Personality Psychology - Exam 3 Dr. Breedin
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
What are the three levels of consciousness according to Freud?
The Conscious, the Preconscious, and the Unconscious.
Conscious Level in Freud's theory of personality development
The Conscious level includes thoughts and feelings that you are currently aware of.
Examples of The Conscious
What am I going to cook tonight, it's cold in here, my boyfriend hasn't texted me back
Preconscious Level in Freud's theory of personality development
The Preconscious contains thoughts that can be easily accessed or recalled with little effort.
Examples of The Preconscious
What did you have for dinner last night, how do you really feel about your boyfriend, what is your earliest memory
Unconscious Level Freud's theory of personality development
The Unconscious contains repressed memories and socially unacceptable thoughts that are not easily accessible.
Examples of The Unconscious
Why are you attracted to your boyfriend, why it is hard to open up to your mom, why you like going to big parties
How can unconscious information be accessed according to empirical research?
With incentives such as time and money.
What is Subliminal Perception?
Refers to the absorption of information below the level of conscious awareness (unconscious, below our awareness)
How can subliminal messages influence behavior?
Subliminal messages can make individuals quicker to think about related information but do not compel them to act.
What effect does 'sleeping on things' have on decision-making?
The unconscious mind may help in making complex decisions, particularly when considering multiple attributes.
Ryan just finished watching a video in which the phrase "shop at Publix" was presented subliminally. How might this affect Ryan?
When asked to make a list of grocery stores, he will think of Publix quickly
Assuming you're only thinking about this question right now, which of the following pieces of information is currently in your conscious mind?
This question
Assuming you're only thinking about this question right now, which of the following pieces of information is currently in your preconscious mind?
Your high school crush & a conversation you had on the phone last night
Assuming you're only thinking about this question right now, which of the following pieces of information is currently in your unconscious mind?
Why you like doing adventurous things (something you have never thought about before)
What is a Repressed Memory?
A Repressed Memory is a memory that has been unconsciously blocked due to its distressing nature.
What are repressors
People who repress things
What did Weinberger et al. (1979) find about repressors?
Repressors reported low anxiety but high defensiveness, showing physiological distress when exposed to unpleasant phrases (despite saying they were not distressed).
What did Davis & Schwarts (1987) discover about repressors' memories?
Repressors remembered fewer bad and good childhood experiences compared to non-repressors.
When do repressors dampen their emotional reactions?
Repressors dampen their emotional reactions during unpleasant experiences, not afterwards.
The extent to which you repress emotional experiences is
Part of your personality
Repressors
are dispositionally anxious and defensive, repress both pleasant and unpleasant experience, and dampen emotion while the unpleasant experiences are happening.
What is a False Memory?
An inaccurate recollection of an event that either did not happen or an inaccurate memory of something that did happen.
How does memory work according to spreading activation?
Memory works through networks of associations, where activating one concept can trigger related concepts.
False memories result from
Repeated associations (we think things are more likely to occur together)
What are Defense Mechanisms in Freud's theory?
Defense Mechanisms are psychological strategies used by the ego to protect itself from anxiety and conflict.
What role does the Ego play in personality according to Freud?
Mediates between id impulses and superego inhibitions, testing reality and operating mainly at the conscious level.
What is the function of the Superego?
Represents ideals and morals, striving for perfection and acting as a person's conscience. Operates mostly at a preconscious level.
What does the Id represent in Freud's model?
The Id represents basic impulses seeking immediate gratification, operating at the unconscious level.
Ego
Conscious Level
Superego
Preconscious level
Id
Unconscious level
Three types of anxiety according to Freud
Objective, Neurotic, and Moral
What is Objective Anxiety?
Anxiety that arises from an obvious reason.
What is Neurotic Anxiety?
Anxiety resulting from a conflict between the id and the ego.
What is Moral Anxiety?
Anxiety that stems from a conflict between the ego and the superego.
What is the purpose of defense mechanisms according to Freud?
To reduce anxiety and maintain self-esteem.
What are examples of defense mechanisms for Freud
Repression, Denial, Displacement, Projection
What is Denial as a defense mechanism?
Refusing to see the facts or minimizing responsibility for failures.
Give an example of Denial.
Saying 'Drinking this much every night isn't that bad'
What is Displacement in terms of defense mechanisms?
Redirecting impulses to something or someone 'safer' to avoid recognizing inappropriate feelings.
Provide an example of Displacement.
Getting mad at your boss but taking it out on your partner.
What is Projection as a defense mechanism?
Attributing one's own unacceptable qualities onto others to avoid self-hatred.
What is the False Consensus effect?
Assuming others are similar to oneself to rationalize one's traits or behaviors.
What is Repression?
The unconscious blocking of unpleasant memories or thoughts.
In 2020 you went to several big group events in spite of the pandemic. You told yourself it was ok because everyone else was doing it.
You were using the false consensus effect
Your beloved fish died when you were 5. This was very difficult. As an adult you no longer remember this happening.
This is an example of repressed memory.
What is Cognition in relation to personality?
The general term referring to awareness and thinking.
What are 3 cognitive effects on personality
1) we perceive the world differently
2) we interpret the world differently
3) we have different conscious goals
What is Perception in relation to personality?
People have different personalities because they perceive because the world around them differently.
Everyone perceives the same reality differently, our personalities influence what we perceive
sometimes we are accurate and sometimes we are not
What is Field Dependence?
individual difference in perception that has implications for our personality
What does it mean if a person is Field Independent
They Focus on the details, but have trouble seeing the big picture; able to see pictures separate from the background
- Socially Independent
- Better at tuning out distractions and focusing on tasks
- good at learning new languages
- choose careers in natural science, math, or engineering
- harder for them to see the bigger picture
What does it mean if a person is Field Dependent
they focus on the big picture, but have trouble seeing the details; trouble seeing embedded pictures; distracted by the background
- Distracted more easily, hard to focus when there are things going on around them.
- See connections between categories of information
- Think in categories or chunks rather than focusing on watch piece of information
- Choose careers in social science or education
- Attentive to social cues
- People-Oriented
What is the Embedded Figures Test used to measure?
Field dependence and independence in perception.
Pain tolerance in relation to personality
Differences in pain tolerance are actually related to differences in personality
What are Reducers in terms of pain tolerance?
Individuals who tolerate pain well and have a nervous system that reduces sensory stimulation.
Traits of Reducers
- Report that noise is less stimulating
- Tend to be higher in sensation seeking
- drink more coffee
- become bored more easily
- similar to extraverts - seek stimulation because of weak perception
What are Augmenters in terms of pain tolerance?
Individuals who do not tolerate pain well and have a nervous system that amplifies sensory stimulation.
Traits of Augmenters
- Sensation-avoiding
- prefer quieter music
- less likely to use drugs
- similar to introverts - see less stimulation because of stronger perception
On group projects, you are good at coming up with a broad goal for the project, are you more field dependent or independent?
Field dependent
Constructs
a concept or provable hypothesis that summarizes a set of observations and conveys the meaning of those observations
People are motivated to find meaning in different circumstances in life and
to predict what is going to happen to them in the future
What is Personal Construct Theory?
A theory developed by George Kelly that describes how people use personal constructs to interpret their experiences.
Personal constructs
lens through which you see the world; beliefs you routinely use to understand your world
What is an Internal Locus of Control?
The belief that one has control over events in their life and can influence outcomes.
What are the benefits of having an Internal Locus of Control?
Positive academic and occupational outcomes, higher self-esteem, and a greater sense of control over life.
What can be a downside of having an Internal Locus of Control?
It may lead to victim blaming and reluctance to give up control.
How do personal constructs affect anxiety?
Anxiety can arise when personal constructs fail to explain life events.
What is an External Locus of Control?
A generalized expectancy that events are outside of your control, leading to beliefs like 'things happen to me' and 'there's nothing I can do.'
How has the population's locus of control changed over time?
People today are more likely to believe that outcomes are due to luck rather than their own control.
What is the relationship between gender and locus of control?
Women tend to endorse a more external locus of control than men.
What is Learned Helplessness?
A condition where individuals, after experiencing inescapable situations, develop a lack of effort to escape in future situations.
What did Seligman's research on Learned Helplessness involve?
Participants were exposed to unpleasant noise during problem-solving tasks, with some assigned to solvable and others to unsolvable tasks, leading to poorer performance in the unsolvable group.
What is Regulatory Focus Theory?
A theory that describes how people regulate their behavior through two focuses: Promotion Focus (approach-oriented) and Prevention Focus (avoidance-oriented).
Promotion Focus
Approach-Oriented; going for the gold; BAS
Prevention Focus
Avoidance-Oriented; protect yourself and stay safe; avoid failures and negative outcomes; BIS
What is the difference between Entity Theory and Incremental Theory of Intelligence?
Entity Theory posits that intelligence is fixed and cannot change, while Incremental Theory suggests that intelligence can grow with effort.
2 Implicit Theories of Intelligence
Entity Theory of Intelligence
Incremental Theory of Intelligence
Entity Theory of Intelligence:
destiny mindset, intelligence cannot change, fixed mindset
Incremental Theory of Intelligence
growth mindset, intelligence is something that can change; with effort, intelligence can increase
Implicit Theories
meta-theory that people think something is fixed or changeable; began to be applied to other areas of research
· Entity (destiny) theory: finding the right person, ghosting
· Incremental (growth) theory: work on fixing problems in the relationship
How do implicit theories influence academic performance?
Students with an Incremental Theory of Intelligence tend to put more effort into school and achieve greater academic success.
You find it easy to remember the broad take away from lecture but struggle to remember definitions
you are field dependent
You believe that people are generally good. When someone treats you bad you feel confused. This belief you hold about people is and example of
a personal construct
What are the three parts of emotion?
The Feeling (affect), Changes in the Body (physiological), and Action Tendencies (behavior).
What are the two approaches to studying emotions?
Categorical (distinct emotions like anger and joy) and Dimensional (emotions measured along dimensions such as valence and arousal).
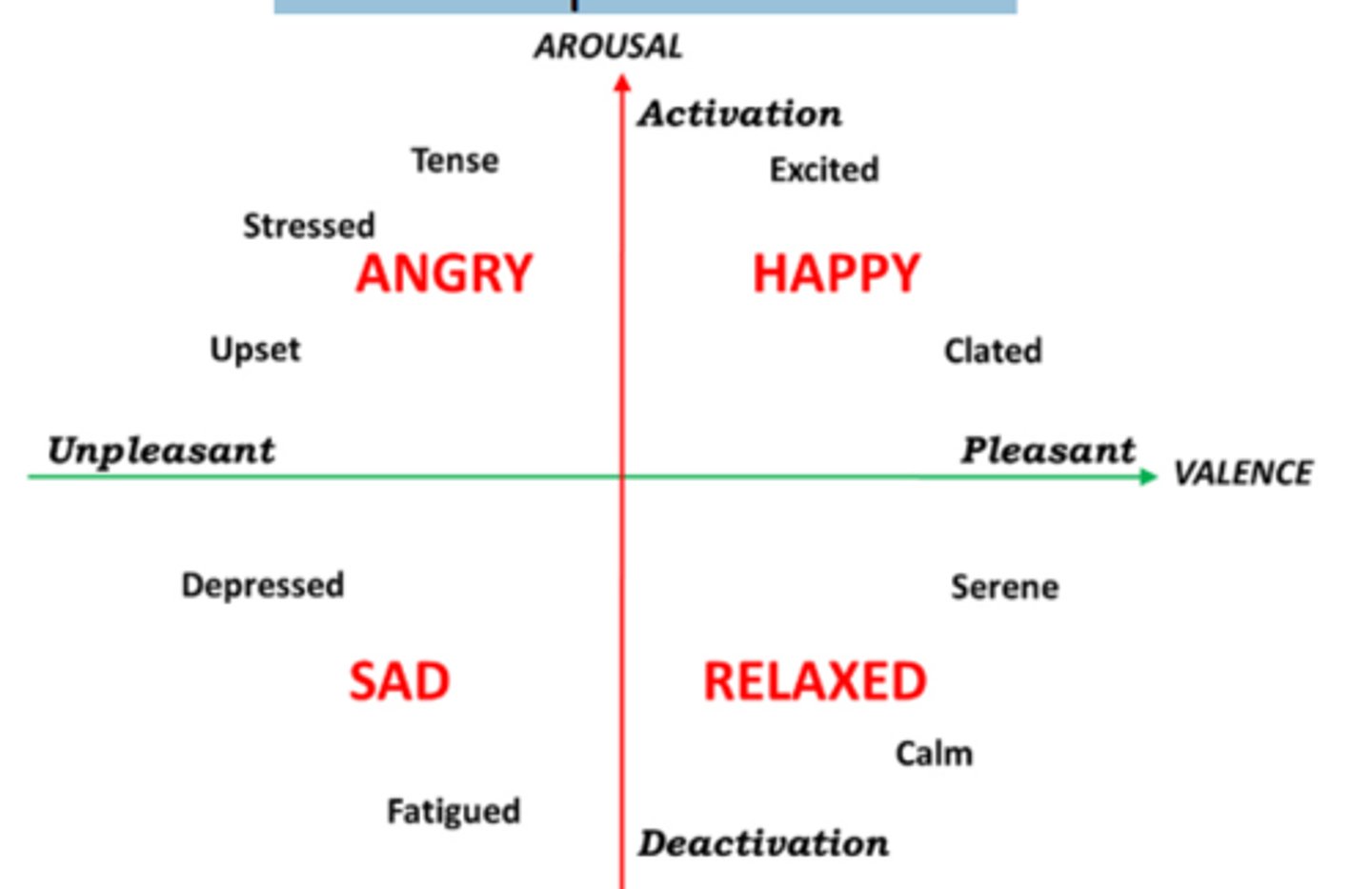
What are the two fundamental dimensions in the circumplex model of emotion
valence and arousal
What does the Circumplex Model of emotion illustrate?
It maps emotions along two dimensions: Valence (pleasant to unpleasant) and Arousal (low to high).
What are the two components of happiness?
Cognitive (life purpose and satisfaction) and Affective (more positive than negative emotions; hedonic component).
What are some correlates of happiness?
Happy people tend to be less hostile, more helpful, physically healthier, and have better social skills.
Is there a difference in happiness between men and women?
No significant difference; happiness levels are similar across genders and cultures.
Is there a difference in happiness regarding age?
No difference but different things make people happy at different ages
How does wealth relate to happiness?
People in wealthier countries tend to report higher happiness, but once basic needs are met, more money does not necessarily increase happiness.
What is the impact of spending money on others versus oneself on happiness?
Spending money on others tends to increase happiness more than spending on oneself.
What personality traits are predictors of happiness?
High extraversion and low neuroticism are strong predictors of happiness.
What is the significance of Costa & McCrae's research on happiness?
They found that happiness is associated with high positive affect and low negative affect.
What is the relationship between neuroticism and happiness?
Individuals low in neuroticism tend to be happier, while those high in neuroticism are likely to experience more negative emotions.
What does the Valence Dimension represent in the Circumplex Model of emotion?
It ranges from unpleasant to pleasant (X-axis).
What does the Arousal Dimension represent in the Circumplex Model of emotion?
It ranges from low arousal to high arousal (Y-axis).