Radiology axial skeleton
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are oblique spine rads used to see?
Artiular facet features
What view is this?
Oblique
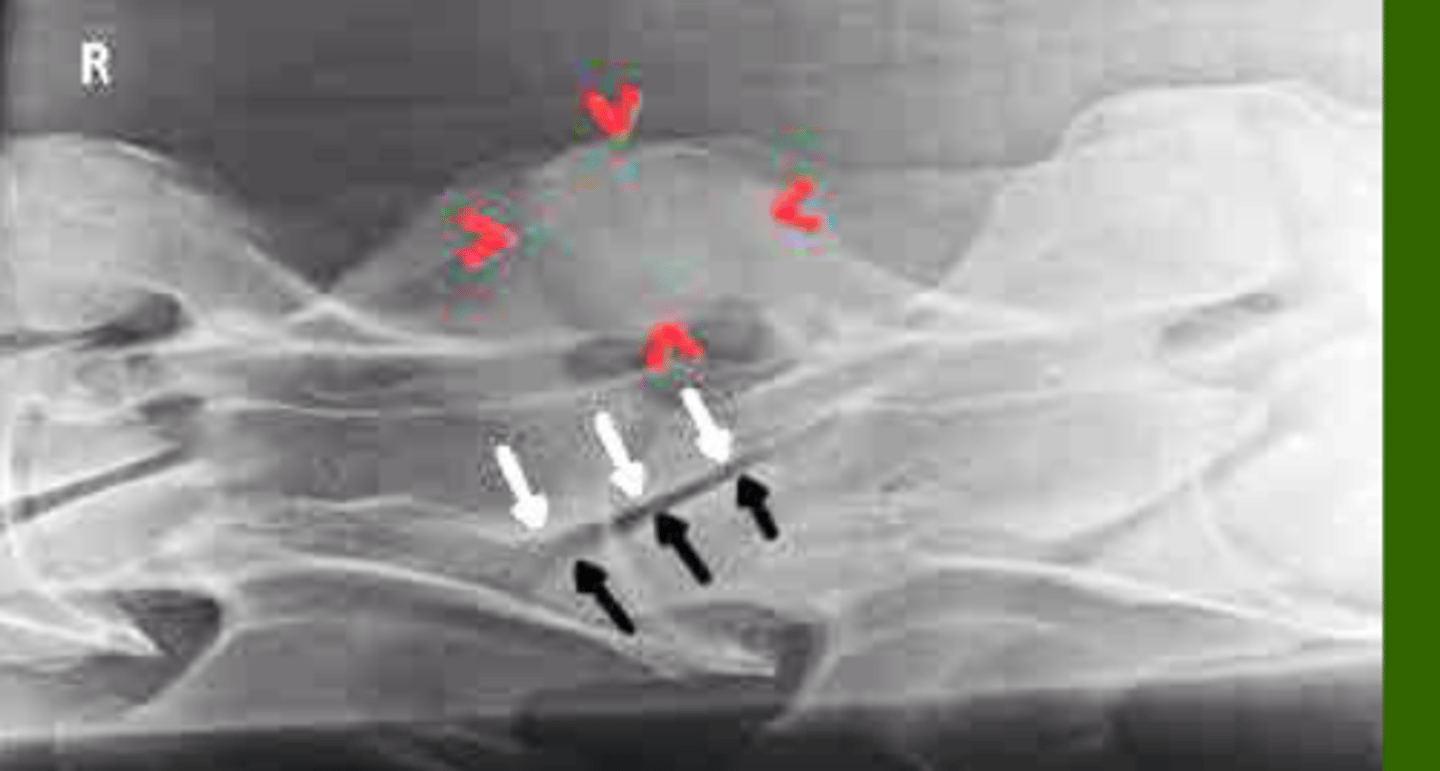
Where is the fracture?
C2 Fracture w/ plow nose
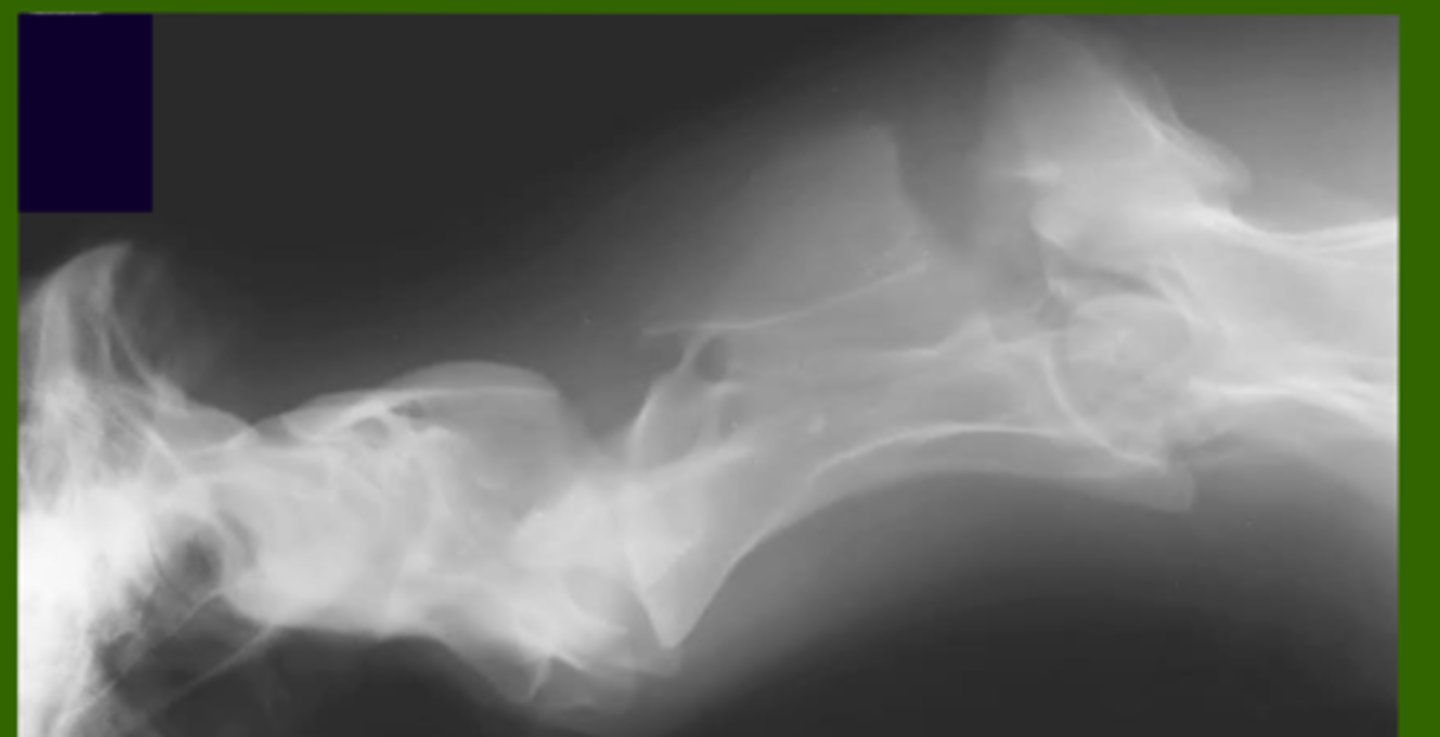
What kind of fracture is this?
Facet fracture
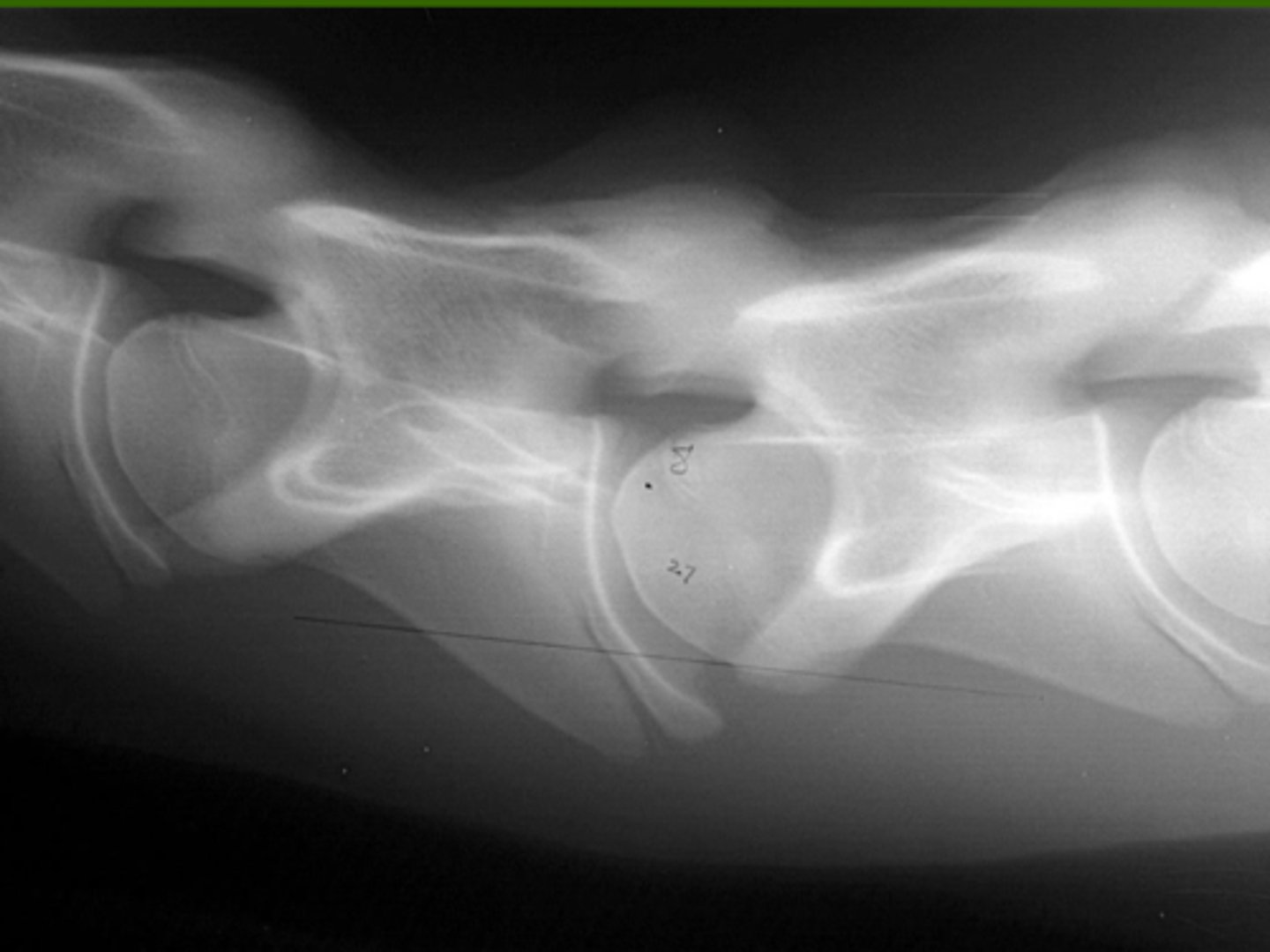
What is the pathology?
Kissing spine
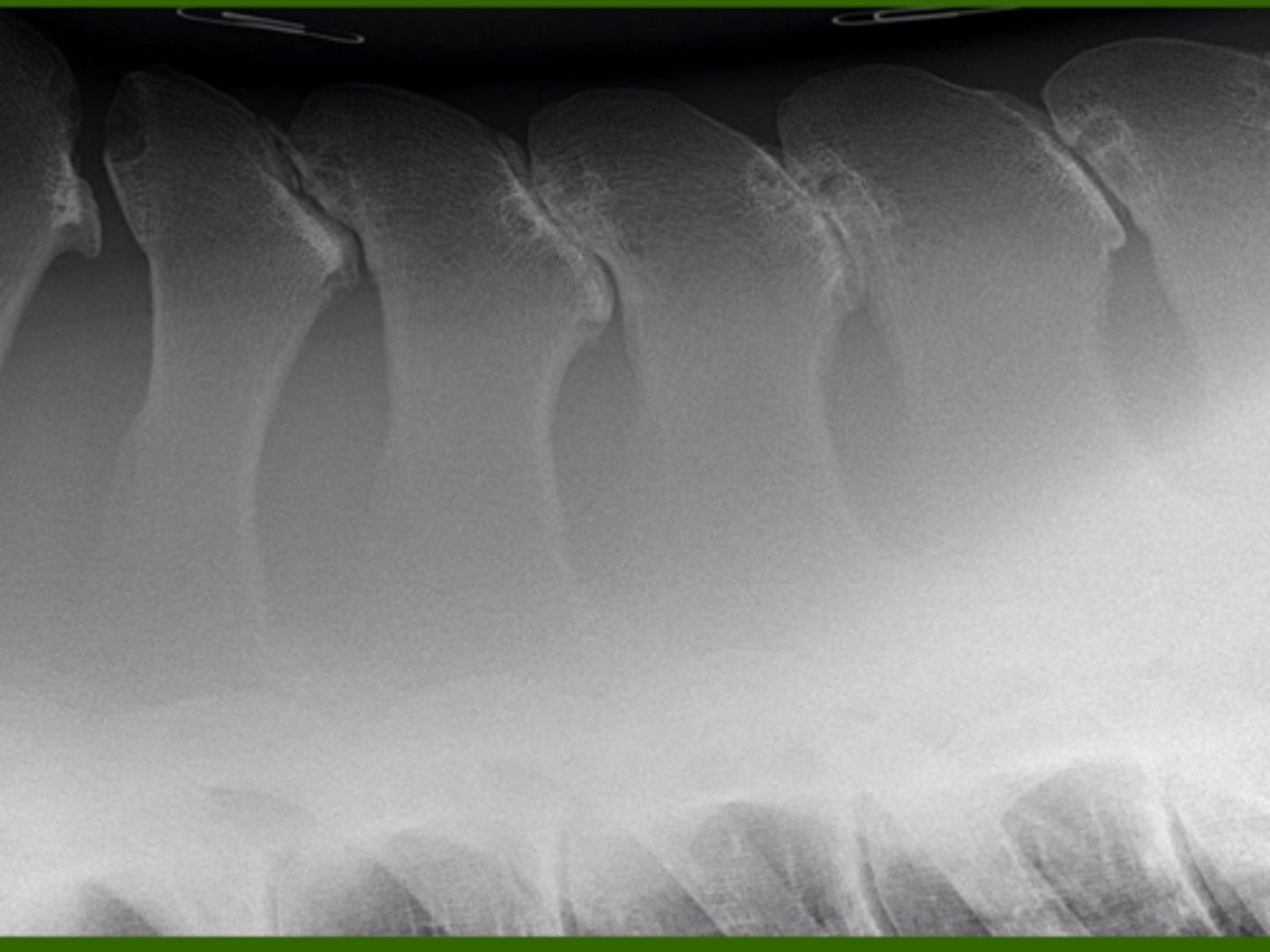
What kind of fracture is this?
Spinous process fracture
What are some signs of cervical vertebral malformations?
DJD of articular facets,
sublet of adj vert
Flare of caudal epiphysis ventral body
OCD
Shortened caudal epiphysis
reduced sagittal ratio
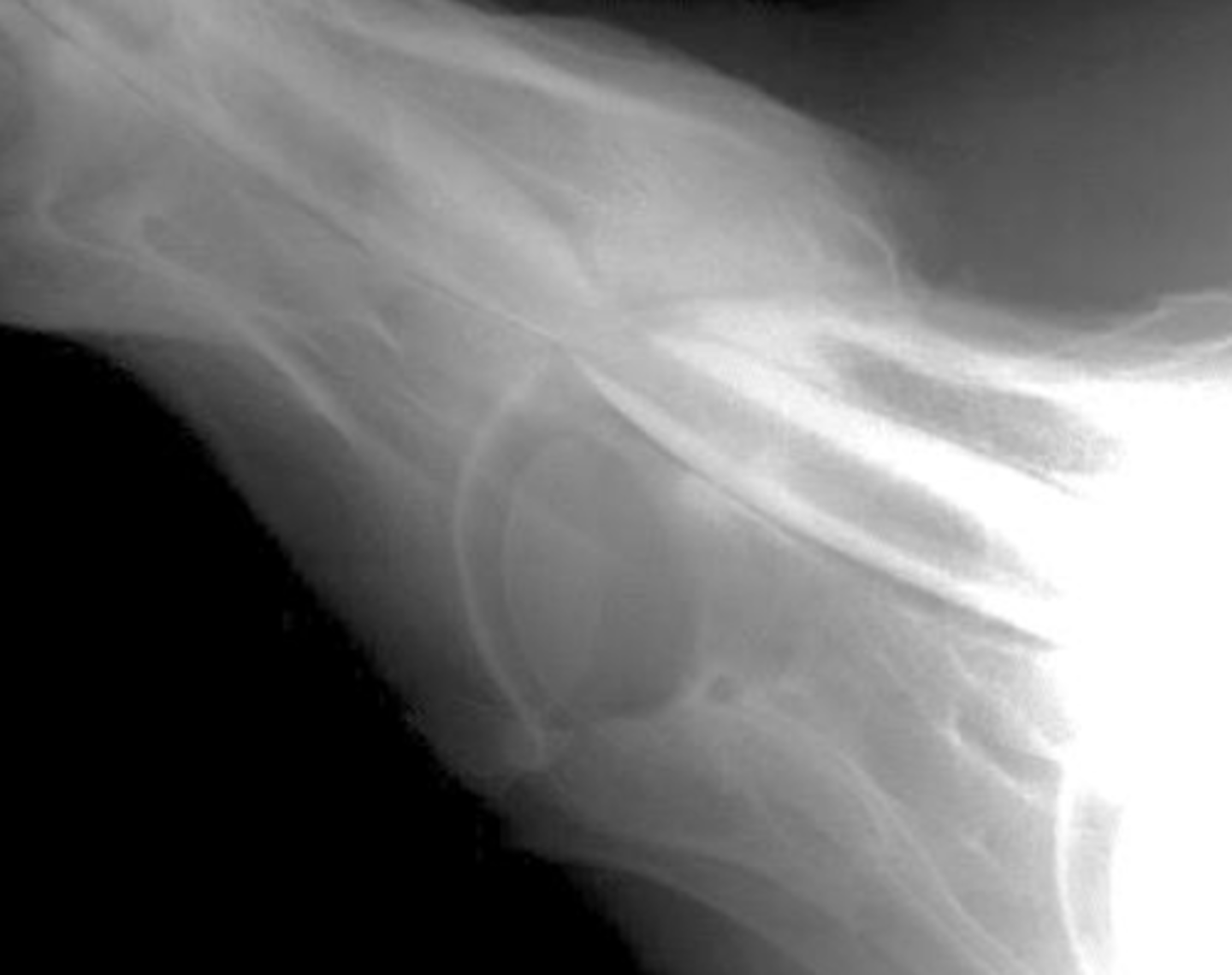
What is the pathology?
Static compression (When horse is standing straight )
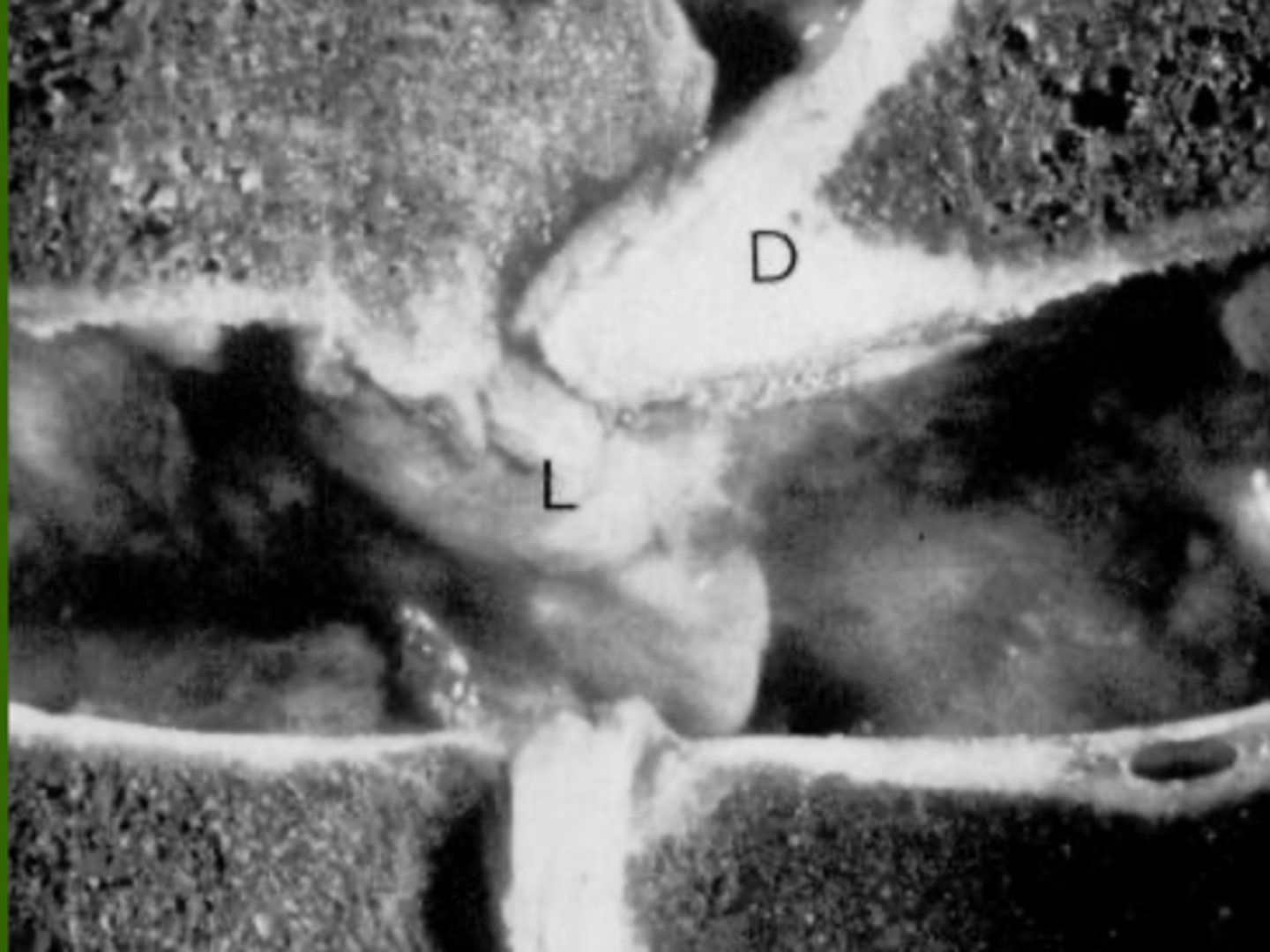
What is the pathology?
Laminar sclerosis and ligament flavum hypertrophy
bones malformed and override to traumatize spinal cord
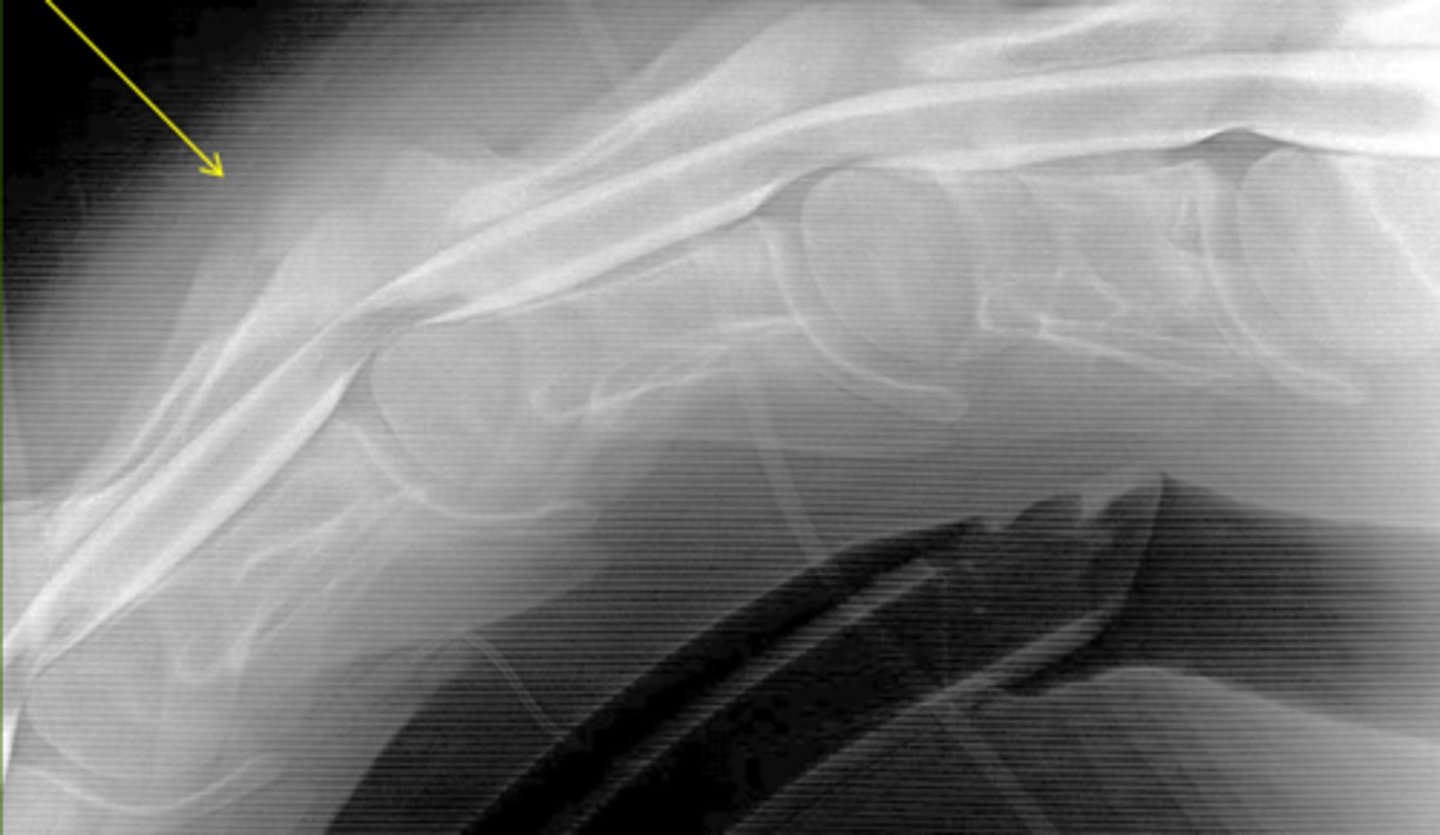
What is the pathology
Dynamic stenosis (can only see when flexed)
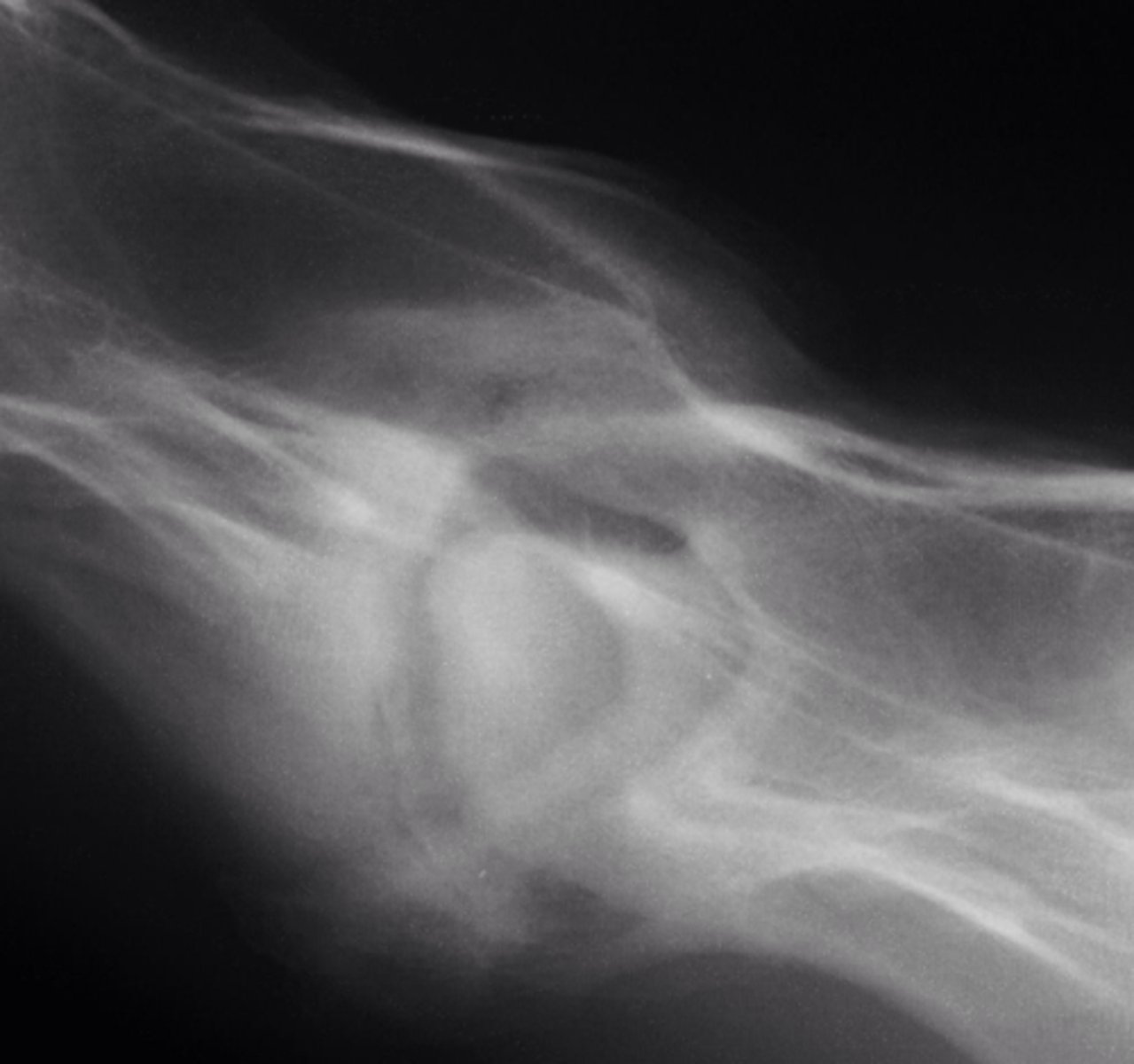
Identify the pathology?
Discospondylitis
moth eatten/rotten space often due to infection
C6 will have a ____?
Costal process
What medication is used to do sedated standing rads?
Xylazine

What view is this?
Oblique of the skull
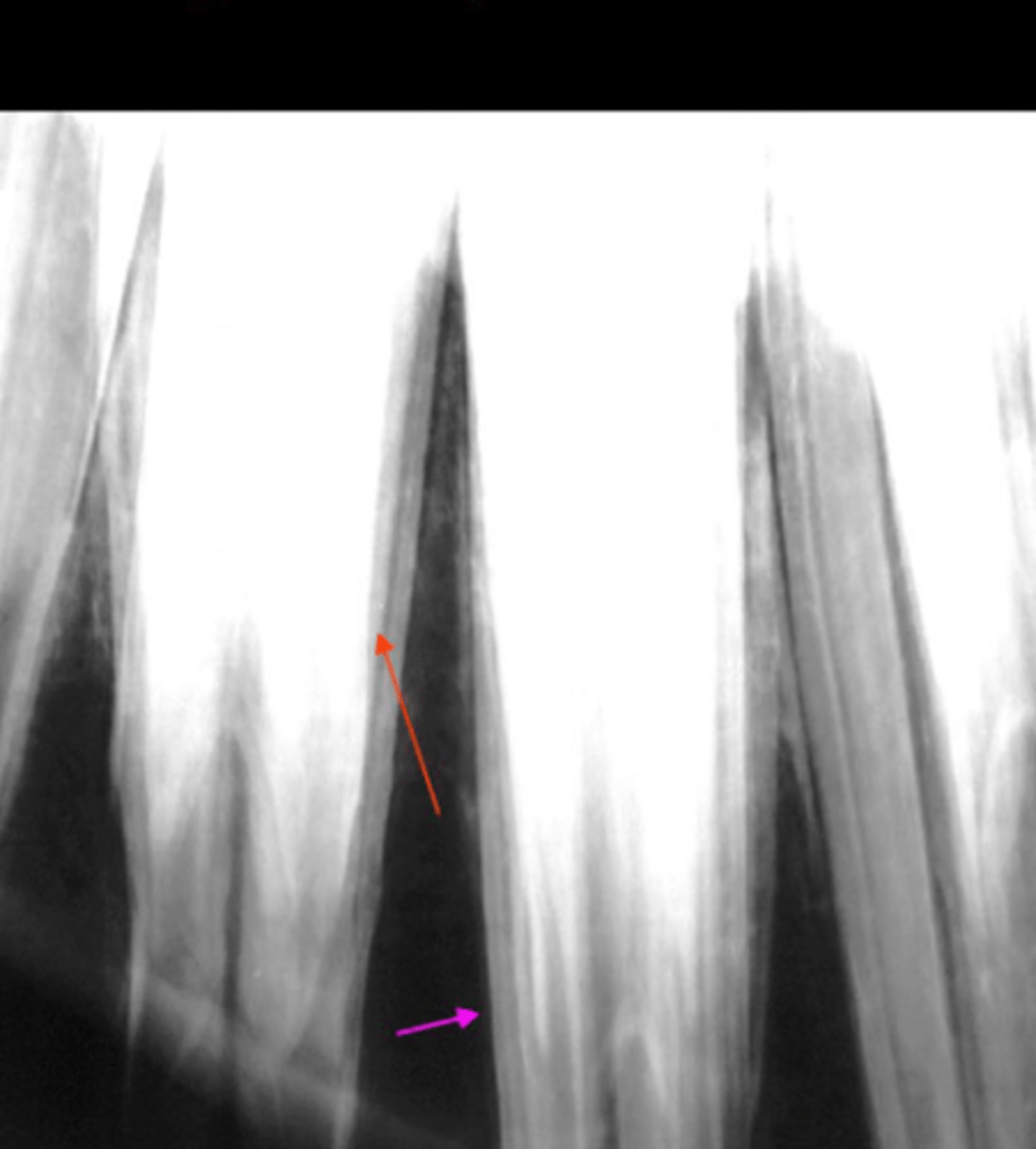
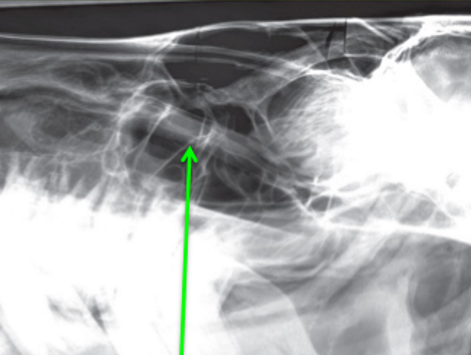
What is the red arrow pointing at?
Periodontal ligament
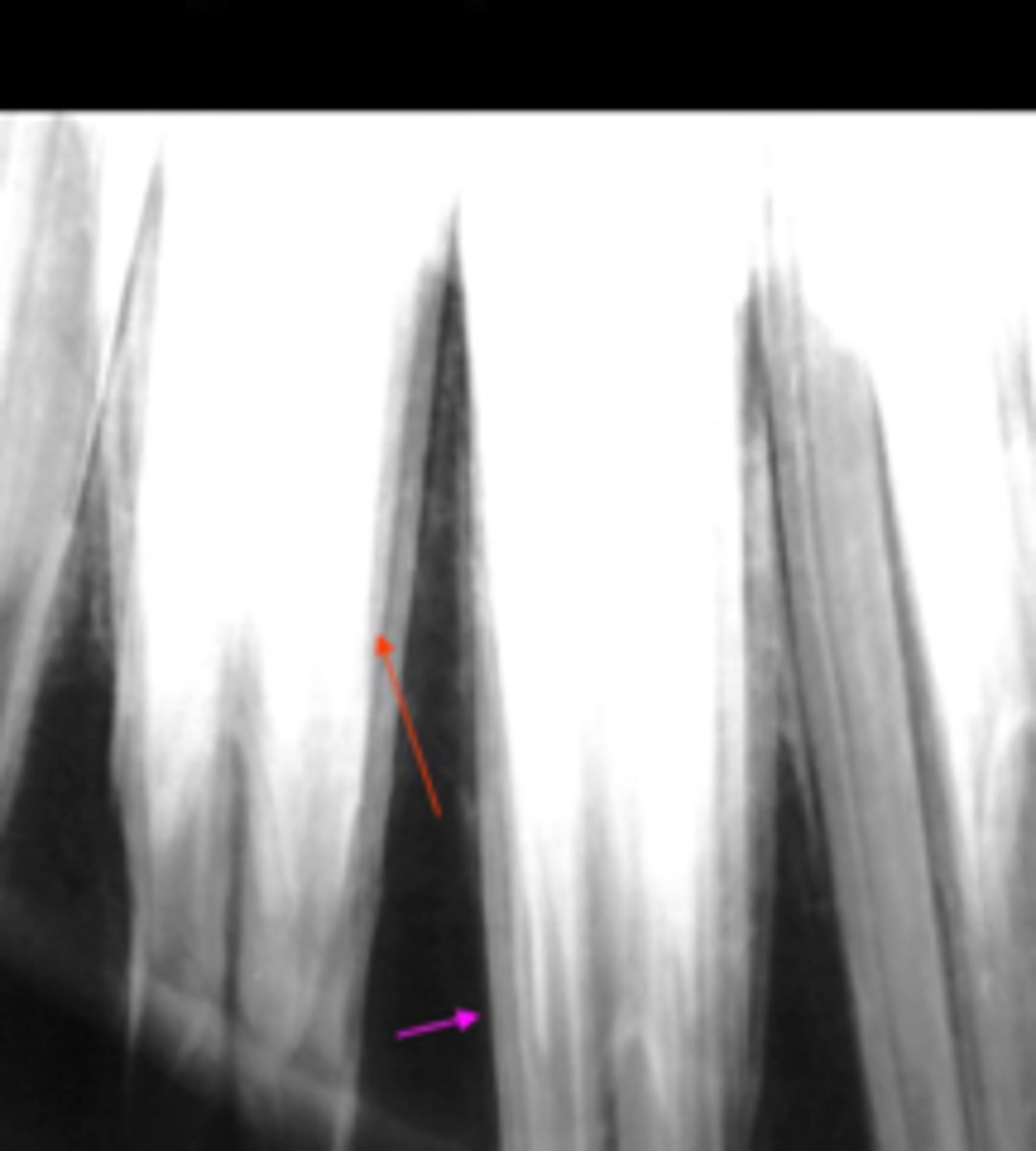
What is the pink arrow pointing at
lamina dura (radiopaque)
How do tooth roots appear?
Flat and square surrounded by round translucent areas.
Frontal sinuses are often ___ structures located where?
Paired
Located in the dorsal portion of the skull medial to the orbit
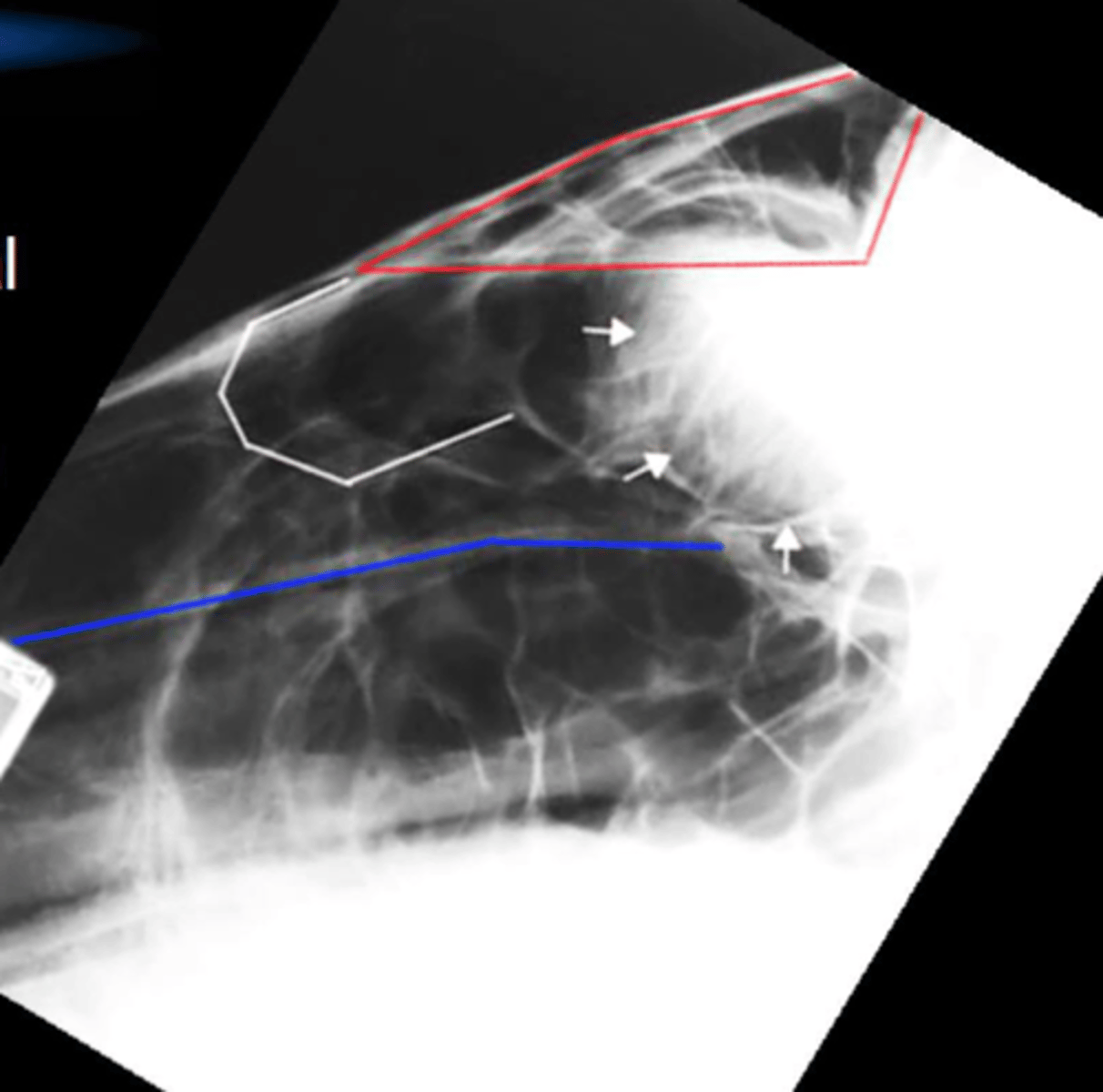
What is the blue line? What is w/in this structure
Infraorbital canal
nerve and lacrimal duct
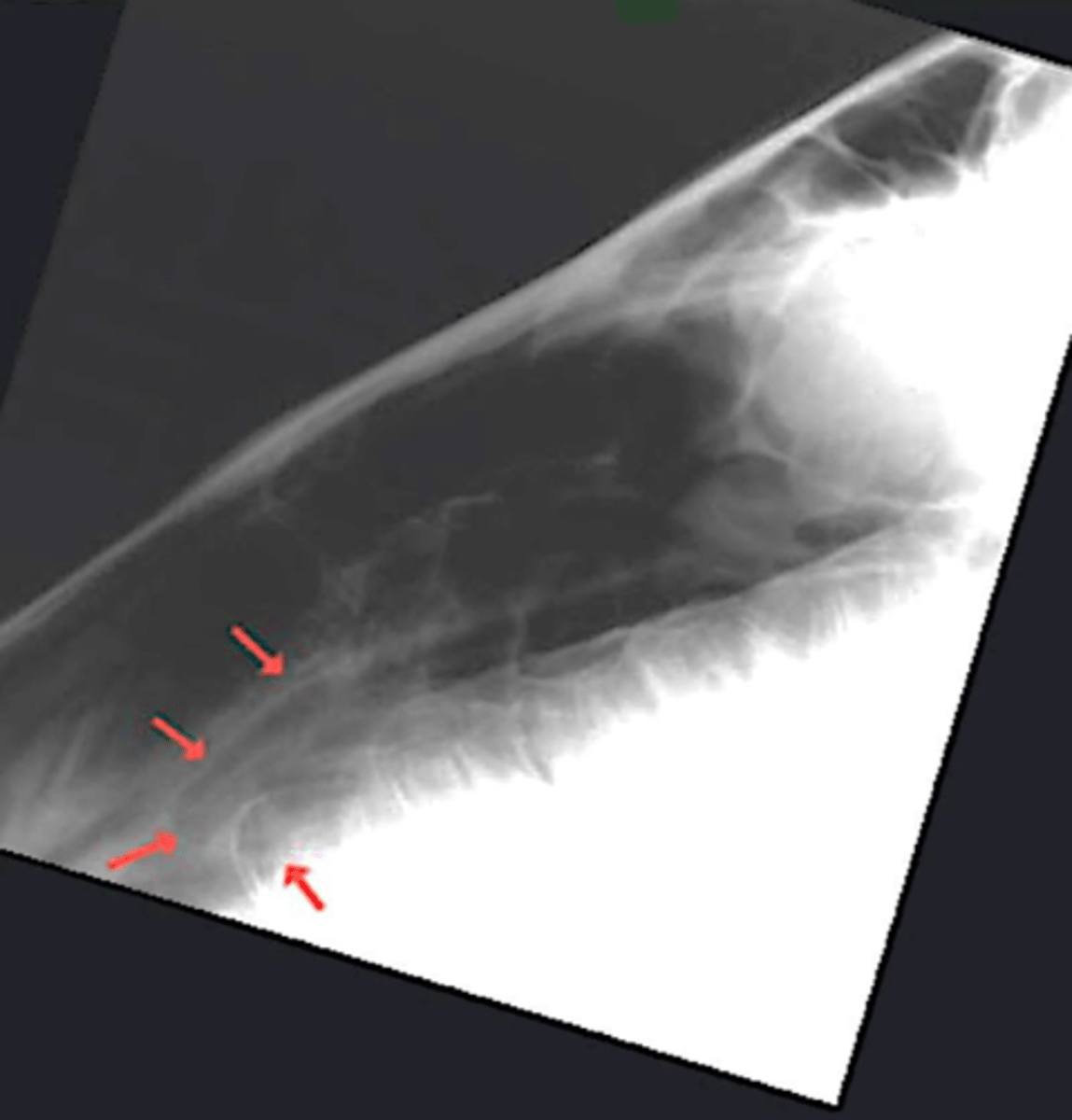
What is the structure shown by the red arrows?
Ventral conchal sinus (ventral turbinate)
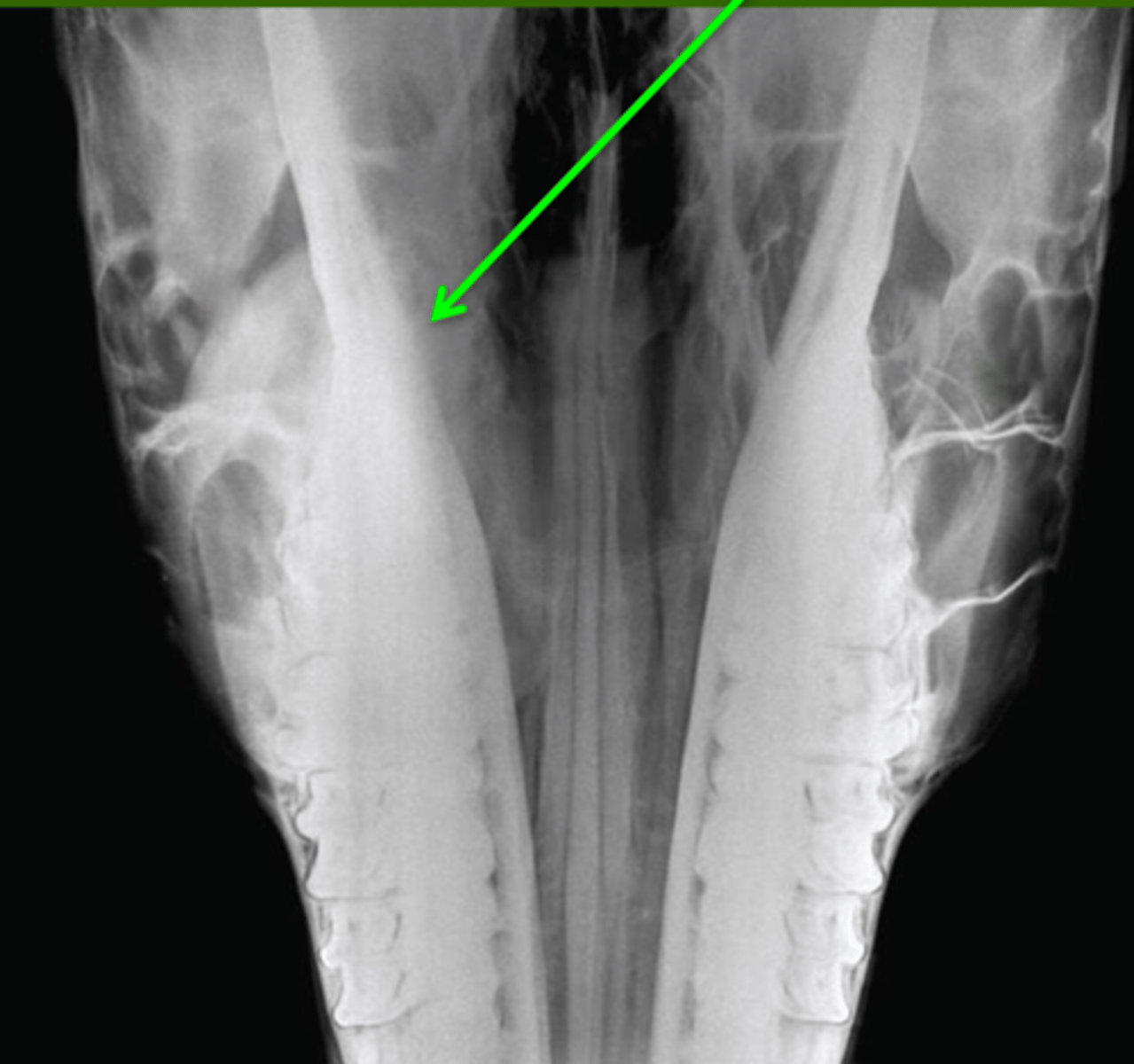
Identify the pathology?
Abscess of ventral conchal bulla
What does the sphenopalatine sinus communicate with?
Caudal maxillary sinus
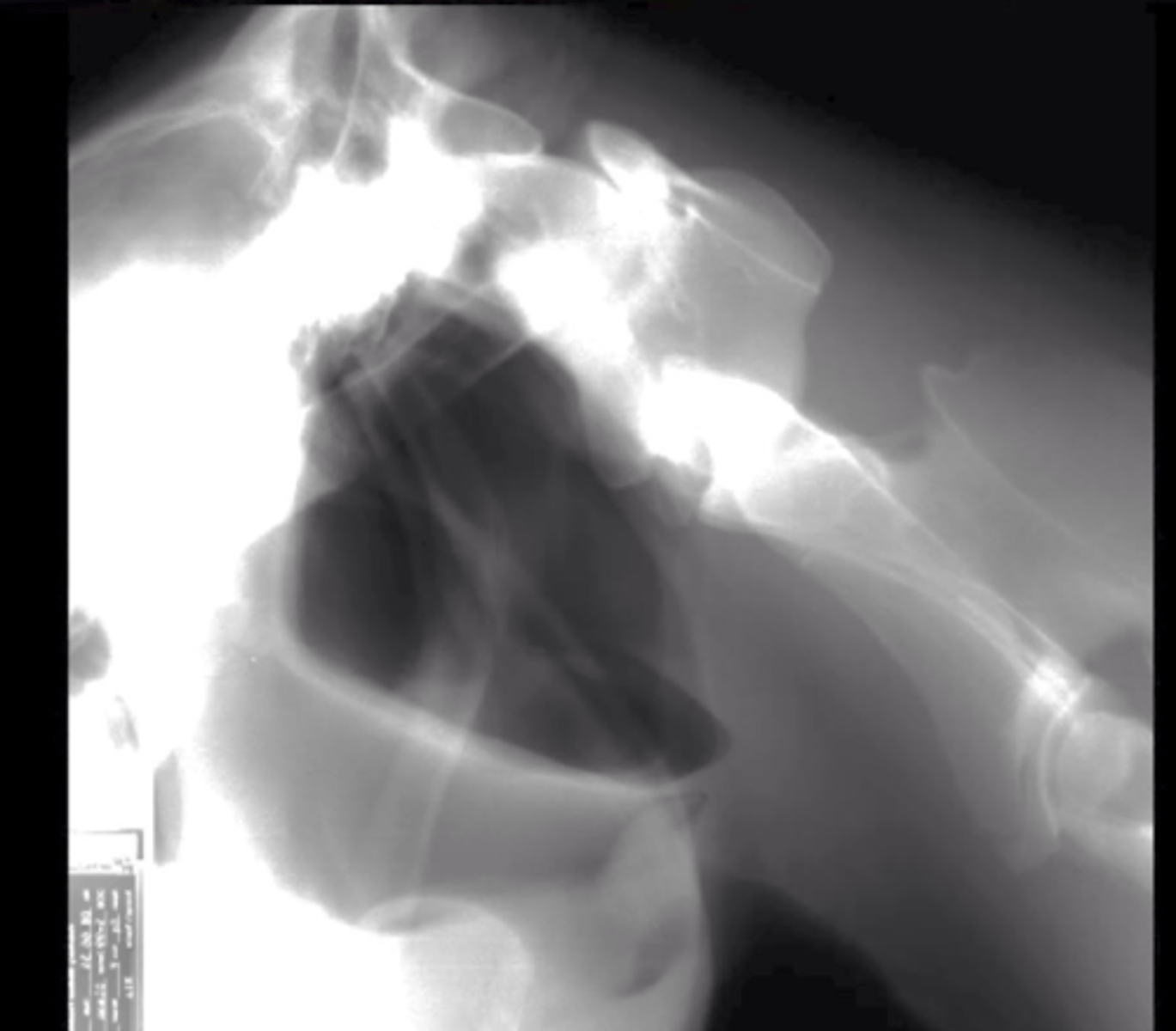
What is the opaque structure? What view must we take to see it?
Guttural pouch - oblique views- filled w/ air
What is temporohyoid osteopathy (THO)
Fusion of temporohyoid joint
-resuction in hyoid motility
-neurological signs (ataxia nystagmus)
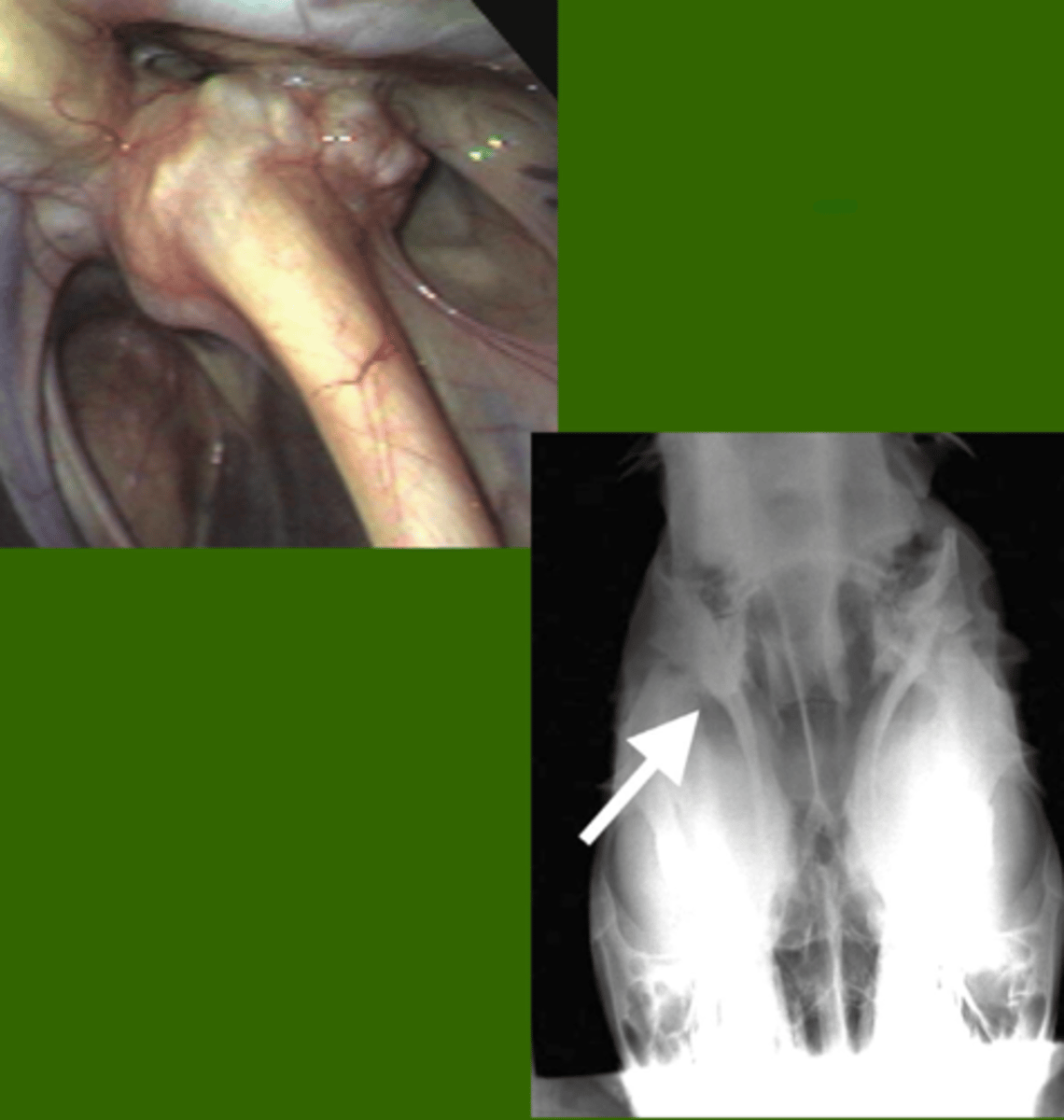
Identify the pathology?
temporohyoid osteopathy (THO)
What is a clinical sign of basisphenoid fractures?
Deteriorating neurological conditions
Hemorrhage from ears
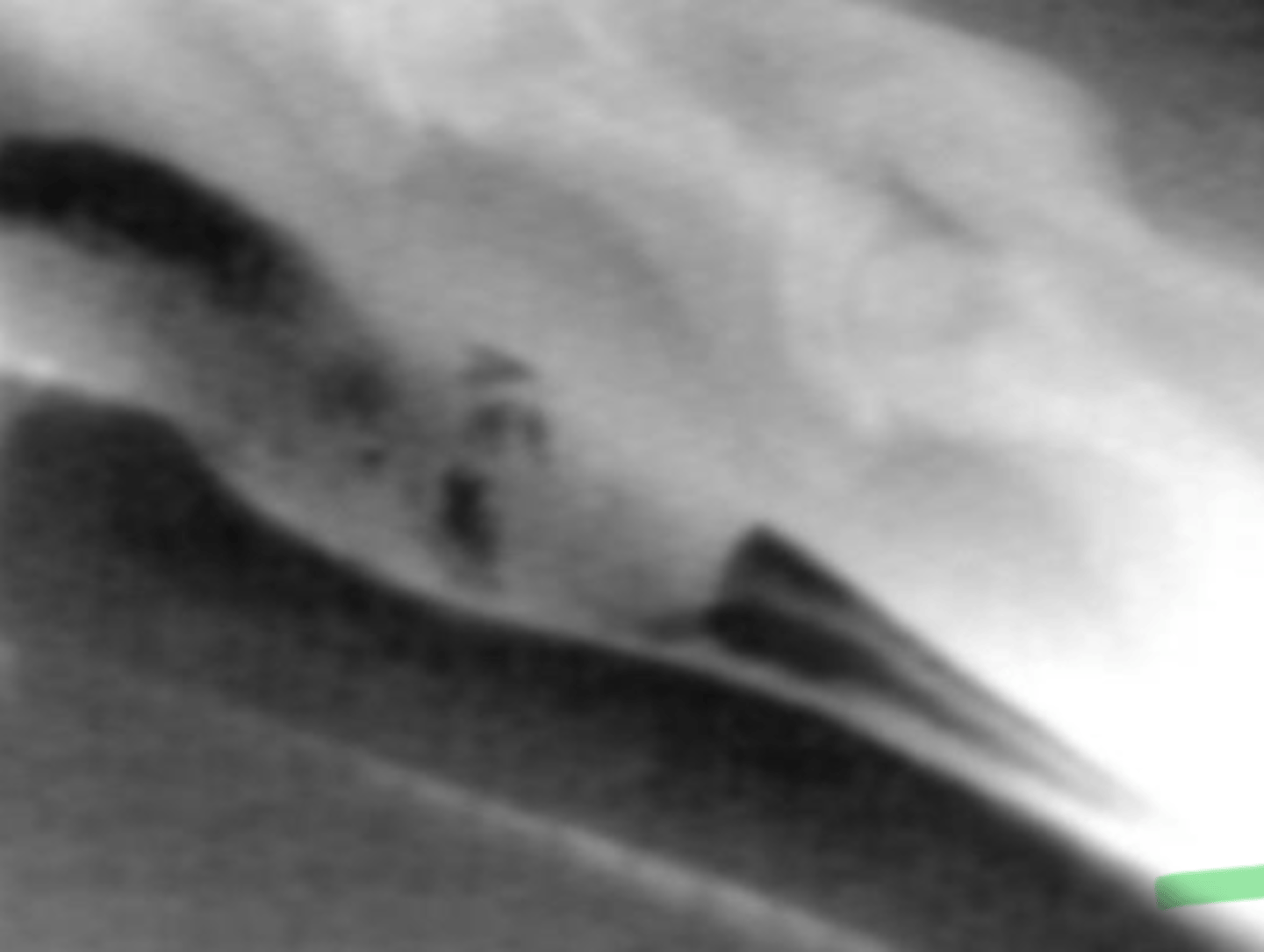
What is the pathology?
Esophageal choke
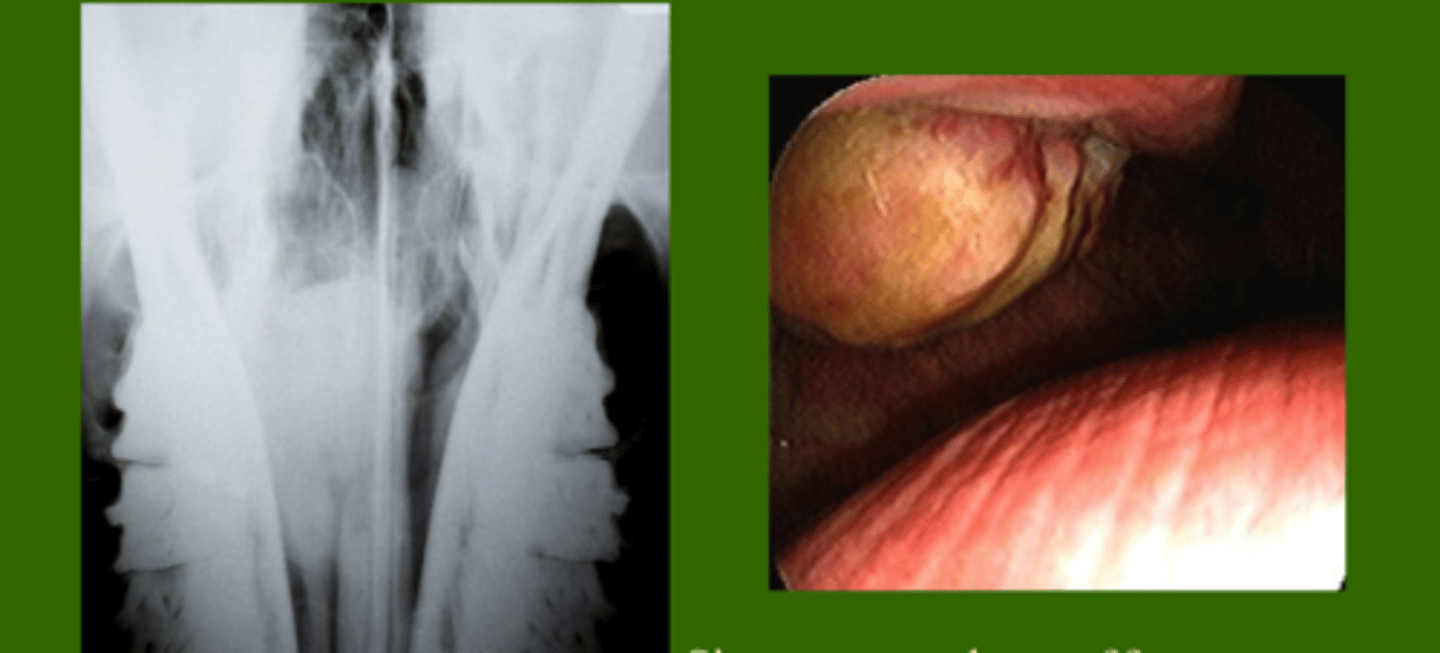
Identify the pathology?
Nasopharyngeal ethmoid hematoma
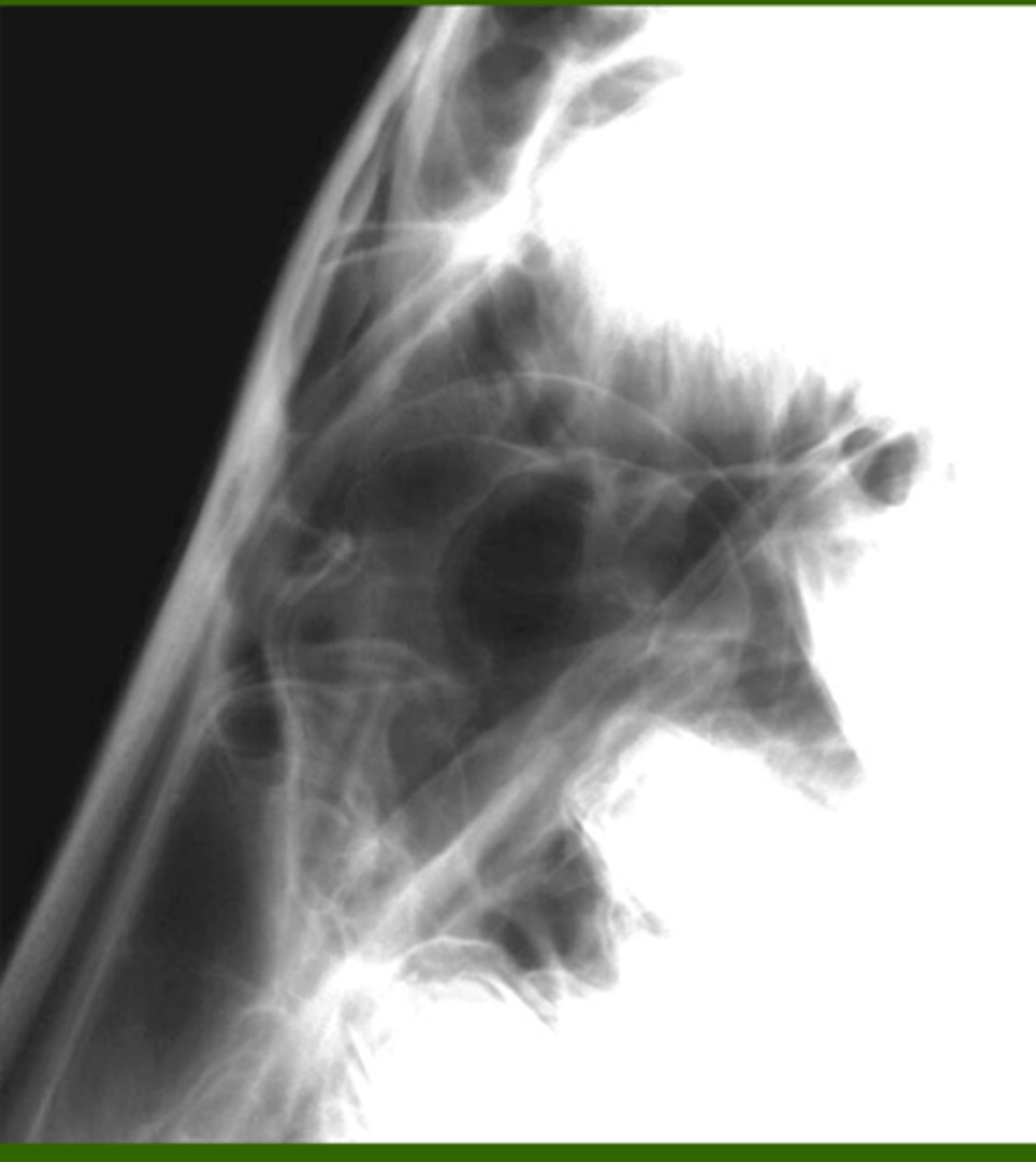
Identify the pathology?
Sinus cyst - not problem unless they occlude drainage
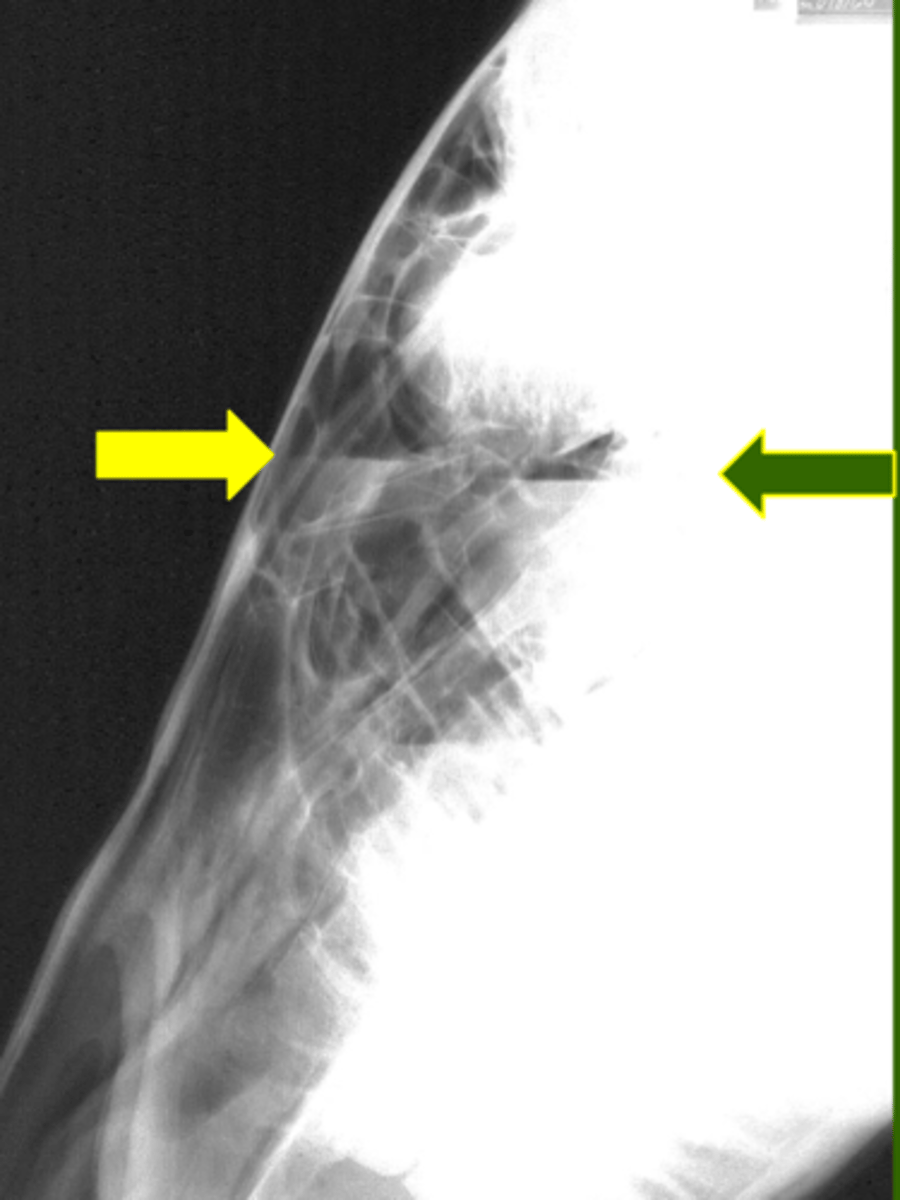
Identify the pathology
Sinitis (fluid lines)
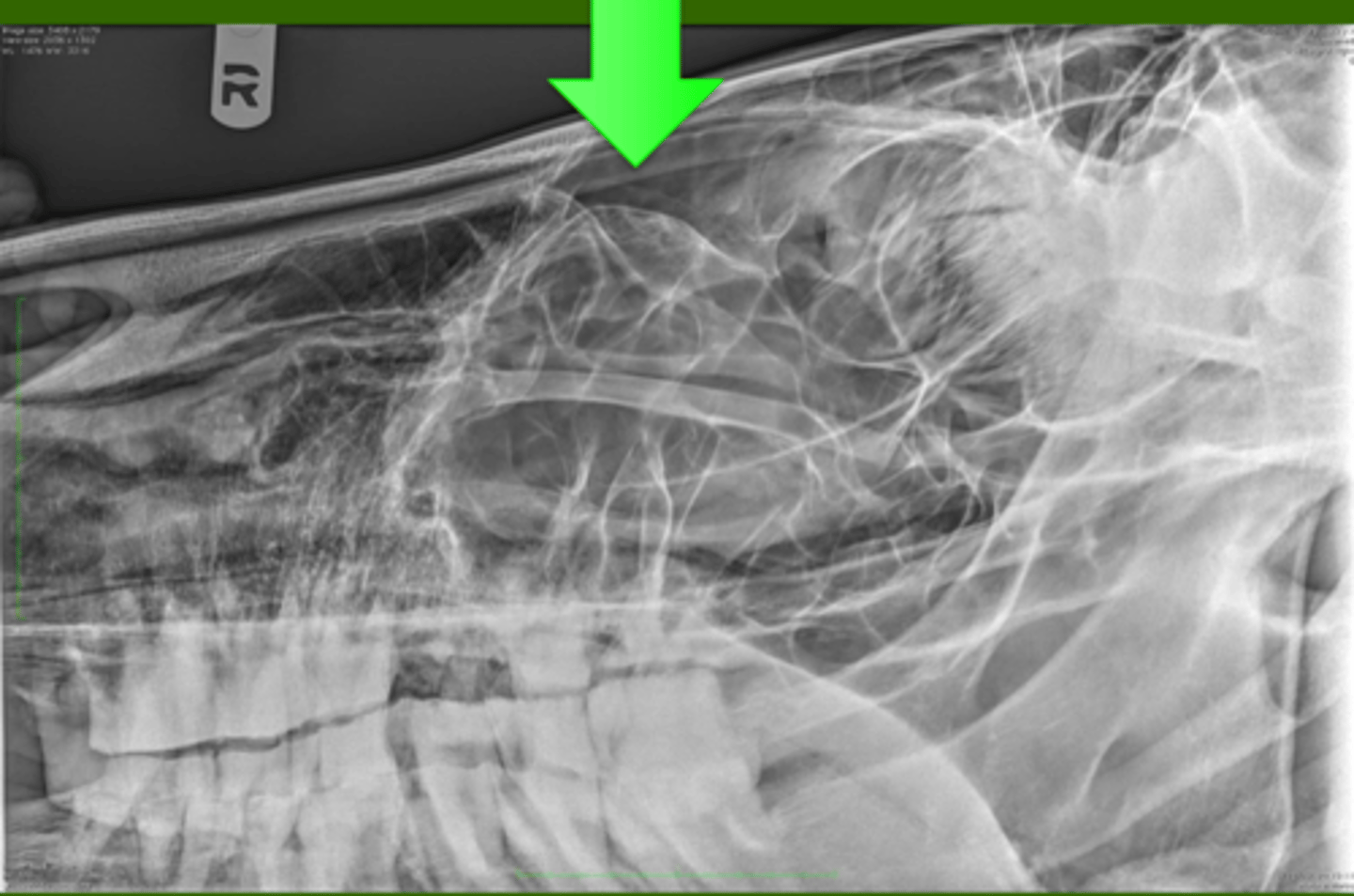
Identify the pathology?
Tooth root abcess (109/209 most common cause of sinusitis)
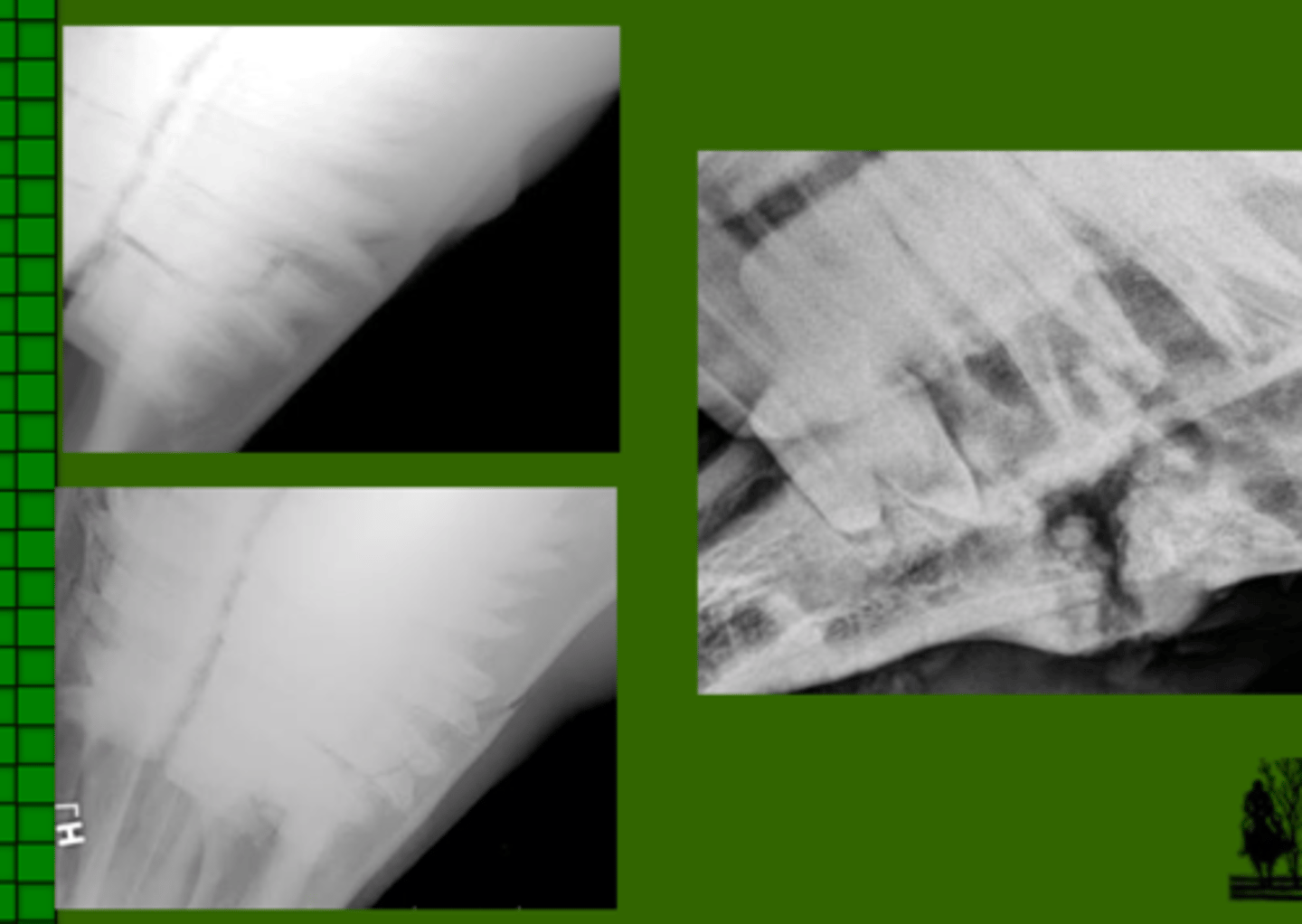
Identify the pathology?
Mandibular fracture - can include tooth fractures)
What view is this?
Offset DV skull
What is offset DV skull most useful for?
Cracks in teeth
What can happen if caps don’t fall off soon enough? Why should you be cautious with treating?
puts pressure on permanent teeth causing bump
if remove at wrong time cause abscess and could loose tooth
How can you differentiate ages of horses via dental x-rays?
young horses tooth roots fill most of the sinus
as age sinus space gets bigger
at 10 yr tooth roots are 50% grown out
What is important to remember about bovine dentition?
no maxillary incisors
have dental pad
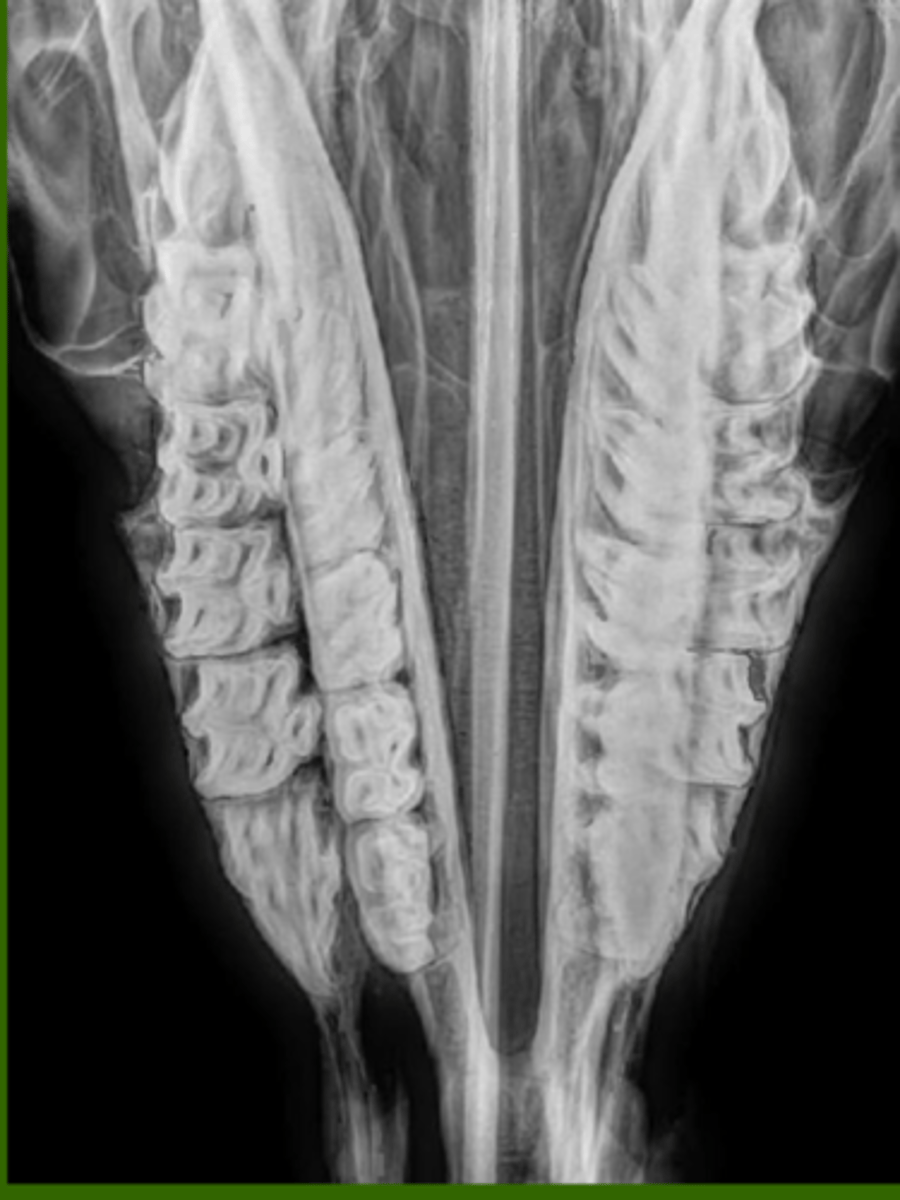
Identify the structure
ventral conchal bulla
dorsal out pouching of sinus
How can you dx THO?
xray (see proliferation of bones)
endoscopy
CT
What are some signs of a basisphenoid fracture?
deteriorating neurologic condition
hemorrhage from ears
endoscopy of guttural pouch
Teeth will always appear _______ on the side that is closest to the generator
larger
When taking cervical x-rays where do you center each view?
C2 then C4 then C6
How can you differentiate the transition from cervical spine to thoracic spine?
C7 has shorter spinous process than T1
What is the minimum sagittal ratio?
predicts stenotic myelopathy
ratio = minimum sagittal diameter of spinal cord/ width of corresponding vertebral bdy
What is required to confirm a compression?
myelogram
What is a common spinal incidental finding?
C6-C7 facet arthritis - head/neck weights a lot and mobility tops at thoracic spine so a lot of focus/pressure on 1 spot