Gram staining & Negative vs Simple stains
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Cell Morphology
Reffers to shape of conglomerate of millions/billions of cells
Size
Shape
Color
margins(edges)
texture/appearance
elevation
Growth Characteristics
growth/no growth- colonies on solid media (agar)
Turbidity on broth (cloudiness)
Contamination
unexpected growth
incorrect species?
Staining purpose
Cells are naturally colorless in bright field microscope
helps to provide information on cell size, shape and arrangement
Cell Morphology (specific)
Coccus- Round
Bacillus- rod
Vibrio- curved rods
Spirochete- Spiral
Spirilla (two sperms joining)
Diplococci
Two round
Tetrad
4 coccci
Sarcina
Cube of cocci
Staphylococci
Bunches of round
Streptococci
Lined up cocci
Diplobacilli
2 rods
Streptobacilli
Line of rods
Palisades
THINK: roman columns next to each other- rods touching at each end
Coccobacilli
Rounder rod
Simple stain
White backround- bacteria color of the stain
Heat fixed so cells(cytoplasm) tend to shrink
Stain has positively charged chromogen (attracted to cell wall)
Negative Stain
India ink
Dark background, bacteria look white
Not heat fixed, better for seeing morphology since cells remain true size
Stain has negatively charged chromogen (repels cell wall)
Negative stain procedure
Small drop india ink near one end
Small amount of culture and disperse in drop of stain without spreading the drop
Use second slide to spread drop of stain + evenly
Rest one end of clean slide on center of draw at an angle until it spreads along edge then push slide toward the clean slide
let air dry and DO NOT heat fix
Simple staining specifics
Enhance visibility; stains cell allowing for contrast with white background
Morphology: cocci, spirilla, bacilli
Arrangement: isolated, clustered, or in chains
Non differential- does not distinguish between bac.
+ charged chromogen= binds to negatively charged lipid membrane (bacteria takes up color)
Gram staining purpose
Most important differential stain
First test run on specimen for identification (cell size, shape, arrangement)
helps doctors determine right antibiotics for infections
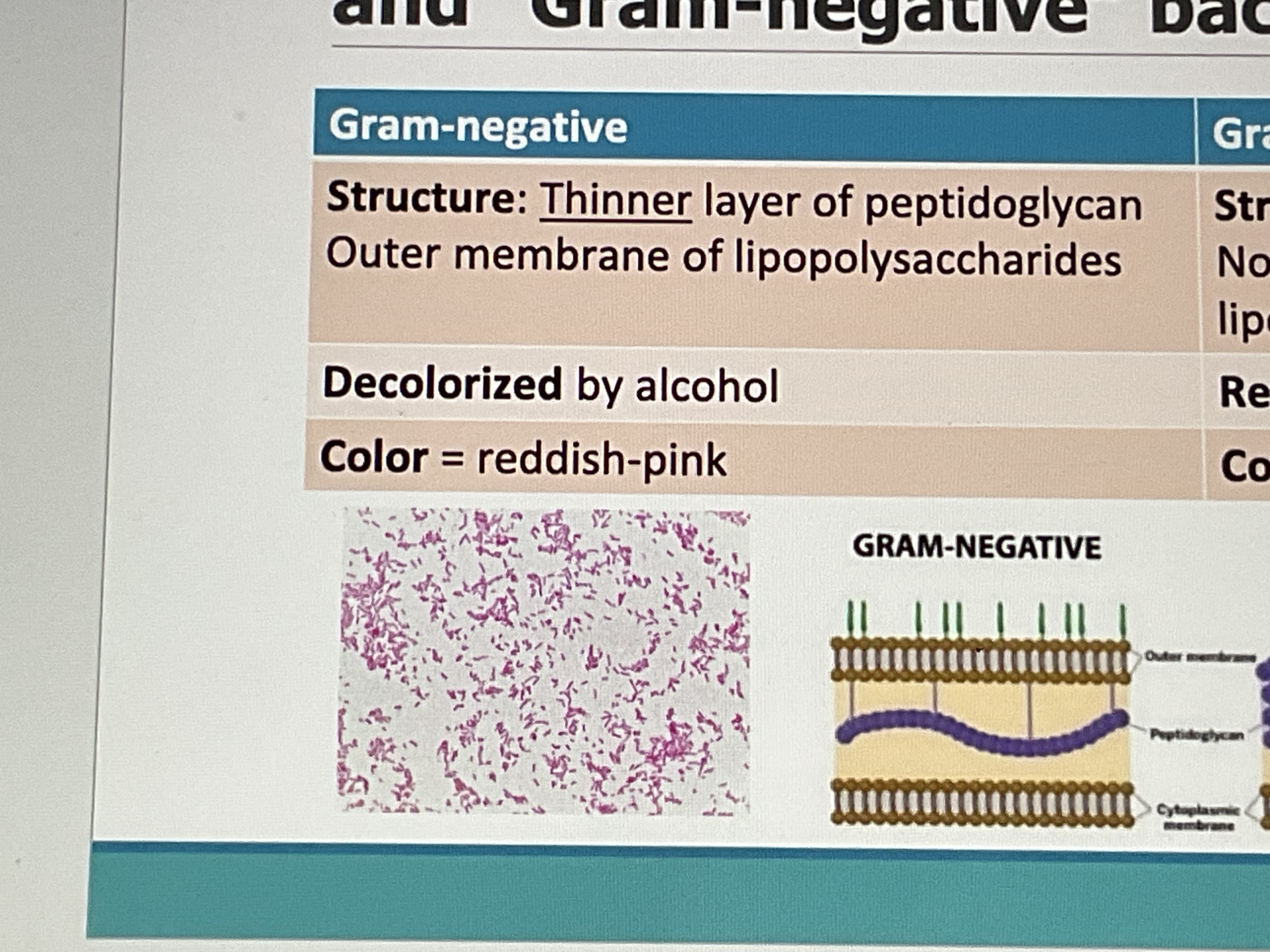
Gram- negative
Structure- thin peptidoglycan, outermembrane of lipopolysaccharides
Decolorized by alcohol
Color: pink
“Sandwich”
Gram-positive
Structure: thick peptidoglycan, no outer membrane of lipopolysaccharides
Resistant to decolorization
Color: purple

Gram staining stages
cells transparent prior to staining
Crystal violet stains both. Iodine = mordant (intensifies and locks in color if g+)
Decolorization (alcohol/acetone) removes crystal violet (if gram -)
Safranin counterstains gram -
Gram stain procedure
mixed smear, air dry, heat fix 10 sec
Crystal violet 60 sec
Iodine 60 sec
Decolorizer (ethanol) for 3 second
Safranin (counterstain) 60 sec
Blot dry w/ bibulous paper
Common mistakes
Over decolorization= redish g+ cells (false negative)
Under decolorization= purple G- cells (false positive
Too much bacteria= thick smear, hard to see individual cells