structure and function of the respiratory system
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
componentss of URT
nasal cavity
oral cavity
nasopharynx
pharynx
oropharynx
epiglottis
larynx
trachea
oesophagus
what is the diaphragm innervatd by
phrenic nerve- which is a somatic motor nerve
what are the external intercostal muscls innervated by
intercostal nerve
respiration in horses
biphasic ventilation
locomotion ventilation coupling
layers of the blood gas barrier
surfactant
type 1 alveolar epithelial cell
basal laminar of epithelial cell
connective tissue
basal lamina of endothelial cell
endothelial cell
plasma
rbc membrane
0.2-0.6 um thick
large surface ae to volume
ficks law
rate of transfer of gas through a sheet of tissue is proportional to the tissue area and the difference in partial pressure between the two sides and inversely proportional to the tissue thickness
oxygen transport in the blood
most carried by haemoglobin in red blood cells
3 percent dissolved in plasma
reversible binding o2 to heme- high po2 is binding, low po2 is release
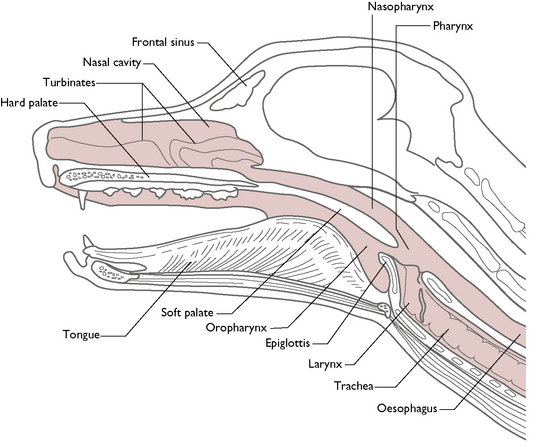
anatomy of urt
oesophagus lies dorsal to larynx
trachea lies ventral to oesophagus
what is the blood gas barrier
surfactant
type 1 alveolar epithelial cell
basal laminar of epithelial cell
connective tissue
basal lamina of endothelial cell
endothelial cell
plasma
rbc membrane
0.2-0.6um thick
large surface area to volume
diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lung
lower partial pressure in venous end compared to arterial end for oxygen
vice versa for carbon dioxide
move from an area of low to high partial pressure
diffusion of oxygen from capillary into tissue
systemic arterial blood partial pressure 95mmHg
Interstitial fluid 40mmHg
large pressure difference meaning rapid diffusion
partial pressure of blood leaving the capillaries drop
oxygen carriage in blood
most carried by haemoglobin, some dissolved in plasma
reversible binding oxygen to haem
high po2 is binding, low po2 is release
carbon dioxide carriage in blood
most as bicarbonate ion which is important for acid base balance
some carried by Hb
some dissolved in plasma
reversible binding of carbon dioxide to amine radicals of Hb- carboaminohaemoglobin
importance of ventilation and perfusion
to maintain proper concentrations of oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen ion concentration in tissues
features of the upper respiratory system
respiratory epithelium- nose to terminal bronchioles, lined by mucus which keeps epithelium moist and traps small particles
cilia beats mucus towards the pharynx
nasal cavity warms, humidifies and filters air, turbulent precipitation
features of the lower respiratory tract
CONDUCTING ZONE
structural support (cartilage which decreases as descend to lower levels)
modulation of airway diameter (smooth muscle)
defence ( mucociliary escalator, mucus production by goblet cells and glands, ciliated epithelium
RESPIRATORY ZONE
gas exchange (type 1 pneumocytes- very thin, and capillaries in intimate contact with air spaces)
redistribution of ventilation (limited smooth muscle)
maintain open alveoli (type 2 pneumocytes- produce surfactant)
pleural cavity
is a potential space between the paritiel and visceral pleura
contains small volume of serous fluid which helps lubrication
surrounds lungs in the thoracic cavity
is a vaccum
negative pressure essential to pull lungs out when ribcage and diaphragm expand thoracic cavity
the pleura
visceral plura
attached to surface of lung inc fissures
elastic fibres
continuous with parietal at the hilium
parietal pleura
covers internal suface of thoracic cavity
mediastinal- lines mediastinum
costal- lateral wall of rib cage
cervical- extension of pleural cavity into neck
diaphragmic- lines cranial surface of diaphraghm