Lesson 2: Series and Parallel Circuit
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
Two types of circuit
Series Circuit
Contains more than one electrical component connected one after the other in a single path.
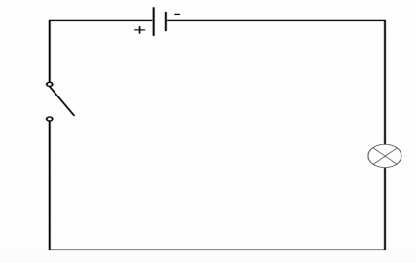
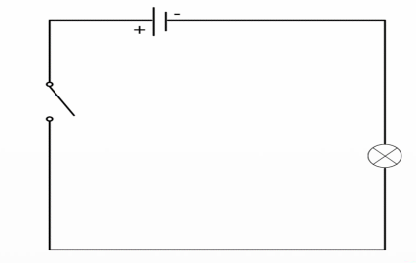
Broken series circuit
A condition where the circuit is interrupted at any point, stopping the flow of current entirely.
Current in series circuit
There is only one path where current can flow and the same in all parts. Calculated using the formula:
𝑰𝑻 = 𝑰𝟏 = 𝑰𝟐 = 𝑰𝟑 ...
Voltage in series circuit
The sum of the potential difference across
individual components is equal to the potential difference across the entire circuit. Calculated using the formula:
𝑽𝑻 = 𝑽𝟏 + 𝑽𝟐 + 𝑽𝟑 ...
Resistance in series circuit
As more resistors are added in series, the
equivalent resistance increases. Calculated using the formula:
𝑹𝑻 = 𝑹𝟏 + 𝑹𝟐 + 𝑹𝟑 ...
Parallel Circuit
Contains two or more electrical component connected across each other in such a way that the current is distributed between them.
Each component operates independently of the others.
Broken parallel circuit
A condition where one branch is interrupted, stopping current flow only in that path while the other branches continue to function.
Current in parallel circuit
Current is distributed between each components. Calculated using the formula:
𝑰𝑻 = 𝑰𝟏 + 𝑰𝟐 + 𝑰𝟑 ...
Voltage in parallel circuit
The potential difference across all the resistors is the same as that across any resistor. Calculated using the formula:
𝑽𝑻 = 𝑽𝟏 = 𝑽𝟐 = 𝑽𝟑 ...
Resistance in parallel circuit
The total resistance decreases as more resistors are added because the current has multiple paths to flow through, calculated using the formula:
1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3…