IGCSE PE - JOINTS
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the six types of synovial joints?
Ball and Socket joints, Hinge joints, planar/plane joint, condyloid joint, saddle joint
Immovable or Fixed joints (FIBROUS)
Held together by tough tissue which develops during childhood
Cranium, Pelvis, Vertebrae
Immovable or fixed joints (FIBROUS)
Slightly Moveable joints (CARTILAGINOUS)
Movement is needed but only to a certain point
Vertebral column
Slightly moveable joint (CARTILAGINOUS)
Freely Moveable Joints (SYNOVIAL)
Allows movement to take place
-6 types
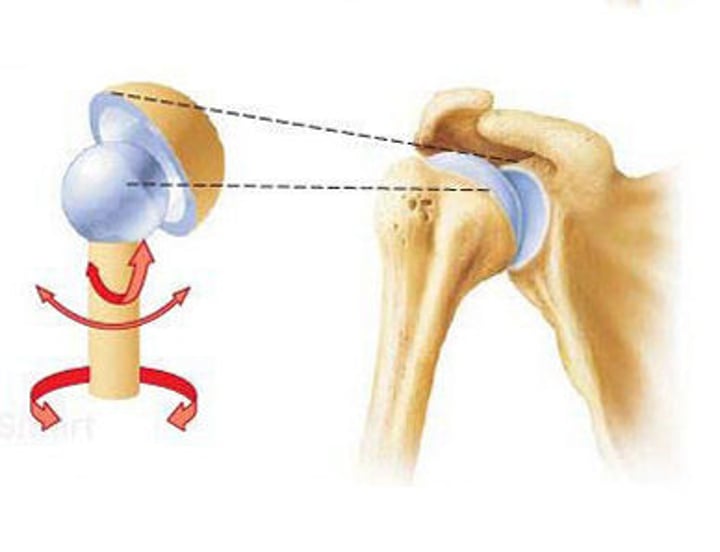
Ball and Socket Joint
Greatest range of movements
(hip, shoulder)
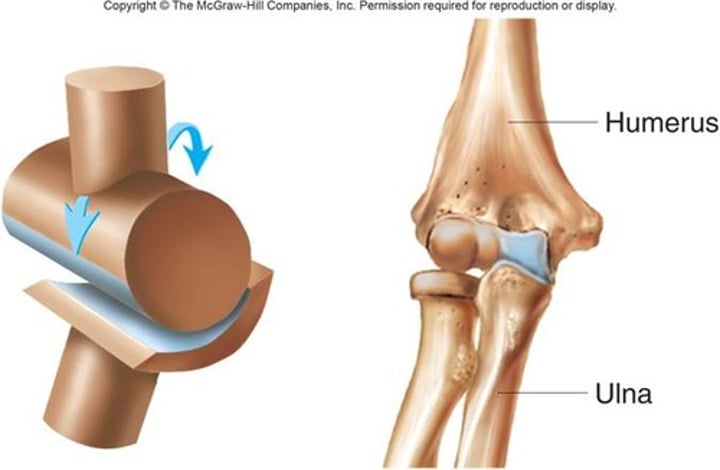
What is the Hinge Joint like and what does it do?
Allow extensive flexion and extension with a small amount of rotation.
-Shaped to move against each other with minimum friction
-Strong ligaments stop the bones from sliding off from one side to another
(elbow)
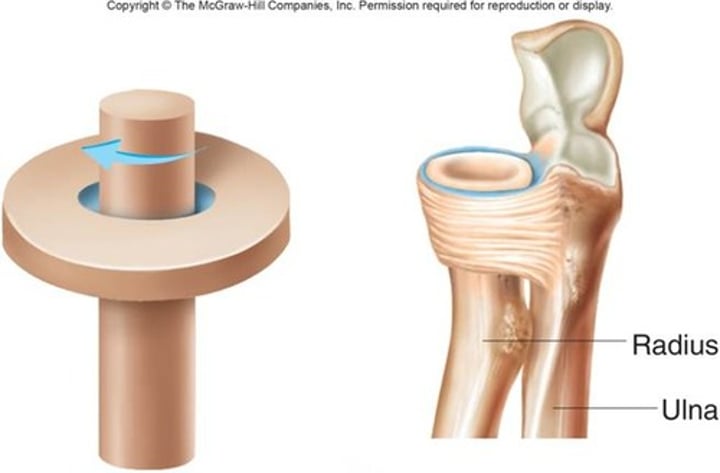
What is the Pivot Joint like and what does it do?
Only allows rotation
- 'Peg' from end of one bone fits into 'ring' of next bone
(neck)
What is the planar/plane Joint like and what does it do?
Allows flexion and extension through a slight gliding motion between the ends of small bones
- Small bones can move over one another to increase flexibility
- Linked by strong ligaments to stop them from moving too far
(finger, hands)
What is the Saddle Joint like and what does it do?
When concave and convex surfaces meet
- Allows the movement of the joint forward and backward, and right to left
(hands)
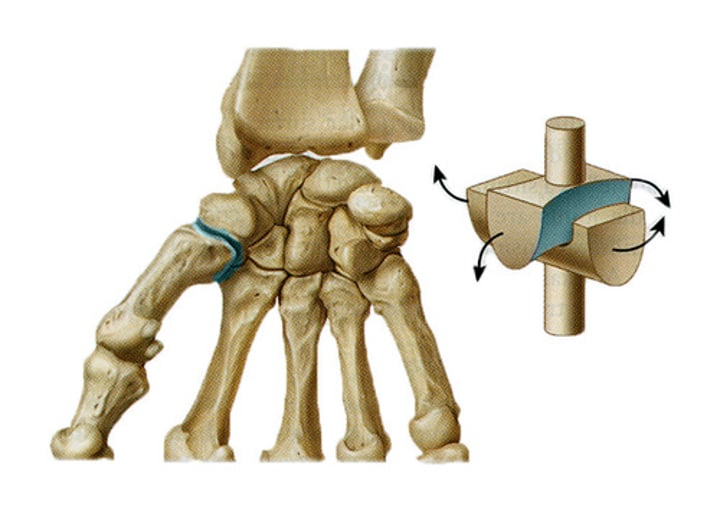
What is the Condyloid Joint like and what does it do?
Full convex shape of one bone end fits into the full concave shape of an adjoining bone
-Allows for movement in all directions. But not full rotations
(wrist)
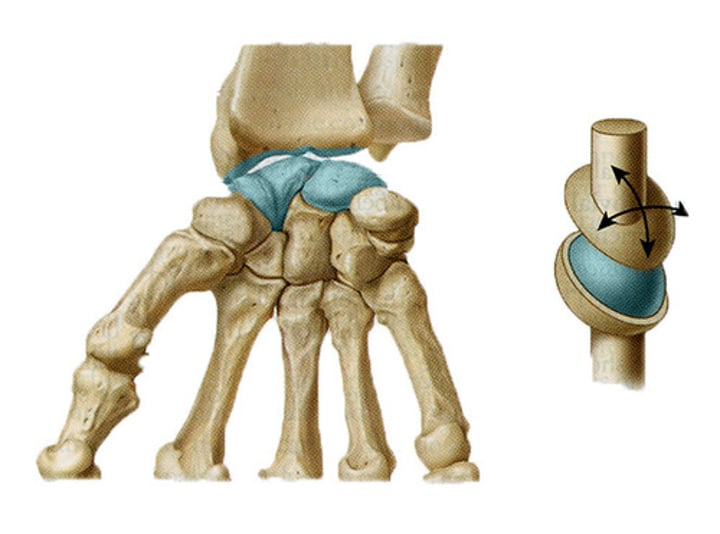
What does the Synovial Joints contain?
They contain SYNOVIAL FLUID
-This lubricates the joint. It enables all parts of the joint to move against each other smoothly.
Cartilage
Forms a cushion between bones in order to stop them rubbing
Ligaments
Very strong string that holds bones together
What does the Tendons do?
Attaches muscles to bones