14 Redox II
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Describe an electrochemical cell.
two different metals dipped in salt solutions of their own ions and connected by a wire- one is an oxidation reaction and one is a reduction reaction.
The more reactive metal gives up its electrons and is oxidised, and this becomes the anode. The less reactive metal becomes the cathode.
Electrons flow through the wire from the most reactive metal to the least.
2 half cells joined by a wire, voltmeter and a salt bridge
Which metal is the anode and which is the cathode?
Anode- where oxidation occurs
Cathode- where reduction occurs
What points are important in setting up an electrochemical cell?
clean the surfaces of the metal strips using sandpaper.
Clean any grease or oil from the strips using propanone.
Create a salt bridge linking the two metal solutions by soaking filter paper in KNO₃
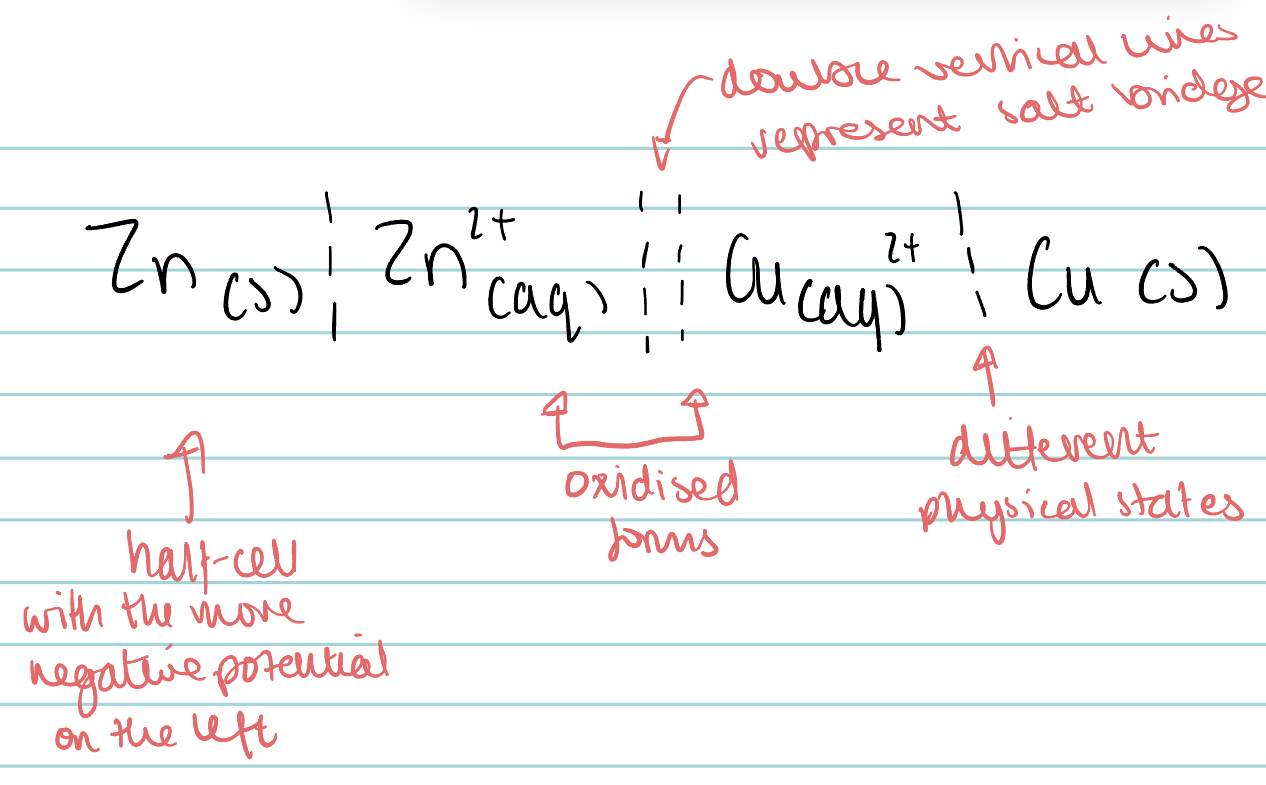
When drawing an electrochemical cell, which node should be drawn on the left?
the anode, where oxidation happens.
EXCEPT HYDROGEN FUEL CELL WHICH IS ALWAYS ON THE LEFT
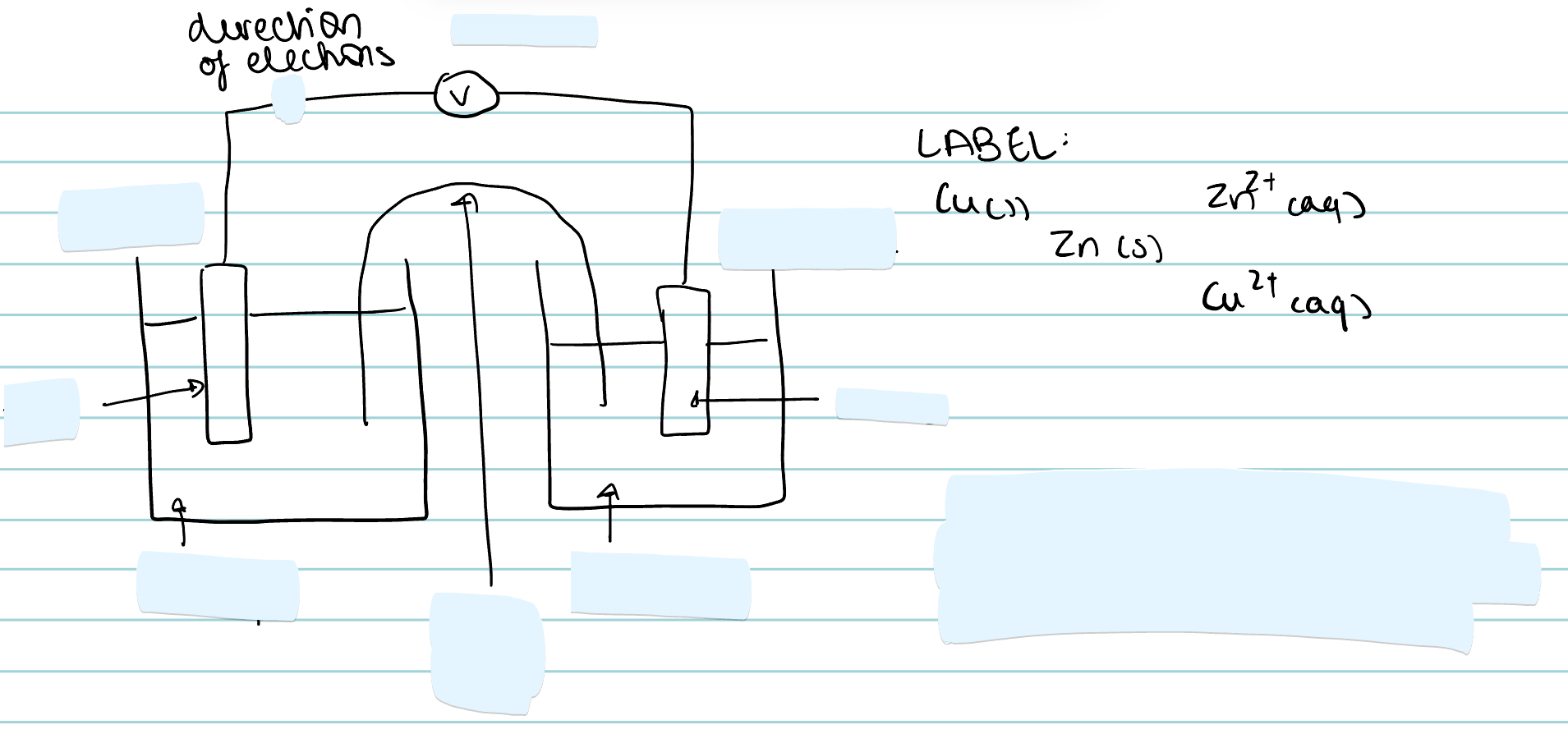
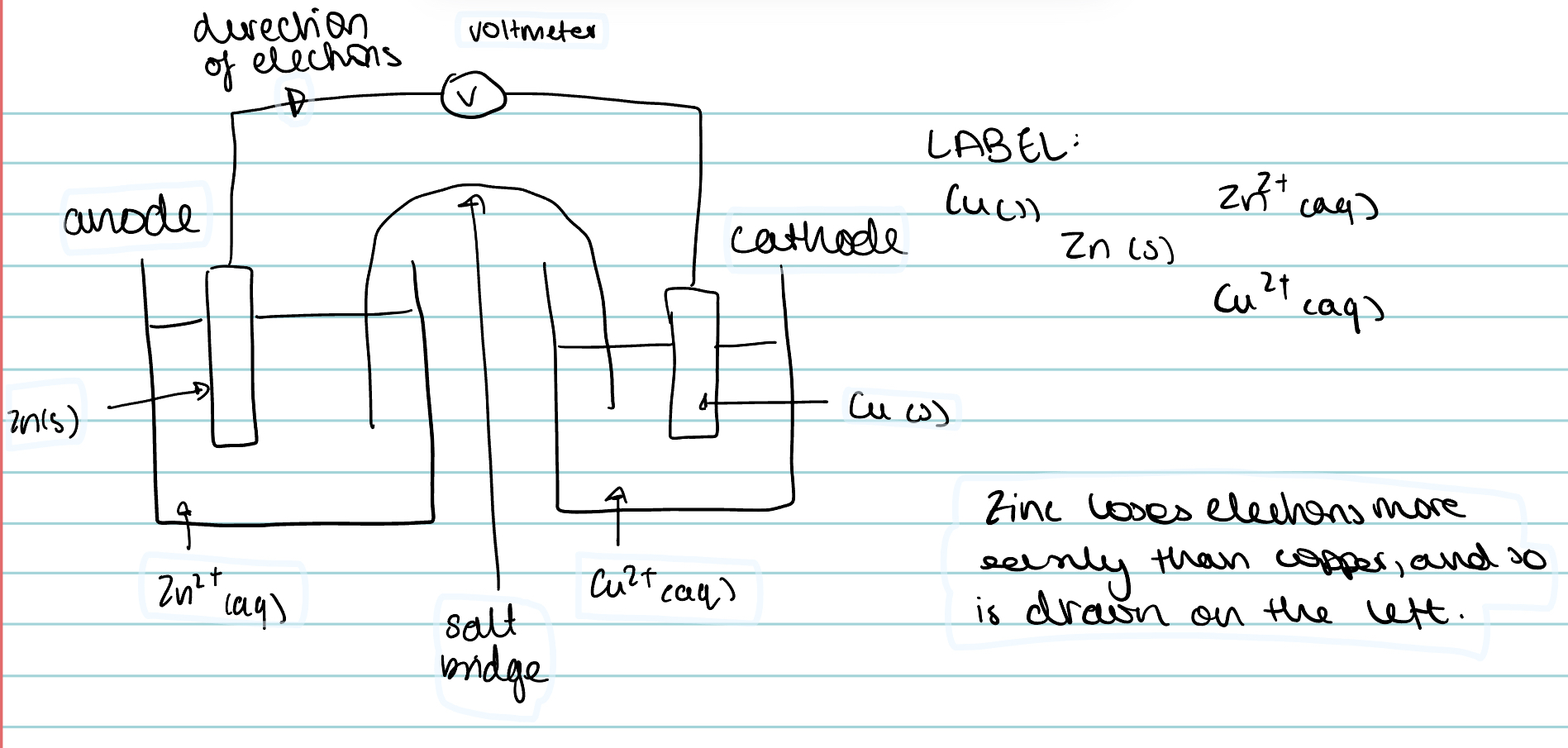
Label this cell. Include the direction of electrons, the anode and the cathode.
How are the reactions in an electrochemical cell written?
They are reversible, with reduction reaction always written going forward with the electrons on the left hand side
When might a platinum or graphite electron be used?
When a half cell involves solutions of two ions of the same element, eg. Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺
The electrode just needs to be inert and conductive electricity.
What is electrode potential?
A measure of how easily the substance in the half cell is oxidised.
How does a potential difference build up in the cell?
Due to the difference in charge between the electrode and the ions in solution.
Out of the half cell with the more positive electrode potential and the half cell with the more negative potential, which is the oxidation reaction and which is the reduction reaction?
More positive electron potential = reduction
More negative potential = oxidation
NO PRoblem
negative oxidation
positive reduction
What is the standard electrode potential of a half cell?
The voltage measured under standard conditions where the half cell is connected to a standard hydrogen electrode.
What are standard conditions?
Solutions must be 1 moldm⁻³
298K
100kPa
What is the equation for the reaction at the hydrogen electrode? What is the electrode potential of the hydrogen cell?
2H⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ H₂
Hydrogen ions are aqueous, product is a gas.
0.00V
What is the equation for the e-cell value?
E cell = (more positive electrode potential) - (more negative electrode potential)
=
E cell = E (reduced) - E (oxidised)
What conditions may affect electrode potential measured?
Temperature
Pressure
Concentration
What is the conventional representation of an electrochemical cell?
A shorthand way of drawing a cell.
Draw the conventional representation of a cell involving zinc, zinc ions, copper and copper ions.
Draw the conventional representation of the electrochemical cell formed between magnesium and the standard hydrogen half cell.
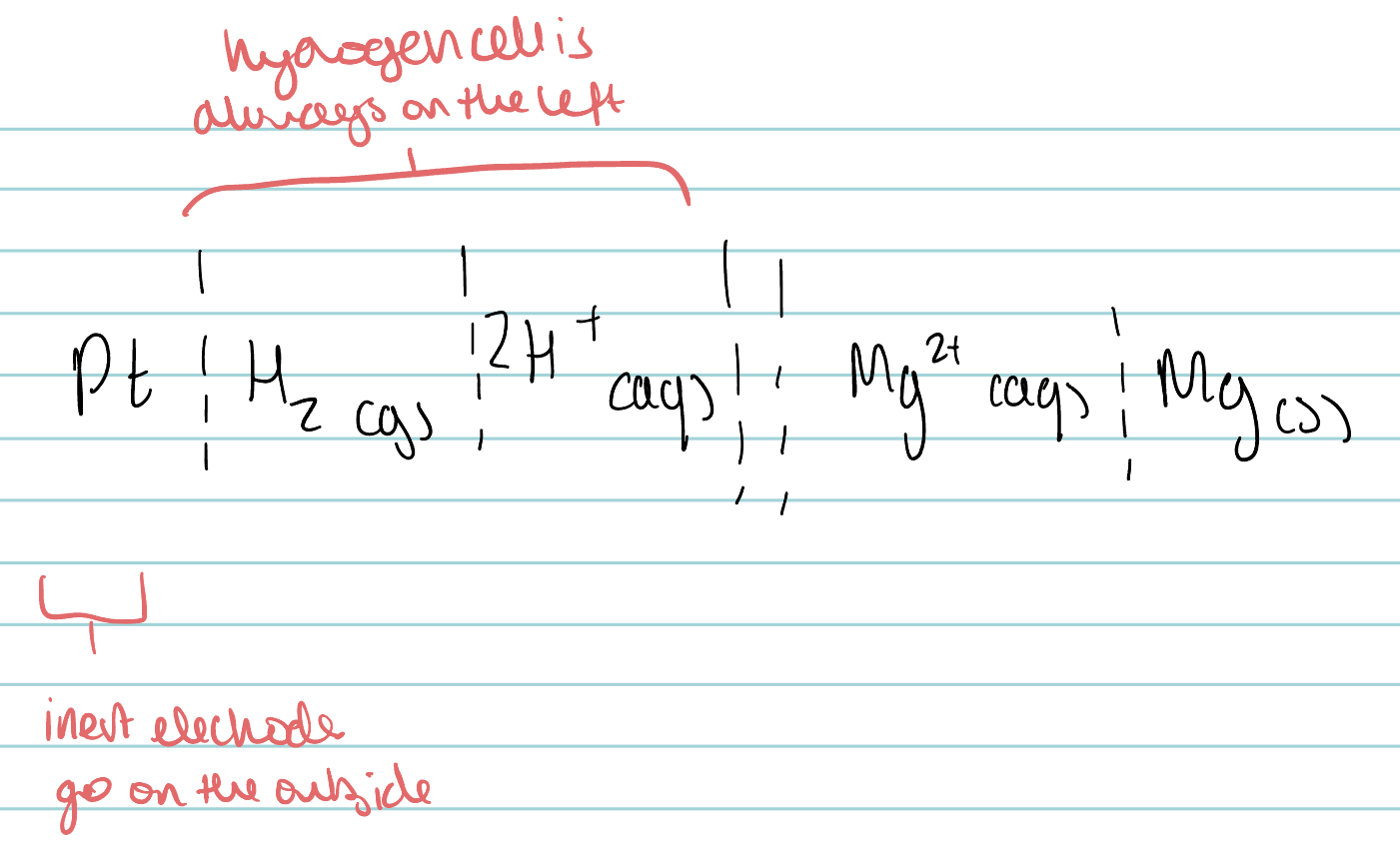
How can electrode potentials be used to work out if a reaction will happen?
If a reaction is thermodynamically feasible, overall potential will be positive.
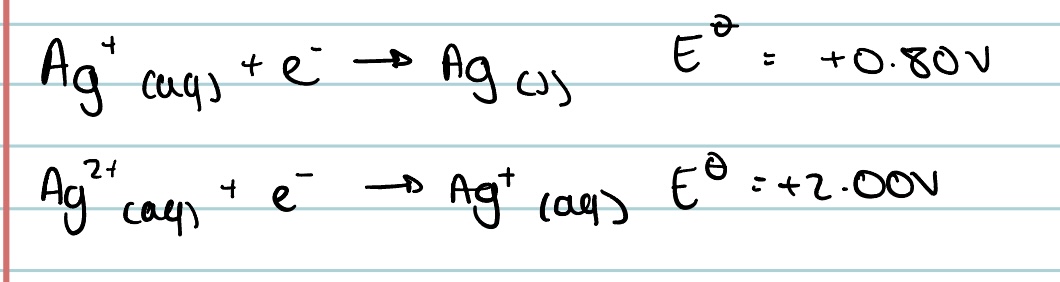
Use the following equations to predict whether silver ions will disproportionate in solution.
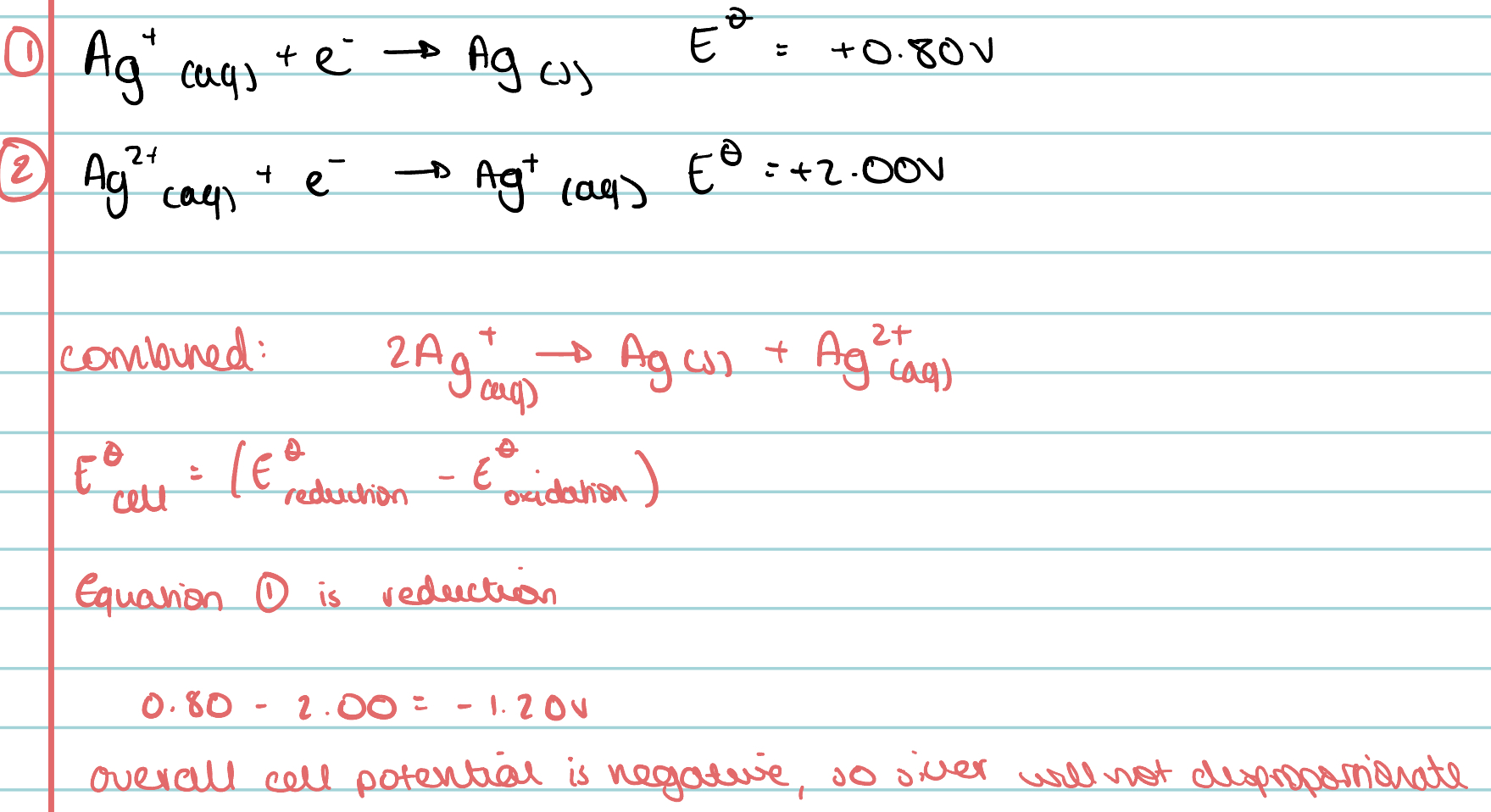
Why might a prediction of whether a reaction is feasible be wrong?
if conditions are not standard
The reaction kinetics are not favourable
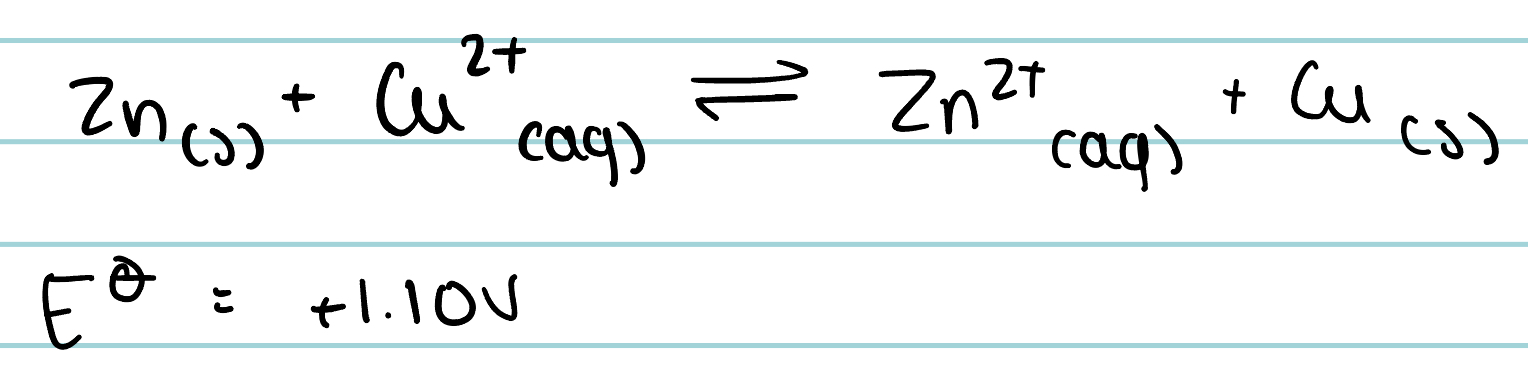
The following reaction occurs. What happens if the concentration of zinc ions is increased. What happens in the concentration of copper ions is increased?
If concentration of zinc ions increases, equilibrium shifts to the left, reducing ease of electron loss of zinc. The electrode potential of Zn/Zn²⁺ will become less negative, and the whole cell potential will be lower.
If concentration of copper ions is increased, equilibrium will shift to the right, increasing ease of electron gain of Cu²⁺. Electrode potential of Cu²⁺/Cu becomes more positive and the cell potential is higher.
How can reaction kinetics affect how accurate a prediction of feasibility is?
the rate of reaction may be so slow that the reaction does not appear to happen.
A high activation energy may stop a reaction from happening.
How is cell potential related to entropy and the equilibrium constant?
Bigger the cell potential, the bigger the total entropy change and the greater the equilibrium constant.
Cell potential is directly proportional to the total entropy change and equilibrium constant
How does an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell work?
-hydrogen is fed into the negative electrode (anode)
Oxygen is fed into the positive electrode (cathode)
Electrons flow from the negative electrode through an external circuit to the positive electrode. Ions pass through the anion-exchange membrane towards the negative electrode.
What equation occurs at the negative electrode of an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
At the positive electrode?
What is the overall equation of an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
Negative electrode: 2H₂ + 4OH⁻ → 4H₂O + 4e⁻
Positive electrode: O₂ + 2H₂O +4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
Overall: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
How do rechargeable batteries work?
Charging- plug in to supply a current. This forces electrons to move the opposite way and reverses the overall discharge equation.