Chemistry - 3.3.14: Organic Synthesis
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Ester hydrolysis by acids?
Reagents: Water, acid
Conditions: Heated under reflux, dilute acid
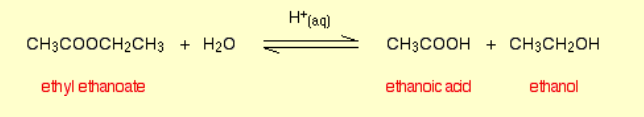
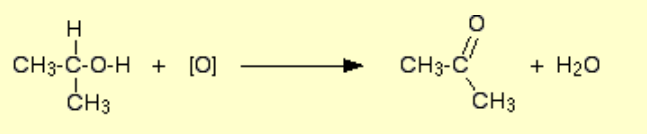
Alcohol to ketone?
Name of reaction: Oxidation
Reagents: Acidified potassium dichromate (acidified with H2SO4)
Conditions: Excess potassium dichromate, concentrated acid, heat under reflux
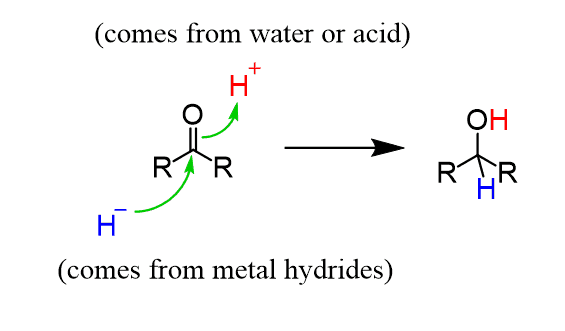
Ketone to secondary alcohol?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic addition
Reagents: NaBH4
Conditions: Aqueous solution
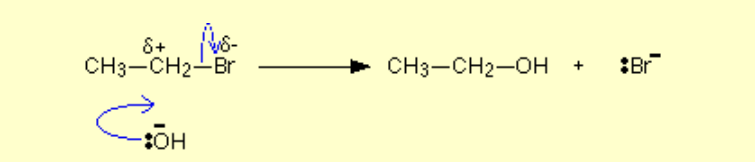
Halogenoalkane to alcohol?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic substitution
Reagents: NaOH / KOH
Conditions: Heat under reflux, aqueous
Halogenoalkane to alkene?
Name of mechanism: Elimination
Reagents: NaOH / KOH
Conditions: Heat under reflux, ethanolic
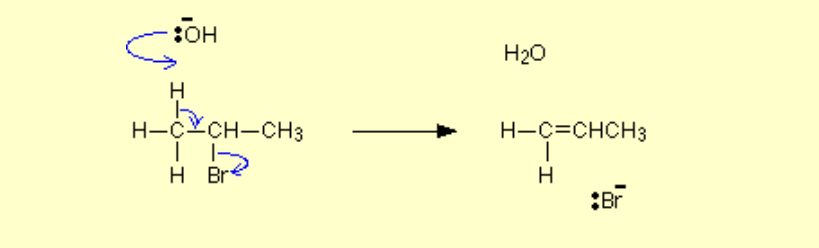
Alcohol to alkene?
Name of mechanism: Elimination / Dehydration
Reagents: -
Conditions: Concentrated H2SO4 / H3PO4, high temperature
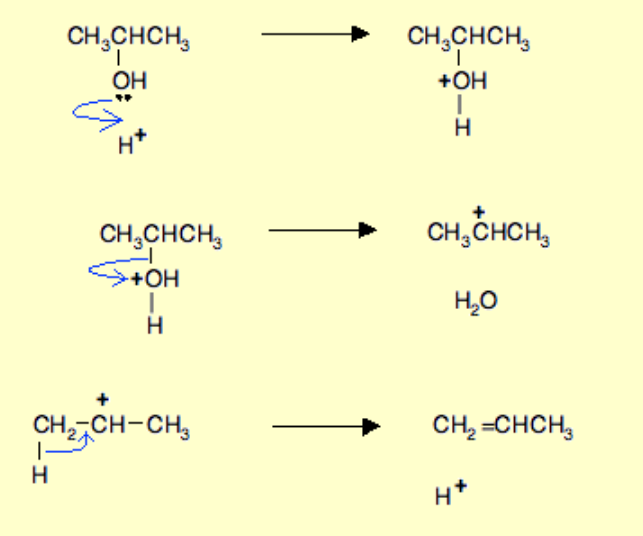
Alcohol to aldehyde?
Name of reaction: Oxidation
Reagents: Acidified potassium dichromate (acidified with H2SO4)
Conditions: Dilute potassium dichromate, dilute acid, distillation

Halogenoalkane to amine?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic substitution
Reagents: Ammonia
Conditions: Heated under pressure, excess ammonia, ethanolic
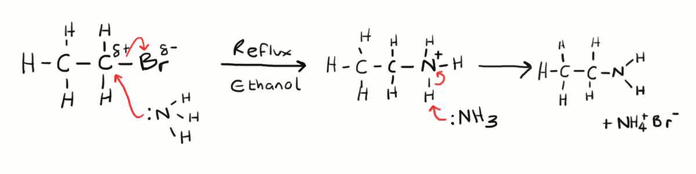
Alkane to halogenoalkane?
Name of mechanism: Free radical substitution
Reagents: X2
Conditions: UV light
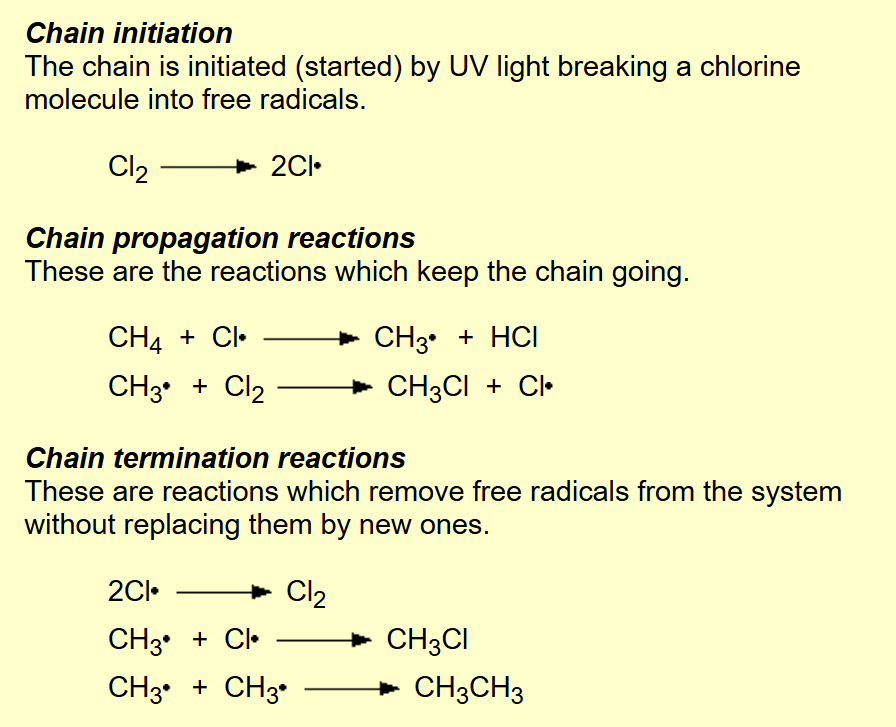
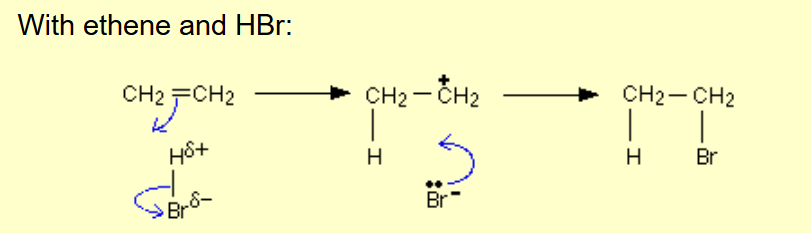
Alkene to halogenoalkane?
Name of mechanism: Electrophilic addition
Reagents: HX, X2 (if di-halo)
Conditions: Room temperature
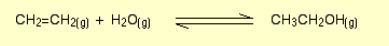
Alkene to alcohol?
Name of reaction: Hydration
Reagents: H2O, phosphoric acid catalyst
Conditions: Concentrated acid, heat, high pressure then distillation
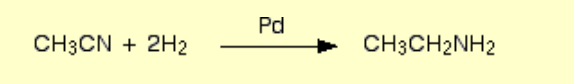
Nitrile to amine?
Name of mechanism: Reduction
Reagents: H2 gas and nickel catalyst
Conditions: High temperature and pressure
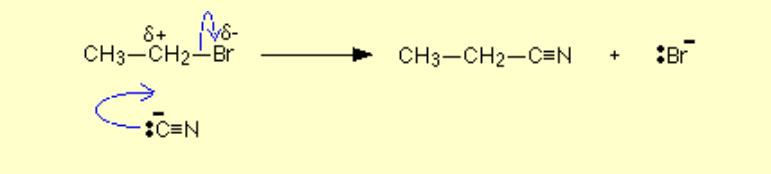
Halogenoalkane to nitrile?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic substitution
Reagents: KCN
Conditions: Heat under reflux, ethanolic and aqueous
Acyl chloride to amide?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Reagents: Ammonia OR an amine for an N-substituted amide
Conditions: Cold, concentrated ammonia
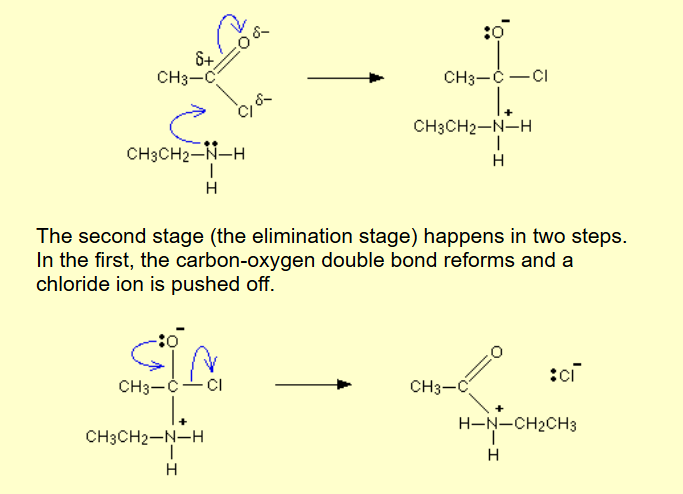
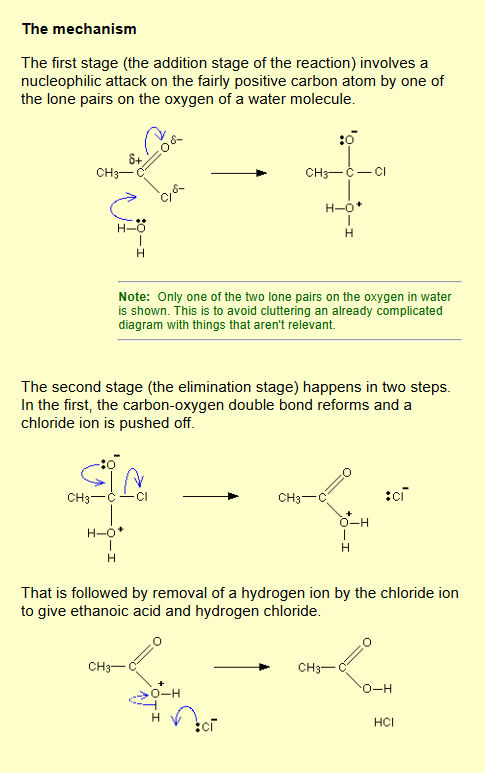
Acyl chloride / acid anhydride to carboxylic acid?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Reagents: Water
Conditions: Cold…water….?
Aldehyde to carboxylic acid?
Name of reaction: Oxidation
Reagents: Acidified potassium dichromate (acidified with H2SO4)
Conditions: Excess potassium dichromate, concentrated acid, heat under reflux
Ester hydrolysis by bases?
Reagents: NaOH, then strong acid to separate carboxylic acid from carboxylate salt
Conditions: Heated under reflux, dilute alkali, excess acid

Formation of an ester?
Name of reaction: Esterification
Reagents: Carboxylic acid, alcohol, H2SO4 catalyst
Conditions: Heat, concentrated acid
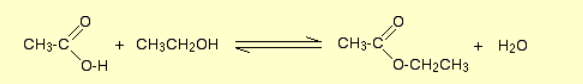
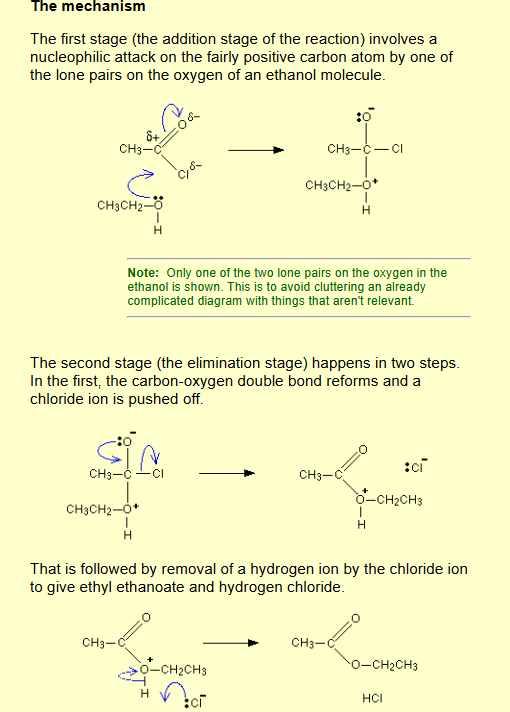
Acyl chloride / acid anhydride to ester?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Reagents: Alcohol
Conditions: Room temperature
Alcohol to carboxylic acid?
Name of reaction: Oxidation
Reagents: Acidified potassium dichromate (acidified with H2SO4)
Conditions: Excess potassium dichromate, concentrated acid, heat under reflux

Aldehyde to primary alcohol?
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic addition
Reagents: NaBH4
Conditions: Aqueous solution
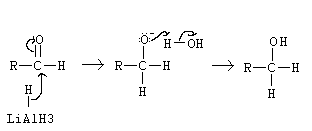
What will NaBH4 reduce? What will it not reduce?
It will reduce C=O
It will NOT reduce C=C
What will H2 with a Ni catalyst reduce? What will it not reduce?
It will reduce C=C
It will NOT reduce C=O
What will Sn and HCl reduce?
R-NO2
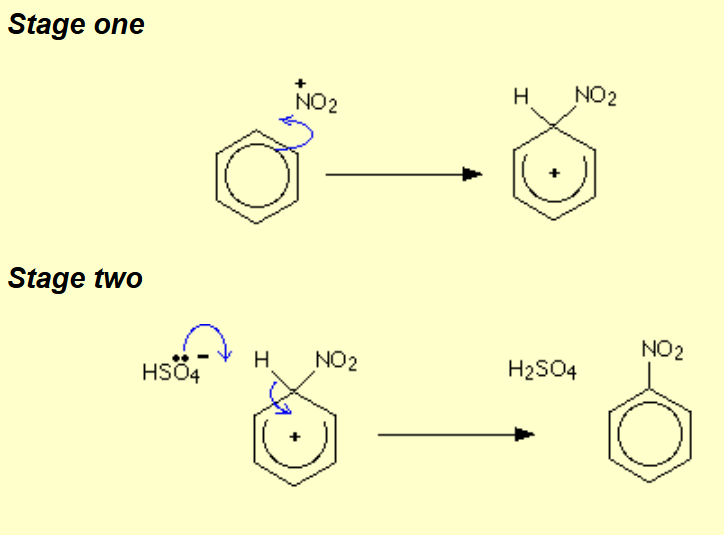
Benzene to nitrobenzene?
Name of mechanism: Electrophilic substitution
Reagents: HNO3 and H2SO4
Conditions: Concentrated acid
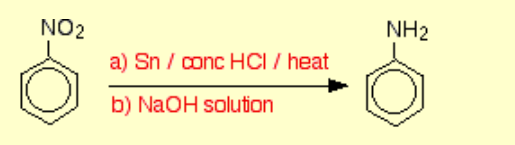
Nitrobenzene to phenylamine?
Name of mechanism: Reduction
Reagents: Sn and HCl, then NaOH
Conditions: Concentrated acid, heat
Test for alkenes?
Add bromine water - changes from orange to colourless (decolourises)
Test for halogenoalkanes?
Warm with NaOH, then add acidified silver nitrate (with HNO3) - coloured silver halide precipitate forms
Test for alcohols?
Add acidified potassium dichromate - primary and secondary alcohols change colour from orange to green, tertiary alcohols will not
Test for aldehydes?
Add Tollens’ reagent - silver mirror forms
OR Add Fehling’s solution - brick red precipitate forms
Test for carboxylic acids?
Add sodium hydrogencarbonate - effervescence
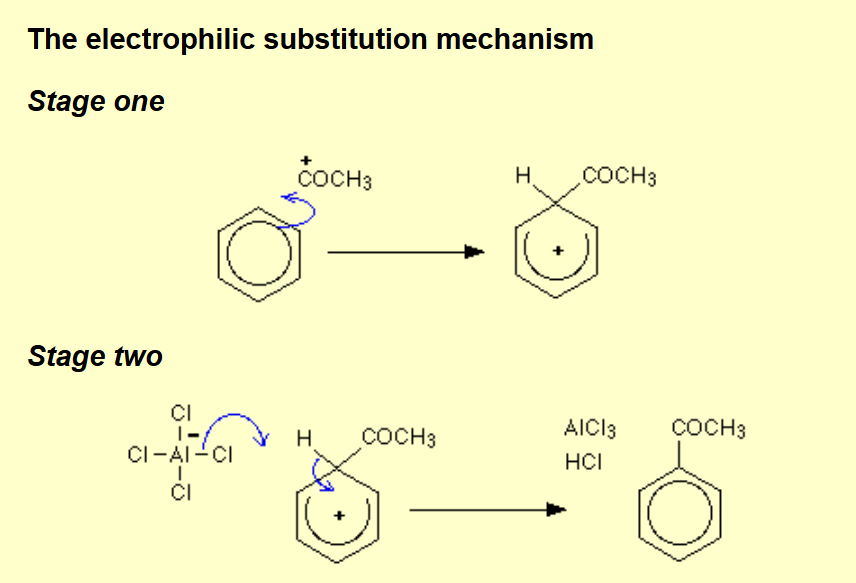
Adding an acyl group to benzene?
Name of mechanism: Electrophilic substitution (Friedel-Crafts acylation)
Reagents: Acyl chloride
Conditions: AlCl3 catalyst, (heat under reflux) in a non-aqueous solvent / dry ether
In the nucleophilic substitution of a halogenoalkane with ammonia, why is heating under reflux not used?
Ammonia would not be condensed by the condenser
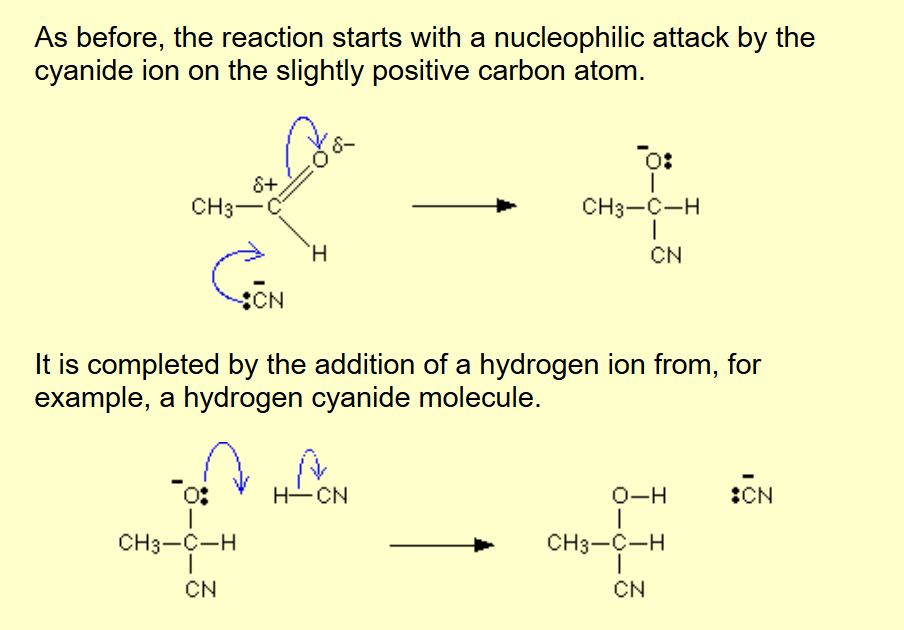
Aldehyde / Ketone to hydroxynitrile
Name of mechanism: Nucleophilic addition
Reagents: KCN
Conditions: (Dilute) H2SO4
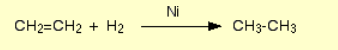
Alkene to alkane
Name of mechanism: Reduction
Reagents: H2 gas, nickel catalyst
Conditions: 150°C
Polyamide hydrolysis
Reagent: HCl / NaOH
Conditions: Heat under reflux
How can silver nitrate solution be used to distinguish between an acyl chloride and a chloroalkane?
Acyl chloride: White precipitate forms (immediately)
Chloroalkane: No visible change (/ white precipitate forms very slowly)