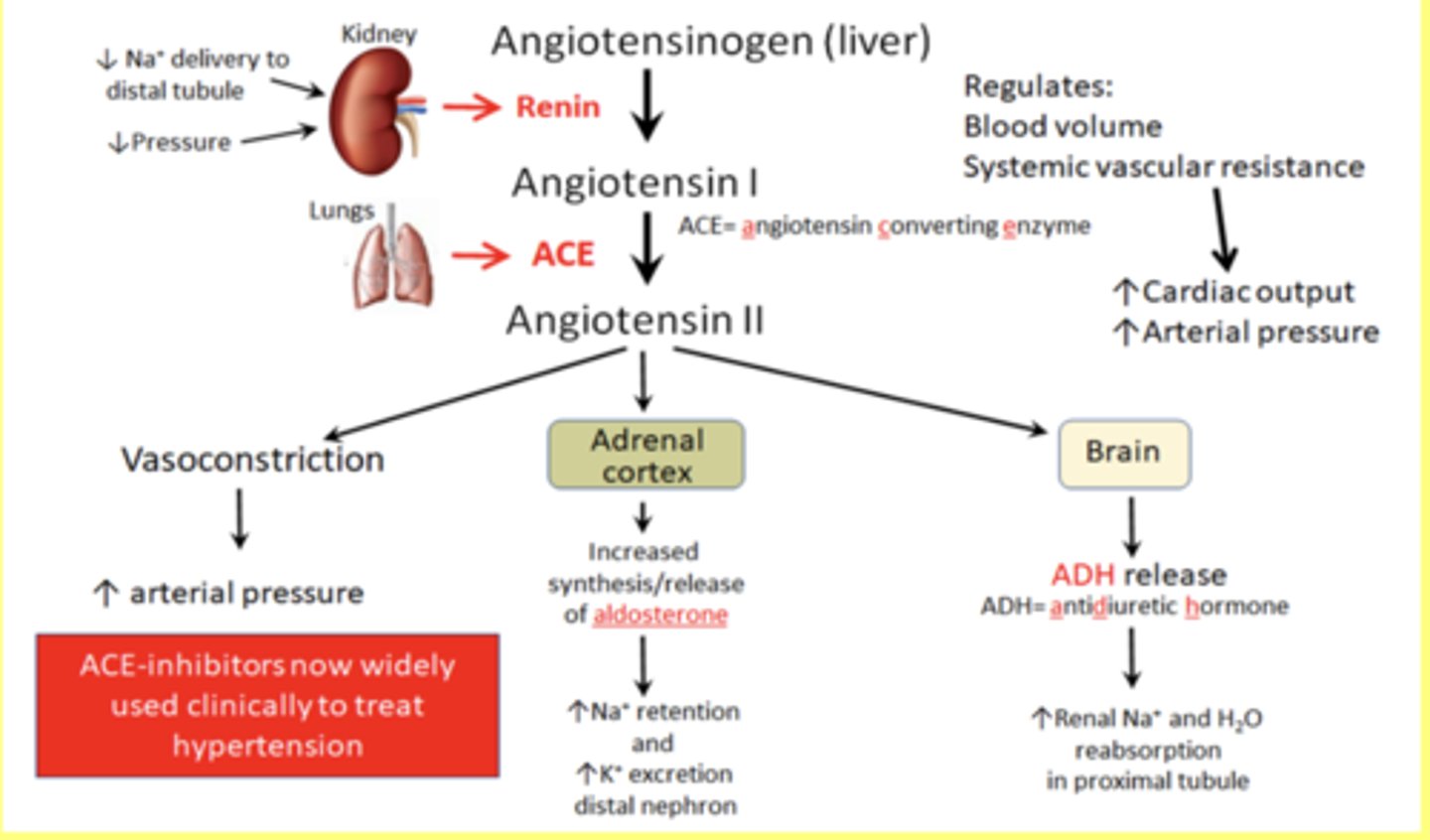
Granular cells release
Renin to control blood pressure (MAP)
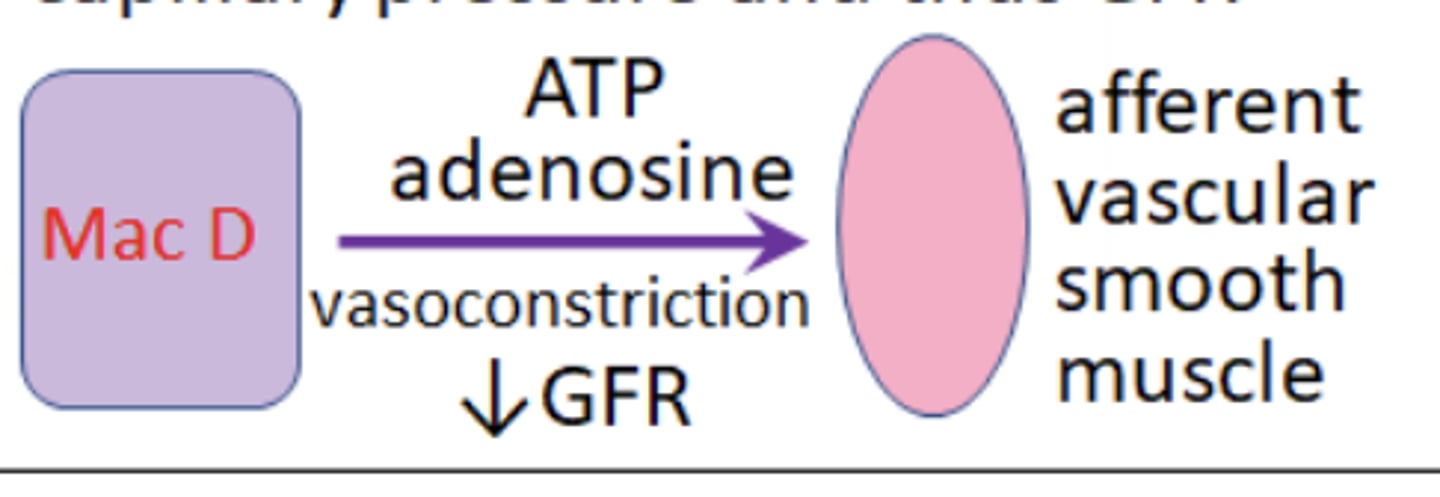
If the salt load is high = GFR high and thus
Macula densa cells scerete ATP and adenosine that signal to P2X receptors on the afferent arterioles causing constriction of the vessel, reducing blood flow, decreasing capillary pressure and thus GFR
If salt load is low = GFR low and thus
Macula densa secrete Nitric Oxide (vasodilator). Causes vasodilation and thus increase GFR
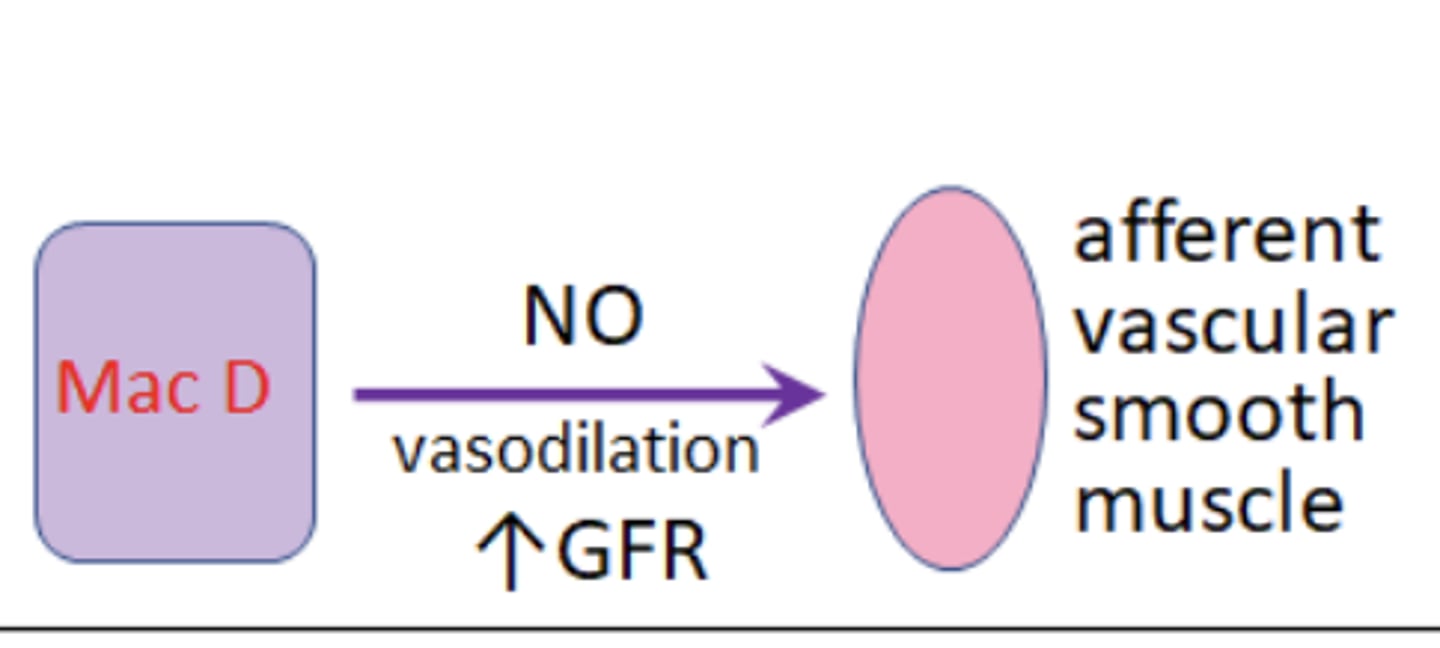
Just gotta know this figure