Cardiac Drugs Diuretics & Nitrates
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Diuretics
Thiazide
Loop
Potassium Sparing
Thiazide Diuretics
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
Drug of choice for hypertension
Routes: PO or IV
Thiazide Diuretics Mechanism of Action
Inhibits reabsorption of sodium & chloride
Increases secretion of sodium and water
Decreases plasma volume
Decreases preload & workload of the heart
Decreases blood pressure
Thiazide Diuretics Uses
Blood pressure management
Fluid retention (edema)
heart failure
Thiazide Diuretics Adverse Effects
Low blood pressure (hypotension)
Electrolyte imbalances
Especially potassium and sodium
Ototoxicity
More likely with existing kidney issues
When taken with other ototoxic drugs concurrently
Drugs that increase the effects of Thiazide Diuretics
ETOH,
barbiturates,
MAOIs,
Beta Blockers,
corticosteroids
Drugs that decrease the effects of Thiazide Diuretics
NSAIDs
Thiazide Diuretics Nursing Implications
Check BP
Check electrolytes
Especially Potassium & sodium
Watch for:
Dehydration
Signs of Hypotension
Thiazide Diuretics Cautions
Caution with allergy to sulfa meds
Caution with pregnancy
Loop Diuretics
Inhibit Na & Cl reabsorption in loop of Henle
Produces significant diuresis
Furosemide (Lasix)
Loop Diuretic
Rapid effect
Diuretic of choice when rapid diuresis is needed.
Recommended when kidney function is impaired
But - pt has to be able to make urine or it won't work
Dosing can be titrated for maximum effect
Most effective and most versatile
Available PO and IV
Furosemide (Lasix) Uses
Heart failure
Pulmonary edema
Hepatic disease
Renal disease
Hypertension
Furosemide (Lasix) Adverse Effects
Electrolyte imbalances
Esp. Na+ & K+
May need supplementation
Dehydration
Ototoxicity
Hypotension
Furosemide (Lasix) Contraindication
No urine output
Furosemide (Lasix) Nursing Implications
Prior to administration check:
BP
Labs (Na, K, BUN/Creat) and glucose levels if pt is diabetic
After administration monitor:
BP
I/O
Signs of fluid reduction: decreased edema, lungs more clear, etc.
Monitor for side effects
Electrolyte disturbances
Dehydration: Skin turgor, tachycardia
Drugs that decrease the effects of Furosemide (Lasix)
Ibuprofen
phenytoin
Drugs that increase effects of Furosemide (Lasix)
Corticosteroids and digoxin
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Potassium Sparing Diuretics
Combine with loop diuretics
Reduces potassium loss
Lower dosage of loop needed
Administered PO
Up to 6 weeks for maximum effect
Potassium Sparing Diuretics Mechanism of Action
Blocks aldosterone
Promotes water and sodium excretion & potassium retention
Spironolactone (Aldactone) Uses
Heart failure
Ascites
Hypokalemia
Hypertension
Hyperaldosteronism
Spironolactone (Aldactone) Adverse Effects
Dizziness
HA
Abd cramping
Diarrhea
Increased serum K+ levels
Spironolactone (Aldactone) Contraindications
Abnormal kidney function
1st trimester of pregnancy
Spironolactone (Aldactone) Black Box Warning
May cause tumor growth
Unnecessary use should be avoided
Spironolactone (Aldactone) Nursing Implications
Give same time each day
Preferably in the morning
Can take with food to help with Gl issues
Take even if they feel fine
Similar to loop diuretics
Check BP, electrolytes, BUN/creatinine before administering
Watch for signs of dehydration, electrolyte imbalance
Spironolactone (Aldactone) Food & Drug Interactions
lithium & digoxin can reach toxic levels
Ginger, licorice increase effects
Drugs that Increase the effects of Spironolactone (Aldactone)
ACE
ARB
K containing drugs
Beta Blockers
Drugs that decrease the effects of Spironolactone (Aldactone)
ETOH,
vasodilators,
salicylates
Angina
Lack of perfusion & oxygenation to heart
Pain in heart
May cause other symptoms too
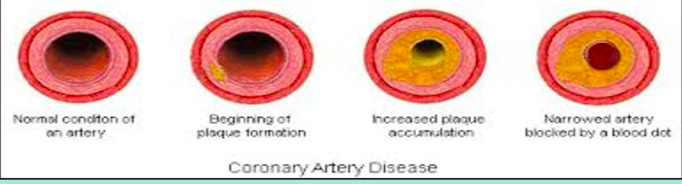
Coronary Artery Disease
Increased plaque accumulation
Narrowed artery blocked by a blood clot
Drugs to treat angina
Organic Nitrates
Beta blockers
Calcium channel blockers
Organic Nitrates
Use
Angina
Usually used PRN
Can be given as ongoing treatment
Works fast
Multiple routes of administration
IV, Sublingual, PO, Topical transdermal & disc
Organic Nitrates Mechanism of Action
Cause vasodilation
Opens coronary arteries
Improves perfusion to heart
Also decreases workload of heart
Via preload and afterload
Organic Nitrates Examples
Nitroglycerin
isosorbide mononitrate
isosorbide dinitrate
Organic Nitrates Adverse Effects
Severe headache
Common
Tx with acetaminophen
Hypotension & Orthostatic Hypotension
Bradycardia
Dizziness
Syncope
Organic Nitrates Contraindications
Erectile Dysfunction Meds
Hypotension Warning!
Severe anemia
Hypotension
Hypovolemia
Organic Nitrates Are Cautioned With
Head injury
Cerebral hemorrhage
Beta Blockers
Abnormal kidney function
Organic Nitrates Nursing Implications
Prior to administration check:
BP (HOLD if systolic < 90 or 30 mm Hg below the pt normal BP)
HR (HOLD HR > 100 )
Chest pain level
Last time ED med taken
If new onset chest pain in hospital call PCP and get EKG order
After administration
Reassess pain, BP
Monitor for adverse effects
Sublingual Organic Nitrates Nursing Implications
Comes in brown bottle / Exposure to light deactivates med
Keep in cool, dry place
Replace every 6 months
Should tingle when placed under tongue or it isn’t going to work
PO Organic Nitrates Nursing Implications
Take in the morning after nitrate free night
Take 1-2 hours before meal
Do not crush/break or chew sustained release form
Ointment Organic Nitrates Nursing Implications
Must use dose measuring application papers
IV Organic Nitrates Nursing Implications
done in ICU or step down units