Chemistry Chapter 4 & 5
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Who was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms?
The Greek philosopher Democritus.
What did Democritus believe about atoms?
He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible.
What four elements did Aristotle propose all substances are made of?
Fire, Air, Earth, and Water.
What was Dalton's contribution to atomic theory?
He proposed that all matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms and that atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios.
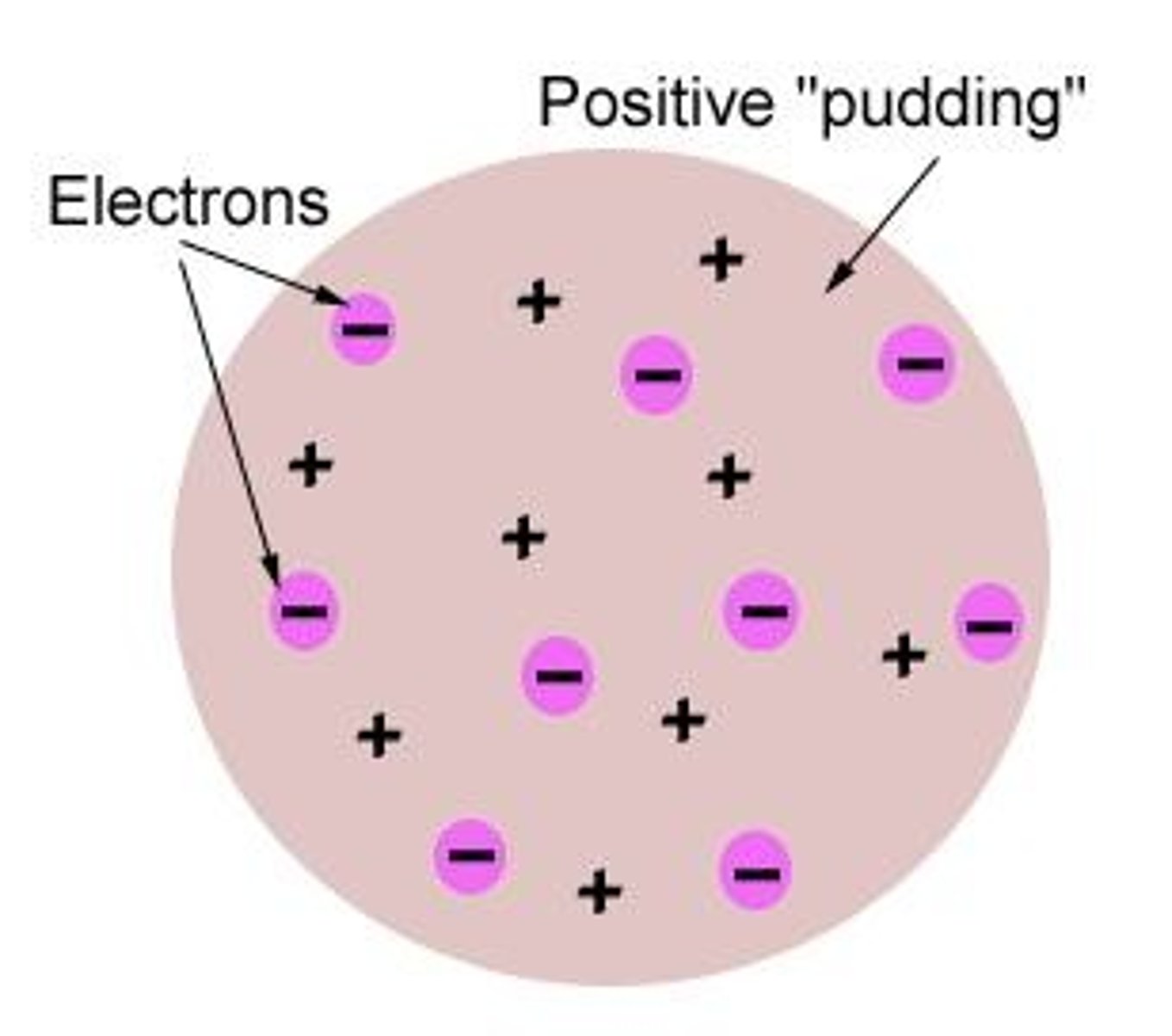
What model did J.J. Thomson propose?
The Plum Pudding Model, which depicted electrons embedded in a positively charged 'pudding.'
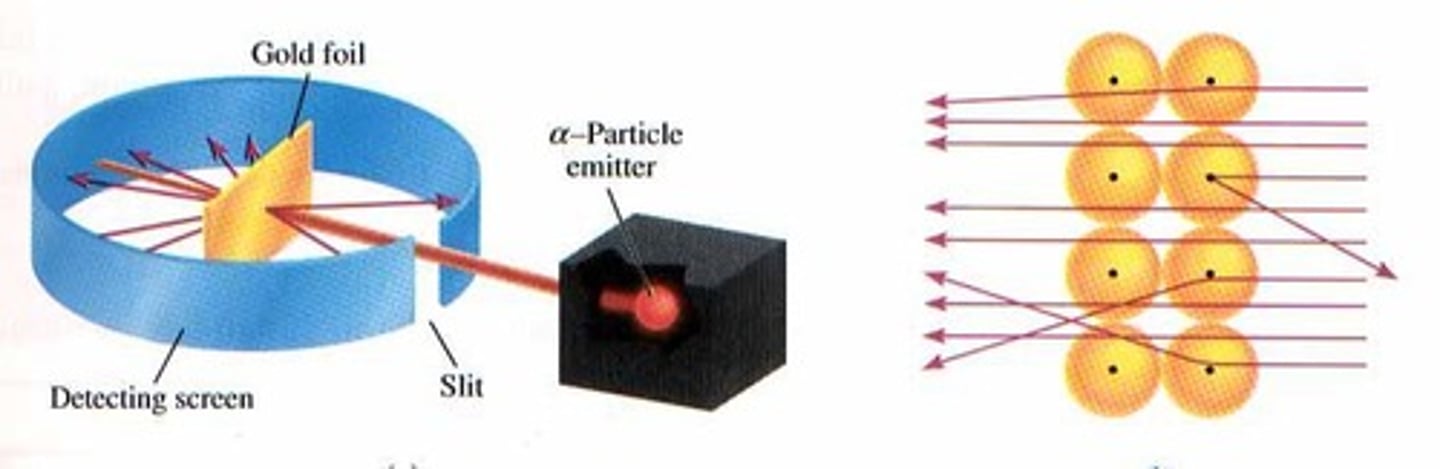
What did Rutherford discover about the atom?
He discovered the positive nucleus at the center of the atom, which contains most of the atomic mass.
What is the Bohr Model of the atom?
It describes electrons orbiting the nucleus like planets around the Sun.
What does the Quantum Mechanical Model describe?
It describes electrons as having wave properties and existing in an electron cloud around the nucleus.
What is the mass of an electron?
9.11 x 10^-28 grams.
What was Robert Millikan's experiment about?
He determined the mass of the electron and its charge using the oil drop apparatus.
What did Millikan conclude about cathode rays?
They have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them, indicating all elements contain identically charged electrons.
What are the three fundamental subatomic particles?
Electrons, protons, and neutrons.
What did Ernest Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment demonstrate?
It showed that the atom is mostly empty space with a dense positive nucleus at its center.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element.
What is the mass number of an atom?
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
What is the charge of a proton?
A proton has a positive charge (+1).
What is the charge of a neutron?
A neutron has no charge (0).
What is the charge of an electron?
An electron has a negative charge (-1).
What is the relative mass of a proton compared to an electron?
A proton has a relative mass of 1, while an electron has a relative mass of 1/1840.
What did Chadwick confirm in 1932?
He confirmed the existence of the neutron.
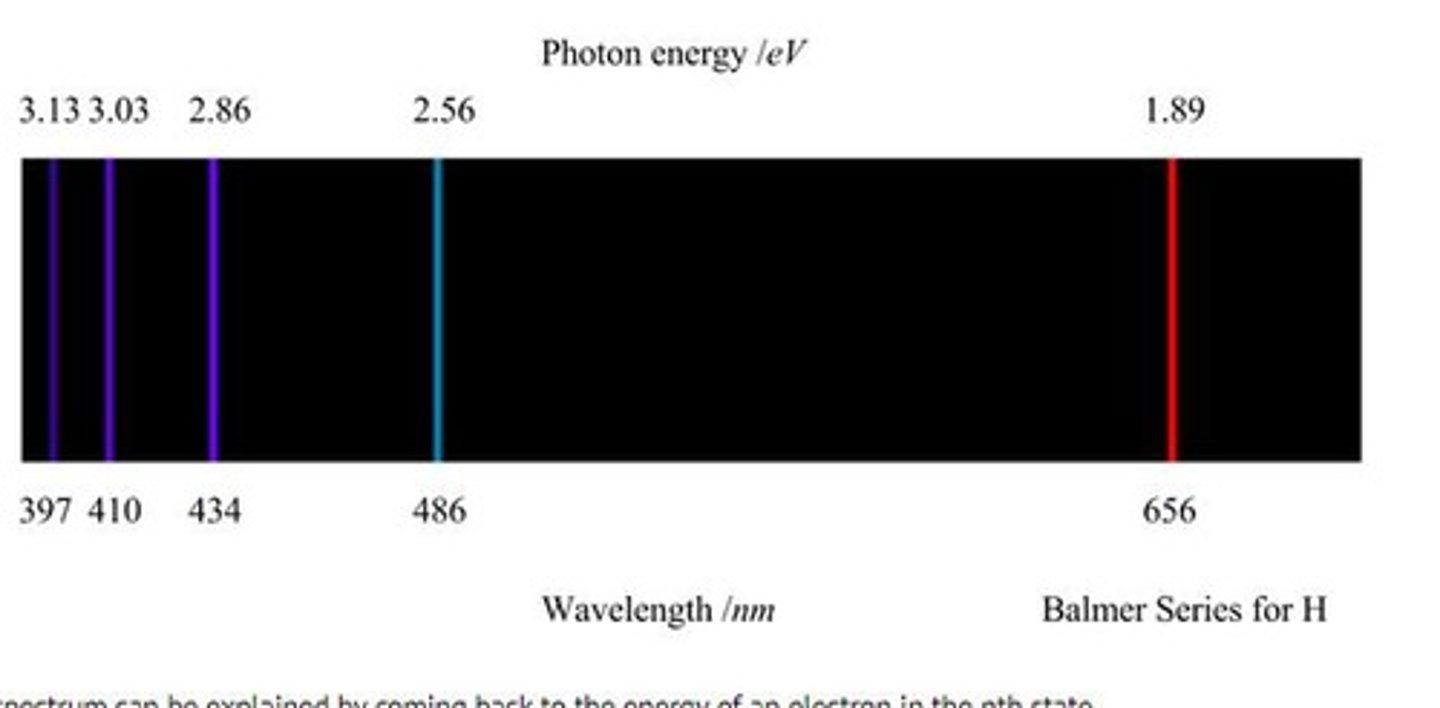
What is the significance of the hydrogen emission spectra?
It provided evidence for the quantized energy levels of electrons in atoms.
What did Rutherford's model fail to explain?
It could not explain why moving electrons do not radiate electromagnetic waves or why atoms do not collapse.
What is the role of electrons in determining the chemical properties of elements?
The behavior and arrangement of electrons determine the chemical properties of elements.
What experimental evidence led to the development of the nuclear model of the atom?
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment provided evidence for the nuclear model.
What is mass number?
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope.
How is mass number calculated?
Mass number = Number of protons (p+) + Number of neutrons (n0).
What does the atomic number represent?
The number of protons in an atom, which is also equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers.
How are isotopes named?
By placing the mass number after the name of the element, e.g., carbon-12 or uranium-235.
What is atomic mass?
The average mass of an atom of an element, typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu).
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
3.00 x 10^8 m/s.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
They are inversely related; as frequency increases, wavelength decreases.
What is the formula relating speed of light, wavelength, and frequency?
c = λν, where c is the speed of light, λ is the wavelength, and ν is the frequency.
What is the photoelectric effect?
The phenomenon where electrons are ejected from a metal when exposed to light of a certain frequency.
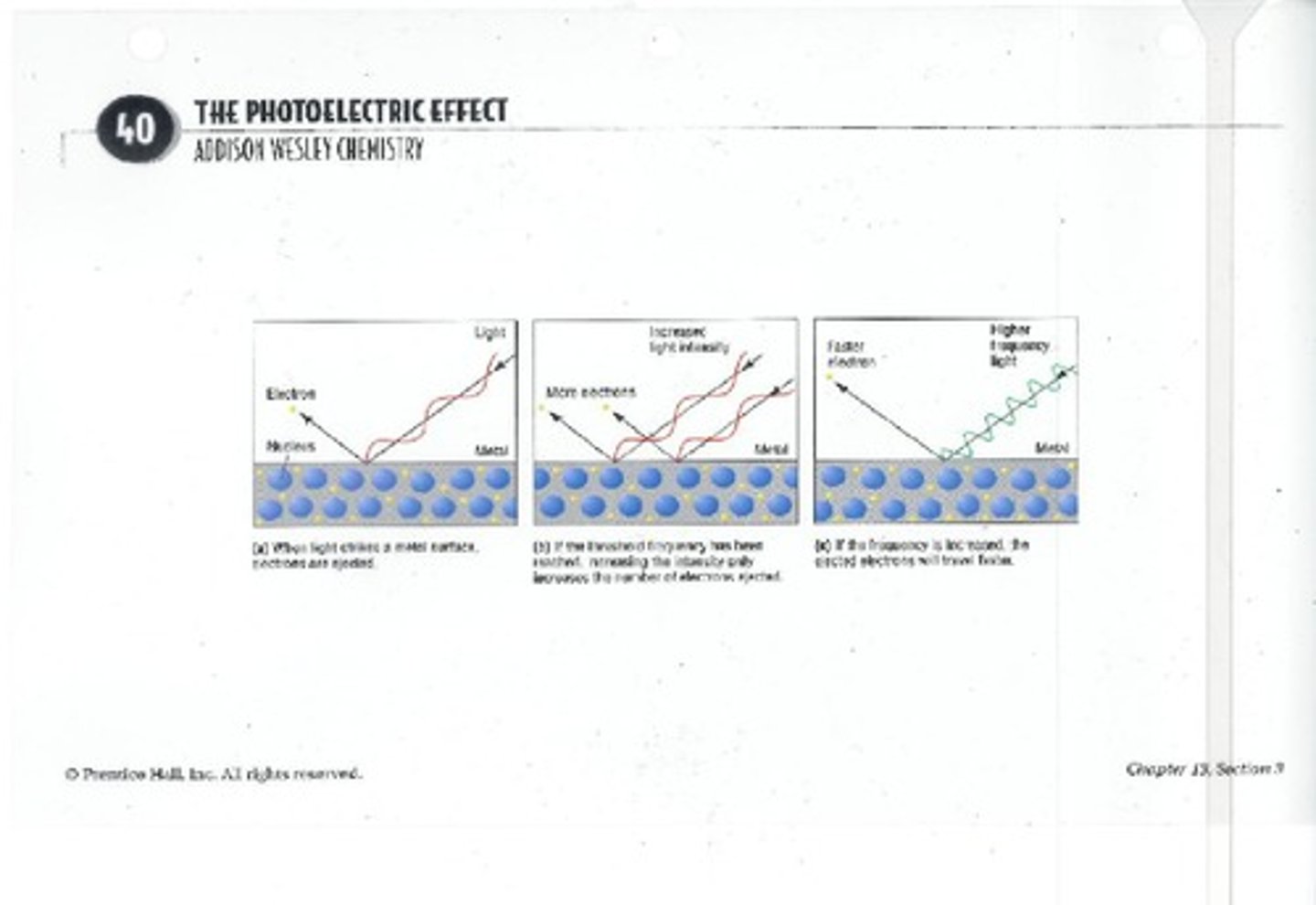
What did Einstein propose about light?
That light has a particle nature and is made up of photons, which carry quantized energy.
What is Planck's constant?
A fundamental constant (h = 6.626 x 10^-34 Joules sec) that relates energy and frequency of light.
What happens when an electron jumps energy levels in the Bohr model?
The electron must gain or lose a specific amount of energy to move between levels.
What is the quantum mechanical model of the atom?
A model that describes electrons as existing in probabilistic clouds rather than fixed orbits.
What is the significance of the atomic emission spectrum?
It shows the characteristic colors emitted by an element, useful for identifying the element.
What is absorption spectra?
The spectrum that shows gaps where specific frequencies of light are absorbed by an element.
What is the relationship between energy and frequency of light?
Energy is directly proportional to frequency; higher frequency light has higher energy.
What is the average atomic mass based on?
The abundance of each isotope of an element in nature.
How do you calculate average mass?
Total mass of all samples divided by the number of samples.
What is the formula for calculating energy of a photon?
E = hν, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, and ν is frequency.
What is the significance of the quantum leap?
It refers to the discrete amount of energy required for an electron to move between energy levels.
What is the role of the nucleus in the Bohr model?
It is the central part of the atom around which electrons orbit.
What does the term 'quantized' mean in the context of energy?
It means that energy can only exist in discrete amounts rather than a continuous range.
What is the significance of the atomic mass unit (amu)?
It is a standard unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights.
What equation did Erwin Schrödinger derive in 1926?
An equation that describes the energy and position of electrons in an atom.
How do electrons behave according to Schrödinger's model?
Electrons are treated as waves.
What happens when an electric current passes through a gas?
Atoms are excited, causing them to emit light as they return to lower energy levels.
What is the ground state of an electron?
The lowest energy level, denoted as n=1.
What is required for an electron to jump to a higher energy level?
A quantum of energy, E = hν, must be absorbed.
What does the term 'quantized energy levels' mean?
Energy levels are discrete and not continuous.
What is the relationship between the energy of a photon and its frequency?
The energy of a photon is proportional to its frequency, E = hν.
What is the significance of the Bohr model for hydrogen?
It explains the emission spectra of hydrogen and quantizes electron orbits.
What are quantum numbers?
A set of four numbers that describe the unique state of an electron in an atom.
What does the principal quantum number (n) indicate?
The energy level of the electron.
What is Hund's Rule?
Electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy singly before pairing up.
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
What is the maximum number of electrons in an s orbital?
2 electrons.
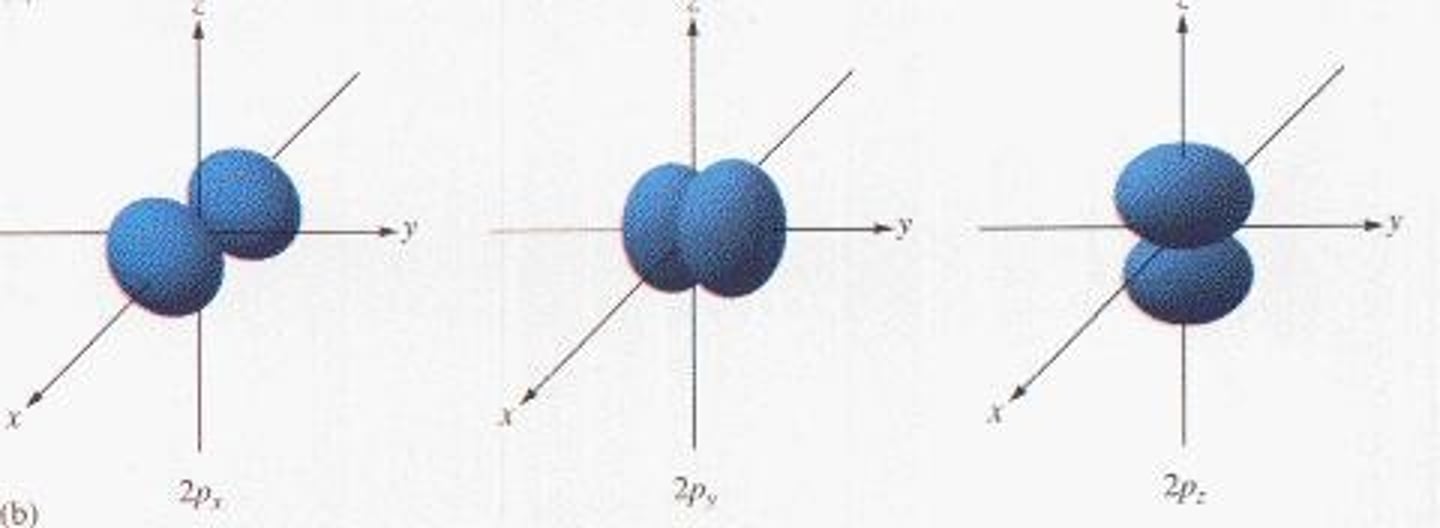
What is the maximum number of electrons in a p orbital?
6 electrons.
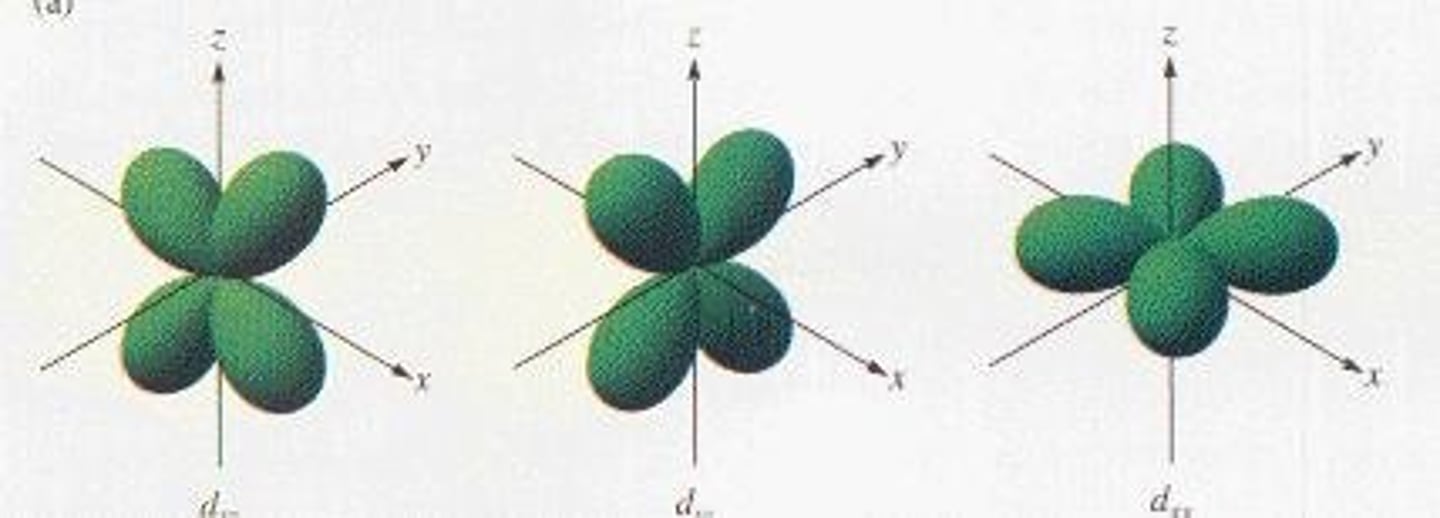
What is the maximum number of electrons in a d orbital?
10 electrons.
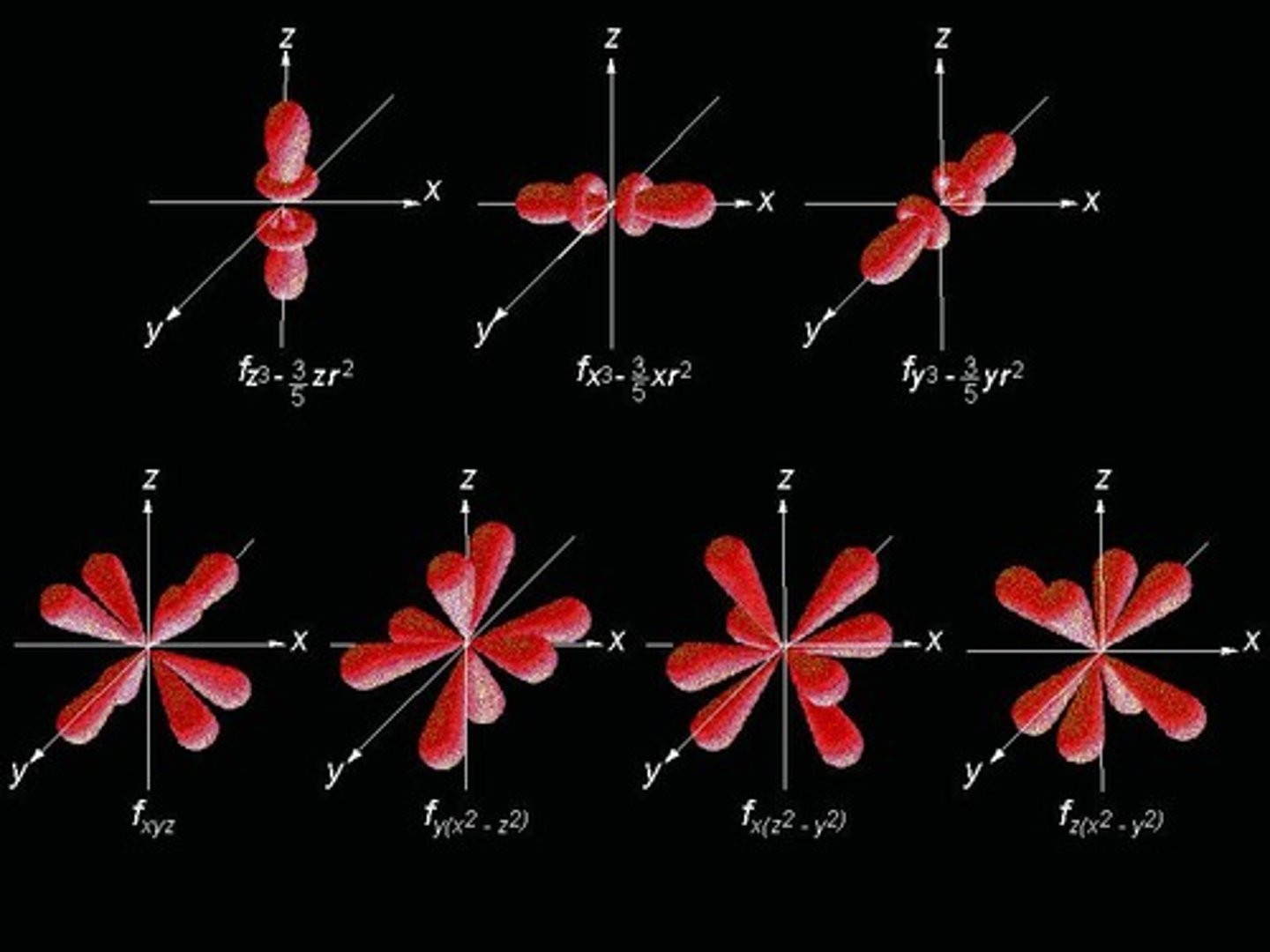
What is the maximum number of electrons in an f orbital?
14 electrons.
What does the Aufbau principle state?
Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first.
What is the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle?
It states that one cannot simultaneously know both the position and momentum of an electron.
What is the significance of Schrödinger's wave equation?
It provides a mathematical model for the probability of finding an electron in an atom.
How does light behave according to quantum mechanics?
Light behaves both as a particle and as a wave.
What is the formula for the speed of light?
c = λν, where c is the speed of light, λ is the wavelength, and ν is the frequency.
What happens to the energy of an electron when it falls back to the ground state?
It emits energy as light.
What is the shape of s orbitals?
Spherical.
What is the shape of p orbitals?
Dumbbell-shaped.
What is the shape of d orbitals?
Complex shapes with five different orientations.
What is the shape of f orbitals?
Even more complex shapes with seven different orientations.
What does the term 'electron configuration' refer to?
The arrangement of electrons in various orbitals around the nucleus of an atom.